Antillen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
nl, In vrijheid verenigd
"Unified by freedom" , national_anthem = , common_languages =

 Spanish-sponsored explorers discovered both the
Spanish-sponsored explorers discovered both the  From 1815 onwards
From 1815 onwards
 Even though the referendums held in the early 1990s resulted in a vote in favour of retaining the Netherlands Antilles, the arrangement continued to be an unhappy one. Between June 2000 and April 2005, each island of the Netherlands Antilles had a new referendum on its future status. The four options that could be voted on were the following:
* closer ties with the Netherlands
* remaining within the Netherlands Antilles
* autonomy as a country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands (''
Even though the referendums held in the early 1990s resulted in a vote in favour of retaining the Netherlands Antilles, the arrangement continued to be an unhappy one. Between June 2000 and April 2005, each island of the Netherlands Antilles had a new referendum on its future status. The four options that could be voted on were the following:
* closer ties with the Netherlands
* remaining within the Netherlands Antilles
* autonomy as a country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands (''
 The islands of the former country of the Netherlands Antilles are currently divided are two main groups for political and constitutional purposes:
* those islands that have the status of constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
* those islands that have the status of special municipality of the Netherlands alone, as distinct from the Kingdom in its entirety.
There are also several smaller islands, like
The islands of the former country of the Netherlands Antilles are currently divided are two main groups for political and constitutional purposes:
* those islands that have the status of constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
* those islands that have the status of special municipality of the Netherlands alone, as distinct from the Kingdom in its entirety.
There are also several smaller islands, like
 The
The
The Times Hague/Amsterdam/Rotterdam, 9 March 2007, page 2. Legislation was produced in Dutch, but parliamentary debate was in Papiamentu or English, depending on the island. Due to a massive influx of immigrants from Spanish-speaking territories such as the Dominican Republic in the Windward Islands, and increased tourism from Venezuela in the Leeward Islands, Spanish had also become increasingly used. The majority of the population were followers of the Christian faith, with a Protestant majority in Sint Eustatius and Sint Maarten, and a Roman Catholic majority in Bonaire, Curaçao and Saba. Curaçao also hosted a sizeable group of followers of the Jewish religion, descendants of a
 The origins of the population and location of the islands gave the Netherlands Antilles a mixed culture.
Tourism and overwhelming media presence from the United States increased the regional United States influence. On all the islands, the holiday of
The origins of the population and location of the islands gave the Netherlands Antilles a mixed culture.
Tourism and overwhelming media presence from the United States increased the regional United States influence. On all the islands, the holiday of
Het Statuut voor het Koninkrijk
', Deventer: Kluwer. * Oostindie, G. and Klinkers, I. (2001) ''Het Koninkrijk inde Caraïben: een korte geschiedenis van het Nederlandse dekolonisatiebeleid 1940–2000''. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
GOV.an
nbsp;– Main governmental site
Antillenhuis
nbsp;– Cabinet of the Netherlands Antilles' Plenipotentiary Minister in the Netherlands
Central Bank
of the Netherlands Antilles ; General information
. ''
Netherlands Antilles
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * * ; History *
Method of Securing the Ports and Populations of All the Coasts of the Indies
from 1694. The last five pages of the book are about life, economy and culture of the Netherlands Antilles. {{Authority control Former countries in the Caribbean Former Dutch colonies Leeward Islands (Caribbean) 20th century in Aruba 20th century in Curaçao 20th century in Bonaire 20th century in Sint Maarten History of Sint Eustatius History of Saba (island) Dutch-speaking countries and territories English-speaking countries and territories Special territories of the European Union States and territories established in 1954 States and territories disestablished in 2010 1954 establishments in the Dutch Empire 2010 disestablishments in the Netherlands Antilles 1954 establishments in North America 2010 disestablishments in North America Articles containing video clips Small Island Developing States
nl, In vrijheid verenigd
"Unified by freedom" , national_anthem = , common_languages =
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
Papiamento
Papiamento () or Papiamentu (; nl, Papiaments) is a Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao), with official status in Arub ...
, demonym = Netherlands Antillean
, capital = Willemstad
Willemstad ( , ; ; en, William I of the Netherlands, William Town, italic=yes) is the capital city of Curaçao, an island in the southern Caribbean Sea that forms a Countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, constituent country of the Kingdo ...
, year_start = 1954
, year_end = 2010
, date_start = 15 December
, date_end = 10 October
, event_start = Established
, event_end = Disestablished
, event2 = Secession of Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of ...
, date_event2 = 1 January 1986
, p1 = Curaçao and Dependencies
, flag_p1 = Flag of the Netherlands.svg
, s1 = Aruba
, flag_s1 = Flag of Aruba.svg
, s2 = Curaçao
, flag_s2 = Flag of Curaçao.svg
, s3 = Sint Maarten
, flag_s3 = Flag of Sint Maarten.svg
, s4 = Caribbean Netherlands
, flag_s4 = Flag of the Netherlands.svg
, legislature = Parliament of the Netherlands Antilles
The Parliament of the Netherlands Antilles (; ), also translated as the Estates of the Netherlands Antilles, was the parliament of the Netherlands Antilles. It comprised 22 members, elected for a four-year term in three multi-seat constituencies a ...
, title_leader = Monarchs
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in ...
, leader1 = Juliana
Juliana (variants Julianna, Giuliana, Iuliana, Yuliana, etc) is a feminine given name which is the feminine version of the Roman name Julianus.
Juliana or Giuliana was the name of a number of early saints, notably Saint Julian the Hospitaller, wh ...
, year_leader1 = 1954–1980
, leader2 = Beatrix
Beatrix is a Latin feminine given name, most likely derived from ''Viatrix'', a feminine form of the Late Latin name ''Viator'' which meant "voyager, traveller" and later influenced in spelling by association with the Latin word ''beatus'' or "bles ...
, year_leader2 = 1980–2010
, title_representative = Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
, representative1 = Teun Struycken
Antoon Arnold Marie "Teun" Struycken (27 December 1906 – 1 December 1977) was a Dutch jurist and politician, co-founder of the Catholic People's Party (KVP) – now merged into the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA).
Struycken worked as a lawy ...
, year_representative1 = 1951-1956 (first)
, representative2 = Frits Goedgedrag
Frits M. de los Santos Goedgedrag (born 1 November 1951 in Aruba) is a Dutch Antillean politician who was the first governor of Curaçao following the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles. During his tenure, he oversaw the dissolution of the Net ...
, year_representative2 = 2002–2010 (last)
, title_deputy = Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
, deputy1 = Moises Frumencio da Costa Gomez
Moises Frumencio da Costa Gomez (27 October 1907 – 22 November 1966) was the president of the first Governing Council of the Netherlands Antilles and the first Prime Minister of the Netherlands Antilles.Emily de Jongh-Elhage
Emily Saïdy de Jongh-Elhage (born 7 December 1946) is a former Curaçaoan politician who served as the 27th prime minister of the Netherlands Antilles from 2006 until its dissolution in 2010. Following the 2010 Curaçao general election
Islan ...
, year_deputy2 = 2006–2010 (last)
, currency =
, cctld = .an
.an was the Internet country code top-level domain ( ccTLD) for the former Netherlands Antilles. It was administered by the University of the Netherlands Antilles. The domain was phased out after the Netherlands Antilles were dissolved in 2010 ...
, calling_code = 599
The Netherlands Antilles ( nl, Nederlandse Antillen, ; pap, Antia Hulandes) was a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
. The country consisted of several island territories located in the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
. The islands were also informally known as the Dutch Antilles. The country came into being in 1954 as the autonomous successor of the Dutch colony of Curaçao and Dependencies
The Colony of Curaçao and Dependencies ( nl, Kolonie Curaçao en onderhorigheden; pap, Kolonia di Kòrsou i dependensianan) was a Dutch colony in the Caribbean Sea from 1815 until 1828 and from 1845 until 1954. Between 1936 and 1948, the area wa ...
. The Antilles were dissolved in 2010. The Dutch colony of Surinam, although it was relatively close by on the continent of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
, did not become part of the Netherlands Antilles but became a separate autonomous country in 1954. All the island territories that belonged to the Netherlands Antilles remain part of the kingdom today, although the legal status of each differs. As a group they are still commonly called the Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-wes ...
, regardless of their legal status. People from this former territory continue to be called Antilleans ('' Antillianen'') in the Netherlands.
Geographical grouping
The islands of the Netherlands Antilles are all part of theLesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
island chain. Within this group, the country was spread over two smaller island groups: a northern group (part of Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
) and a western group (part of the Leeward Antilles
The Leeward Antilles ( nl, Benedenwindse Eilanden) are a chain of islands in the Caribbean – specifically, the southerly islands of the Lesser Antilles (and, in turn, the Antilles and the West Indies) along the southeastern fringe of the C ...
). No part of the country was in the southern Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth ...
.
Islands located in the Leeward Islands
This islandsubregion
A subregion is a part of a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south are commonly used to define a subregion.
United Nations subregions
The United Nations Statistics Division, Statistics ...
was located in the eastern Caribbean Sea, to the east of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
. There were three islands, collectively known as the "SSS Islands
The SSS islands (), locally also known as the Windward Islands ( or ), is a collective term for the three territories of the Dutch Caribbean (formerly the Netherlands Antilles) that are located within the Leeward Islands group of the Lesser Anti ...
":
*
*
* (the southern part of the island of Saint Martin)
They lie approximately north-east of the ABC Islands.
Islands located in the Leeward Antilles
This island subregion was located in the southern Caribbean Sea off the north coast ofVenezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. There were three islands collectively known as the " ABC Islands":
* (until 1 January 1986)
* including an islet called Klein Bonaire
Klein Bonaire (Dutch for "Little Bonaire") is a small uninhabited islet off the west coast of the Caribbean island of Bonaire, and is part of the Dutch special municipality of Bonaire.
Geography
The Klein Bonaire islet, which sits within th ...
("Little Bonaire")
* , including an islet called Klein Curaçao
Klein Curaçao (English: ''Little Curaçao'') is a uninhabited island belonging to, and lying 10 km south-east of, Curaçao, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Dutch Caribbean.
Description
Klein Curaçao has a ...
("Little Curaçao")

Climate
The Netherlands Antilles have a tropical trade-windclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
, with hot weather all year round. The Leeward islands are subject to hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
in the summer months, while those islands located in the Leeward Antilles are warmer and drier.
History
 Spanish-sponsored explorers discovered both the
Spanish-sponsored explorers discovered both the leeward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
(Alonso de Ojeda
Alonso de Ojeda (; c. 1466 – c. 1515) was a Spanish explorer, governor and conquistador. He travelled through modern-day Guyana, Venezuela, Trinidad, Tobago, Curaçao, Aruba and Colombia. He navigated with Amerigo Vespucci who is famous ...
, 1499) and windward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
(Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
, 1493) island groups. However, the Spanish Crown only founded settlements in the Leeward Islands. In the 17th century the islands were conquered by the Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company ( nl, Geoctrooieerde Westindische Compagnie, ''WIC'' or ''GWC''; ; en, Chartered West India Company) was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx ( ...
and colonized by Dutch settlers. From the last quarter of the 17th century, the group consisted of six Dutch islands: Curaçao
Curaçao ( ; ; pap, Kòrsou, ), officially the Country of Curaçao ( nl, Land Curaçao; pap, Pais Kòrsou), is a Lesser Antilles island country in the southern Caribbean Sea and the Dutch Caribbean region, about north of the Venezuela coast ...
(settled in 1634), Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of ...
(settled in 1636), Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
(settled in 1636), Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
(settled in 1636), Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), L ...
(settled in 1640) and Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. With a population of 41,486 as of January 2019 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin, while the north ...
(settled in 1648). In the past, Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territo ...
(1631–1650), the present-day British Virgin Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = Territorial song
, song = "Oh, Beautiful Virgin Islands"
, image_map = File:British Virgin Islands on the globe (Americas centered).svg
, map_caption =
, mapsize = 290px
, image_map2 = Brit ...
(1612–1672), St. Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
and Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
had also been Dutch. During the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
Sint Eustatius, along with Curaçao, was a major trade center in the Caribbean, with Sint Eustatius a major source of supplies for the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
. It had been called "the Golden Rock" because of the number of wealthy merchants and volume of trade there. The British sacked its only town, Oranjestad, in 1781 and the economy of the island never recovered. Unlike many other regions, few immigrants went to the Dutch islands, due to the weak economy. However, with the discovery of oil in Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
in the nineteenth century, the Anglo-Dutch Shell Oil Company established refineries in Curaçao, while the U.S. processed Venezuelan crude oil in Aruba. This resulted in booming economies on the two islands, which turned to bust in the 1980s when the oil refineries were closed. The various islands were united as a single country – the Netherlands Antilles – in 1954, under the Dutch crown. The country was dissolved on 10 October 2010.
Curaçao and Sint Maarten became distinct constituent countries alongside Aruba which had become a distinct constituent country in 1986; whereas Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba (the "BES Islands") became special municipalities within the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
proper.
 From 1815 onwards
From 1815 onwards Curaçao and Dependencies
The Colony of Curaçao and Dependencies ( nl, Kolonie Curaçao en onderhorigheden; pap, Kolonia di Kòrsou i dependensianan) was a Dutch colony in the Caribbean Sea from 1815 until 1828 and from 1845 until 1954. Between 1936 and 1948, the area wa ...
formed a colony of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Slavery was abolished in 1863, and in 1865 a government regulation for Curaçao was enacted that allowed for some very limited autonomy for the colony. Although this regulation was replaced by a constitution ( nl, Staatsregeling) in 1936, the changes to the government structure remained superficial and Curaçao continued to be ruled as a colony.
The island of Curaçao was hit hard by the abolition of slavery in 1863. Its prosperity (and that of neighboring Aruba) was restored in the early 20th century with the construction of oil refineries to service the newly discovered Venezuelan oil fields.
Colonial rule ended after the conclusion of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Queen Wilhelmina
Wilhelmina (; Wilhelmina Helena Pauline Maria; 31 August 1880 – 28 November 1962) was Queen of the Netherlands
The monarchy of the Netherlands is a constitutional monarchy. As such, the role and position of the monarch are governed by the ...
had promised in a 1942 speech to offer autonomy to the overseas territories of the Netherlands. During the war, the British and American occupation of the islands – with the consent of the Dutch government – led to increasing demands for autonomy within the population as well.
In May 1948 a new constitution for the territory entered into force, allowing the largest amount of autonomy possible under the Dutch constitution of 1922. Among other things, universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stanc ...
was introduced. The territory was also renamed "Netherlands Antilles". After the Dutch constitution was revised in 1948, a new interim Constitution of the Netherlands Antilles was enacted in February 1951. Shortly afterwards, on 3 March 1951, the Island Regulation of the Netherlands Antilles
The Islands Regulation of the Netherlands Antilles (, ERNA; , RIAH) described the autonomy of the island territories of the Netherlands Antilles. It was enacted on 3 March 1951 by royal decree and remained in force, in a consolidated form, until t ...
( nl, Eilandenregeling Nederlandse Antillen or ERNA) was issued by royal decree
A decree is a legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state (such as the president of a republic or a monarch), according to certain procedures (usually established in a constitution). It has the force of law. The particular term used for ...
, giving fairly wide autonomy to the various island territories in the Netherlands Antilles. A consolidated version of this regulation remained in force until the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles in 2010.
The new constitution was only deemed an interim arrangement, as negotiations for a Charter for the Kingdom were already under way. On 15 December 1954 the Netherlands Antilles, Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
and the Netherlands acceded as equal partners to an overarching Kingdom of the Netherlands, established by the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands. With this move, the United Nations deemed decolonization of the territory complete and removed the Netherlands Antilles from the United Nations list of non-self-governing territories
Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter defines a non-self-governing territory (NSGT) as a territory "whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government". In practice, an NSGT is a territory deemed by the United Nations Gener ...
.
Aruba seceded from the Netherlands Antilles on 1 January 1986, paving the way for a series of referendums among the remaining islands on the future of the Netherlands Antilles. Whereas the ruling parties campaigned for the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, the people voted for a restructuring of the Netherlands Antilles. The coalition campaigning for this option became the Party for the Restructured Antilles
The Real Alternative Party ( nl, Echte Alternatieve Partij; pap, Partido Alternativa Real, PAR), formerly the Party for the Restructured Antilles ( nl, Partij voor Geherstructureerde Antillen, pap, Partido Antiá Restrukturá) until 2016, is a p ...
, which ruled the Netherlands Antilles for much of the time until its dissolution on 10 October 2010.
Dissolution
status aparte
''Status aparte'' refers to the special status of Aruba between 1986 and 2010 as a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, separate from the Netherlands Antilles to which it belonged until 1986. With the dissolution of the Net ...
'')
* independence
Of the five islands, Sint Maarten and Curaçao voted for ''status aparte'', Saba and Bonaire voted for closer ties with the Netherlands, and Sint Eustatius voted to stay within the Netherlands Antilles.
On 26 November 2005, a Round Table Conference (RTC) was held between the governments of the Netherlands, Aruba, the Netherlands Antilles, and each island in the Netherlands Antilles. The final statement to emerge from the RTC stated that autonomy for Curaçao and Sint Maarten, plus a new status for Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba (BES) would come into effect by 1 July 2007.
On 12 October 2006, the Netherlands reached an agreement with Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba: this agreement would make these islands special municipalities.
On 3 November 2006, Curaçao and Sint Maarten were granted autonomy in an agreement, but this agreement was rejected by the then island council of Curaçao on 28 November. The Curaçao government was not sufficiently convinced that the agreement would provide enough autonomy for Curaçao. On 9 July 2007 the new island council of Curaçao approved the agreement previously rejected in November 2006. A subsequent referendum approved the agreement as well.
The acts of parliament integrating the "BES" islands (Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba) into the Netherlands were given royal assent on 17 May 2010. After ratification by the Netherlands (6 July), the Netherlands Antilles (20 August), and Aruba (4 September), the ''Kingdom act amending the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands with regard to the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles'' was signed by the three countries in the closing Round Table Conference on 9 September 2010 in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
.
Political grouping
Constitutional grouping at time of dissolution
The Island Regulation had divided the Netherlands Antilles into four island territories: Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao (ABC), and the islands in the Leeward Islands. In 1983, the island territory of the Leeward was split up to form the new island territories of Sint Maarten, Saba, and Sint Eustatius (SSS). In 1986, Aruba seceded from the Netherlands Antilles, reducing the number of island territories to five. After the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles in 2010, Curaçao and Sint Maarten became autonomous countries within the Kingdom and Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba (BES) became special municipalities of the Netherlands.Current constitutional grouping
Klein Curaçao
Klein Curaçao (English: ''Little Curaçao'') is a uninhabited island belonging to, and lying 10 km south-east of, Curaçao, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Dutch Caribbean.
Description
Klein Curaçao has a ...
and Klein Bonaire
Klein Bonaire (Dutch for "Little Bonaire") is a small uninhabited islet off the west coast of the Caribbean island of Bonaire, and is part of the Dutch special municipality of Bonaire.
Geography
The Klein Bonaire islet, which sits within th ...
, that belong to one of the island countries or special municipalities.
Constituent countries
There are three Caribbean islands that arecountries
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, so ...
( nl, landen) within the Kingdom of the Netherlands: Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of ...
, Curaçao
Curaçao ( ; ; pap, Kòrsou, ), officially the Country of Curaçao ( nl, Land Curaçao; pap, Pais Kòrsou), is a Lesser Antilles island country in the southern Caribbean Sea and the Dutch Caribbean region, about north of the Venezuela coast ...
, and Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. With a population of 41,486 as of January 2019 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin, while the north ...
. (The Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
is the fourth constituent country in the Kingdom of the Netherlands.)
Sint Maarten covers approximately 40% of the island of Saint Martin; the remaining northern part of the island – the '' Collectivity of Saint-Martin'' – is an overseas territory of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
Special municipalities
There are three Caribbean islands that are special municipalities of theNetherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
alone: Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
, Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
, and Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), L ...
. Collectively, these special municipalities of the Netherlands are also known as the BES islands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographic ...
.
Constitution
 The
The Constitution of the Netherlands Antilles
The Constitution of the Netherlands Antilles ( nl, Staatsregeling van de Nederlandse Antillen) was proclaimed on 29 March 1955 by Order-in-Council for the Kingdom. Its proclamation was specifically mandated by article 59(4) of the Charter for the ...
was proclaimed on 29 March 1955 by Order-in-Council for the Kingdom. Together with the Islands Regulation of the Netherlands Antilles
The Islands Regulation of the Netherlands Antilles (, ERNA; , RIAH) described the autonomy of the island territories of the Netherlands Antilles. It was enacted on 3 March 1951 by royal decree and remained in force, in a consolidated form, until t ...
it formed the constitutional basis for the Netherlands Antilles. Because the Constitution depended on the Islands Regulation, which gave fairly large autonomy to the different island territories, and the Islands Regulation was older than the Constitution, many scholars describe the Netherlands Antilles as a federal arrangement.
The head of state was the monarch of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, who was represented in the Netherlands Antilles by a governor. The governor and the council of ministers, chaired by a prime minister, formed the government. The Netherlands Antilles had a unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
legislature called the Parliament of the Netherlands Antilles
The Parliament of the Netherlands Antilles (; ), also translated as the Estates of the Netherlands Antilles, was the parliament of the Netherlands Antilles. It comprised 22 members, elected for a four-year term in three multi-seat constituencies a ...
. Its 22 members were fixed in number for the islands making up the Netherlands Antilles: fourteen for Curaçao, three each for Sint Maarten and Bonaire, and one each for Saba and Sint Eustatius.
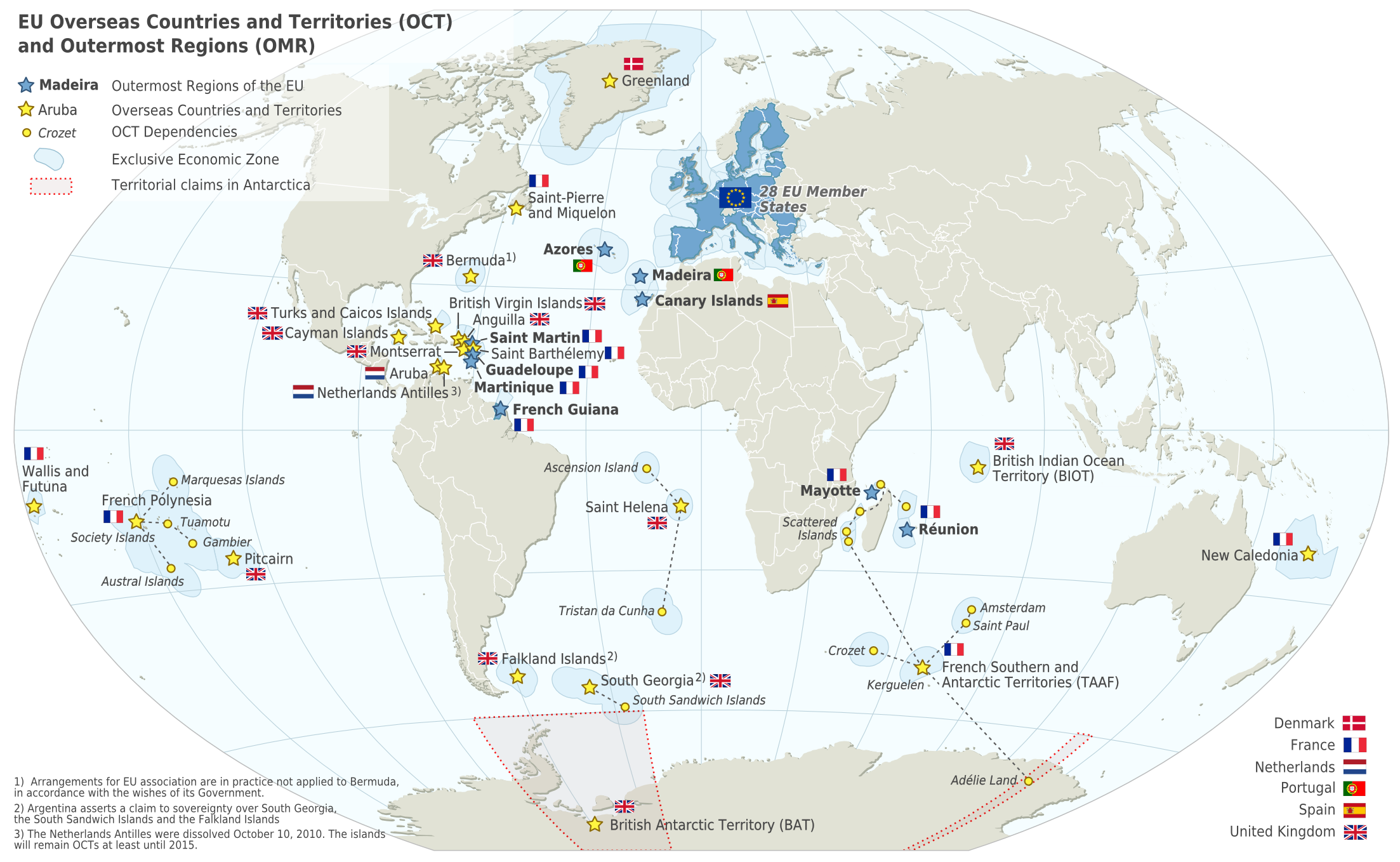
The Netherlands Antilles were not part of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, but instead listed as overseas countries and territories
The special territories of members of the European Economic Area (EEA) are the 32 special territories of EU member states and EFTA member states which, for historical, geographical, or political reasons, enjoy special status within or outside ...
(OCTs). This status was kept for all the islands after dissolution, and will be kept until at least 2015.
Economy
Tourism, petroleum transshipment and oil refinement (on Curaçao), as well as offshore finance were the mainstays of this small economy, which was closely tied to the outside world. The islands enjoyed a high per capita income and a well-developed infrastructure as compared with other countries in the region.COUNTRY COMPARISON GDPCentral Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Almost all consumer and capital goods were imported, with Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, the United States, and Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
being the major suppliers, as well as the Dutch government which supports the islands with substantial development aid
Development aid is a type of aid, foreign/international/overseas aid given by governments and other agencies to support the economic, environmental, social, and political International development, development of developing countries. Closely-rel ...
. Poor soils and inadequate water supplies hampered the development of agriculture. The Antillean guilder
The Netherlands Antillean guilder ( nl, gulden) is the currency of Curaçao and Sint Maarten, which until 2010 formed the Netherlands Antilles along with Bonaire, Saba (island), Saba, and Sint Eustatius. It is subdivided into 100 ''cents'' (Dutch ...
had a fixed exchange rate with the United States dollar of 1.79:1.
Demographics
A large percentage of the Netherlands Antilleans descended from European colonists and Africanslaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
who were brought and traded there from the 17th to 19th centuries. The rest of the population originated from other Caribbean islands as well as Latin America, East Asia and elsewhere in the world. In Curaçao there was a strong Jewish element going back to the 17th century slave trade.
The language Papiamentu
Papiamento () or Papiamentu (; nl, Papiaments) is a Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao), with official status in Arub ...
was predominant on Curaçao and Bonaire (as well as the neighboring island of Aruba). This creole descended from Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and West African languages with a strong admixture of Dutch, plus subsequent lexical contributions from Spanish and English. An English-based creole dialect, formally known as Netherlands Antilles Creole, was the native dialect of the inhabitants of Sint Eustatius, Saba and Sint Maarten.
After a decades-long debate, English and Papiamentu were made official languages alongside Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
in early March 2007."Antilles allow Papiamentu as official language"The Times Hague/Amsterdam/Rotterdam, 9 March 2007, page 2. Legislation was produced in Dutch, but parliamentary debate was in Papiamentu or English, depending on the island. Due to a massive influx of immigrants from Spanish-speaking territories such as the Dominican Republic in the Windward Islands, and increased tourism from Venezuela in the Leeward Islands, Spanish had also become increasingly used. The majority of the population were followers of the Christian faith, with a Protestant majority in Sint Eustatius and Sint Maarten, and a Roman Catholic majority in Bonaire, Curaçao and Saba. Curaçao also hosted a sizeable group of followers of the Jewish religion, descendants of a
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
group of Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), ...
Jews that arrived from Amsterdam and Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
from 1654. In 1982, there was a population of about 2,000 Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
, with an Islamic association and a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
in the capital.
Most Netherlands Antilleans were Dutch citizens and this status permitted and encouraged the young and university-educated to emigrate to the Netherlands. This exodus was considered to be to the islands' detriment, as it created a brain drain. On the other hand, immigrants from the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
, Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, the Anglophone Caribbean
The languages of the Caribbean reflect the region's diverse history and culture. There are six official languages spoken in the Caribbean:
:*Spanish (official language of Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, Bay Islands (Honduras), Corn Isl ...
and Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
had increased their presence on these islands in later years.
Antillean diaspora in the Netherlands
Culture
 The origins of the population and location of the islands gave the Netherlands Antilles a mixed culture.
Tourism and overwhelming media presence from the United States increased the regional United States influence. On all the islands, the holiday of
The origins of the population and location of the islands gave the Netherlands Antilles a mixed culture.
Tourism and overwhelming media presence from the United States increased the regional United States influence. On all the islands, the holiday of Carnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival typi ...
had become an important event after its importation from other Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
and Latin American countries in the 1960s. Festivities included "jump-up" parades with beautifully colored costumes, floats, and live bands as well as beauty contests and other competitions. Carnival on the islands also included a middle-of-the-night j'ouvert
J'ouvert ( ) or Jour ouvert is a traditional festival known as "break day" or the unofficial start of Carnival, which takes place on the Monday before Ash Wednesday. The festival, with origins in Trinidad, traditionally begins at 2 a.m. and conti ...
(juvé) parade that ended at sunrise with the burning of a straw King Momo
King Momo or King Momos or King Momus, (Rei Momo in Portuguese or Rey Momo in Spanish) is considered the king of Carnivals in numerous Latin American festivities, mainly in Brazil and Colombia. His appearance signifies the beginning of the Carn ...
, cleansing the island of sins and bad luck.
Sports
Netherlands Lesser Antilles competed in the Winter Olympics of 1988, notably finishing 29th in the bobsled, ahead of Jamaica who famously competed but finished 30th. Baseball is by far the most popular sport. Several players have made it to the Major Leagues, such asXander Bogaerts
Xander Jan Bogaerts (born October 1, 1992; ), nicknamed "the X-Man" and "Bogey" or "Bogie", is an Aruban professional baseball shortstop for the San Diego Padres of Major League Baseball (MLB). He has previously played in MLB for the Boston Red ...
, Andrelton Simmons
Andrelton A. Simmons (born September 4, 1989) is a Curaçaoan professional baseball shortstop who is a free agent. He previously played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Atlanta Braves, Los Angeles Angels, Minnesota Twins, and Chicago Cubs. D ...
, Hensley Meulens
Hensley Filemon Acasio Meulens (; born June 23, 1967), nicknamed "Bam Bam", is a Curaçaoan professional baseball coach and retired player. He is the hitting coach for the Colorado Rockies of Major League Baseball (MLB).
A native of Curaçao, he ...
, Randall Simon
Randall Carlito Simon (born May 25, 1975) is a Curaçaoan former professional baseball first baseman. He has played all or parts of eight seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB), LVBP and one in Nippon Professional Baseball (NPB) between 1997 a ...
, Andruw Jones
Andruw Rudolf Jones (; born April 23, 1977) is a Curaçaoan former baseball outfielder and designated hitter who played 17 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB), most notably for the Atlanta Braves. Jones also played for the Los Angeles Dodgers, ...
, Kenley Jansen
Kenley Geronimo Jansen (born September 30, 1987) is a Curaçaoan professional baseball pitcher for the Boston Red Sox of Major League Baseball (MLB). He has previously played in MLB for the Los Angeles Dodgers and Atlanta Braves.
Signed by the ...
, Jair Jurrjens
Jair Francoise Jurrjens ( ; born January 29, 1986) is a Curaçaoan professional baseball pitcher for the Acereros de Monclova of the Mexican League. He has played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Detroit Tigers, Atlanta Braves (with whom h ...
, Roger Bernadina
Rogearvin Argelo "Roger" Bernadina (born June 12, 1984) is a Dutch Curaçaoan professional baseball outfielder for Curaçao Neptunus of the Honkbal Hoofdklasse. He has played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Washington Nationals, Philadelphi ...
, Sidney Ponson
Sidney Alton Ponson (; born November 2, 1976) is an Aruban former Major League Baseball pitcher. As a player, Ponson stood at tall and weighed . He threw right-handed with a fastball that clocked out at 95 mph. When he made his major league ...
, Didi Gregorius
Mariekson Julius "Didi" Gregorius (born February 18, 1990) is a Dutch professional baseball shortstop who is a free agent. He has played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Cincinnati Reds, Arizona Diamondbacks, New York Yankees and Philadel ...
, Shairon Martis
Shairon Benjamin Martis (born March 30, 1987) is a Dutch-Curaçaoan professional baseball pitcher for L&D Amsterdam of the Honkbal Hoofdklasse. He has previously pitched for the Washington Nationals and Minnesota Twins of Major League Baseball. ...
, Wladimir Balentien
Wladimir Ramon Balentien (; born July 2, 1984), nicknamed "Coco", is a Curaçaoan-Dutch professional baseball outfielder who is currently a free agent. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Seattle Mariners and Cincinnati Reds, and in ...
, and Yurendell DeCaster
Yurendell Eithel DeCaster (born September 26, 1979) is a Dutch professional baseball third baseman. He played part of one season in Major League Baseball with the Pittsburgh Pirates. He played for Team Netherlands in the 2019 European Baseball Ch ...
. Xander Bogaerts competed in the 2013 World Series for the Boston Red Sox against the St. Louis Cardinals. Andruw Jones played for the Atlanta Braves in the 1996 World Series hitting two home runs in his first game against the New York Yankees.
Three athletes from the former Netherlands Antilles competed in the 2012 Summer Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012) was an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
. They, alongside one athlete from South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the C ...
, competed under the banner of Independent Olympic Athletes
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independen ...
.
The Netherlands Antilles, though a non-existing entity since 2010, are allowed to field teams at the Chess Olympiad
The Chess Olympiad is a biennial chess tournament in which teams representing nations of the world compete. FIDE organises the tournament and selects the host nation. Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, FIDE held an Online Chess Olympiad in 2020 and ...
under this name, because the Curaçao Chess Federation remains officially registered as representing the dissolved country in the FIDE
The International Chess Federation or World Chess Federation, commonly referred to by its French acronym FIDE ( Fédération Internationale des Échecs), is an international organization based in Switzerland that connects the various national c ...
Directory.
Miscellaneous topics
Unlike the metropolitan Netherlands,same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same Legal sex and gender, sex or gender. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 33 countries, with the most recent being ...
s were not performed in the Netherlands Antilles, but those performed in other jurisdictions were recognised.
The main prison of the Netherlands Antilles was Koraal Specht, later known as Bon Futuro. It was known for ill treatment of prisoners and bad conditions throughout the years.
The late Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez
Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías (; 28 July 1954 – 5 March 2013) was a Venezuelan politician who was president of Venezuela from 1999 until his death in 2013, except for a brief period in 2002. Chávez was also leader of the Fifth Republ ...
claimed that the Netherlands was helping the United States to invade Venezuela due to military games in 2006.
See also
* Index of Netherlands Antilles-related articles *Outline of the Netherlands Antilles
The following Outline (list), outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Netherlands Antilles:
The Netherlands Antilles (Dutch language, Dutch: , Papiamento: ''Antia Hulandes''Papiamentu/Ingles Dikshonario, Ratzlaff, Bett ...
* British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grena ...
* Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies ( da, Dansk Vestindien) or Danish Antilles or Danish Virgin Islands were a Danish colonization of the Americas, Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, Saint Thomas ...
* French West Indies
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloupe, ...
* Spanish West Indies
The Spanish West Indies or the Spanish Antilles (also known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or simply "Las Antillas Españolas" in Spanish language, Spanish) were Spanish colonies in the Caribbean. In terms of governance of the Spanish Empire, The ...
Notes
References
* Borman, C. (2005)Het Statuut voor het Koninkrijk
', Deventer: Kluwer. * Oostindie, G. and Klinkers, I. (2001) ''Het Koninkrijk inde Caraïben: een korte geschiedenis van het Nederlandse dekolonisatiebeleid 1940–2000''. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
External links
; GovernmentGOV.an
nbsp;– Main governmental site
Antillenhuis
nbsp;– Cabinet of the Netherlands Antilles' Plenipotentiary Minister in the Netherlands
Central Bank
of the Netherlands Antilles ; General information
. ''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Netherlands Antilles
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * * ; History *
Method of Securing the Ports and Populations of All the Coasts of the Indies
from 1694. The last five pages of the book are about life, economy and culture of the Netherlands Antilles. {{Authority control Former countries in the Caribbean Former Dutch colonies Leeward Islands (Caribbean) 20th century in Aruba 20th century in Curaçao 20th century in Bonaire 20th century in Sint Maarten History of Sint Eustatius History of Saba (island) Dutch-speaking countries and territories English-speaking countries and territories Special territories of the European Union States and territories established in 1954 States and territories disestablished in 2010 1954 establishments in the Dutch Empire 2010 disestablishments in the Netherlands Antilles 1954 establishments in North America 2010 disestablishments in North America Articles containing video clips Small Island Developing States