Aposemantic Coloration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential
Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential
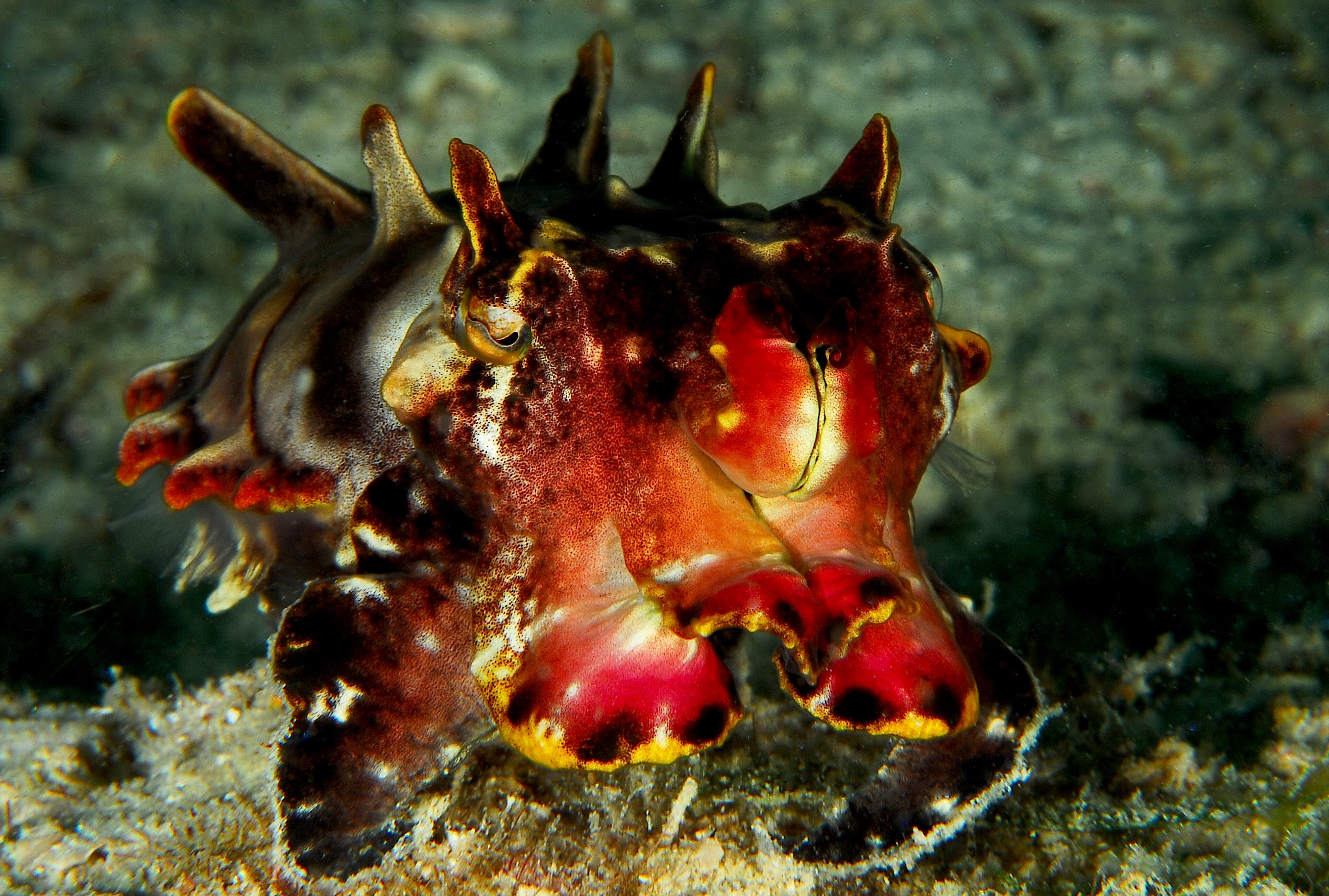 The function of aposematism is to prevent attack, by warning potential predators that the prey animal has defences such as being unpalatable or poisonous. The easily detected warning is a primary defence mechanism, and the non-visible defences are secondary. Aposematic signals are primarily visual, using bright colours and high-contrast patterns such as stripes. Warning signals are honest indications of noxious prey, because conspicuousness evolves in tandem with noxiousness. Thus, the brighter and more conspicuous the organism, the more toxic it usually is. This is in contrast to
The function of aposematism is to prevent attack, by warning potential predators that the prey animal has defences such as being unpalatable or poisonous. The easily detected warning is a primary defence mechanism, and the non-visible defences are secondary. Aposematic signals are primarily visual, using bright colours and high-contrast patterns such as stripes. Warning signals are honest indications of noxious prey, because conspicuousness evolves in tandem with noxiousness. Thus, the brighter and more conspicuous the organism, the more toxic it usually is. This is in contrast to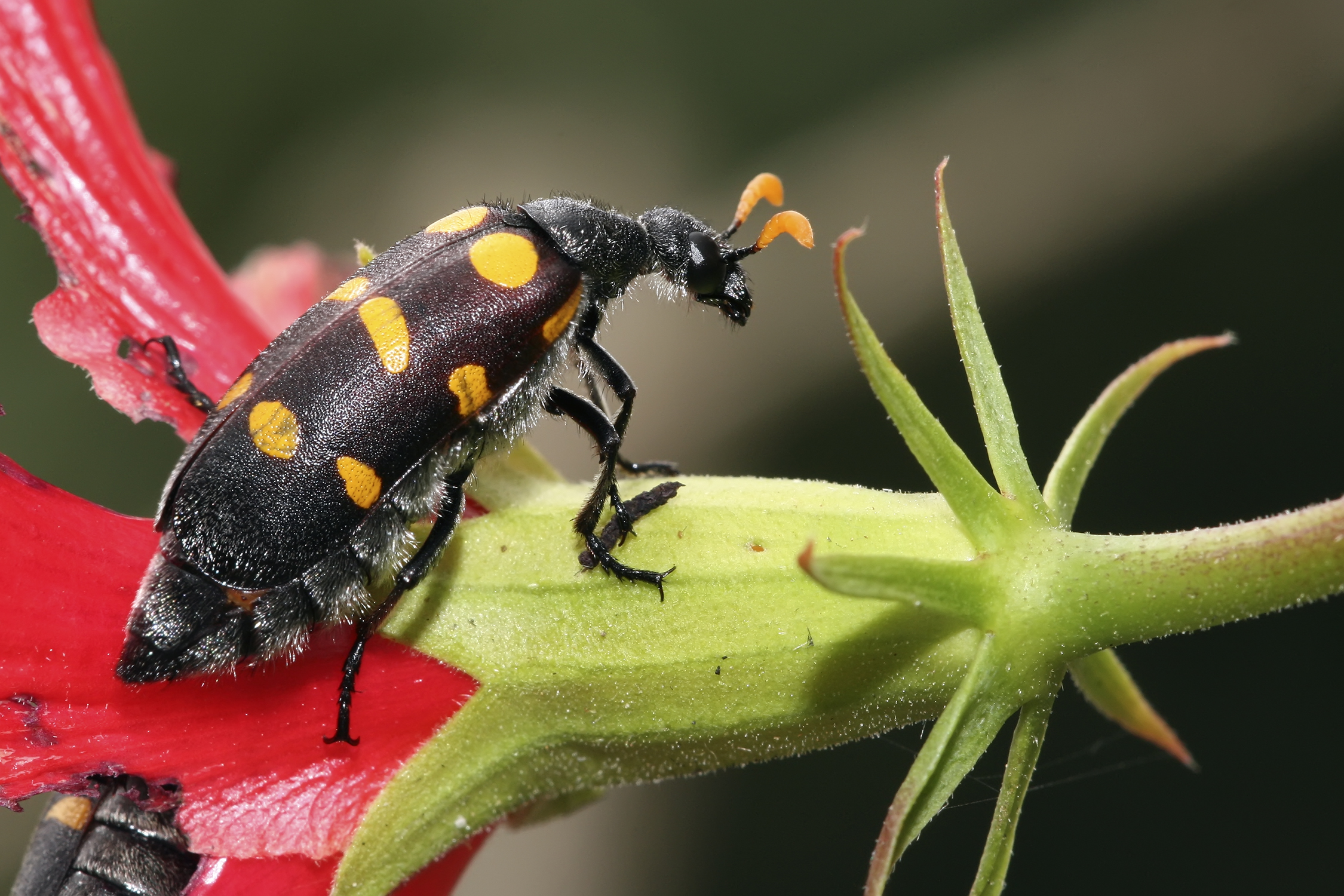  Unpalatability, broadly understood, can be created in a variety of ways. Some insects such as the
Unpalatability, broadly understood, can be created in a variety of ways. Some insects such as the
 Aposematism is widespread in insects, but less so in vertebrates, being mostly confined to a smaller number of
Aposematism is widespread in insects, but less so in vertebrates, being mostly confined to a smaller number of
 The
The

at a kind not fit for food, & thus they would escape seizure which is as bad as being eaten."
Since Darwin was enthusiastic about the idea, Wallace asked the Entomological Society of London to test the hypothesis. In response, the entomologist
 Wallace coined the term "warning colours" in an article about animal coloration in 1877. In 1890 Edward Bagnall Poulton renamed the concept ''aposematism'' in his book ''
Wallace coined the term "warning colours" in an article about animal coloration in 1877. In 1890 Edward Bagnall Poulton renamed the concept ''aposematism'' in his book ''
File:Micrurus tener.jpg, A model (to be mimicked), the venomous and genuinely aposematic coral snake
File:Red milk snake.JPG, The harmless

 Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential
Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, such as toxicity, venom, foul taste or smell, sharp spines, or aggressive nature. These advertising signals may take the form of conspicuous coloration, sounds, odours, or other perceivable characteristics. Aposematic signals are beneficial for both predator and prey, since both avoid potential harm.
The term was coined in 1877 by Edward Bagnall Poulton for Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural se ...
's concept of warning coloration. Aposematism is exploited in Müllerian mimicry, where species with strong defences evolve to resemble one another. By mimicking similarly coloured species, the warning signal to predators is shared, causing them to learn more quickly at less of a cost.
A genuine aposematic signal that a species actually possesses chemical or physical defences is not the only way to deter predators. In Batesian mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, after his work on bu ...
, a mimicking species resembles an aposematic model closely enough to share the protection, while many species have bluffing deimatic displays
Deimatic behaviour or startle display means any pattern of bluffing behaviour in an animal that lacks strong defences, such as suddenly displaying conspicuous eyespots, to scare off or momentarily distract a predator, thus giving the prey anima ...
which may startle a predator long enough to enable an otherwise undefended prey to escape.
There is good evidence for aposematism in terrestrial animals; its existence in marine animals is possible but disputed.
Etymology
The term aposematism was coined by the English zoologist Edward Bagnall Poulton in his 1890 book ''The Colours of Animals
''The Colours of Animals'' is a zoology book written in 1890 by Sir Edward Bagnall Poulton (1856–1943). It was the first substantial textbook to argue the case for Darwinian selection applying to all aspects of animal coloration. The book al ...
''. He based the term on the Ancient Greek words ἀπό ''apo'' 'away' and σῆμα ''sēma'' 'sign', referring to signs that warn other animals away.
Defence mechanism
 The function of aposematism is to prevent attack, by warning potential predators that the prey animal has defences such as being unpalatable or poisonous. The easily detected warning is a primary defence mechanism, and the non-visible defences are secondary. Aposematic signals are primarily visual, using bright colours and high-contrast patterns such as stripes. Warning signals are honest indications of noxious prey, because conspicuousness evolves in tandem with noxiousness. Thus, the brighter and more conspicuous the organism, the more toxic it usually is. This is in contrast to
The function of aposematism is to prevent attack, by warning potential predators that the prey animal has defences such as being unpalatable or poisonous. The easily detected warning is a primary defence mechanism, and the non-visible defences are secondary. Aposematic signals are primarily visual, using bright colours and high-contrast patterns such as stripes. Warning signals are honest indications of noxious prey, because conspicuousness evolves in tandem with noxiousness. Thus, the brighter and more conspicuous the organism, the more toxic it usually is. This is in contrast to deimatic displays
Deimatic behaviour or startle display means any pattern of bluffing behaviour in an animal that lacks strong defences, such as suddenly displaying conspicuous eyespots, to scare off or momentarily distract a predator, thus giving the prey anima ...
, which attempt to startle a predator with a threatening appearance but which are bluffing, unsupported by any strong defences.
The most common and effective colours are red, yellow, black, and white. These colours provide strong contrast with green foliage, resist changes in shadow and lighting, are highly chromatic, and provide distance dependent camouflage. Some forms of warning coloration provide this distance dependent camouflage by having an effective pattern and colour combination that do not allow for easy detection by a predator from a distance, but are warning-like from a close proximity, allowing for an advantageous balance between camouflage and aposematism. Warning coloration evolves in response to background, light conditions, and predator vision. Visible signals may be accompanied by odours, sounds or behaviour to provide a multi-modal signal which is more effectively detected by predators.
 Unpalatability, broadly understood, can be created in a variety of ways. Some insects such as the
Unpalatability, broadly understood, can be created in a variety of ways. Some insects such as the ladybird
Coccinellidae () is a widespread family of small beetles ranging in size from . They are commonly known as ladybugs in North America and ladybirds in Great Britain. Some entomologists prefer the names ladybird beetles or lady beetles as they ...
or tiger moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. ...
contain bitter-tasting chemicals, while the skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginge ...
produces a noxious odour, and the poison glands of the poison dart frog
Poison dart frog (also known as dart-poison frog, poison frog or formerly known as poison arrow frog) is the common name of a group of frogs in the family Dendrobatidae which are native to tropical Central and South America. These species are ...
, the sting
Sting may refer to:
* Stinger or sting, a structure of an animal to inject venom, or the injury produced by a stinger
* Irritating hairs or prickles of a stinging plant, or the plant itself
Fictional characters and entities
* Sting (Middle-eart ...
of a velvet ant
The Mutillidae are a family of more than 7,000 species of wasps whose wingless females resemble large, hairy ants. Their common name velvet ant refers to their dense pile of hair, which most often is bright scarlet or orange, but may also be bl ...
or neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature ner ...
in a black widow spider
''Latrodectus'' is a broadly distributed genus of spiders with several species that are commonly known as the true widows. This group is composed of those often loosely called black widow spiders, brown widow spiders, and similar spiders. Howeve ...
make them dangerous or painful to attack. Tiger moths advertise their unpalatability by either producing ultrasonic noises which warn bats to avoid them, or by warning postures which expose brightly coloured body parts (see Unkenreflex), or exposing eyespots. Velvet ants (actually parasitic wasps) such as ''Dasymutilla occidentalis
''Dasymutilla occidentalis'' (red velvet ant, eastern velvet ant, cow ant or cow killer), is a species of parasitoid wasp native to the eastern United States. It is commonly mistaken for a member of the true ant family, as the female is wingless. ...
'' both have bright colours and produce audible noises when grabbed (via stridulation), which serve to reinforce the warning. Among mammals, predators can be dissuaded when a smaller animal is aggressive and able to defend itself, as for example in honey badgers.
Prevalence
In terrestrial ecosystems
 Aposematism is widespread in insects, but less so in vertebrates, being mostly confined to a smaller number of
Aposematism is widespread in insects, but less so in vertebrates, being mostly confined to a smaller number of reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
, and fish species, and some foul-smelling or aggressive mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s. Pitohui
The pitohuis are bird species endemic to New Guinea. The onomatopoeic name is thought to be derived from that used by New Guineans from nearby Dorey (Manokwari), but it is also used as the name of a genus '' Pitohui'' which was established by the ...
s, red and black birds whose toxic feathers and skin apparently comes from the poisonous beetles they ingest, could be included. It has been proposed that aposematism played a role in human evolution, body odour carrying a warning to predators of large hominins able to defend themselves with weapons.
Perhaps the most numerous aposematic vertebrates are the poison dart frogs (family: Dendrobatidae
Poison dart frog (also known as dart-poison frog, poison frog or formerly known as poison arrow frog) is the common name of a group of frogs in the Family (biology), family Dendrobatidae which are native to tropical Central and South America. T ...
). These neotropical anuran amphibians exhibit a wide spectrum of coloration and toxicity. Some species in this poison frog family (particularly ''Dendrobates
''Dendrobates'' is a genus of poison dart frogs native to Central and South America. It once contained numerous species, but most originally placed in this genus have been split off into other genera such as ''Adelphobates'', '' Ameerega'', '' A ...
'', ''Epipedobates
''Epipedobates'' is a genus of poison dart frogs native to northern South America (Colombia and Ecuador) west of the Andes, including the western slopes. Common name phantasmal poison frogs has been suggested for the genus.
Taxonomy
''Epipedobat ...
'', and '' Phyllobates'') are conspicuously coloured and sequester one of the most toxic alkaloids among all living species. Within the same family, there are also cryptic frogs (such as ''Colostethus
''Colostethus'' is a genus of poison dart frogs native to Central and South America, from Panama south to Colombia, Ecuador, and northern Peru. Their common name is rocket frogs, but this name may refer to frogs in other genera and families, foll ...
'' and ''Mannophryne
''Mannophryne'' is a genus of frogs native to Venezuela and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands ...
'') that lack these toxic alkaloids. Although these frogs display an extensive array of coloration and toxicity, there is very little genetic difference between the species. Evolution of their conspicuous coloration is correlated to traits such as chemical defense, dietary specialization, acoustic diversification, and increased body mass.
Some plants are thought to employ aposematism to warn herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s of unpalatable chemicals or physical defences such as prickled leaves or thorns. Many insects, such as cinnabar moth
The cinnabar moth (''Tyria jacobaeae'') is a brightly coloured arctiid moth found as a native species in Europe and western and central Asia then east across the Palearctic to Siberia to China. It has been introduced into New Zealand, Australia a ...
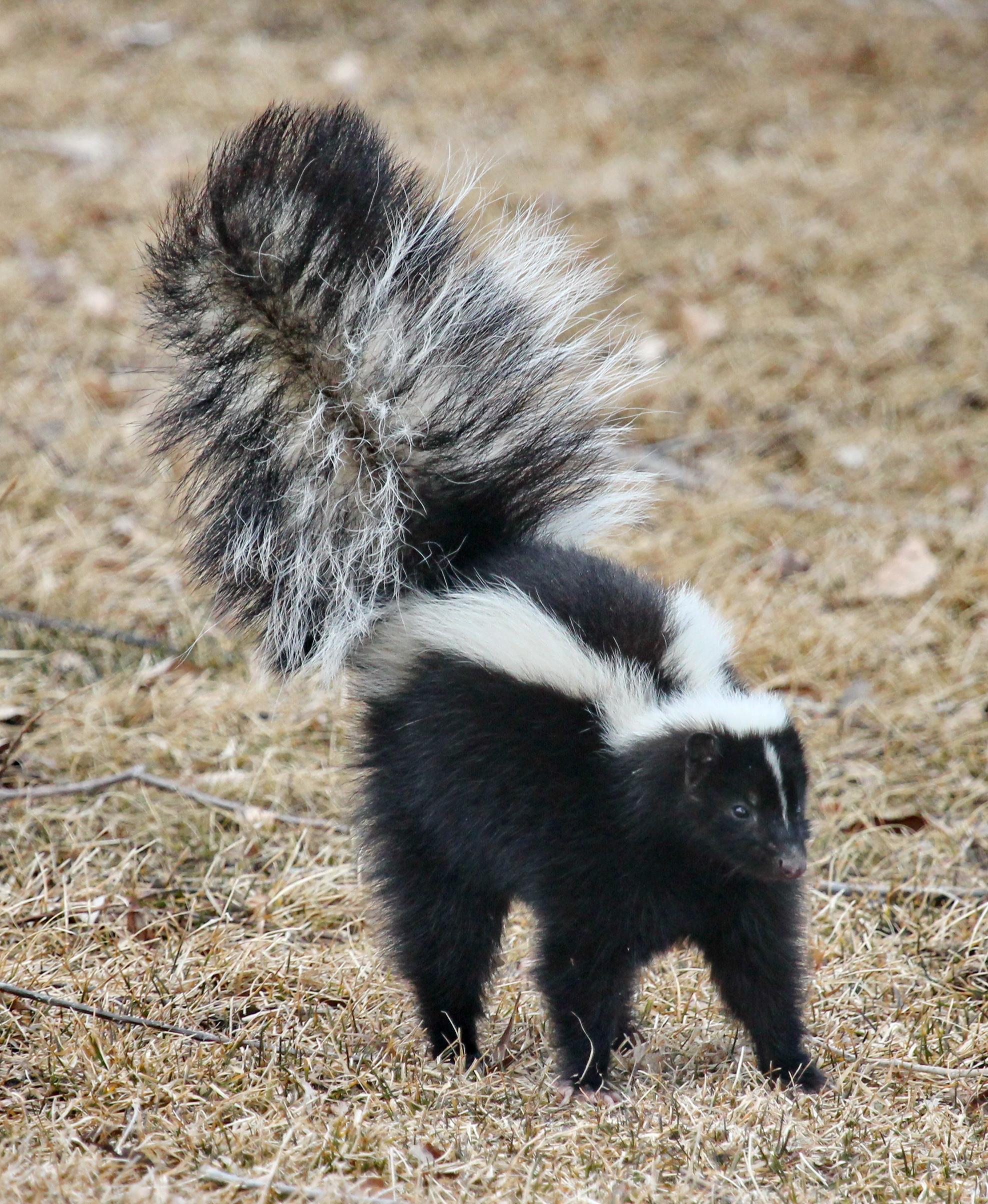
caterpillars, acquire toxic chemicals from their host plants. Among mammals, skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginge ...
s and zorilla
The striped polecat (''Ictonyx striatus''), also called the African polecat, zoril, zorille, zorilla, Cape polecat, and African skunk, is a member of the family Mustelidae that resembles a skunk (of the family Mephitidae). The name "zorilla" c ...
s advertise their foul-smelling chemical defences with sharply contrasting black-and-white patterns on their fur, while the similarly-patterned badger and honey badger advertise their sharp claws, powerful jaws, and aggressive natures. Some brightly coloured birds such as passerines with contrasting patterns may also be aposematic, at least in females; but since male birds are often brightly coloured through sexual selection, and their coloration is not correlated with edibility, it is unclear whether aposematism is significant.
The sound-producing rattle of rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small anim ...
s is an acoustic form of aposematism. Sound production by the caterpillar of the Polyphemus moth, '' Antheraea polyphemus'', may similarly be acoustic aposematism, connected to and preceded by chemical defences. Similar acoustic defences exist in a range of Bombycoidea caterpillars.
In marine ecosystems
The existence of aposematism in marine ecosystems is controversial. Many marine organisms, particularly those on coral reefs, are brightly coloured or patterned, including sponges, corals, molluscs and fish, with little or no connection to chemical or physical defenses. Caribbean reef sponges are brightly coloured, and many species are full of toxic chemicals, but there is no statistical relationship between the two factors. Nudibranch molluscs are the most commonly cited examples of aposematism in marine ecosystems, but the evidence for this has been contested, mostly because (1) there are few examples of mimicry among species, (2) many species are nocturnal or cryptic, and (3) bright colours at the red end of the colour spectrum are rapidly attenuated as a function of water depth. For example, the Spanish Dancer nudibranch (genus ''Hexabranchus
Hexabranchidae is a monotypic family of colorful nudibranchs (often called "sea slugs") which contains only a single genus ''Hexabranchus'', with two species, and has no subfamilies.
This family is one of the many families of dorid nudibranchs ...
''), among the largest of tropical marine slugs, potently chemically defended, and brilliantly red and white, is nocturnal and has no known mimics. Mimicry is to be expected as Batesian mimics with weak defences can gain a measure of protection from their resemblance to aposematic species. Other studies have concluded that nudibranchs such as the slugs of the family Phyllidiidae from Indo-Pacific coral reefs are aposematically coloured. Müllerian mimicry has been implicated in the coloration of some Mediterranean nudibranchs, all of which derive defensive chemicals from their sponge diet.
 The
The crown-of-thorns starfish
The crown-of-thorns starfish (frequently abbreviated to COTS), ''Acanthaster planci'', is a large starfish that preys upon hard, or stony, coral polyps (Scleractinia). The crown-of-thorns starfish receives its name from venomous thorn-like spine ...
, like other starfish such as ''Metrodira subulata
''Metrodira subulata'' is a species of starfish in the family Echinasteridae. It is found on the seabed in shallow parts of the Indo-Pacific region.
Description
''Metrodira subulata'' has long, slender tapering arms. The aboral (upper) surface h ...
'', has conspicuous coloration and conspicuous long, sharp spines, as well as cytolytic
Cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to diffuse into the cell. Water can enter the cell by diffusion through the cell membrane or through selective membrane channels ...
saponin
Saponins (Latin "sapon", soap + "-in", one of), also selectively referred to as triterpene glycosides, are bitter-tasting usually toxic plant-derived organic chemicals that have a foamy quality when agitated in water. They are widely distributed ...
s, chemicals which could function as an effective defence; this evidence is argued to be sufficient for such species to be considered aposematic.
It has been proposed that aposematism and mimicry is less evident in marine invertebrates than terrestrial insects because predation is a more intense selective force for many insects, which disperse as adults rather than as larvae and have much shorter generation times. Further, there is evidence that fish predators such as blueheads may adapt to visual cues more rapidly than do birds, making aposematism less effective.
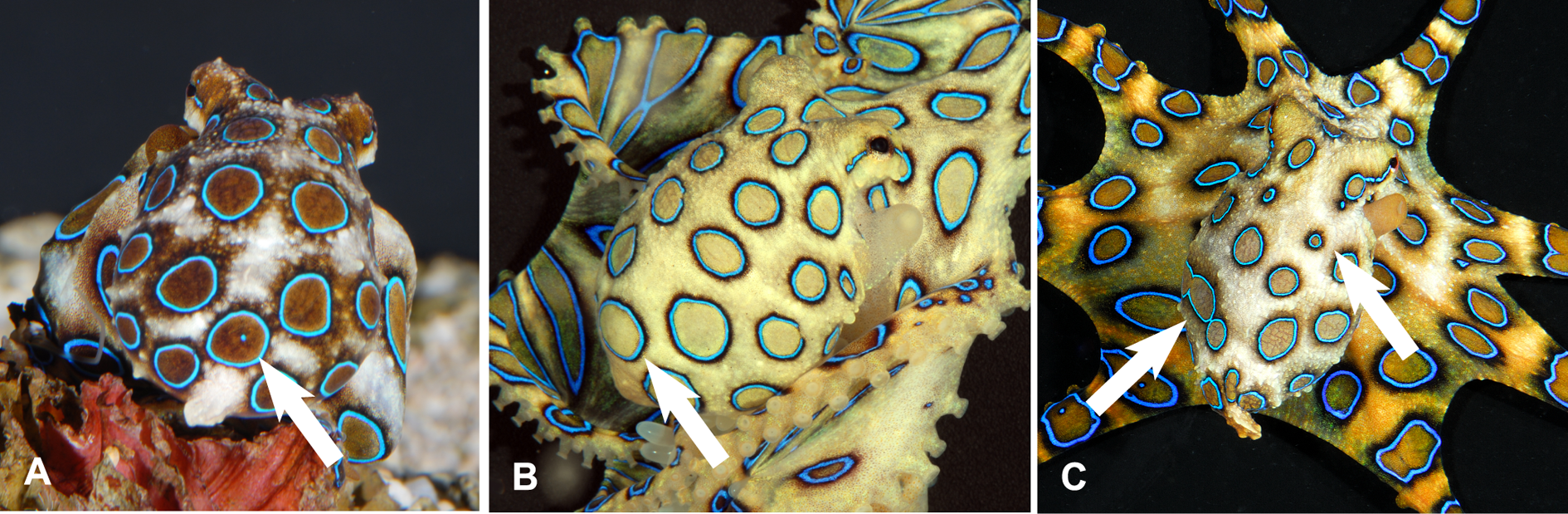
Blue-ringed octopuses are venomous. They spend much of their time hiding in crevices whilst displaying effective camouflage patterns with their dermal chromatophore cells. However, if they are provoked, they quickly change colour, becoming bright yellow with each of the 50-60 rings flashing bright iridescent blue within a third of a second. It is often stated this is an aposematic warning display, but the hypothesis has rarely if ever been tested.
Behaviour
The mechanism of defence relies on the memory of the would-be predator; a bird that has once experienced a foul-tastinggrasshopper
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are among what is possibly the most ancient living group of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.
Grasshopp ...
will endeavour to avoid a repetition of the experience. As a consequence, aposematic species are often gregarious. Before the memory of a bad experience attenuates, the predator may have the experience reinforced through repetition. Aposematic organisms often move in a languid fashion, as they have little need for speed and agility. Instead, their morphology is frequently tough and resistant to injury, thereby allowing them to escape once the predator is warned off.
Aposematic species do not need to hide or stay still as cryptic organisms do, so aposematic individuals benefit from more freedom in exposed areas and can spend more time foraging, allowing them to find more and better quality food. They may also be able to make use of conspicuous mating displays, including vocal signals, which may then develop through sexual selection.
Origins of the theory

Wallace, 1867
In a letter toAlfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural se ...
dated 23 February 1867, Charles Darwin wrote, "On Monday evening I called on Bates
Bates may refer to:
Places
* Bates, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Bates, Illinois. an unincorporated community in Sangamon County
* Bates, Michigan, a community in Grand Traverse County
* Bates, New York, a hamlet in the town of Elli ...
& put a difficulty before him, which he could not answer, & as on some former similar occasion, his first suggestion was, 'you had better ask Wallace'. My difficulty is, why are caterpillars sometimes so beautifully & artistically coloured?" Darwin was puzzled because his theory of sexual selection (where females choose their mates based on how attractive they are) could not apply to caterpillars since they are immature and hence not sexually active.
Wallace replied the next day with the suggestion that since some caterpillars "...are protected by a disagreeable taste or odour, it would be a positive advantage to them never to be mistaken for any of the palatable catterpillars 'sic'' because a slight wound such as would be caused by a peck of a bird’s bill almost always I believe kills a growing . Any gaudy & conspicuous colour therefore, that would plainly distinguish them from the brown & green eatable , would enable birds to recognise them easily as John Jenner Weir
John Jenner Weir, FLS, FZS (9 August 1822 – 23 March 1894) was an English amateur entomologist, ornithologist and British civil servant. He is best known today for being one of the naturalists who corresponded with and provided important data ...
conducted experiments with caterpillars and birds in his aviary, and in 1869 he provided the first experimental evidence for warning coloration in animals. The evolution of aposematism surprised 19th-century naturalists because the probability of its establishment in a population was presumed to be low, since a conspicuous signal suggested a higher chance of predation.
Poulton, 1890
 Wallace coined the term "warning colours" in an article about animal coloration in 1877. In 1890 Edward Bagnall Poulton renamed the concept ''aposematism'' in his book ''
Wallace coined the term "warning colours" in an article about animal coloration in 1877. In 1890 Edward Bagnall Poulton renamed the concept ''aposematism'' in his book ''The Colours of Animals
''The Colours of Animals'' is a zoology book written in 1890 by Sir Edward Bagnall Poulton (1856–1943). It was the first substantial textbook to argue the case for Darwinian selection applying to all aspects of animal coloration. The book al ...
''. He described the derivation of the term as follows:
Evolution
Aposematism is paradoxical in evolutionary terms, as it makes individuals conspicuous to predators, so they may be killed and the trait eliminated before predators learn to avoid it. If warning coloration puts the first few individuals at such a strong disadvantage, it would never last in the species long enough to become beneficial.Supported explanations
There is evidence for explanations involvingdietary conservatism Dietary conservatism is a foraging strategy in which individuals show a prolonged reluctance to eat novel foods, even after neophobia has been overcome. Within any given population of foragers, some will be conservative and some will be adventurous, ...
, in which predators avoid new prey because it is an unknown quantity; this is a long-lasting effect. Dietary conservatism has been demonstrated experimentally in some species of birds and fish.
Further, birds recall and avoid objects that are both conspicuous and foul-tasting longer than objects that are equally foul-tasting but cryptically coloured. This suggests that Wallace's original view, that warning coloration helped to teach predators to avoid prey thus coloured, was correct. However, some birds (inexperienced starlings and domestic chicks) also innately avoid conspicuously coloured objects, as demonstrated using mealworms painted yellow and black to resemble wasps, with dull green controls. This implies that warning coloration works at least in part by stimulating the evolution of predators to encode the meaning of the warning signal, rather than by requiring each new generation to learn the signal's meaning. All of these results contradict the idea that novel, brightly coloured individuals would be more likely to be eaten or attacked by predators.
Alternative hypotheses
Other explanations are possible. Predators might innately fear unfamiliar forms (neophobia
Neophobia is the fear of anything new, especially a persistent and abnormal fear. In its milder form, it can manifest as the unwillingness to try new things or break from routine. In the context of children the term is generally used to indicate a ...
) long enough for them to become established, but this is likely to be only temporary.
Alternatively, prey animals might be sufficiently gregarious to form clusters tight enough to enhance the warning signal. If the species was already unpalatable, predators might learn to avoid the cluster, protecting gregarious individuals with the new aposematic trait. Gregariousness would assist predators to learn to avoid unpalatable, gregarious prey. Aposematism could also be favoured in dense populations even if these are not gregarious.
Another possibility is that a gene for aposematism might be recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
and located on the X chromosome. If so, predators would learn to associate the colour with unpalatability from males with the trait, while heterozygous females carry the trait until it becomes common and predators understand the signal. Well-fed predators might also ignore aposematic morphs, preferring other prey species.
A further explanation is that females might prefer brighter males, so sexual selection could result in aposematic males having higher reproductive success than non-aposematic males if they can survive long enough to mate. Sexual selection is strong enough to allow seemingly maladaptive traits to persist despite other factors working against the trait.
Once aposematic individuals reach a certain threshold population, for whatever reason, the predator learning process would be spread out over a larger number of individuals and therefore is less likely to wipe out the trait for warning coloration completely. If the population of aposematic individuals all originated from the same few individuals, the predator learning process would result in a stronger warning signal for surviving kin, resulting in higher inclusive fitness for the dead or injured individuals through kin selection.
A theory for the evolution of aposematism posits that it arises by reciprocal selection between predators and prey, where distinctive features in prey, which could be visual or chemical, are selected by non-discriminating predators, and where, concurrently, avoidance of distinctive prey is selected by predators. Concurrent reciprocal selection (CRS) may entail learning by predators or it may give rise to unlearned avoidances by them. Aposematism arising by CRS operates without special conditions of the gregariousness or the relatedness of prey, and it is not contingent upon predator sampling of prey to learn that aposematic cues are associated with unpalatability or other unprofitable features.
Mimicry
Aposematism is a sufficiently successful strategy to have had significant effects on the evolution of both aposematic and non-aposematic species. Non-aposematic species have often evolved to mimic the conspicuous markings of their aposematic counterparts. For example, the hornet moth is a deceptive mimic of the yellowjacket wasp; it resembles the wasp, but has no sting. A predator which avoids the wasp will to some degree also avoid the moth. This is known asBatesian mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, after his work on bu ...
, after Henry Walter Bates, a British naturalist who studied Amazonian butterflies in the second half of the 19th century. Batesian mimicry is frequency dependent: it is most effective when the ratio of mimic to model is low; otherwise, predators will encounter the mimic too often.
A second form of mimicry occurs when two aposematic organisms share the same anti-predator adaptation and non-deceptively mimic each other, to the benefit of both species, since fewer individuals of either species need to be attacked for predators to learn to avoid both of them. This form of mimicry is known as Müllerian mimicry, after Fritz Müller
Johann Friedrich Theodor Müller (31 March 1822 – 21 May 1897), better known as Fritz Müller, and also as Müller-Desterro, was a German biologist who emigrated to southern Brazil, where he lived in and near the German community of Blumenau, ...
, a German naturalist who studied the phenomenon in the Amazon in the late 19th century. Many species of bee and wasp that occur together are Müllerian mimics; their similar coloration teaches predators that a striped pattern is associated with being stung. Therefore, a predator which has had a negative experience with any such species will likely avoid any that resemble it in the future. Müllerian mimicry is found in vertebrates such as the mimic poison frog ('' Ranitomeya imitator'') which has several morphs throughout its natural geographical range, each of which looks very similar to a different species of poison frog which lives in that area.
red milk snake
''Lampropeltis triangulum syspila'', commonly known as the red milk snake or red milksnake, is a subspecies of the milk snake ''(Lampropeltis triangulum)''. The nonvenomous, colubrid snake is indigenous to the central United States.
Geographic ...
, a Batesian mimic of the coral snake
See also
* Handicap principleReferences
Sources
* * *External links
* {{Vision in animals Animal communication Antipredator adaptations Evolution by phenotype Warning coloration Ecology Chemical ecology