A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to the Islamic prophet
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
and a leader of the entire
Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
(
ummah
' (; ar, أمة ) is an Arabic word meaning "community". It is distinguished from ' ( ), which means a nation with common ancestry or geography. Thus, it can be said to be a supra-national community with a common history.
It is a synonym for ' ...
).
Historically, the caliphates were
polities
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the
Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
(661–750), and the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
(750–1258). In the fourth major caliphate, the
Ottoman Caliphate
The Caliphate of the Ottoman Empire ( ota, خلافت مقامى, hilâfet makamı, office of the caliphate) was the claim of the heads of the Turkish Ottoman dynasty to be the caliphs of Islam in the late medieval and the early modern era. ...
, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517. Throughout the history of Islam, a few other Muslim states, almost all
hereditary monarchies
A hereditary monarchy is a form of government and succession of power in which the throne passes from one member of a ruling family to another member of the same family. A series of rulers from the same family would constitute a dynasty.
It is h ...
such as the
Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo)
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16t ...
and
Ayyubid Caliphate, have claimed to be caliphates.
The first caliphate, the Rashidun Caliphate, was established in 632 immediately after Muhammad's death. It was followed by the Umayyad Caliphate and the Abbasid Caliphate. The last caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, existed until it was abolished in 1924 by the
Turkish Republic
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
. Not all Muslim states have had caliphates, and only a minority of Muslims recognize any particular caliph as legitimate in the first place. The
Sunni branch of Islam stipulates that, as a head of state, a caliph should be elected by Muslims or their representatives. Followers of
Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
, however, believe a caliph should be an Imam chosen by God from the
Ahl al-Bayt (the "Household of the Prophet").
In the early 21st century, following the failure of the
Arab Spring
The Arab Spring ( ar, الربيع العربي) was a series of anti-government protests, uprisings and armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began in Tunisia in response to corruption and econo ...
and related protests, some have argued for a return to the concept of a caliphate to better unify Muslims. The caliphate system was abolished in Turkey in 1924 during the secularization of Turkey as part of
Atatürk's Reforms.
Etymology
Before the advent of Islam, Arabian
monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power i ...
s traditionally used the title ''
malik ''(King, ruler), or another from the same
root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
.
The term ''caliph'' (), derives from the
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
word ' (, ), which means "successor", "steward", or "deputy" and has traditionally been considered a shortening of ''Khalīfat Rasūl Allāh'' ("successor of the messenger of God"). However, studies of pre-Islamic texts suggest that the original meaning of the phrase was "successor ''selected by'' God".
History
Rashidun Caliphate (632–661)
Succession to Muhammad
In the immediate aftermath of the death of Muhammad, a gathering of the
Ansar (natives of
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
) took place in the ''Saqifah'' (courtyard) of the
Banu Sa'ida clan. The general belief at the time was that the purpose of the meeting was for the Ansar to decide on a new leader of the
Muslim community
' (; ar, أمة ) is an Arabic word meaning "community". It is distinguished from ' ( ), which means a nation with common ancestry or geography. Thus, it can be said to be a supra-national community with a common history.
It is a synonym for ' ...
among themselves, with the intentional exclusion of the
Muhajirun (migrants from
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
), though this has later become the subject of debate.
Nevertheless,
Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
and
Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
, both prominent companions of Muhammad, upon learning of the meeting became concerned of a potential coup and hastened to the gathering. Upon arriving, Abu Bakr addressed the assembled men with a warning that an attempt to elect a leader outside of Muhammad's own tribe, the
Quraysh, would likely result in dissension as only they can command the necessary respect among the community. He then took Umar and another companion,
Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah
ʿĀmir ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Jarrāḥ ( ar, عامر بن عبدالله بن الجراح; 583–639 CE), better known as Abū ʿUbayda ( ar, أبو عبيدة ) was a Muslim commander and one of the Companions of the Islamic prophet ...
, by the hand and offered them to the Ansar as potential choices. He was countered with the suggestion that the Quraysh and the Ansar choose a leader each from among themselves, who would then rule jointly. The group grew heated upon hearing this proposal and began to argue amongst themselves. Umar hastily took Abu Bakr's hand and swore his own allegiance to the latter, an example followed by the gathered men.
Abu Bakr was near-universally accepted as head of the Muslim community (under the title of Caliph) as a result of Saqifah, though he did face contention as a result of the rushed nature of the event. Several companions, most prominent among them being
Ali ibn Abi Talib, initially refused to acknowledge his authority. Ali may have been reasonably expected to assume leadership, being both cousin and son-in-law to Muhammad. The theologian
Ibrahim al-Nakha'i
( ar, أبو عمران إبراهيم بن يزيد النخعي), also known as , c. 670 CE/50 AH - 714 CE/96 AH), was an Islamic theologian and jurist (). Though belonging to the generation following the companions of Muhammad (the ), he ...
stated that Ali also had support among the Ansar for his succession, explained by the genealogical links he shared with them. Whether his candidacy for the succession was raised during Saqifah is unknown, though it is not unlikely. Abu Bakr later sent Umar to confront Ali to gain his allegiance, resulting in
an altercation which may have involved violence. However, after six months the group made peace with Abu Bakr and Ali offered him his fealty.
Rāshidun Caliphs
Abu Bakr nominated Umar as his successor on his deathbed. Umar, the second caliph, was killed by a Persian slave called
Abu Lu'lu'a Firuz. His successor, Uthman, was elected by a council of electors (
majlis). Uthman was killed by members of a disaffected group.
Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
then took control but was not universally accepted as caliph by the governors of Egypt and later by some of his own guard. He faced two major rebellions and was assassinated by
Abd-al-Rahman ibn Muljam
ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn Muljam al-Murādī ( ar, عبد الرحمن بن ملجم المرادي) was a Kharijite primarily known for having assassinated Ali ibn Abi Talib, the fourth caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate.
Assassination plot
There ...
, a
Khawarij
The Kharijites (, singular ), also called al-Shurat (), were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the ...
. Ali's tumultuous rule lasted only five years. This period is known as the
Fitna, or the first Islamic civil war. The followers of Ali later became the Shi'a ("shiaat Ali", partisans of Ali.
) minority sect of Islam and reject the legitimacy of the first 3 caliphs. The followers of all four Rāshidun Caliphs (Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman and Ali) became the majority Sunni sect.
Under the Rāshidun each region (
Sultanate,
Wilayah
A wilayah ( ar, وَلاية, wālāya or ''wilāya'', plural ; Urdu and fa, ولایت, ''velâyat''; tr, vilayet) is an administrative division, usually translated as "state", "province" or occasionally as " governorate". The word comes f ...
, or
Emirate
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalen ...
) of the Caliphate had its own governor (Sultan,
Wāli or
Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
).
Muāwiyah, a relative of Uthman and governor (''Wali'') of
Syria, succeeded Ali as Caliph. Muāwiyah transformed the caliphate into a
hereditary office, thus founding the Umayyad
dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
.
In areas which were previously under
Sasanian Empire or
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
rule, the Caliphs lowered taxes, provided greater local autonomy (to their delegated governors), greater religious freedom for
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and some indigenous
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, and brought peace to peoples demoralised and disaffected by the casualties and heavy taxation that resulted from the decades of
Byzantine-Persian warfare.
Ali's caliphate, Hasan and the rise of the Umayyad dynasty
Ali's reign was plagued by turmoil and internal strife. The Persians, taking advantage of this, infiltrated the two armies and attacked the other army causing chaos and internal hatred between the
companions at the
Battle of Siffin
The Battle of Siffin was fought in 657 CE (37 AH) between Ali ibn Abi Talib, the fourth of the Rashidun Caliphs and the first Shia Imam, and Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan, the rebellious governor of Syria. The battle is named after its location ...
. The battle lasted several months, resulting in a stalemate. In order to avoid further bloodshed, Ali agreed to negotiate with Mu'awiyah. This caused a faction of approximately 4,000 people, who would come to be known as the
Kharijites, to abandon the fight. After defeating the Kharijites at the
Battle of Nahrawan
The Battle of Nahrawan ( ar, معركة النهروان, Ma'rakat an-Nahrawān) was fought between the army of Caliph Ali and the rebel group Kharijites in July 658 CE (Safar 38 AH). They used to be a group of pious allies of Ali during the ...
, Ali was later assassinated by the Kharijite Ibn Muljam. Ali's son
Hasan was elected as the next caliph, but abdicated in favor of Mu'awiyah a few months later to avoid any conflict within the Muslims. Mu'awiyah became the sixth caliph, establishing the Umayyad Dynasty, named after the great-grandfather of Uthman and Mu'awiyah,
Umayya ibn Abd Shams
Umayya ibn ʿAbd Shams ( ar, أمية بن عبد شمس) was the son of Abd Shams and is said to be the progenitor of the line of the Umayyad Caliphs. Ibn al-Kalbi says that his name is derived from , a diminutive of the word for slave-girl a ...
.
Umayyad Caliphate (661–750)

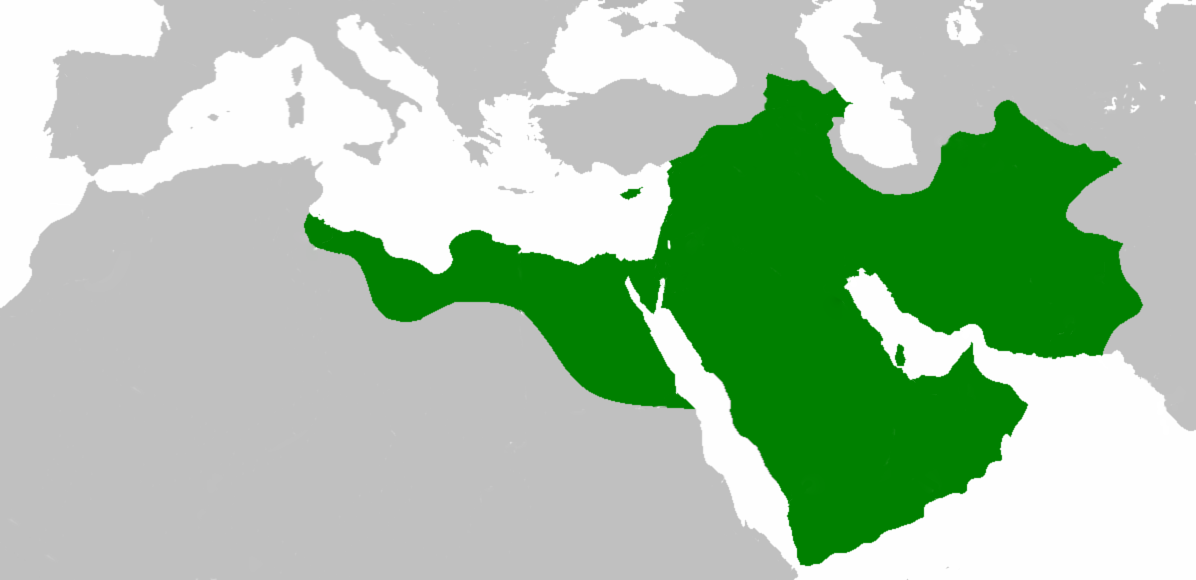
Beginning with the Umayyads, the title of the caliph became hereditary. Under the Umayyads, the Caliphate grew rapidly in territory, incorporating the
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
,
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
,
Sindh, the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
and most of the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
(
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
) into the Muslim world. At its greatest extent, the Umayyad Caliphate covered 5.17 million square miles (13,400,000 km
2), making it the
largest empire
Several empires in human history have been contenders for the largest of all time, depending on definition and mode of measurement. Possible ways of measuring size include area, population, economy, and power. Of these, area is the most commonly ...
the world had yet seen and the
sixth-largest ever to exist in history.
Geographically, the empire was divided into several provinces, the borders of which changed numerous times during the Umayyad reign. Each province had a governor appointed by the caliph. However, for a variety of reasons, including that they were not elected by
Shura
Shura ( ar, شُورَىٰ, translit=shūrā, lit=consultation) can for example take the form of a council or a referendum. The Quran encourages Muslims to decide their affairs in consultation with each other.
Shura is mentioned as a praisewort ...
and suggestions of impious behaviour, the Umayyad dynasty was not universally supported within the Muslim community. Some supported prominent early Muslims like
Zubayr ibn al-Awwam
Az Zubayr ( ar, الزبير) is a city in and the capital of Al-Zubair District, part of the Basra Governorate of Iraq. The city is just south of Basra. The name can also refer to the old Emirate of Zubair.
The name is also sometimes written ...
; others felt that only members of Muhammad's clan, the
Banu Hashim, or his own lineage, the descendants of Ali, should rule.
There were numerous rebellions against the Umayyads, as well as splits within the Umayyad ranks (notably, the rivalry between
Yaman and Qays). At the command of Yazid son of Muawiya, an army led by Umar ibn Saad, a commander by the name of Shimr Ibn Thil-Jawshan killed Ali's son
Hussein
Hussein, Hussain, Hossein, Hossain, Huseyn, Husayn, Husein or Husain (; ar, حُسَيْن ), coming from the triconsonantal root Ḥ-S-i-N ( ar, ح س ی ن, link=no), is an Arabic name which is the diminutive of Hassan, meaning "good", " ...
and his family at the
Battle of Karbala
The Battle of Karbala ( ar, مَعْرَكَة كَرْبَلَاء) was fought on 10 October 680 (10 Muharram in the year 61 AH of the Islamic calendar) between the army of the second Umayyad Caliph Yazid I and a small army led by Husayn ...
in 680, solidifying the
Shia-Sunni split.
[ Eventually, supporters of the Banu Hashim and the supporters of the lineage of Ali united to bring down the Umayyads in 750. However, the ''Shi‘at ‘Alī'', "the Party of Ali", were again disappointed when the Abbasid dynasty took power, as the Abbasids were descended from Muhammad's uncle, ]‘Abbas ibn ‘Abd al-Muttalib
Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib ( ar, ٱلْعَبَّاسُبْنُ عَبْدِ ٱلْمُطَّلِبِ, al-ʿAbbās ibn ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib; CE) was a paternal uncle and Sahabi (companion) of Muhammad, just three years older than his ...
and not from Ali.
Abbasid Caliphate (750–1517)
Abbasid Caliphs at Baghdad
 In 750, the Umayyad dynasty was overthrown by another family of
In 750, the Umayyad dynasty was overthrown by another family of Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
n origin, the Abbasids. Their time represented a scientific, cultural and religious flowering. Islamic art and music also flourished significantly during their reign. Their major city and capital Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
began to flourish as a center of knowledge, culture and trade. This period of cultural fruition ended in 1258 with the sack of Baghdad
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sack of ...
by the Mongols under Hulagu Khan
Hulagu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulegu ( mn, Хүлэгү/ , lit=Surplus, translit=Hu’legu’/Qülegü; chg, ; Arabic: fa, هولاکو خان, ''Holâku Khân;'' ; 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of We ...
. The Abbasid Caliphate had however lost its effective power outside Iraq already by c. 920. By 945, the loss of power became official when the Buyids
The Buyid dynasty ( fa, آل بویه, Āl-e Būya), also spelled Buwayhid ( ar, البويهية, Al-Buwayhiyyah), was a Shia Iranian dynasty of Daylamite origin, which mainly ruled over Iraq and central and southern Iran from 934 to 1062. Coup ...
conquered Baghdad and all of Iraq. The empire fell apart and its parts were ruled for the next century by local dynasties.
In the 9th century, the Abbasids created an army loyal only to their caliphate, composed predominantly of Turkic Cuman, Circassian and Georgian slave origin known as Mamluks. By 1250 the Mamluks came to power in Egypt. The Mamluk army, though often viewed negatively, both helped and hurt the caliphate. Early on, it provided the government with a stable force to address domestic and foreign problems. However, creation of this foreign army and al-Mu'tasim's transfer of the capital from Baghdad to Samarra created a division between the caliphate and the peoples they claimed to rule. In addition, the power of the Mamluks steadily grew until Ar-Radi
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad (Muhammad) ibn Ja'far al-Muqtadir ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد (محمد) بن جعفر المقتدر, Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad (Muḥammad) ibn al-Muqtadir; December 909 – 23 December 940), usually simply known by his ...
(934–41) was constrained to hand over most of the royal functions to Muhammad ibn Ra'iq
Abu Bakr Muhammad ibn Ra'iq (died 13 February 942), usually simply known as Ibn Ra'iq, was a senior official of the Abbasid Caliphate, who exploited the caliphal government's weakness to become the first '' amir al-umara'' ("commander of commander ...
.
Under the Mamluk Sultanate of Cairo (1261–1517)
In 1261, following the Mongol conquest of Baghdad
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sack of ...
, the Mamluk rulers of Egypt tried to gain legitimacy for their rule by declaring the re-establishment of the Abbasid caliphate in Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
. The Abbasid caliphs in Egypt had little political power; they continued to maintain the symbols of authority, but their sway was confined to religious matters. The first Abbasid caliph of Cairo was Al-Mustansir (r. June–November 1261). The Abbasid caliphate of Cairo lasted until the time of Al-Mutawakkil III
Al-Mutawakkil III () (died 1543) was the seventeenth Abbasid caliph of Cairo for the Mamluk Sultanate from 1508 to 1516, and again in 1517.
Life
He was the last caliph of the later Egyptian-based Caliphate. Since the Mongol sack of Baghdad ...
, who ruled as caliph from 1508 to 1516, then he was deposed briefly in 1516 by his predecessor Al-Mustamsik
Al-Mustamsik (), (died 1521) was the sixteenth Abbasid caliph of Cairo under the tutelage of the Mamluk Sultanate. He served as caliph twice, his first term from 1497 to 1508 and his second term from 1516 to 1517, when he abdicated the position to ...
, but was restored again to the caliphate in 1517.
The Ottoman Great Sultan Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
defeated the Mamluk Sultanate and made Egypt part of the Ottoman Empire in 1517. Al-Mutawakkil III was captured together with his family and transported to Constantinople as a prisoner where he had a ceremonial role. He died in 1543, following his return to Cairo.
Parallel regional caliphates in the later Abbasid Era
The Abbasid dynasty lost effective power over much of the Muslim realm by the first half of the tenth century.
The Umayyad dynasty, which had survived and come to rule over Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
, reclaimed the title of Caliph in 929, lasting until it was overthrown in 1031.
= Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba (929–1031)
=
 During the Umayyad dynasty, the
During the Umayyad dynasty, the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
was an integral province of the Umayyad Caliphate ruling from Damascus. The Umayyads lost the position of Caliph in Damascus in 750, and Abd al-Rahman I became Emir of Córdoba in 756 after six years in exile. Intent on regaining power, he defeated the existing Islamic rulers of the area who defied Umayyad rule and united various local fiefdoms into an emirate.
Rulers of the emirate used the title "emir" or "sultan" until the 10th century, when Abd al-Rahman III
ʿAbd al-Rahmān ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn al-Ḥakam al-Rabdī ibn Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān al-Dākhil () or ʿAbd al-Rahmān III (890 - 961), was the Umayyad Emir of Córdoba from 912 to 92 ...
was faced with the threat of invasion by the Fatimid Caliphate. To aid his fight against the invading Fatimids, who claimed the caliphate in opposition to the generally recognised Abbasid Caliph of Baghdad, Al-Mu'tadid
Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Ṭalḥa al-Muwaffaq ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد بن طلحة الموفق), 853/4 or 860/1 – 5 April 902, better known by his regnal name al-Muʿtaḍid bi-llāh ( ar, المعتضد بالله, link=no, ...
, Abd al-Rahman III claimed the title of caliph himself. This helped Abd al-Rahman III gain prestige with his subjects, and the title was retained after the Fatimids were repulsed. The rule of the Caliphate is considered as the heyday of Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsula, before it fragmented into various taifa
The ''taifas'' (singular ''taifa'', from ar, طائفة ''ṭā'ifa'', plural طوائف ''ṭawā'if'', a party, band or faction) were the independent Muslim principalities and kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula (modern Portugal and Spain), re ...
s in the 11th century. This period was characterised by a flourishing in technology, trade and culture; many of the buildings of al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
were constructed in this period.
= Almohad Caliphate (1147–1269)
=
 The Almohad Caliphate ( ber, Imweḥḥden, from
The Almohad Caliphate ( ber, Imweḥḥden, from Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
', " the Monotheists" or "the Unifiers") was a Moroccan Berber Muslim movement founded in the 12th century.Ibn Tumart
Abu Abd Allah Amghar Ibn Tumart (Berber: ''Amghar ibn Tumert'', ar, أبو عبد الله امغار ابن تومرت, ca. 1080–1130 or 1128) was a Muslim Berber religious scholar, teacher and political leader, from the Sous in southern Mor ...
among the Masmuda
The Masmuda ( ar, المصمودة, Berber: ⵉⵎⵙⵎⵓⴷⵏ) is a Berber tribal confederation of Morocco and one of the largest in the Maghreb, along with the Zanata and the Sanhaja. They were composed of several sub-tribes: Berghouat ...
tribes of southern Morocco. The Almohads first established a Berber state in Tinmel
Tinmel (Berber: Tin Mel or Tin Mal, ar, تينمل) is a small mountain village in the High Atlas 100 km from Marrakesh, Morocco. Tinmel was the cradle of the Berber Almohad empire, from where the Almohads started their military campaigns a ...
in the Atlas Mountains in roughly 1120.Almoravid dynasty
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century tha ...
in governing Morocco by 1147, when Abd al-Mu'min
Abd al Mu'min (c. 1094–1163) ( ar, عبد المؤمن بن علي or عبد المومن الــكـومي; full name: ʿAbd al-Muʾmin ibn ʿAlī ibn ʿAlwī ibn Yaʿlā al-Kūmī Abū Muḥammad) was a prominent member of the Almohad mov ...
(r. 1130–1163) conquered Marrakech and declared himself Caliph. They then extended their power over all of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
by 1159. Al-Andalus followed the fate of Africa and all Islamic Iberia was under Almohad rule by 1172.
The Almohad dominance of Iberia continued until 1212, when Muhammad al-Nasir
Muhammad al-Nasir (,'' al-Nāṣir li-dīn Allāh Muḥammad ibn al-Manṣūr'', – 1213) was the fourth Almohad Caliph from 1199 until his death. Évariste Lévi-Provençalal-Nāṣir Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Brill Online, 2013 ...
(1199–1214) was defeated at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa
The Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa, known in Islamic history as the Battle of Al-Uqab ( ar, معركة العقاب), took place on 16 July 1212 and was an important turning point in the ''Reconquista'' and the medieval history of Spain. The Chris ...
in the Sierra Morena
The Sierra Morena is one of the main systems of mountain ranges in Spain. It stretches for 450 kilometres from east to west across the south of the Iberian Peninsula, forming the southern border of the ''Meseta Central'' plateau and providi ...
by an alliance of the Christian princes of Castile, Aragon, Navarre and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
. Nearly all of the Moorish dominions in Iberia were lost soon after, with the great Moorish cities of Córdoba and Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula ...
falling to the Christians in 1236 and 1248, respectively.
The Almohads continued to rule in northern Africa until the piecemeal loss of territory through the revolt of tribes and districts enabled the rise of their most effective enemies, the Marinid dynasty, in 1215. The last representative of the line, Idris al-Wathiq
Abu Idris al-Wathiq ( ar, أبو العلا أبو الدبوس الواثق بالله إدريس بن محمد بن أبي عبد الله محمد بن أبي حفص بن عبد المؤمن; died 1269), known as Abu Dabbus, was the last Almo ...
, was reduced to the possession of Marrakesh, where he was murdered by a slave in 1269; the Marinids seized Marrakesh, ending the Almohad domination of the Western Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
.
Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171)
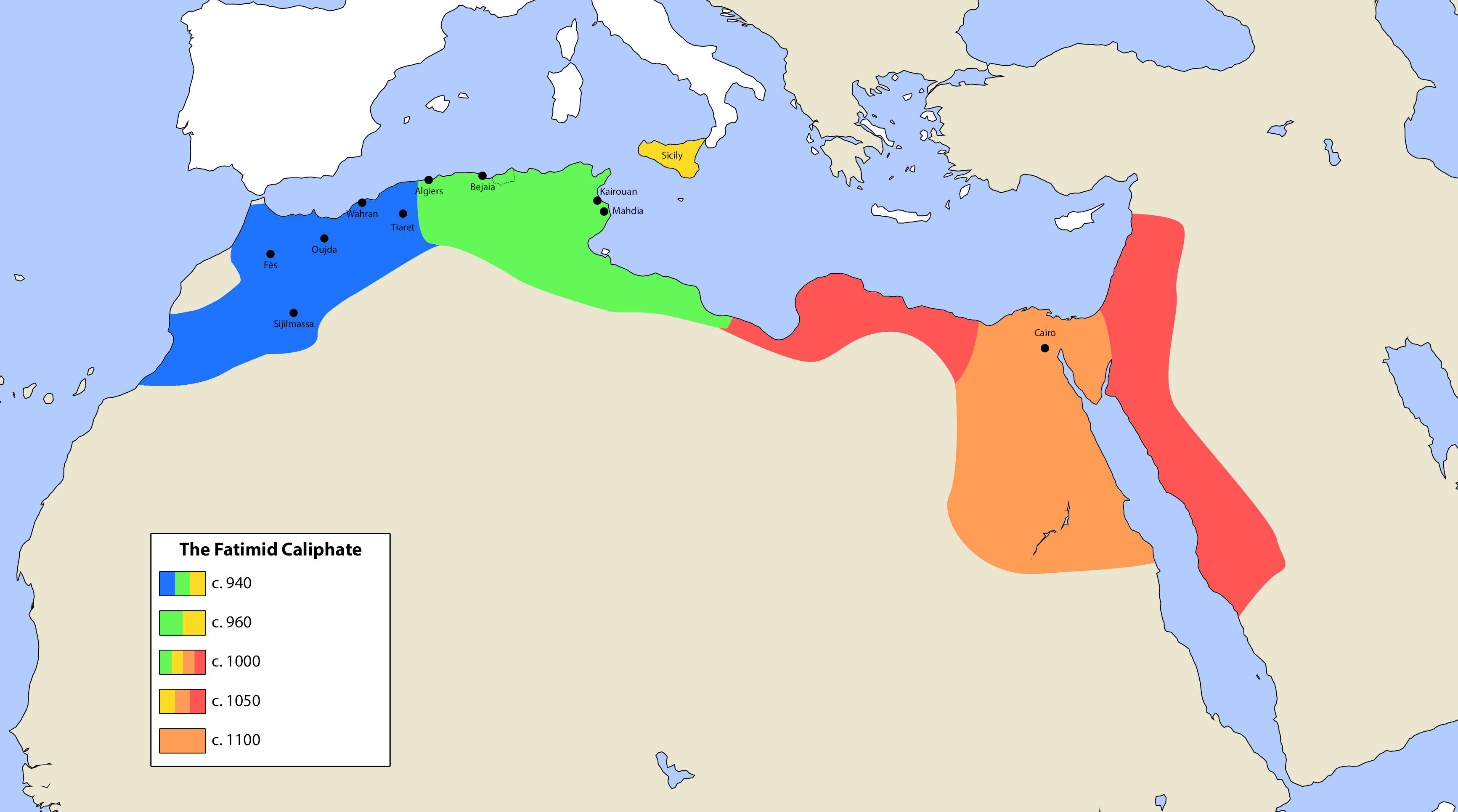 The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ili Shi'i caliphate, originally based in
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ili Shi'i caliphate, originally based in Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, that extended its rule across the Mediterranean coast
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the eas ...
of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and ultimately made Egypt the centre of its caliphate. At its height, in addition to Egypt, the caliphate included varying areas of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
and the Hejaz.
The Fatimids established the Tunisian city of Mahdia
Mahdia ( ar, المهدية ') is a Tunisian coastal city with 62,189 inhabitants, south of Monastir and southeast of Sousse.
Mahdia is a provincial centre north of Sfax. It is important for the associated fish-processing industry, as well as w ...
and made it their capital city, before conquering Egypt and building the city of Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
there in 969. Thereafter, Cairo became the capital of the caliphate, with Egypt becoming the political, cultural and religious centre of the state. Islam scholar Louis Massignon
Louis Massignon (25 July 1883 – 31 October 1962) was a Catholic scholar of Islam and a pioneer of Catholic-Muslim mutual understanding. He was an influential figure in the twentieth century with regard to the Catholic church's relationship w ...
dubbed the 4th century AH /10th century CE as the " Ismaili century in the history of Islam".
The term ''Fatimite'' is sometimes used to refer to the citizens of this caliphate. The ruling elite of the state belonged to the Ismaili branch of Shi'ism. The leaders of the dynasty were Ismaili imams
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( imām) to Ja'far al- ...
and had a religious significance to Ismaili Muslims. They are also part of the chain of holders of the office of the Caliphate, as recognised by some Muslims. Therefore, this constitutes a rare period in history in which the descendants of Ali (hence the name Fatimid, referring to Ali's wife Fatima) and the Caliphate were united to any degree, excepting the final period of the Rashidun Caliphate under Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
himself.
The caliphate was reputed to exercise a degree of religious tolerance towards non-Ismaili sects of Islam as well as towards Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Maltese Christians and Copts.
The Shiʻa Ubayd Allah al-Mahdi Billah
Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh/ʿUbayd Allāh ibn al-Ḥusayn (), 873 – 4 March 934, better known by his regnal name al-Mahdi Billah, was the founder of the Isma'ili Fatimid Caliphate, the only major Shi'a caliphate in Islamic history, and th ...
of the Fatimid dynasty
The Fatimid dynasty () was an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty of Arab descent that ruled an extensive empire, the Fatimid Caliphate, between 909 and 1171 CE. Claiming descent from Fatima and Ali, they also held the Isma'ili imamate, claiming to be the r ...
, who claimed descent from Muhammad through his daughter, claimed the title of Caliph in 909, creating a separate line of caliphs in North Africa. Initially controlling Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, the Fatimid caliphs extended their rule for the next 150 years, taking Egypt and Palestine, before the Abbasid dynasty was able to turn the tide, limiting Fatimid rule to Egypt. The Fatimid dynasty finally ended in 1171 and was overtaken by Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
of the Ayyubid dynasty.
Ayyubid Caliphate (1171–1260)
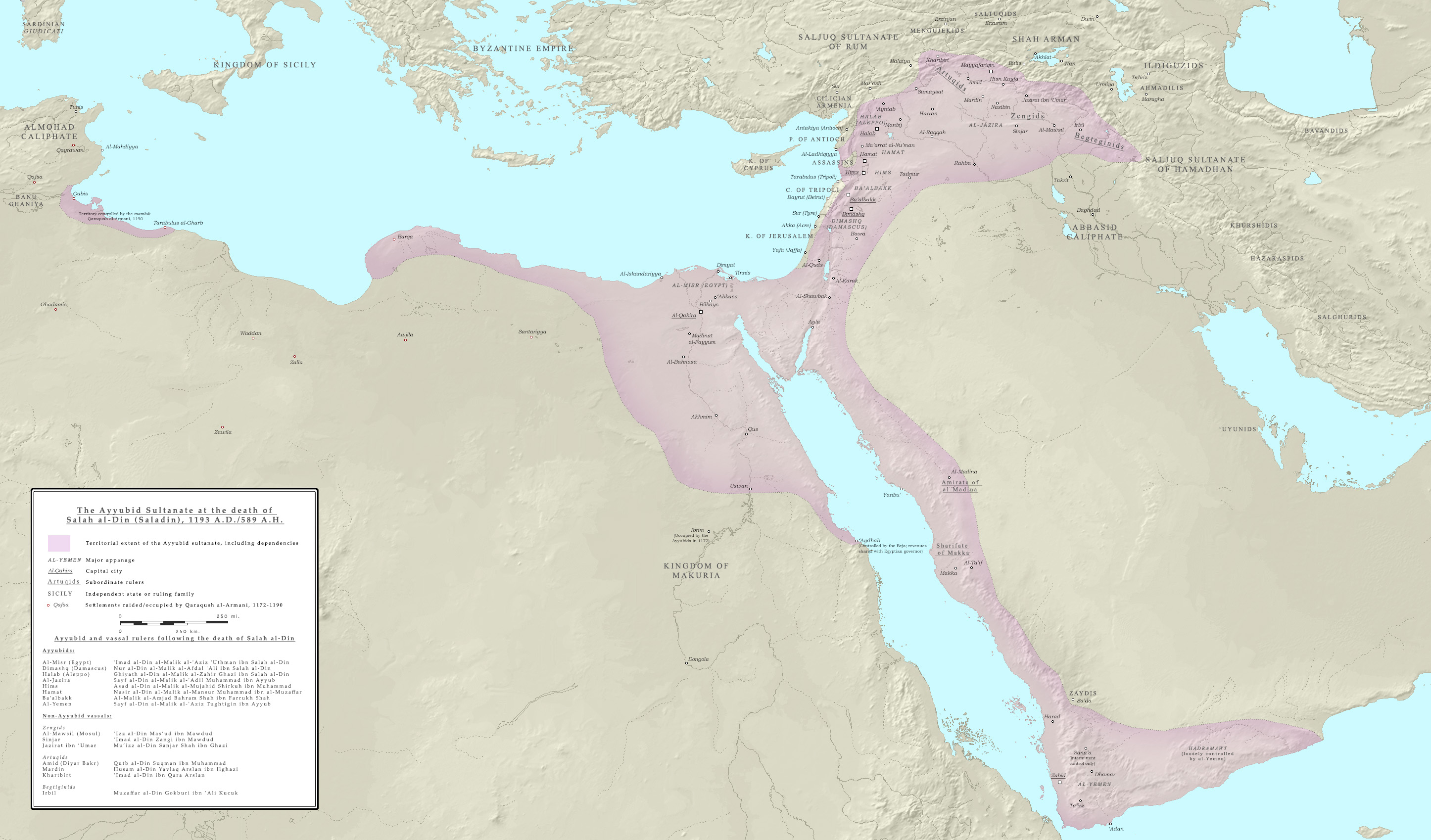 The Ayyubid Empire overtook the Fatimids by incorporating the empire into the .
The Ayyubid Empire overtook the Fatimids by incorporating the empire into the .Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
himself has been a widely celebrated caliph in Islamic history.[Natho, Kadir I. ''Circassian History''. Pages 150]
Ottoman Caliphate (1517–1924)

 The caliphate was claimed by the
The caliphate was claimed by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire ( tr, Osmanlı padişahları), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to its dissolution in 1922. At its hei ...
beginning with Murad I
Murad I ( ota, مراد اول; tr, I. Murad, Murad-ı Hüdavendigâr (nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'', from fa, خداوندگار, translit=Khodāvandgār, lit=the devotee of God – meaning "sovereign" in this context); 29 June 1326 – 15 Jun ...
(reigned 1362 to 1389),Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders ...
. In 1453, after Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
's conquest of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
, the seat of the Ottomans moved to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, present-day Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
. In 1517, the Ottoman sultan Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
defeated and annexed the Mamluk Sultanate of Cairo into his empire.Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
and Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, which further strengthened the Ottoman claim to the caliphate in the Muslim world. Ottomans gradually came to be viewed as the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' leaders and representatives of the Islamic world. However, the earlier Ottoman caliphs did not officially bear the title of caliph in their documents of state, inscriptions, or coinage.[Dominique Sourdel]
"The history of the institution of the caliphate"
(1978) It was only in the late eighteenth century that the claim to the caliphate was discovered by the sultans to have a practical use, since it allowed them to counter Russian claims to protect Ottoman Christians with their own claim to protect Muslims under Russian rule.Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, were lost to the Russian Empire.Abdul Hamid I
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid I ( ota, عبد الحميد اول, ''`Abdü’l-Ḥamīd-i evvel''; tr, Birinci Abdülhamid; 20 March 1725 – 7 April 1789) was the 27th Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, reigning over the Ottoman Empire from 1774 ...
claimed a diplomatic victory by being allowed to remain the religious leaders of Muslims in the now-independent Crimea as part of the peace treaty; in return Russia became the official protector of Christians in Ottoman territory.Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayn ...
with the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
in 1774, when the Empire retained moral authority Moral authority is authority premised on principles, or fundamental truths, which are independent of written, or positive, laws. As such, moral authority necessitates the existence of and adherence to truth. Because truth does not change, the princi ...
on territory whose sovereignty was ceded to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. By the eve of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Ottoman state, despite its weakness relative to Europe, represented the largest and most powerful independent Islamic political entity. The sultan also enjoyed some authority beyond the borders of his shrinking empire as caliph of Muslims in Egypt, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
.
In 1899 John Hay, U.S. Secretary of State, asked the American ambassador to Ottoman Turkey
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, Oscar Straus, to approach Sultan Abdul Hamid II to use his position as caliph to order the Tausūg people
The Tausūg or Suluk ( tsg, Tau Sūg), are an ethnic group of the Philippines and Malaysia. A small population can also be found in the northern part of North Kalimantan, Indonesia. The Tausūg are part of the wider political identity of Musli ...
of the Sultanate of Sulu
The Sultanate of Sulu ( Tausūg: ''Kasultanan sin Sūg'', كاسولتانن سين سوڬ; Malay: ''Kesultanan Sulu''; fil, Sultanato ng Sulu; Chavacano: ''Sultanato de Sulu/Joló''; ar, سلطنة سولك) was a Muslim state that ruled ...
in the Philippines to submit to American suzerainty and American military rule; the Sultan obliged them and wrote the letter which was sent to Sulu via Mecca. As a result, the "Sulu Mohammedans ... refused to join the insurrectionists and had placed themselves under the control of our army, thereby recognizing American sovereignty."
Abolition of the Caliphate (1924)
 After the
After the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
of October 1918 with the military occupation of Constantinople
The occupation of Istanbul ( tr, İstanbul'un İşgali; 12 November 1918 – 4 October 1923), the capital of the Ottoman Empire, by British, French, Italian, and Greek forces, took place in accordance with the Armistice of Mudros, which ended Ot ...
and Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
(1919), the position of the Ottomans was uncertain. The movement to protect or restore the Ottomans gained force after the Treaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well ...
(August 1920) which imposed the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire
The partition of the Ottoman Empire (30 October 19181 November 1922) was a geopolitical event that occurred after World War I and the occupation of Constantinople by British, French and Italian troops in November 1918. The partitioning was ...
and gave Greece a powerful position in Anatolia, to the distress of the Turks. They called for help and the movement was the result. The movement had collapsed by late 1922.
On 3 March 1924, the first President of the Turkish Republic, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, as part of his reforms, constitutionally abolished the institution of the caliphate.claimed
"Claimed" is the eleventh episode of the The Walking Dead (season 4), fourth season of the Apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction, post-apocalyptic Horror fiction, horror television series ''The Walking Dead (TV series), The Walking Dead'', wh ...
by Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca and Hejaz, leader of the Arab Revolt, but his kingdom was defeated and annexed by ibn Saud in 1925.
Egyptian scholar Ali Abdel Raziq published his 1925 book ''Islam and the Foundations of Governance''. The argument of this book has been summarized as "Islam does not advocate a specific form of government". He focussed his criticism both at those who use religious law as contemporary political proscription and at the history of rulers claiming legitimacy by the caliphate.[Bertrand Badie, Dirk Berg-Schlosser, Leonardo Morlino (eds). International Encyclopedia of Political Science, Volume 1. Sage, 2011. p. 1350.] Raziq wrote that past rulers spread the notion of religious justification for the caliphate "so that they could use religion as a shield protecting their thrones against the attacks of rebels".
A summit was convened at Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
in 1926 to discuss the revival of the caliphate, but most Muslim countries did not participate and no action was taken to implement the summit's resolutions. Though the title ''Ameer al-Mumineen'' was adopted by the King of Morocco and by Mullah Omar, Mohammed Omar, former head of the Taliban of Afghanistan, neither claimed any legal standing or authority over Muslims outside the borders of their respective countries.
Since the end of the Ottoman Empire, occasional demonstrations have been held calling for the re-establishment of the caliphate. Organisations which call for the re-establishment of the caliphate include Hizb ut-Tahrir and the Muslim Brotherhood.[Jay Tolson, "Caliph Wanted: Why An Old Islamic Institution Resonates With Many Muslims Today", ''U.S News & World Report'' 144.1 (14 January 2008): 38–40.]
Parallel regional caliphates to the Ottomans
=Indian subcontinent
=
 After the Umayyad campaigns in India and the conquest on small territories of the western part of the Indian peninsula, early Indian Muslim dynasties were founded by the Ghurid dynasty and the Ghaznavids, most notably the Delhi Sultanate. The Indian sultanates did not extensively strive for a caliphate since the Ottoman Empire was already observing the caliphate. Although the Mughal Empire is not recognised as a caliphate, its sixth emperor Aurangzeb, Muhammad Alamgir Aurangzeb has often been regarded as one of the few Islamic caliphs to have ruled the Indian peninsula. He received support from Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans such as Suleiman II of the Ottoman Empire, Suleiman II and Mehmed IV. As a memorizer of Quran, Aurangzeb fully established sharia in South Asia via his Fatawa 'Alamgiri. He re-introduced jizya and banned Islamically unlawful activities. However, Aurangzeb's personal expenses were covered by his own incomes, which included the sewing of caps and trade of his written copies of the Quran. Thus he has been compared to the 2nd Caliph Umar, Umar bin Khattab and Kurdish conqueror
After the Umayyad campaigns in India and the conquest on small territories of the western part of the Indian peninsula, early Indian Muslim dynasties were founded by the Ghurid dynasty and the Ghaznavids, most notably the Delhi Sultanate. The Indian sultanates did not extensively strive for a caliphate since the Ottoman Empire was already observing the caliphate. Although the Mughal Empire is not recognised as a caliphate, its sixth emperor Aurangzeb, Muhammad Alamgir Aurangzeb has often been regarded as one of the few Islamic caliphs to have ruled the Indian peninsula. He received support from Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans such as Suleiman II of the Ottoman Empire, Suleiman II and Mehmed IV. As a memorizer of Quran, Aurangzeb fully established sharia in South Asia via his Fatawa 'Alamgiri. He re-introduced jizya and banned Islamically unlawful activities. However, Aurangzeb's personal expenses were covered by his own incomes, which included the sewing of caps and trade of his written copies of the Quran. Thus he has been compared to the 2nd Caliph Umar, Umar bin Khattab and Kurdish conqueror Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
. Other notable rulers such as Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji, Alauddin Khilji, Firuz Shah Tughlaq, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, Babur, Sher Shah Suri, Nasir I of Kalat, Tipu Sultan, and the Nawabs of Bengal were popularly given the term Khalifa.
=Bornu Caliphate (1472–1893)
=
The Bornu Caliphate, which was headed by the Bornu Emperors, began in 1472. A rump state of the larger Kanem-Bornu Empire, its rulers held the title of Caliph until 1893, when it was absorbed into the British Colony of Nigeria and British Cameroon, Northern Cameroons Protectorate. The British recognized them as the 'Sultans of Bornu', one step down in Muslim royal titles. After Nigeria became independent, its rulers became the 'Emirs of Bornu', another step down.
=Yogyakarta Caliphate (1755–2015)
=
The Indonesian Yogyakarta Sultanate, Sultan of Yogyakarta historically used ''Khalifatullah'' (Caliph of God) as one of his many titles. In 2015 sultan Hamengkubuwono X renounced any claim to the Caliphate in order to facilitate his Princess Mangkubumi, daughter's inheritance of the throne, as the theological opinion of the time was that a woman may hold the secular office of sultan but not the spiritual office of caliph.
=Sokoto Caliphate (1804–1903)
=
The Sokoto Caliphate was an Islamic state in what is now Nigeria led by Usman dan Fodio. Founded during the Fulani War in the early 19th century, it controlled one of the most powerful empires in sub-Saharan Africa prior to European conquest and colonisation. The caliphate remained extant through the colonial period and afterwards, though with reduced power. The current head of the Sokoto Caliphate is Sa'adu Abubakar.
=Toucouleur Empire (1848–1893)
=
The Toucouleur Empire, also known as the Tukular Empire, was one of the Fulani jihad states in sub-saharan Africa. It was eventually pacified and annexed by the French Colonial Empire, French Republic, being incorporated into French West Africa.
=Khilafat Movement (1919–1924)
=
The Khilafat Movement was launched by Muslims in Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India in 1920 to defend the Ottoman Caliphate Aftermath of World War I, at the end of the First World War and it spread throughout the British colonial territories. It was strong in British India where it formed a rallying point for some Indian Muslims as one of many anti-British Indian political movements. Its leaders included Mohammad Ali Jouhar, his brother Shawkat Ali and Abul Kalam Azad, Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, Mukhtar Ahmed Ansari, Dr. Mukhtar Ahmed Ansari, Hakim Ajmal Khan and Barrister Muhammad Jan Abbasi. For a time it was supported by Mahatma Gandhi, Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, who was a member of the Central Khilafat Committee. However, the movement lost its momentum after the abolition of the Caliphate in 1924. After further arrests and flight of its leaders, and a series of offshoots splintered off from the main organisation, the Movement eventually died down and disbanded.
Sharifian Caliphate (1924–25)
The Sharifian Caliphate ( ar, خلافة شريفية) was an Arab caliphate proclaimed by the Sharif of Mecca, Sharifian rulers of Kingdom of Hejaz, Hejaz in 1924 previously known as Hejaz Vilayet, Vilayet Hejaz, declaring independence from the Ottoman Caliphate
The Caliphate of the Ottoman Empire ( ota, خلافت مقامى, hilâfet makamı, office of the caliphate) was the claim of the heads of the Turkish Ottoman dynasty to be the caliphs of Islam in the late medieval and the early modern era. ...
. The idea of the Sharifian Caliphate had been floating around since at least the 15th century. Toward the end of the 19th century, it started to gain importance due to the decline of the Ottoman Empire, which was heavily defeated in the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78. There is little evidence, however, that the idea of a Sharifian Caliphate ever gained wide grassroots support in the Middle East or anywhere else in the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
.
Non-political caliphates
Though non-political, some Sufism, Sufi tariqa, orders and the Khalifatul Masih, Ahmadiyya movement define themselves as caliphates. Their leaders are thus commonly referred to as ''khalifas'' (caliphs).
Sufi caliphates
In Sufism, tariqas (orders) are led by spiritual leaders (khilafah ruhaniyyah), the main khalifas, who nominate local khalifas to organize zaouias.
Sufi caliphates are not necessarily hereditary. Khalifas are aimed to serve the ''silsilah'' in relation to spiritual responsibilities and to propagate the teachings of the tariqa.
Ahmadiyya Caliphate (1908–present)
 The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community is a self-proclaimed Islamic revivalist movement founded in 1889 by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad of Qadian, India, who claimed to be the promised Jesus, Messiah and Mahdi, awaited by Muslims. He also claimed to be a follower-prophet subordinate to Muhammad, the prophet of Islam. The group are traditionally shunned by the majority of Muslims.
After Ahmad's death in 1908, his first successor, Hakeem Noor-ud-Din, became the caliph of the community and assumed the title of ''Khalifatul Masih'' (Successor or Caliph of the Messiah). After Hakeem Noor-ud-Din, the first caliph, the title of the Ahmadiyya caliph continued under Mirza Basheer-ud-Din Mahmood Ahmad, Mirza Mahmud Ahmad, who led the community for over 50 years. Following him were Mirza Nasir Ahmad and then Mirza Tahir Ahmad who were the third and fourth caliphs respectively. The current caliph is Mirza Masroor Ahmad, who lives in London.
The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community is a self-proclaimed Islamic revivalist movement founded in 1889 by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad of Qadian, India, who claimed to be the promised Jesus, Messiah and Mahdi, awaited by Muslims. He also claimed to be a follower-prophet subordinate to Muhammad, the prophet of Islam. The group are traditionally shunned by the majority of Muslims.
After Ahmad's death in 1908, his first successor, Hakeem Noor-ud-Din, became the caliph of the community and assumed the title of ''Khalifatul Masih'' (Successor or Caliph of the Messiah). After Hakeem Noor-ud-Din, the first caliph, the title of the Ahmadiyya caliph continued under Mirza Basheer-ud-Din Mahmood Ahmad, Mirza Mahmud Ahmad, who led the community for over 50 years. Following him were Mirza Nasir Ahmad and then Mirza Tahir Ahmad who were the third and fourth caliphs respectively. The current caliph is Mirza Masroor Ahmad, who lives in London.
Period of dormancy
Once the subject of intense conflict and rivalry amongst Muslim rulers, the caliphate lay dormant and largely unclaimed since the 1920s. For the vast majority of Muslims the caliph, as leader of the ummah
' (; ar, أمة ) is an Arabic word meaning "community". It is distinguished from ' ( ), which means a nation with common ancestry or geography. Thus, it can be said to be a supra-national community with a common history.
It is a synonym for ' ...
, "is cherished both as memory and ideal"[''Washington Post'',]
Reunified Islam: Unlikely but Not Entirely Radical, Restoration of Caliphate resonates With Mainstream Muslims
. as a time when Muslims "enjoyed scientific and military superiority globally". The Islamic prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
is reported to have prophesied:
"Kalifatstaat": Federated Islamic State of Anatolia (1994–2001)
The '':de:Kalifatstaat, Kalifatstaat'' ("Caliphate State") was the name of an Islamist organization in Germany that was proclaimed at an event in Cologne in 1994 and banned in December 2001 after an amendment to the Association Act, which abolished the religious privilege. However, this caliphate was never institutionalized under international law, but only an intention for an Islamic "state within the state".
The caliphate emerged in 1994 from the "Federated Islamic State of Anatolia" ( tr, Anadolu Federe İslam Devleti, AFİD), which existed in Germany from 1992 to 1994 as the renaming of the Association of Islamic Associations and Municipalities (İCCB). In 1984 the latter split off from the Islamist organization Millî Görüş. The leader of the association proclaimed himself the caliph, the worldwide spiritual and worldly head of all Muslims. Since then, the organization has seen itself as a "Caliphate State" ( tr, Hilafet Devleti). From an association law perspective, the old name remained.
The leader was initially :de:Cemaleddin Kaplan, Cemalettin Kaplan, who was nicknamed "Ruhollah Khomeini, Khomeini of Cologne" by the German public. In Turkish media he was referred to as the "Dark Voice" ( tr, Kara Ses). At an event in honor of Kaplan in 1993, the German convert to Islam :de:Andreas Abu Bakr Rieger, Andreas Abu Bakr Rieger publicly "regretted" in front of hundreds of listeners that the Germans had not completely destroyed the Jews: "Like the Turks, we Germans have often had a good cause in history fought, although I have to admit that my grandfathers weren't thorough with our main enemy."
Abu Issa caliphate (1993 – circa 2014)
A contemporary effort to re-establish the caliphate by supporters of armed jihad that predates Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi and the Islamic State and was much less successful, was "the forgotten caliphate" of Muhammad bin ʿIssa bin Musa al Rifaʿi ("known to his followers as Abu ʿIssa"). This "microcaliphate" was founded on 3 April 1993 on the Pakistan-Afghanistan border, when Abu Issa's small number of "Afghan Arabs" followers swore loyalty (bay'ah) to him.[Wood, ''The Way of the Strangers'', 2017, p.153] Abu Issa, was born in the city of Zarqa, Jordan and like his followers had come to Afghanistan to wage jihad against the Soviets. Unlike them he had ancestors in the tribe of Quraysh, a traditional requirement for a caliph. The caliphate was ostensibly an attempt to unite the many other jihadis who were not his followers and who were quarrelling amongst each other. It was not successful. Abu Issa's efforts to compel them to unite under his command were met "with mockery and then force". Local Afghans also despised him and his followers. Like the later Islamic State he tried to abolition of infidel currency and rejected nationalism.[ According to scholar Kevin Jackson,
]"Abu ʿIssa issued 'sad and funny' fatwas, as Abu al-Walid puts it, notably sanctioning the use of drugs. A nexus had been forged between [Abu Issa's group] and local drug smugglers. (The fatwa led one jihadist author to dismiss Abu Issa as the 'caliph of the Muslims among drug traffickers and takfir') Abu ʿIssa also prohibited the use of paper currency and ordered his men to burn their passports."
The territory under his control "did not extend beyond a few small towns" in Afghanistan's Kunar Province, Kunar province. Eventually he did not even control this area after the Taliban took it over in the late 1990s. The caliphate then moved to London, where they "preaching to a mostly skeptical jihadi intelligentsia about the obligation of establishing a caliphate".[Wood, The Way of the Strangers, 2017, p.155] They succeeded in attracting some jihadis (Yahya al-Bahrumi, Abu Umar al Kuwaiti) who later joined the Islamic State.
Abu Issa died in 2014, "after spending most of his final years in prison in London"[ Abu Umar al Kuwaiti became a judge for the Islamic state but was later executed for extremism after he "took takfir to new levels... pronouncing death sentences for apostasy on those who were ignorant of scripture – and then pronouncing takfir on those too reluctant to pronounce takfir."
]
Islamic State (2014–present)

 The group Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn, Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (Al-Qaeda in Iraq) formed as an affiliate of Al-Qaeda network of Islamism, Islamist militants during the Iraq War. The group eventually expanded into Syria and rose to prominence as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the Syrian Civil War. In the summer of 2014, the group launched the Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014), Northern Iraq offensive, seizing the city of Mosul. The group declared itself a caliphate under Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi on 29 June 2014 and renamed itself as the "Islamic State". ISIL's claim to be the highest authority of Muslims has been widely rejected. No prominent Muslim scholar has supported its declaration of caliphate; even Salafi jihadism, Salafi-jihadist preachers accused the group of engaging in political showmanship and bringing disrepute to the notion of Islamic state.
ISIL has been at war with armed forces including the Iraqi Army, the Syrian Army, the Free Syrian Army, Al-Nusra Front, Syrian Democratic Forces, and Iraqi Kurdistan's ''Peshmerga'' and People's Protection Units (YPG) along with a 60 nation coalition in its efforts to establish a ''de facto'' state on Iraqi and Syrian territory. At its height in 2014, the Islamic State held "about a third of Syria and 40 percent of Iraq". By December 2017 it had lost 95% of that territory, including Mosul, Iraq's second largest city, and the northern Syrian city of Raqqa, its "capital".
The group Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn, Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (Al-Qaeda in Iraq) formed as an affiliate of Al-Qaeda network of Islamism, Islamist militants during the Iraq War. The group eventually expanded into Syria and rose to prominence as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the Syrian Civil War. In the summer of 2014, the group launched the Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014), Northern Iraq offensive, seizing the city of Mosul. The group declared itself a caliphate under Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi on 29 June 2014 and renamed itself as the "Islamic State". ISIL's claim to be the highest authority of Muslims has been widely rejected. No prominent Muslim scholar has supported its declaration of caliphate; even Salafi jihadism, Salafi-jihadist preachers accused the group of engaging in political showmanship and bringing disrepute to the notion of Islamic state.
ISIL has been at war with armed forces including the Iraqi Army, the Syrian Army, the Free Syrian Army, Al-Nusra Front, Syrian Democratic Forces, and Iraqi Kurdistan's ''Peshmerga'' and People's Protection Units (YPG) along with a 60 nation coalition in its efforts to establish a ''de facto'' state on Iraqi and Syrian territory. At its height in 2014, the Islamic State held "about a third of Syria and 40 percent of Iraq". By December 2017 it had lost 95% of that territory, including Mosul, Iraq's second largest city, and the northern Syrian city of Raqqa, its "capital".
Ahmadiyya view
The members of the Ahmadiyya, Ahmadiyya community believe that the Ahmadiyya Caliphate (Arabic: ''Khilāfah'') is the continuation of the Islamic caliphate, first being the ''Rāshidūn'' (rightly guided) Caliphate (of Righteous Caliphs). This is believed to have been suspended with Ali, the son-in-law of Muhammad and re-established with the appearance of Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835–1908, the founder of the movement) whom Ahmadis identify as the Promised Messiah and Mahdi.
Ahmadis maintain that in accordance with Quranic verses (such as ) and numerous ahadith on the issue, ''Khilāfah'' can only be established by God Himself and is a divine blessing given to ''those who believe and work righteousness'' and uphold the unity of God, therefore any movement to establish the ''Khilāfah'' centered on human endeavours alone is bound to fail, particularly when the condition of the people diverges from the ‘precepts of prophethood’ and they are as a result disunited, their inability to establish a ''Khilāfah'' caused fundamentally by the lack of righteousness in them. Although the khalifa is elected it is believed that God himself directs the hearts of believers towards an individual. Thus the khalifa is designated neither necessarily by right (i.e. the rightful or competent one in the eyes of the people at that time) nor merely by election but primarily by God.
According to Ahmadiyya thought, a khalifa need not be the head of a state; rather the Ahmadiyya community emphasises the spiritual and organisational significance of the Khilāfah. It is primarily a religious/spiritual office, with the purpose of upholding, strengthening and spreading Islam and of maintaining the high spiritual and moral standards within the global community established by Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
– who was not merely a political leader but primarily a religious leader. If a khalifa does happen to bear governmental authority as a head of state, it is incidental and subsidiary in relation to his overall function as khalifa which is applicable to believers transnationally and not limited to one particular state.
Ahmadi Muslims believe that God has assured them that this Caliphate will endure to the end of time, depending on their righteousness and faith in God. The Khalifa provides unity, security, moral direction and progress for the community. It is required that the Khalifa carry out his duties through consultation and taking into consideration the views of the members of the ''Shura'' (consultative body). However, it is not incumbent upon him to always accept the views and recommendations of the members. The Khalifatul Masih has overall authority for all religious and organisational matters and is bound to decide and act in accordance with the Qur'an and sunnah.
Islamic call
A number of Islamist political parties and mujahideen called for the restoration of the caliphate by uniting Muslim nations, either through political action (e.g., Hizb ut-Tahrir), or through force (e.g., al-Qaeda). Various Islamist movements gained momentum in recent years with the ultimate aim of establishing a Caliphate. In 2014, ISIL/ISIS made a claim to re-establishing the Caliphate. Those advocating the re-establishment of a Caliphate differed in their methodology and approach. Some were locally oriented, mainstream political parties that had no apparent transnational objectives.
Abul A'la Maududi believed the caliph was not just an individual ruler who had to be restored, but was man's representation of God's authority on Earth:
The Muslim Brotherhood advocates Pan-Islamism, pan-Islamic unity and the implementation of Sharia, Islamic law. Founder Hassan al-Banna wrote about the restoration of the Caliphate.
One transnational group whose ideology was based specifically on restoring the caliphate as a pan-Islamic state is Hizb ut-Tahrir (literally, "Party of Liberation"). It is particularly strong in Central Asia and Europe and is growing in strength in the Arab world. It is based on the claim that Muslims can prove that God exists and that the Qur'an is the word of God. Hizb ut-Tahrir's stated strategy is a non-violent political and intellectual struggle.
In Southeast Asia, groups such as Jemaah Islamiyah aimed to establish a Caliphate across Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and parts of Thailand, the Philippines and Cambodia.
Al-Qaeda's Caliphate goals
Al-Qaeda has as one of its clearly stated goals the re-establishment of a caliphate. Its former leader, Osama bin Laden, called for Muslims to "establish the righteous caliphate of our umma". Al-Qaeda chiefs released a statement in 2005, under which, in what they call "phase five" there will be "an Islamic state, or caliphate". Al-Qaeda has named its Internet newscast from Iraq "The Voice of the Caliphate". According to author and Egyptian native Lawrence Wright, Ayman al-Zawahiri, bin Laden's mentor and al-Qaeda's second-in-command until 2011, once "sought to restore the caliphate... which had formally ended in 1924 following the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire but which had not exercised real power since the thirteenth century." Zawahiri believes that once the caliphate is re-established, Egypt would become a rallying point for the rest of the Islamic world, leading the ''jihad'' against the West. "Then history would make a new turn, God willing", Zawahiri later wrote, "in the opposite direction against the empire of the United States and the world's Jewish government".
Opposition
Scholar Olivier Roy (professor), Olivier Roy writes that "early on, Islamists replace the concept of the caliphate ... with that of the emir." There were a number of reasons including "that according to the classical authors, a caliph must be a member of the tribe of the Prophet (the Quraysh) ... moreover, caliphs ruled societies that the Islamists do not consider to have been Islamic (the Ottoman Empire)." This is not the view of the majority of Islamist groups, as both the Muslim Brotherhood and Hizb ut-Tahrir view the Ottoman state as a caliphate.
Religious basis
Qur'an
The Quran uses the term ''khalifa'' twice. First, in al-Baqara, 30, it refers to God in Islam, God creating humanity as his ''khalifa'' on Earth. Second, in Sad (sura), Sad, 26, it addresses King David in Islam, David as God's ''khalifa ''and reminds him of his obligation to rule with justice.
In addition, the following excerpt from the Quran, known as the 'Istikhlaf Verse', is used by some to argue for a Quranic basis for Caliphate:
In the above verse, the word ''Khulifa'' (the plural of ''Khalifa'') has been variously translated as "successors" and "ones who accede to power".
Several schools of jurisprudence and thought within Sunni Islam argue that to govern a state by Sharia is, by definition, to rule via the Caliphate and use the following verses to sustain their claim.
''Hadith''
The following ''hadith'' from Musnad Ahmad ibn Hanbal can be understood to prophesy two eras of Caliphate (both on the lines/precepts of prophethood).
In the above, the first era of Caliphate is commonly accepted by Muslims to be that of the Rashidun Caliphate.
Nafi'a reported saying:
Hisham ibn Urwah reported on the authority of Abu Saleh on the authority of Abu Hurairah that Muhammad said:
Muslim narrated on the authority of al-A'araj, on the authority of Abu Hurairah, that Muhammad said:
Muslim reported on the authority of Abdel Aziz al-Muqrin, who said:
Prophesied Caliphate of the Mahdi
Many Islamic texts, including several ahadith, state that the Mahdi will be elected caliph and rule over a caliphate. A number of Islamic figures titled themselves both "caliph" and "al-Mahdi", including the first Abbasid caliph As-Saffah.
The ''Sahaba'' of Muhammad
Al-Habbab Ibn ul-Munthir said, when the Sahaba met in the wake of the death of Muhammad, (at the Saqifah, thaqifa hall) of Bani Sa’ida: Upon this Abu Bakr replied:
Then he got up and addressed the Muslims.
It has additionally been reported that Abu Bakr went on to say on the day of Al-Saqifa:
The Sahaba agreed to this and selected Abu Bakr as their first Khaleef. Habbab ibn Mundhir who suggested the idea of two Ameers corrected himself and was the first to give Abu Bakr the Bay'ah. This indicates an Ijma as-Sahaba of all of the Sahaba. Ali ibni abi Talib, who was attending the body of Muhammad at the time, also consented to this.
Imam Ali whom the Shia revere said:
Views of Islamic theologians
Scholars like Al-Mawardi, Ibn Hazm, Ahmad al-Qalqashandi, and Al-Sha`rani stated that the global Muslim community can have only one leader at any given time. Al-Nawawi and Abd al-Jabbar ibn Ahmad declared it impermissible to give oaths of loyalty to more than one leader.
Al-Joziri said:
Shia scholars have expressed similar opinions. However, the Shia school of thought states that the Imamah (Shia), leader must not be appointed by the Islamic ummah, but must be appointed by God.
Al-Qurtubi said that the caliph is the "pillar upon which other pillars rest", and said of the Quranic verse, "Indeed, man is made upon this earth a Caliph":
An-Nawawi said:
Al-Ghazali when writing of the potential consequences of losing the Caliphate said:
Ibn Taymiyyah said:
Government
Electing or appointing a Caliph
In his book ''The Early Islamic Conquests'' (1981), Fred Donner argues that the standard Arabian practice during the early Caliphates was for the prominent men of a kinship group, or tribe, to gather after a leader's death and elect a leader from amongst themselves, although there was no specified procedure for this shura, or consultative assembly. Candidates were usually from the same lineage as the deceased leader, but they were not necessarily his sons. Capable men who would lead well were preferred over an ineffectual direct heir, as there was no basis in the majority Sunni view that the head of state or governor should be chosen based on lineage alone. Since the Umayyads, all caliphates have been dynastic.
Traditionally, Sunni Muslim madhhabs all agreed that a Caliph must be a descendant of the Quraysh. Al-Baqillani has said that the leader of the Muslims simply should be from the majority.
Sunni belief
Following the death of Muhammad, a meeting took place at Saqifah. At that meeting, Abu Bakr was elected caliph by the Muslim community. Sunni Muslims developed the belief that the caliph is a temporal political ruler, appointed to rule within the bounds of Islamic law (Sharia). The job of adjudicating orthodoxy and Islamic law was left to Ijtihad#Qualifications of a mujtahid, mujtahids, legal specialists collectively called the Ulama. Many Muslims call the first four caliphs the Rashidun, meaning the Rightly-Guided, because they are believed to have followed the Qur'an and the sunnah (example) of Muhammad.
Shi'a belief
With the exception of Zaidiyyah, Zaidis,Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
, his cousin and son-in-law, as his successor. For the Twelvers, Ali and his eleven descendants, the twelve Imams, are believed to have been considered, even before their birth, as the only valid Islamic rulers appointed and decreed by God. Shia Muslims believe that all the Muslim caliphs following Muhammad's death to be illegitimate due to their unjust rule and that Muslims have no obligation to follow them, as the only guidance that was left behind, as ordained in the hadith of the Hadith of the two weighty things, two weighty things, was the Islamic holy book, the Quran and Ahl al-Bayt, Muhammad's family and offspring, who are believed to be Infallibility, infallible, therefore able to lead society and the Muslim community with complete justice and equity.
''Majlis al-Shura''
The Majlis-ash-Shura, Majlis al-Shura (literally "consultative assembly") was a representation of the idea of consultative governance. The importance of this is premised by the following verses of the Qur'an:
*
*
The majlis is also the means to elect a new caliph.[
Some Islamist interpretations of the role of the Majlis al-Shura are the following:
In an analysis of the shura chapter of the Qur'an, Islamist author Sayyid Qutb argues that Islam only requires the ruler to consult with some of the representatives of the ruled and govern within the context of the Sharia. Taqiuddin al-Nabhani, the founder of a transnational political movement devoted to the revival of the Caliphate, writes that although the Shura is an important part of "the ruling structure" of the Islamic caliphate, "(it is) not one of its pillars", meaning that its neglect would not make a Caliph's rule un-Islamic such as to justify a rebellion. However, the Muslim Brotherhood, the largest Islamic movement in Egypt, has toned down these Islamist views by accepting in principle that in the modern age the Majlis al-Shura is democracy but during its governance of Egypt in 2013, the Muslim Brotherhood did not put that principle into practice.
]
Accountability of rulers
Al-Mawardi said that if the rulers meet their Islamic responsibilities to the public the people must obey their laws, but a Caliph or ruler who becomes either unjust or severely ineffective must be impeached via the Majlis al-Shura. Al-Juwayni argued that Islam is the goal of the ummah, so any ruler who deviates from this goal must be impeached. Al-Ghazali believed that oppression by a caliph is sufficient grounds for impeachment. Rather than just relying on impeachment, Ibn Hajar al-Asqalani stated that the people have an obligation to rebel if the caliph begins to act with no regard for Islamic law. Ibn Hajar al-Asqalani said that to ignore such a situation is ''haraam'' and those who cannot revolt from inside the caliphate should launch a struggle from outside. Al-Asqalani used two ayahs from the Qur'an to justify this:
Islamic lawyers commented that when the rulers refuse to step down after being impeached through the Majlis, becoming dictators through the support of a corrupt army, if the majority is in agreement they have the option to launch a revolution. Many noted that this option is to be exercised only after factoring in the potential cost of life.[
]
Rule of law
The following hadith establishes the principle of rule of law in relation to nepotism and accountability
Various Islamic lawyers, however, place multiple conditions and stipulations on the execution of such a law, making it difficult to implement. For example, the poor cannot be penalised for stealing out of poverty, and during a time of drought in the Rashidun Empire, Rashidun caliphate, capital punishment was suspended until the effects of the drought passed.
Ulema, Islamic jurists later formulated the concept that all classes were subject to the law of the land, and no person is above the law; officials and private citizens alike have a duty to obey the same law. Furthermore, a Qadi (Islamic judge) was not allowed to discriminate on the grounds of religion, Race (classification of human beings), race, Human skin color, colour, kinship or prejudice. In a number of cases, Caliphs had to appear before judges as they prepared to render their verdict.
According to Noah Feldman, a law professor at Harvard University, the system of legal scholars and jurists responsible for the rule of law was replaced by the Codification (law), codification of Sharia by the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century:
Economy
During the Muslim Agricultural Revolution, the Caliphate understood that real incentives were needed to increase productivity and wealth and thus enhance tax revenues. A social transformation took place as a result of changing land ownership[Zohor Idrisi (2005)]
The Muslim Agricultural Revolution and its influence on Europe
FSTC. giving individuals of any gender, ethnic or religious background the right to buy, sell, mortgage law, mortgage and inheritance, inherit land for farming or any other purpose. Signatures were required on contracts for every major financial transaction concerning agriculture, Industrial sector, industry, commerce and employment. Copies of the contract were usually kept by both parties involved.[
Early forms of proto-capitalism and free markets were present in the Caliphate, since an early market economy and early form of merchant capitalism developed between the 8th and 12th centuries, which some refer to as "Islamic capitalism". A vigorous monetary economy developed based on the List of circulating currencies, circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar) and the integration of previously independent monetary areas. Business techniques and forms of Company, business organisation employed during this time included early contracts, bills of exchange, long-distance international trade, early forms of partnership (''mufawada'') such as limited partnerships (''mudaraba'') and early forms of Credit (finance), credit, debt, Profit (accounting), profit, Income statement, loss, Capital (economics), capital (''al-mal''), capital accumulation (''nama al-mal''),][ circulating capital, capital expenditure, revenue, cheques, promissory notes, trusts (''waqf''), startup companies, savings accounts, transactional accounts, Pawnshop, pawning, loaning, exchange rates, bankers, money changers, ledgers, Deposit account, deposits, Assignment (law), assignments, the double-entry bookkeeping system, and lawsuits. Organisational Business, enterprises similar to corporations independent from the Sovereign state, state also existed in the medieval Islamic world. Many of these concepts were adopted and further advanced in medieval Europe from the 13th century onwards.]Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
added to the duties of the state an allowance, paid on behalf of every man woman and child, starting at birth, creating the world's first state run social welfare program.
Maya Shatzmiller states that the demographic behavior of medieval Islamic society varied in some significant aspects from other agricultural societies. Nomadic groups within places like the deserts of Egypt and Morocco maintained high birth rates compared to rural and urban populations, though periods of extremely high nomadic birth rates seem to have occurred in occasional baby boom, "surges" rather than on a continuous basis. Individuals living in large cities had much lower birth rates, possibly due to the use of birth control methods and political or economic instability. This led to population declines in some regions. While several studies have shown that Ulema, Islamic scholars enjoyed a life expectancy of 59–75 years between the eleventh and thirteenth centuries,
Notable caliphs
* ''Rashidun'' ("Righteously Guided")
** Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
, first Rashidun Caliph. Subdued rebel tribes in the Ridda wars.
** Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
(Umar ibn al-Khattab), second Rashidun Caliph. During his reign, the Islamic empire expanded to include Egypt, Jerusalem and Persia.
** Uthman, (Uthman ibn Affan) third Rashidun Caliph, When Caliph Umar died in office aged 59/60 years, Uthman, aged 64/65 years, succeeded him and was the second-oldest to rule as Caliph. Under Uthman's leadership, the Islamic empire expanded into Fars (present-day Iran) in 650, and some areas of Khorasan (present-day Afghanistan) in 651. The conquest of Armenia had begun by the 640s.
** Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam ...
(Ali ibn Abu Talib), fourth Rashidun Caliph. Considered by Shi'a Muslims however to be the first Imam. His reign was fraught with internal conflict, with Muawiyah ibn Abi Sufyan (Muawiyah I) and Amr ibn al-As controlling the Levant and Egypt regions independently of Ali.
** Hasan ibn Ali, fifth Caliph. Considered as "rightly guided" by several historians. He abdicated his right to the caliphate in favour of Muawiyah I in order to end the potential for ruinous civil war.
* "Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
"
**Muawiyah I, the first caliph of the Umayyad dynasty. Muawiyah instituted dynastic rule by appointing his son Yazid I as his successor, a trend that would continue through subsequent caliphates.
** Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, Abd al-Malik was the fifth Umayyad caliph, ruling from April 685 until his death in 705. A member of the first generation of born Muslims, his early life in Medina was occupied with pious pursuits. He held administrative and military posts under Caliph Mu'awiya I (r. 661–680) and his own father, Caliph Marwan I (r. 684–685).
** Al-Walid I was the sixth Umayyad caliph, ruling from October 705 until his death. He was the eldest son of his predecessor Caliph Abd al-Malik.
** Umar II, Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz (Umar II), Umayyad caliph who is considered one of the finest rulers in Muslim history. He is also considered by some (mainly Sunnis) to be among the "rightly guided" caliphs.
** Yazid II was the ninth Umayyad caliph, ruling from February 720 until his death in 724.
** Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik, Hisham was the tenth Umayyad caliph who ruled from 724 until his death in 743. Hisham was a great patron of the arts, and he again encouraged arts in the empire. He also encouraged the growth of education by building more schools, and perhaps most importantly, by overseeing the translation of numerous literary and scientific masterpieces into Arabic. He returned to a stricter interpretation of the Sharia as Umar II, Umar had, and enforced it, even upon his own family.
** Al-Walid II was an Umayyad Caliph who ruled from 743 until his death in the year 744.
** Yazid III was the twelfth Umayyad caliph. He reigned for six months, from April 15 to October 3 or 4, 744, and died in that office.
** Marwan II was the fourteenth and last Umayyad caliph, ruling from 744 until his death in 750.
* "Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
"
** As-Saffah was the first caliph of the Abbasid caliphate, one of the longest and most important caliphates (Islamic dynasties) in Islamic history.
** Al-Mansur was the second Abbasid Caliph reigning from 136 AH to 158 AH (754–775) and succeeding his brother al-Saffah. Al-Mansur is generally regarded as the greatest Caliph of the Abbasid dynasty. He is also known for founding the 'round city' of Round city of Baghdad, Madinat al-Salam which was to become the core of imperial Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
** Al-Mahdi was the third Abbasid Caliph who reigned from 775 to his death in 785.
** Harun al-Rashid, Abbasid caliph during whose reign Baghdad became the world's prominent centre of trade, learning and culture. Harun is the subject of many stories in the famous ''One Thousand and One Nights.''
** Al-Ma'mun, a great Abbasid patron of Islamic philosophy and science
** Al-Mu'tasim was the eighth Abbasid caliph, ruling from 833 until his death in 842. The younger son of Caliph Harun al-Rashid. He is also known for founding the city of Abbasid Samarra, Samarra.
** Al-Mutawakkil was the tenth Abbasid caliph who reigned from 847 until 861. He was the son of al-Mu'tasim. He is considered an influential Abbasid Caliph.
** Al-Mu'tadid
Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Ṭalḥa al-Muwaffaq ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد بن طلحة الموفق), 853/4 or 860/1 – 5 April 902, better known by his regnal name al-Muʿtaḍid bi-llāh ( ar, المعتضد بالله, link=no, ...
was the Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate from 892 until his death in 902.
** Ar-Radi
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad (Muhammad) ibn Ja'far al-Muqtadir ( ar, أبو العباس أحمد (محمد) بن جعفر المقتدر, Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad (Muḥammad) ibn al-Muqtadir; December 909 – 23 December 940), usually simply known by his ...
was the twentieth Abbasid Caliph, reigning from 934 to his death. He died on 23 December 940 at the age of 31. He is considered the last Caliph of ''early Abbasid'' period.
** Al-Qadir, famous Caliph of later Abbasid period, 991–1031.
** Al-Muqtafi, famous Caliph of later Abbasid period, who reigned 1136–1160.
** Al-Nasir was the Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad from 1180 until his death in 1225. According to the historian, Angelika Hartmann, Al-Nasir was the last effective later Abbasid Caliph.
** Al-Musta'sim was the 37th and last Abbasid caliph to rule from Baghdad. He ruled from 1242 until his death in 1258.
*"Ottoman Caliphate
The Caliphate of the Ottoman Empire ( ota, خلافت مقامى, hilâfet makamı, office of the caliphate) was the claim of the heads of the Turkish Ottoman dynasty to be the caliphs of Islam in the late medieval and the early modern era. ...
"
** Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
, the 9th Sultan, the 1st Caliph and maiden title holder of "Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques" of the Ottoman Empire. Under his reign, the Empire grew by seventy percent.
** Suleiman the Magnificent, the 2nd Ottoman caliph, during whose reign the Ottoman Empire reached its zenith
** Ahmed I, the 8th Ottoman Caliph, who is well known for his construction of the Sultan Ahmed Mosque, Blue Mosque, one of the most famous mosques and tourist attraction in Turkey.
** Abdul Hamid II, the 25th and the last Ottoman caliph to rule with independent, absolute power
** Mehmed V, the 26th Ottoman Caliph, who made the Ottoman Empire enter into World War I in 1914, which would ultimately lead to the Empire's end.
** Abdulmejid II, the 28th and the last caliph of the Ottoman dynasty. Nominally the 37th Head of the Ottoman dynasty. In 1924, Grand National Assembly of Turkey Abolition of the Caliphate, abolished the Ottoman Caliphate and sent Mejid in exile.
See also
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
The theory of government in Islam
by The Internet Islamic University
The History of Al-Khilafah Ar-Rashidah (The Rightly Guided Caliphates)
School Textbook, By Dr. 'Abdullah al-Ahsan, `Abdullah Ahsan
The Crisis of the Early Caliphate
By Richard Stephen Humphreys, Stephen (EDT) Humphreys from The History of Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, al-Tabari
The Reunification of the Abbasid Caliphate
By Clifford Edmund (TRN) Bosworth, from The History of Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, al-Tabari
Return of the Caliphate to Baghdad
By Franz Rosenthal from The History of Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, al-Tabari
Pan-Islamism: Indian Muslims, the Ottomans and Britain (1877–1924)
By Azmi Özcan
Baghdad during the Abbasid Caliphate from Contemporary Arabic and Persian Sources
By Guy Le Strange
The Fall of the Caliphate of Cordoba: Berbers and Andalusis in conflict
By Peter C. Scales
Khilafat and Caliphate
By Mubasher Ahmad
The abolition of the Caliphate
From The Economist 8 March 1924
*''The Clash of the Caliphates: Understanding the real war of ideas'', by Tony Corn, Small Wars Journal, March 2011
*Hüseyin Yılmaz. ''Caliphate Redefined: The Mystical Turn in Ottoman Political Thought''. Princeton University Press, 2018. .
External links
– a three-part documentary by Al Jazeera English
The return of the caliphate
''The Guardian''.
Islamists urge caliphate revival
BBC News.
{{Authority control
Caliphates,
Islamic states by type
Pan-Islamism
Religious leadership roles
Islamic terminology
 In 750, the Umayyad dynasty was overthrown by another family of
In 750, the Umayyad dynasty was overthrown by another family of  The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ili Shi'i caliphate, originally based in
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ili Shi'i caliphate, originally based in  The Ayyubid Empire overtook the Fatimids by incorporating the empire into the . However,
The Ayyubid Empire overtook the Fatimids by incorporating the empire into the . However, 
 The caliphate was claimed by the
The caliphate was claimed by the  After the
After the  After the Umayyad campaigns in India and the conquest on small territories of the western part of the Indian peninsula, early Indian Muslim dynasties were founded by the Ghurid dynasty and the Ghaznavids, most notably the Delhi Sultanate. The Indian sultanates did not extensively strive for a caliphate since the Ottoman Empire was already observing the caliphate. Although the Mughal Empire is not recognised as a caliphate, its sixth emperor Aurangzeb, Muhammad Alamgir Aurangzeb has often been regarded as one of the few Islamic caliphs to have ruled the Indian peninsula. He received support from Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans such as Suleiman II of the Ottoman Empire, Suleiman II and Mehmed IV. As a memorizer of Quran, Aurangzeb fully established sharia in South Asia via his Fatawa 'Alamgiri. He re-introduced jizya and banned Islamically unlawful activities. However, Aurangzeb's personal expenses were covered by his own incomes, which included the sewing of caps and trade of his written copies of the Quran. Thus he has been compared to the 2nd Caliph Umar, Umar bin Khattab and Kurdish conqueror
After the Umayyad campaigns in India and the conquest on small territories of the western part of the Indian peninsula, early Indian Muslim dynasties were founded by the Ghurid dynasty and the Ghaznavids, most notably the Delhi Sultanate. The Indian sultanates did not extensively strive for a caliphate since the Ottoman Empire was already observing the caliphate. Although the Mughal Empire is not recognised as a caliphate, its sixth emperor Aurangzeb, Muhammad Alamgir Aurangzeb has often been regarded as one of the few Islamic caliphs to have ruled the Indian peninsula. He received support from Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans such as Suleiman II of the Ottoman Empire, Suleiman II and Mehmed IV. As a memorizer of Quran, Aurangzeb fully established sharia in South Asia via his Fatawa 'Alamgiri. He re-introduced jizya and banned Islamically unlawful activities. However, Aurangzeb's personal expenses were covered by his own incomes, which included the sewing of caps and trade of his written copies of the Quran. Thus he has been compared to the 2nd Caliph Umar, Umar bin Khattab and Kurdish conqueror 
 The group Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn, Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (Al-Qaeda in Iraq) formed as an affiliate of Al-Qaeda network of Islamism, Islamist militants during the Iraq War. The group eventually expanded into Syria and rose to prominence as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the Syrian Civil War. In the summer of 2014, the group launched the Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014), Northern Iraq offensive, seizing the city of Mosul. The group declared itself a caliphate under Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi on 29 June 2014 and renamed itself as the "Islamic State". ISIL's claim to be the highest authority of Muslims has been widely rejected. No prominent Muslim scholar has supported its declaration of caliphate; even Salafi jihadism, Salafi-jihadist preachers accused the group of engaging in political showmanship and bringing disrepute to the notion of Islamic state.
ISIL has been at war with armed forces including the Iraqi Army, the Syrian Army, the Free Syrian Army, Al-Nusra Front, Syrian Democratic Forces, and Iraqi Kurdistan's ''Peshmerga'' and People's Protection Units (YPG) along with a 60 nation coalition in its efforts to establish a ''de facto'' state on Iraqi and Syrian territory. At its height in 2014, the Islamic State held "about a third of Syria and 40 percent of Iraq". By December 2017 it had lost 95% of that territory, including Mosul, Iraq's second largest city, and the northern Syrian city of Raqqa, its "capital". It's caliph, Al-Baghdadi, was killed in a raid by U.S. forces on October 26, 2019, its "last holdout", the town of Al-Baghuz Fawqani, fell to Syrian Democratic Forces on March 23, 2019.
The group Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn, Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (Al-Qaeda in Iraq) formed as an affiliate of Al-Qaeda network of Islamism, Islamist militants during the Iraq War. The group eventually expanded into Syria and rose to prominence as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the Syrian Civil War. In the summer of 2014, the group launched the Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014), Northern Iraq offensive, seizing the city of Mosul. The group declared itself a caliphate under Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi on 29 June 2014 and renamed itself as the "Islamic State". ISIL's claim to be the highest authority of Muslims has been widely rejected. No prominent Muslim scholar has supported its declaration of caliphate; even Salafi jihadism, Salafi-jihadist preachers accused the group of engaging in political showmanship and bringing disrepute to the notion of Islamic state.
ISIL has been at war with armed forces including the Iraqi Army, the Syrian Army, the Free Syrian Army, Al-Nusra Front, Syrian Democratic Forces, and Iraqi Kurdistan's ''Peshmerga'' and People's Protection Units (YPG) along with a 60 nation coalition in its efforts to establish a ''de facto'' state on Iraqi and Syrian territory. At its height in 2014, the Islamic State held "about a third of Syria and 40 percent of Iraq". By December 2017 it had lost 95% of that territory, including Mosul, Iraq's second largest city, and the northern Syrian city of Raqqa, its "capital". It's caliph, Al-Baghdadi, was killed in a raid by U.S. forces on October 26, 2019, its "last holdout", the town of Al-Baghuz Fawqani, fell to Syrian Democratic Forces on March 23, 2019.