Anisodus Tanguticus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Anisodus tanguticus (ཐང་ཕྲོམ་ནག་པོ། in Tibetan) '' is a species of flowering plant belonging to tribe
 ''Anisodus tanguticus'' is a
''Anisodus tanguticus'' is a
 Due to its distribution on the Tibetan Plateau, which includes many mountains and valleys, ''A. tanguticus'' can be found in very isolated areas relative to another patch of the same plant. This has led to a high level of genetic differentiation of ''A. tanguticus''.
It is frequently found growing in the vicinity of settlements and monasteries, thriving as it does in soils nutrient-rich through the regular depositing of horse and cattle dung.
Due to its distribution on the Tibetan Plateau, which includes many mountains and valleys, ''A. tanguticus'' can be found in very isolated areas relative to another patch of the same plant. This has led to a high level of genetic differentiation of ''A. tanguticus''.
It is frequently found growing in the vicinity of settlements and monasteries, thriving as it does in soils nutrient-rich through the regular depositing of horse and cattle dung.
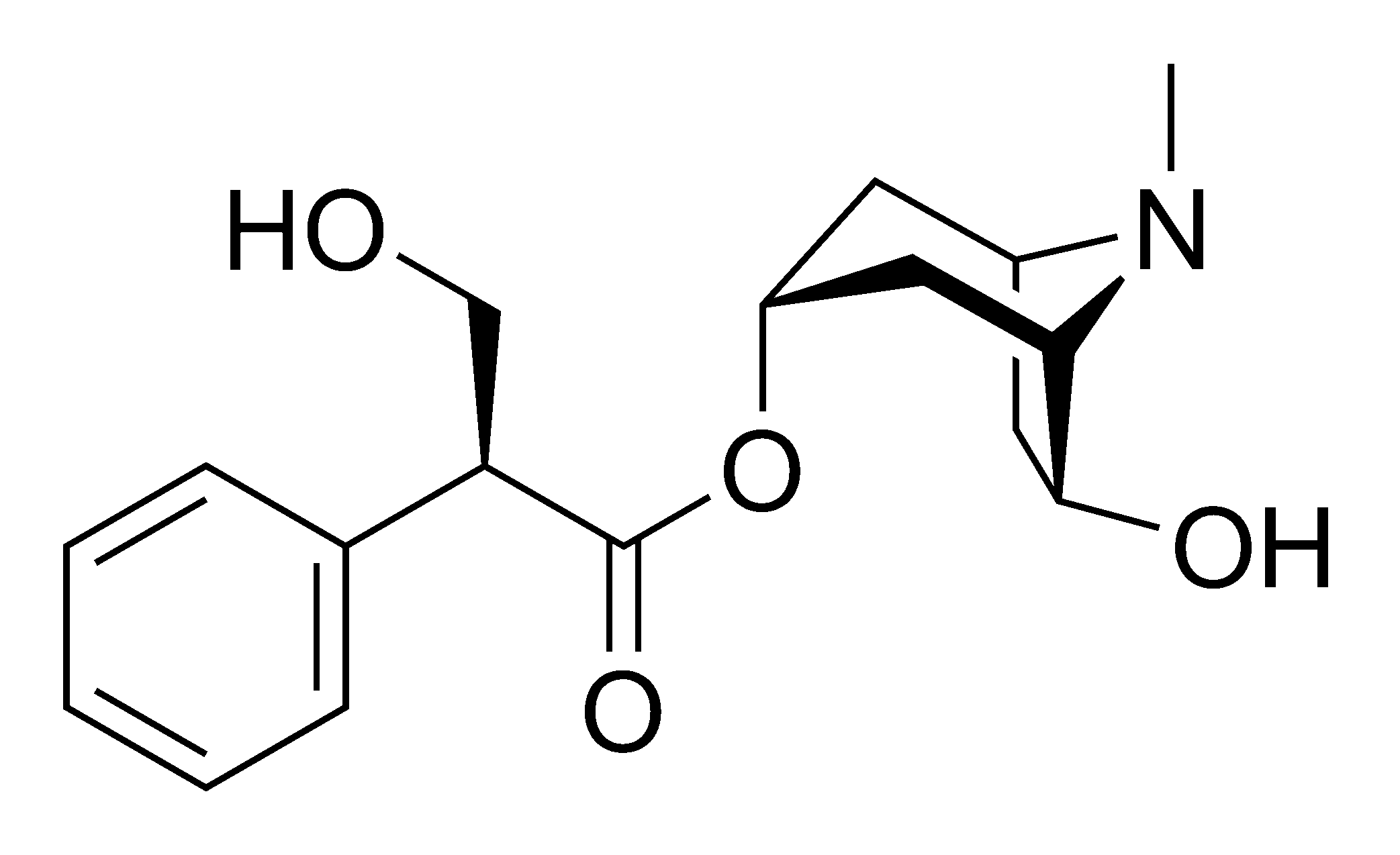
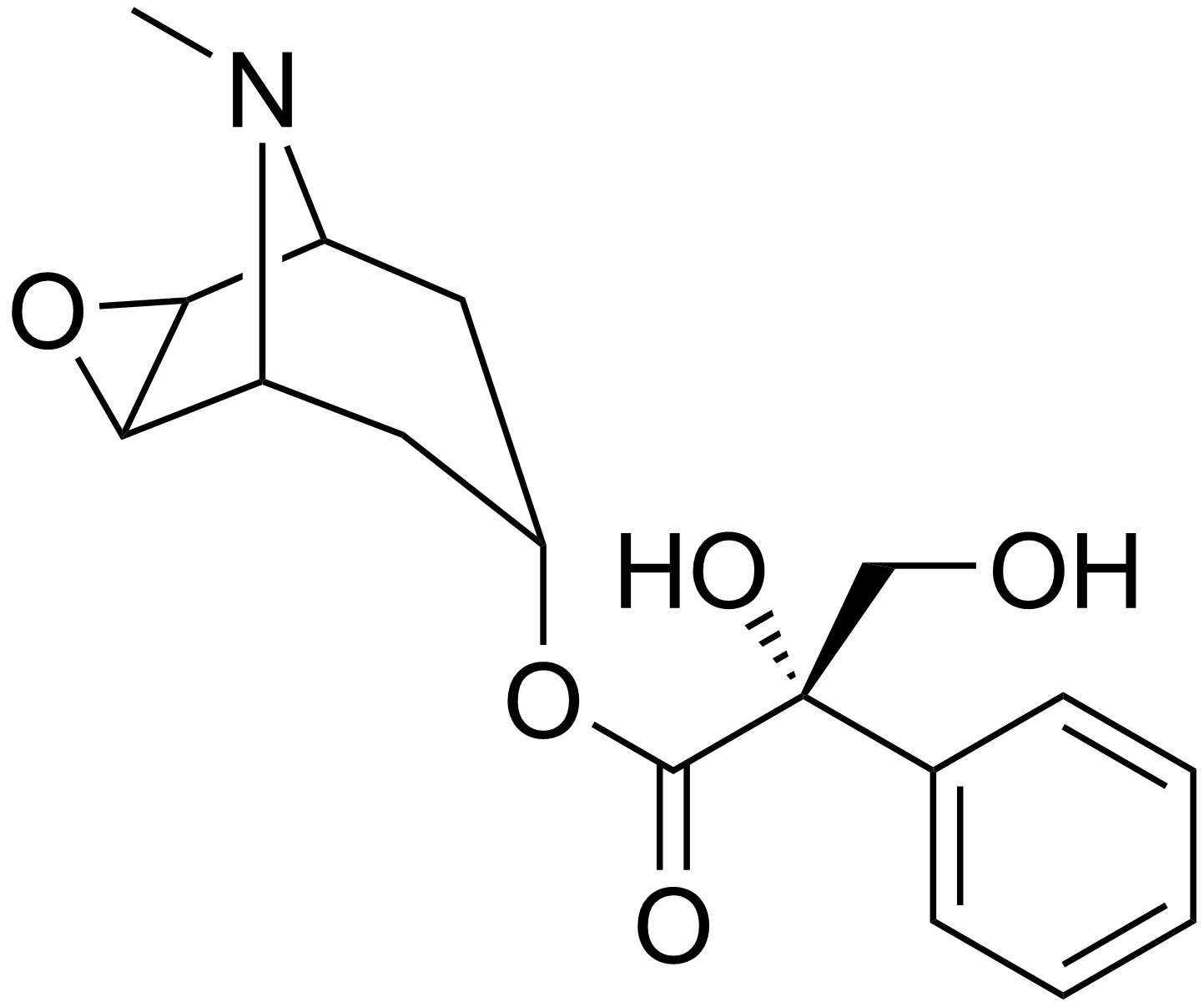 ''Anisodus tanguticus'' is grown and harvested in order to extract two
''Anisodus tanguticus'' is grown and harvested in order to extract two
''Anisodus'' page''Anisodus tanguticus'' (Dr. Duke's Databases)
{{Taxonbar, from=Q549066 Hyoscyameae Flora of Tibet Flora of China Dietary supplements Plants used in traditional Chinese medicine Deliriants
Hyoscyameae
Hyoscyameae is an Old World tribe of the subfamily Solanoideae of the flowering plant family Solanaceae. It comprises eight genera: ''Anisodus'', '' Archihyoscyamus'', ''Atropa'', ''Atropanthe'', ''Hyoscyamus'', ''Physochlaina'', ''Przewalskia'' ...
of subfamily Solanoideae
Solanoideae is a subfamily of the flowering plant family Solanaceae, and is sister to the subfamily Nicotianoideae. Within Solanaceae, Solanoideae contains some of the most economically important genera and species, such as the tomato (''Solanum l ...
of the nightshade family Solanaceae
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and orn ...
. It is thus closely related to Henbane
''Hyoscyamus niger'', commonly known as henbane, black henbane, or stinking nightshade, is a poisonous plant in the nightshade family Solanaceae. It is native to temperate Europe and Siberia, and naturalised in Great Britain and Ireland.
Histor ...
and Deadly Nightshade
''Atropa belladonna'', commonly known as belladonna or deadly nightshade, is a toxic perennial herbaceous plant in the nightshade family Solanaceae, which also includes tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplant (aubergine). It is native to Europe, North ...
. Solanaceae is a plant family which includes many important agricultural plants such as the potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
and the tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
. It is mostly found growing in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Tib ...
. ''A. tanguticus'' is collected and used mostly for its medicinal effects caused by the plant's biologically active nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
and tropane alkaloids
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic .2.1alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloi ...
. It has a significant impact in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
as one of the 50 fundamental herbs
Chinese herbology () is the theory of traditional Chinese herbal therapy, which accounts for the majority of treatments in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). A ''Nature'' editorial described TCM as "fraught with pseudoscience", and said that t ...
used in traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action ...
.
Scientific name
The generic name ''Anisodus'' is a compound of theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
words (, 'unequal') and (, 'tooth'), hence signifying 'having teeth of different lengths' – so called from the observation that certain species have calyces featuring lobes or teeth of unequal length.
The specific name ''tanguticus'' is a geographical epithet, signifying 'belonging to the Tangut region' i.e. 'growing in the land of the Tangut people
The Tangut people ( Tangut: , ''mjɨ nja̱'' or , ''mji dzjwo''; ; ; mn, Тангуд) were a Tibeto-Burman tribal union that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted t ...
' – which includes the region of Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being U-Tsang in the west and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Amdo is also the bi ...
, one of the three traditional regions of Tibet (taking in the modern Chinese province of Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
and part of the south of the modern Chinese province of Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
). Historically, the Tangut, or Western Xia empire included, at its greatest extent, also parts of what are now the Chinese provinces
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions of China, au ...
of Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
, northern Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, § Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichu ...
, northeastern Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, southwestern Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
and southernmost Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
– all of which in fact lie outside the range of ''Anisodus tanguticus''.
Alternative names
''Anisodus tanguticus'' is more commonly known in China as 山莨菪 (shān làngdàng = 'mountain henbane') or Zang Qie (transliterated also Tsang-ch'ieh).Description
 ''Anisodus tanguticus'' is a
''Anisodus tanguticus'' is a perennial plant
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wide ...
. It has flowers that are mostly solitary and borne in leaf axils. The flowers are mostly cup-shaped and radial. Most of them are nodding but they can sometimes become erect.
The pedicel
Pedicle or pedicel may refer to:
Human anatomy
*Pedicle of vertebral arch, the segment between the transverse process and the vertebral body, and is often used as a radiographic marker and entry point in vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty procedures
...
s are of variable length, averaging around and may be either glabrous or pubescent.
The calyx is usually broadly infundibuliform (funnel-shaped) and around in length.
Most of the calyx lobes of A. tanguticus appear broadly dentate. Closer examination of these lobes generally reveals one or two lobes to be broader and longer than the others. The apices of these lobes may be either acute or obtuse and the lobes themselves are slightly unequal and glabrous.
The infundibuliform corolla ranges in colour through varying shades and zonations of purple through to occasional wholly pale yellow to green forms, the individual petals making up the corolla reaching between in length.
The stamens
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filame ...
are inserted at the base of the corolla tube and are half the length of the corolla. The filaments are about long and are hairless.
The anthers are oblong in shape and around in length, dehiscing longitudinally at maturity.
The ovary is conical, bearing styles that are approximately long. The stigma is discoidal and somewhat dehiscent at maturity.
Insect pollinators of the plant include flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
, honeybees
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmo ...
, and ants
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of 22,00 ...
.
Distribution
''Anisodus tanguticus'' is found growing (on grassy sunny slopes) principally on the Tibetan Plateau, its range extending from the Hengduan Mountains ofSichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
and Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
in the east, through Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
and Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
to the northwest, Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
in the west, and Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
in the south. It is present from altitudes of . Populations of ''A. tanguticus'' in this region have decreased significantly due to extensive harvesting of the species for medicinal purposes, resulting (since the roots are the part harvested) in the removal of plants in their entirety.
 Due to its distribution on the Tibetan Plateau, which includes many mountains and valleys, ''A. tanguticus'' can be found in very isolated areas relative to another patch of the same plant. This has led to a high level of genetic differentiation of ''A. tanguticus''.
It is frequently found growing in the vicinity of settlements and monasteries, thriving as it does in soils nutrient-rich through the regular depositing of horse and cattle dung.
Due to its distribution on the Tibetan Plateau, which includes many mountains and valleys, ''A. tanguticus'' can be found in very isolated areas relative to another patch of the same plant. This has led to a high level of genetic differentiation of ''A. tanguticus''.
It is frequently found growing in the vicinity of settlements and monasteries, thriving as it does in soils nutrient-rich through the regular depositing of horse and cattle dung.
Traditional medicine
''Anisodus tanguticus'' () is one of the50 fundamental herbs
Chinese herbology () is the theory of traditional Chinese herbal therapy, which accounts for the majority of treatments in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). A ''Nature'' editorial described TCM as "fraught with pseudoscience", and said that t ...
used in traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action ...
.
It contains high levels of the tropane alkaloid
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic .2.1alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkal ...
s hyoscyamine
Hyoscyamine (also known as daturine or duboisine) is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid and plant toxin. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including henbane, mandrake, angel's trumpets, jimsonweed ...
and scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a natural or synthetically produced tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic drug that is formally used as a medication for treating motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting ...
, which affect primarily the parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of ...
and can act as anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the neurotransmitter called acetylcholine (ACh) at synapses in the central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system ...
agents.
Pharmaceutical use

 ''Anisodus tanguticus'' is grown and harvested in order to extract two
''Anisodus tanguticus'' is grown and harvested in order to extract two alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
s, anisodamine
Anisodamine, also known as 7''β''-hydroxyhyoscyamine, is an anticholinergic and α1 adrenergic receptor antagonist used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China. It is given orally or by injection, as a racemic mixture (racanisodami ...
and anisodine
Anisodine, also known as daturamine and α-hydroxyscopolamine, is an antispasmodic and anticholinergic drug used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China. It is a tropane alkaloid and is found naturally in plants of the family Solanac ...
, which can be obtained from the roots of the plant. These alkaloids are used as anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the neurotransmitter called acetylcholine (ACh) at synapses in the central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system ...
drugs in China for acute circulatory shock. Anisodamine in particular was introduced into clinical use in China in 1965 through the manufacture of a synthetic drug that concentrated the alkaloids from the plant. It was first used to treat epidemic meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
, but was later used to treat other ailments, including glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys). Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involv ...
, hemorrhagic necrotic enteritis, eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
, pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
, and circulatory shock
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thi ...
.
Anisodamine has also been found to be highly beneficial in cases of noise-induced hearing loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a Hearing loss, hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of Frequency, frequencies or impaired perception of sound including hyperacusi ...
, dilating the capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
and improving microcirculation
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. ...
in the bony labyrinth
The bony labyrinth (also osseous labyrinth or otic capsule) is the rigid, bony outer wall of the inner ear in the temporal bone. It consists of three parts: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. These are cavities hollowed out of the s ...
; while Anisodine has been used clinically for migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
and diseases of the fundus occuli due to vasospasm
Vasospasm refers to a condition in which an arterial spasm leads to vasoconstriction. This can lead to tissue ischemia and tissue death (necrosis). Cerebral vasospasm may arise in the context of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Symptomatic vasospasm or de ...
.
Attempts to increase population
The population of ''A. tanguticus'' is starting to dwindle in its main habitat of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. This can be attributed not only to the effects of over-collection, as a medicinal species, but also to a low rate ofseed germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an flowering plant, angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spor ...
in ''A. tanguticus'' – even under most natural conditions. This is probably due to the relative impermeability of the testa of its seeds which tends to prevent water absorption and acts also to inhibit gaseous exchange. The seeds of ''A. tanguticus'' are therefore classified as having coat-imposed dormancy.
A study was conducted in an effort to find the most effective method of breaking seed dormancy
Seed dormancy is an evolutionary adaptation that prevents seeds from germinating during unsuitable ecological conditions that would typically lead to a low probability of seedling survival. Dormant seeds do not germinate in a specified period of ...
in the species in order to increase rates of germination. Several combinations of treatments (which included chilling, gibberellic acid
Gibberellic acid (also called gibberellin A3, GA, and GA3) is a hormone found in plants and fungi. Its chemical formula is C19H22O6. When purified, it is a white to pale-yellow solid.
Plants in their normal state produce large amounts of GA3. It ...
, and mechanical scarification) were employed.
The mechanical scarification method (which involves the breaking, scratching, or softening of the seed coat) was found to be the only way to increase germination. The rate improved to about 70% and the germination time was improved to 4.1 days.
The study was undertaken in an effort to find ways of increasing the population of the plant.
References
External links
''Anisodus'' page
{{Taxonbar, from=Q549066 Hyoscyameae Flora of Tibet Flora of China Dietary supplements Plants used in traditional Chinese medicine Deliriants