Approach Chord on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

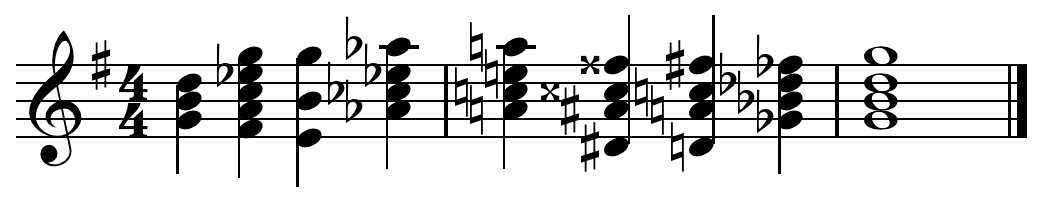

 In
In

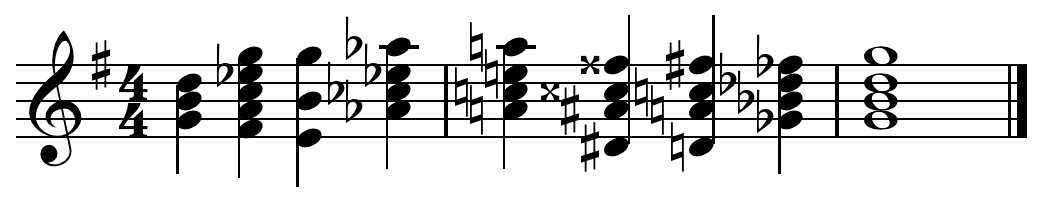

 In
In music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, an approach chord (also chromatic approach chord and dominant approach chord) is a chord one half-step
A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest interval (music), musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most Consonance and dissonance#Dissonance, dissonant when sounded harmonically ...
higher or lower than the goal, especially in the context of turnarounds and cycle-of-fourths progressions, for example the two bar 50s progression:
, G / Em / , Am / D7 / , ,
may be filled in with approach chords:
, G F9 Em Abm , Am D#7 D7 Gb7 , ,
F9 being the half-step to Em, Am being the half-step to Am, D7 being the half-step to D7, and G7 being the half-step to G. G being I, Em being vi, Am being ii, and D7 being V7 (see ii-V-I turnaround and circle progression
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is const ...
).
An approach chord may also be the chord immediately preceding the target chord such as the subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdomina ...
(F Maj7) preceding the tonic (CMaj7) creating a strong cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (19 ...
through the contrast of no more than two common tones: ''FA''CE – CE''GB''.
Approach chords may thus be a semitone or a fifth or fourth from their target.
Approach chords create the harmonic space of the modes
Mode ( la, modus meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* '' MO''D''E (magazine)'', a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is ...
in jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major ...
rather than secondary dominants.Pease, Ted (2003). ''Jazz Composition: Theory and Practice'', p.68. .
See also
*Passing chord
In music, a passing chord is a chord that connects, or passes between, the notes of two diatonic chords. "Any chord that moves between one diatonic chord and another one nearby may be loosely termed a passing chord. A diatonic passing chord ma ...
*Predominant chord
In music theory, a predominant chord (also pre-dominant) is any chord which normally resolves to a dominant chord.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II'', Glossary, p.359. Eighth Edition. . "Any chord in functional ...
*Tritone substitution
The tritone substitution is a common chord substitution found in both jazz and classical music. Where jazz is concerned, it was the precursor to more complex substitution patterns like Coltrane changes. Tritone substitutions are sometimes used in ...
References
Further reading
* R., Ken (2012). ''DOG EAR Tritone Substitution for Jazz Guitar'', Amazon Digital Services, Inc., ASIN: B008FRWNIW {{DEFAULTSORT:Approach Chord Chords