While the
Tibetan plateau has been inhabited since pre-historic times, most of
Tibet's history went unrecorded until the introduction of
Tibetan Buddhism around the 6th century. Tibetan texts refer to the kingdom of
Zhangzhung (c. 500 BCE – 625 CE) as the precursor of later Tibetan kingdoms and the originators of the
Bon religion. While mythical accounts of early rulers of the
Yarlung Dynasty exist, historical accounts begin with the introduction of
Buddhism from India in the 6th century and the appearance of envoys from the unified Tibetan Empire in the 7th century. Following the dissolution of the empire and a period of fragmentation in the 9th-10th centuries, a Buddhist revival in the 10th–12th centuries saw the development of three of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism.
After a period of control by the
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
and
Yuan dynasty, Tibet became effectively independent in the 14th century and was ruled by a succession of noble houses for the next 300 years. In the 17th century, the senior lama of the
Gelug school, the
Dalai Lama, became the head of state with the aid of the
Khoshut Khanate. In the early 18th century, the
Dzungar Khanate occupied Tibet and a
Qing dynasty expeditionary force attacked them, conquering Tibet in 1720. It remained a Qing territory until the fall of the dynasty. In 1959, the
14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as ...
went into exile in India in response to hostilities with the PRC. The Chinese invasion and flight of the Dalai Lama created several waves of Tibetan refugees and led to the creation of Tibetan diasporas in India, the United States, and Europe.
Following the Chinese invasion, Tibetan independence and human rights emerged as international issues, gaining significant visibility alongside the
14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as ...
in the 1980s and 90s. Chinese authorities have sought to assert control over Tibet and has been accused of the destruction of religious sites and banning possession of pictures of the Dalai Lama and other Tibetan religious practices. During the crises created by the
Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward (Second Five Year Plan) of the People's Republic of China (PRC) was an economic and social campaign led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1958 to 1962. CCP Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to reconstruc ...
, Tibet was subjected to mass starvation, allegedly because of the appropriation of Tibetan crops and foodstuffs by the PRC government. The PRC disputes these claims and points to their investments in Tibetan infrastructure, education, and industrialization as evidence that they have replaced a theocratic feudal government with a modern state.
Geographical setting
Tibet lies between the civilizations of
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and
India. Extensive mountain ranges to the east of the
Tibetan Plateau mark the border with China, and the
Himalayas of
Nepal and India separate Tibet and India. Tibet has been called the "roof of the world" and "the land of snows".
Linguists classify the
Tibetan language and its dialects as belonging to the
Tibeto-Burman languages, the non-
Sinitic members of the
Sino-Tibetan language family.
Prehistory
Some archaeological data suggest
archaic humans
A number of varieties of ''Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
passed through Tibet at the time India was first inhabited, half a million years ago.
Impressions of hands and feet suggest
hominins were present at the above 4,000 meters above sea level high Tibetan Plateau 169,000–226,000 years ago.
Modern humans first inhabited the Tibetan Plateau at least twenty-one thousand years ago.
This population was largely replaced around 3000 years ago by
Neolithic immigrants from
northern China
Northern China () and Southern China () are two approximate regions within China. The exact boundary between these two regions is not precisely defined and only serve to depict where there appears to be regional differences between the climate ...
. However, there is a "partial genetic continuity between the Paleolithic inhabitants and the contemporary Tibetan populations". The vast majority of Tibetan maternal mtDNA components can trace their ancestry to both paleolithic and Neolithic during the mid-Holocene.
ic monuments dot the Tibetan Plateau and may have been used in ancestor worship.
Prehistoric
Iron Age hillforts and burial complexes have recently been found on the Tibetan Plateau, but the remote high altitude location makes archaeological research difficult.
Early history (c. 500 BC – AD 618)
Zhangzhung kingdom (c. 500 BC – AD 625)
According to
Namkhai Norbu some Tibetan historical texts identify the Zhang Zhung culture as a people who migrated from the
Amdo region into what is now the region of
Guge
Guge (; ) was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast ...
in western Tibet. Zhang Zhung is considered to be the original home of the
Bön
''Bon'', also spelled Bön () and also known as Yungdrung Bon (, "eternal Bon"), is a Tibetan culture, Tibetan religious tradition with many similarities to Tibetan Buddhism and also many unique features.Samuel 2012, pp. 220-221. Bon initiall ...
religion.
[Helmut Hoffman in ]
By the 1st century BC, a neighboring kingdom arose in the
Yarlung Valley, and the Yarlung king,
Drigum Tsenpo, attempted to remove the influence of the Zhang Zhung by expelling the Zhang's
Bön
''Bon'', also spelled Bön () and also known as Yungdrung Bon (, "eternal Bon"), is a Tibetan culture, Tibetan religious tradition with many similarities to Tibetan Buddhism and also many unique features.Samuel 2012, pp. 220-221. Bon initiall ...
priests from Yarlung. Tsenpo was assassinated and Zhang Zhung continued its dominance of the region until it was annexed by Songtsen Gampo in the 7th century.
Tibetan tribes (2nd century AD)
In AD 108, "the Kiang or Tibetans, a nomad from south-west of
Koko-nor
Qinghai Lake or Ch'inghai Lake, also known by other names, is the largest lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline salt lake. The lake has fluctuated ...
, attacked the Chinese posts of
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
, threatening to cut the
Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major ...
road. Liang Kin, at the price of some fierce fighting, held them off." Similar incursions were repelled in AD 168–169 by the Chinese general Duan Gong.
Chinese sources of the same era mention of a Fu state () of either Qiang or Tibetan ethnicity "more than two thousand miles northwest of
Shu County". Fu state was pronounced as "bod" or "phyva" in Archaic Chinese. Whether this polity is the precursor of Tufan is still unknown.
First kings of the pre-Imperial Yarlung dynasty (2nd–6th centuries)
The pre-Imperial Yarlung Dynasty rulers are considered mythological because sufficient evidence of their existence has not been found.
Nyatri Tsenpo is considered by traditional histories to have been the first king of the Yarlung Dynasty, named after the river valley where its capital city was located, approximately fifty-five miles south-east from present-day Lhasa. The dates attributed to the first Tibetan king,
Nyatri Tsenpo (), vary. Some Tibetan texts give 126 BC, others 414 BC.
Nyatri Tsenpo is said to have descended from a one-footed creature called the Theurang, having webbed fingers and a tongue so large it could cover his face. Due to his terrifying appearance he was feared in his native Puwo and exiled by the
Bön
''Bon'', also spelled Bön () and also known as Yungdrung Bon (, "eternal Bon"), is a Tibetan culture, Tibetan religious tradition with many similarities to Tibetan Buddhism and also many unique features.Samuel 2012, pp. 220-221. Bon initiall ...
to Tibet. There he was greeted as a fearsome being, and he became king.
The Tibetan kings were said to remain connected to the heavens via a ''dmu'' cord (''dmu thag'') so that rather than dying, they ascended directly to heaven, when their sons achieved their majority. According to various accounts, king
Drigum Tsenpo (''Dri-gum-brtsan-po'') either challenged his clan heads to a fight, or provoked his groom ''Longam'' (''Lo-ngam'') into a duel. During the fight the king's ''dmu'' cord was cut, and he was killed. Thereafter Drigum Tsenpo and subsequent kings left corpses and the Bön conducted funerary rites.
In a later myth, first attested in the ''Maṇi bka' 'bum'', the Tibetan people are the progeny of the union of the monkey
Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa
Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa is a mythical monkey-ancestor of the Tibetan people. With King Gesar and Avalokiteśvara, of whom he is an incarnation, he is one of the most important figures in Tibetan culture. ''Pha'' means "father", ''Trelgen'' ...
and rock ogress Ma Drag Sinmo. But the monkey was a manifestation of the
bodhisattva Chenresig, or
Avalokiteśvara (Tib. ''Spyan-ras-gzigs'') while the ogress in turn incarnated Chenresig's consort
Dolma
Dolma (Turkish for “stuffed”) is a family of stuffed dishes associated with Ottoman cuisine, and common in modern national cuisines of regions and countries that once were part of the Ottoman Empire. Some types of dolma are made with whol ...
(Tib. ''
'Grol-ma'').
Tibetan Empire (618–842)

The Yarlung kings gradually extended their control, and by the early 6th century most of the Tibetan tribes were under its control, when
Namri Songtsen (570?–618?/629), the 32nd King of Tibet of the Yarlung Dynasty, gained control of all the area around what is now Lhasa by 630, and conquered Zhangzhung.
With this extent of power the Yarlung kingdom turned into the Tibetan Empire.
The government of Namri Songtsen sent two embassies to China in 608 and 609, marking the appearance of Tibet on the international scene. From the 7th century AD Chinese historians referred to Tibet as
Tubo (), though four distinct characters were used. The first externally confirmed contact with the Tibetan kingdom in recorded Tibetan history occurred when King
Namri Löntsän
Namri Songtsen (), also known as "Namri Löntsen" () (died 618) was according to tradition, the 32nd King of Tibet of the Yarlung Dynasty. (Reign: 570 – 618) During his 48 years of reign, he expanded his kingdom to rule the central part of the ...
(''Gnam-ri-slon-rtsan'') sent an ambassador to China in the early 7th century.
Traditional Tibetan history preserves a lengthy list of rulers whose exploits become subject to external verification in the Chinese histories by the 7th century. From the 7th to the 11th centuries a series of
emperors ruled Tibet (see
List of emperors of Tibet) of whom the three most important in later religious tradition were
Songtsen Gampo,
Trisong Detsen and
Ralpacan
Tritsuk Detsen (), better known by his nickname Ralpachen () (c. 806 CE–838), according to traditional sources, was the 41st king of the Yarlung Dynasty of Tibet. He reigned after the death of his father, Sadnalegs, in c. 815, and grew the emp ...
, "the three religious kings" (''mes-dbon gsum''), who were assimilated to the three protectors (''rigs-gsum mgon-po''), respectively,
Avalokiteśvara,
Mañjuśrī and
Vajrapāni
(Sanskrit; Pali: Vajirapāṇi, meaning, " Vajra in ishand") is one of the earliest-appearing bodhisattvas in Mahayana Buddhism. He is the protector and guide of Gautama Buddha and rose to symbolize the Buddha's power.
Vajrapāni is also ...
. Songtsen Gampo (c. 604–650) was the first great emperor who expanded Tibet's power beyond Lhasa and the
Yarlung Valley, and is traditionally credited with introducing
Buddhism to Tibet.
Throughout the centuries from the time of the emperor the power of the empire gradually increased over a diverse terrain so that by the reign of the emperor in the opening years of the 9th century, its influence extended as far south as
Bengal and as far north as
Mongolia. Tibetan records claim that the
Pala Empire was conquered and that the Pala emperor
Dharmapala submitted to Tibet, though no independent evidence confirms this.
The varied terrain of the empire and the difficulty of transportation, coupled with the new ideas that came into the empire as a result of its expansion, helped to create stresses and power blocs that were often in competition with the ruler at the center of the empire. Thus, for example, adherents of the
Bön
''Bon'', also spelled Bön () and also known as Yungdrung Bon (, "eternal Bon"), is a Tibetan culture, Tibetan religious tradition with many similarities to Tibetan Buddhism and also many unique features.Samuel 2012, pp. 220-221. Bon initiall ...
religion and the supporters of the ancient noble families gradually came to find themselves in competition with the recently introduced
Buddhism.
Era of Fragmentation and Cultural Renaissance (9th–12th centuries)
Fragmentation of political power (9th–10th centuries)
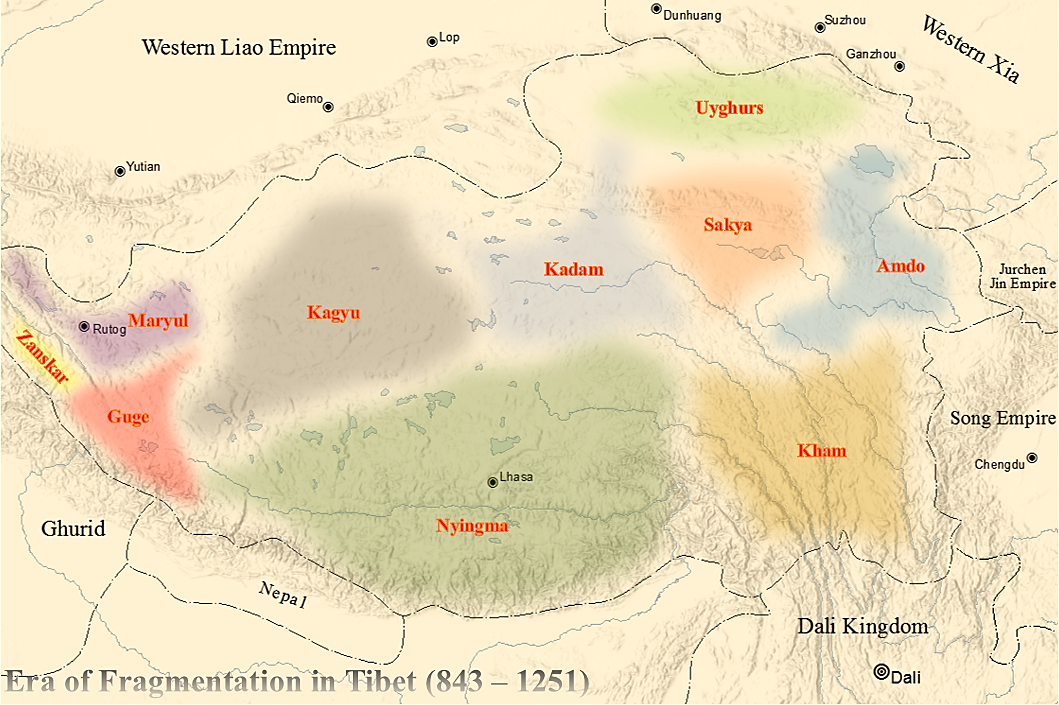

The Era of Fragmentation was a period of Tibetan history in the 9th and 10th centuries. During this era, the political centralization of the earlier
Tibetan Empire collapsed. The period was dominated by rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Upon the death of
Langdarma, the last emperor of a unified Tibetan empire, there was a controversy over whether he would be succeeded by his alleged heir Yumtän (''Yum brtan''), or by another son (or nephew) Ösung (''Od-srung'') (either 843–905 or 847–885). A civil war ensued, which effectively ended centralized Tibetan administration until the Sa-skya period. Ösung's allies managed to keep control of Lhasa, and Yumtän was forced to go to Yalung, where he established a separate line of kings. In 910, the tombs of the emperors were defiled.
The son of Ösung was Pälkhortsän (''Dpal 'khor brtsan'') (865–895 or 893–923). The latter apparently maintained control over much of central Tibet for a time, and sired two sons, Trashi Tsentsän (''Bkra shis brtsen brtsan'') and Thrikhyiding (''Khri khyi lding''), also called
Kyide Nyimagön
Kyide Nyimagon () (), whose original name was Khri-skyid-lding, was a member of the Yarlung dynasty of Tibet and a descendant of emperor Langdarma. He migrated to Western Tibet and founded the kingdom of Ngari Khorsum ("the three divisions o ...
(''Skyid lde nyi ma mgon'') in some sources. Thrikhyiding migrated to the western Tibetan region of
upper Ngari (''Stod Mnga ris'') and married a woman of high central Tibetan nobility, with whom he founded a local dynasty.
After the breakup of the Tibetan empire in 842, Nyima-Gon, a representative of the ancient Tibetan royal house, founded the
first Ladakh dynasty. Nyima-Gon's kingdom had its centre well to the east of present-day
Ladakh. Kyide Nyigön's eldest son became ruler of the
Maryul
Maryul (also called ''Mar-yul'' of ''mNgah-ris''), later the Kingdom of Ladakh, was a west Tibetan kingdom based in modern-day Ladakh and Tibet. The kingdom had its capital at Shey.
The kingdom was founded by Lhachen Palgyigon, during the rul ...
(Ladakh region), and his two younger sons ruled western Tibet, founding the Kingdom of
Guge
Guge (; ) was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast ...
–
Purang and
Zanskar–
Spiti. Later the king of Guge's eldest son, Kor-re, also called Jangchub
Yeshe-Ö
Yeshe-Ö ( 959–1040) (spiritual names: Jangchub Yeshe-Ö, Byang Chub Ye shes' Od, Lha Bla Ma, Hla Lama Yeshe O, Lalama Yixiwo, also Dharmaraja ('Noble King') was the first notable lama-king in Tibet. Born as Khor-re, he is better known as Lh ...
(''Byang Chub Ye shes' Od''), became a Buddhist monk. He sent young scholars to
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
for training and was responsible for inviting
Atiśa to Tibet in 1040, thus ushering in the Chidar (''Phyi dar'') phase of Buddhism in Tibet. The younger son, Srong-nge, administered day-to-day governmental affairs; it was his sons who carried on the royal line.
Tibetan Renaissance (10th–12th centuries)
According to traditional accounts, Buddhism had survived surreptitiously in the region of
Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
. The late 10th century and 11th century saw a revival of Buddhism in Tibet. Coinciding with the early discoveries of "hidden treasures" (
''terma''),
[Berzin, Alexander. ''The Four Traditions of Tibetan Buddhism: Personal Experience, History, and Comparisons''](_blank)
/ref> the 11th century saw a revival of Buddhist influence originating in the far east and far west of Tibet.
Muzu Saelbar (''Mu-zu gSal-'bar''), later known as the scholar Gongpa Rabsal (''bla chen dgongs pa rab gsal'') (832–915), was responsible for the renewal of Buddhism in northeastern Tibet, and is counted as the progenitor of the Nyingma (''Rnying ma pa'') school of Tibetan Buddhism. In the west, Rinchen Zangpo (958–1055) was active as a translator and founded temples and monasteries. Prominent scholars and teachers were again invited from India.
In 1042 Atiśa (982–1054 CE) arrived in Tibet at the invitation of a west Tibetan king. This renowned exponent of the Pāla form of Buddhism from the Indian university of Vikramashila later moved to central Tibet. There his chief disciple, Dromtonpa, founded the Kadampa school of Tibetan Buddhism under whose influence the New Translation schools of today evolved.
The Sakya, the ''Grey Earth'' school, was founded by Khön Könchok Gyelpo (, 1034–1102), a disciple of the great Lotsawa, Drogmi Shākya (). It is headed by the Sakya Trizin, traces its lineage to the mahasiddha Virūpa,[Berzin. Alexander (2000). ''How Did Tibetan Buddhism Develop?'']
StudyBuddhism.com
/ref> and represents the scholarly tradition. A renowned exponent, Sakya Pandita (1182–1251CE), was the great-grandson of Khön Könchok Gyelpo.
Other seminal Indian teachers were Tilopa (988–1069) and his student Naropa
Nāropā (Prakrit; sa, Nāropāda, Naḍapāda or Abhayakirti) or Abhayakirti was an Indian Buddhist Mahasiddha. He was the disciple of Tilopa and brother, or some sources say partner and pupil, of Niguma. As an Indian Mahasiddha, Naropa's ...
(probably died ca. 1040 CE). The Kagyu
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineag ...
, the ''Lineage of the (Buddha's) Word'', is an oral tradition which is very much concerned with the experiential dimension of meditation. Its most famous exponent was Milarepa, an 11th-century mystic. It contains one major and one minor subsect. The first, the Dagpo Kagyu, encompasses those Kagyu schools that trace back to the Indian master Naropa
Nāropā (Prakrit; sa, Nāropāda, Naḍapāda or Abhayakirti) or Abhayakirti was an Indian Buddhist Mahasiddha. He was the disciple of Tilopa and brother, or some sources say partner and pupil, of Niguma. As an Indian Mahasiddha, Naropa's ...
via Marpa Lotsawa, Milarepa and Gampopa.
Mongol conquest and Yuan administrative rule (1240–1354)
 During this era, the region was dominated by the Sakya lama with the Mongols' support, so it is also called the Sakya dynasty. The first documented contact between the Tibetans and the Mongols occurred when the missionary Tsang-pa Dung-khur (''gTsang-pa Dung-khur-ba'') and six disciples met
During this era, the region was dominated by the Sakya lama with the Mongols' support, so it is also called the Sakya dynasty. The first documented contact between the Tibetans and the Mongols occurred when the missionary Tsang-pa Dung-khur (''gTsang-pa Dung-khur-ba'') and six disciples met Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
, probably on the Tangut border where he may have been taken captive, around 1221–22. He left Mongolia as the Quanzhen sect of Daoism gained the upper hand, but remet Genghis Khan when Mongols conquered Tangut shortly before the Khan's death. Closer contacts ensued when the Mongols successively sought to move through the Sino-Tibetan borderlands to attack the Jin dynasty and then the Southern Song, with incursions on outlying areas. One traditional Tibetan account claims that there was a plot to invade Tibet by Genghis Khan in 1206, which is considered anachronistic as there is no evidence of Mongol-Tibetan encounters prior to the military campaign in 1240. The mistake may have arisen from Genghis's real campaign against the Tangut Xixia.
The Mongols invaded Tibet in 1240 with a small campaign led by the Mongol general Doorda Darkhan that consisted of 30,000 troops. The battle resulted in Darkhan's troops suffering 500 casualties. The Mongols withdrew their soldiers from Tibet in 1241, as all the Mongol princes were recalled back to Mongolia in preparation for the appointment of a successor to Ögedei Khan. They returned to the region in 1244, when Köten delivered an ultimatum, summoning the abbot of Sakya (''Kun-dga' rGyal-mtshan'') to be his personal chaplain, on pains of a larger invasion were he to refuse. Sakya Paṇḍita took almost 3 years to obey the summons and arrive in Kokonor in 1246, and met Prince Köten in Lanzhou
Lanzhou (, ; ) is the capital and largest city of Gansu Province in Northwest China. Located on the banks of the Yellow River, it is a key regional transportation hub, connecting areas further west by rail to the eastern half of the country. H ...
the following year. The Mongols had annexed Amdo and Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
to the east, and appointed Sakya Paṇḍita Viceroy of Central Tibet by the Mongol court in 1249.
Tibet was incorporated into the Mongol Empire, retaining nominal power over religious and regional political affairs, while the Mongols managed a structural and administrative rule over the region, reinforced by the rare military intervention. This existed as a "diarchic
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally misspelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate (from Latin ', "the office of ...
structure" under the Mongol emperor, with power primarily in favor of the Mongols.Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs __NOTOC__
The Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan () was a government agency of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China to handle Buddhist affairs across the empire in addition to managing the territory of Tibet. It was original ...
or Xuanzheng Yuan, separate from other Yuan provinces such as those governed the former Song dynasty of China. One of the department's purposes was to select a dpon-chen, usually appointed by the lama and confirmed by the Yuan emperor in Beijing.Drogön Chögyal Phagpa
Drogön Chogyal Phagpa (; ; 1235 – 15 December 1280), was the fifth leader of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. He was also the first Imperial Preceptor of the Yuan dynasty, and was concurrently named the director of the Bureau of Buddhist ...
(1235–1280) succeeded Sakya Pandita at the Mongol court. Phagpa became a religious teacher to Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of th ...
. Kublai Khan appointed Chögyal Phagpa as his Imperial Preceptor (originally State Preceptor) in 1260, the year when he became Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
. Phagpa developed the priest-patron concept that characterized Tibeto-Mongolian relations from that point forward.F. W. Mote
Frederick Wade "Fritz" Mote (June 2, 1922 – February 10, 2005) was an American sinologist and a professor of History at Princeton University for nearly 50 years. His research and teaching interests focused on China during the Yuan and Min ...
. ''Imperial China 900-1800''. Harvard University Press, 1999. p.501.Guge
Guge (; ) was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast ...
and Pu-ran retained their internal autonomy.
The Sakya hegemony over Tibet continued into the mid-14th century, although it was challenged by a revolt of the Drikung Kagyu sect with the assistance of Duwa Khan of the Chagatai Khanate in 1285. The revolt was suppressed in 1290 when the Sakyas and eastern Mongols burned Drikung Monastery and killed 10,000 people.
Between 1346 and 1354, towards the end of the Yuan dynasty, the House of Pagmodru
The Phagmodrupa dynasty or Pagmodru (, ; ) was a dynastic regime that held sway over Tibet or parts thereof from 1354 to the early 17th century. It was established by Tai Situ Changchub Gyaltsen of the Lang () family at the end of the Yuan dynast ...
would topple the Sakya. The rule over Tibet by a succession of Sakya lamas came to a definite end in 1358, when central Tibet came under control of the Kagyu
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineag ...
sect. "By the 1370s, the lines between the schools of Buddhism were clear."
The following 80-or-so years were a period of relative stability. They also saw the birth of the Gelugpa school (also known as ''Yellow Hats'') by the disciples of Tsongkhapa Lobsang Dragpa, and the founding of the Ganden, Drepung, and Sera monasteries near Lhasa. After the 1430s, the country entered another period of internal power struggles.
Tibetan independence (14th-18th century)
With the decline of the Yuan dynasty, Central Tibet was ruled by successive families from the 14th to the 17th centuries, to be succeeded by the Dalai Lama's rule in the 17th and 18th centuries. Tibet would be de facto independent from the mid-14th century on, for nearly 400 years. In spite of the weakening of central authority, the neighbouring Ming dynasty of China made little effort to impose direct rule, although it had nominal claims of the Tibetan territory by establishing the U-Tsang Regional Military Commission and Do-Kham Regional Military Commission in 1370s. They also kept friendly relations with some of the Buddhism religious leaders known as Princes of Dharma and granted some other titles to local leaders including the Grand Imperial Tutor.
Family rule (14th–17th centuries)
Phagmodrupa (14th–15th centuries)
The Phagmodru (Phag mo gru) myriarchy centered at Neudong (Sne'u gdong) was granted as an appanage to Hülegü in 1251. The area had already been associated with the Lang (Rlang) family, and with the waning of Ilkhanate influence it was ruled by this family, within the Mongol-Sakya framework headed by the Mongol appointed Pönchen (dpon-chen) at Sakya. The areas under Lang administration were continually encroached upon during the late 13th and early 14th centuries. Jangchub Gyaltsän (Byang chub rgyal mtshan, 1302–1364) saw these encroachments as illegal and sought the restoration of Phagmodru lands after his appointment as the Myriarch in 1322. After prolonged legal struggles, the struggle became violent when Phagmodru was attacked by its neighbours in 1346. Jangchub Gyaltsän was arrested and released in 1347. When he later refused to appear for trial, his domains were attacked by the Pönchen in 1348. Janchung Gyaltsän was able to defend Phagmodru, and continued to have military successes, until by 1351 he was the strongest political figure in the country. Military hostilities ended in 1354 with Jangchub Gyaltsän as the unquestioned victor, who established the Phagmodrupa dynasty in that year. He continued to rule central Tibet until his death in 1364, although he left all Mongol institutions in place as hollow formalities. Power remained in the hands of the Phagmodru family until 1434.
The rule of Jangchub Gyaltsän and his successors implied a new cultural self-awareness where models were sought in the age of the ancient Tibetan Kingdom. The relatively peaceful conditions favoured the literary and artistic development. During this period the reformist scholar Je Tsongkhapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Budd ...
(1357–1419) founded the Gelug sect which would have a decisive influence on Tibet's history.
Rinpungpa family (15th–16th centuries)
Internal strife within the Phagmodrupa dynasty and the strong localism of the various fiefs and political-religious factions led to a long series of internal conflicts. The minister family Rinpungpa, based in Tsang (West Central Tibet), dominated politics after 1435.
Tsangpa dynasty (16th–17th centuries)
In 1565 they were overthrown by the Tsangpa Dynasty of Shigatse which expanded its power in different directions of Tibet in the following decades and favoured the Karma Kagyu sect. They would play a pivotal role in the events which led to the rise of power of the Dalai Lama's in the 1640s.
Ganden Phodrang government (17th–18th centuries)
 The ''Ganden Phodrang'' was the Tibetan government established in 1642 by the
The ''Ganden Phodrang'' was the Tibetan government established in 1642 by the 5th Dalai Lama
Ngawang Lobsang Gyatso (; ; 1617–1682) was the 5th Dalai Lama and the first Dalai Lama to wield effective temporal and spiritual power over all Tibet. He is often referred to simply as the Great Fifth, being a key religious and temporal leader ...
with the military assistance of Güshi Khan of the Khoshut Khanate. Lhasa became the capital of Tibet in the beginning of this period, with all temporal power being conferred to the 5th Dalai Lama by Güshi Khan in Shigatse.
Rise of the Gelugpa school and the Dalai Lama
The rise of the Dalai Lamas was intimately connected with the military power of Mongolian clans. Altan Khan
Altan Khan of the Tümed (1507–1582; mn, ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠨ ᠬᠠᠨ, Алтан хан; Chinese language, Chinese: 阿勒坦汗), whose given name was Anda (Mongolian language, Mongolian: ; Chinese language, Chinese: 俺答), was the leader of ...
, the king of the Tümed Mongols, first invited Sonam Gyatso, the head of the Gelugpa school of Tibetan Buddhism (later known as the third Dalai Lama), to Mongolia in 1569 and again in 1578, during the reign of the Tsangpa family. Gyatso accepted the second invitation. They met at the site of Altan Khan's new capital, Koko Khotan (Hohhot), and the Dalai Lama taught a large crowd there.
Sonam Gyatso publicly announced that he was a reincarnation of the Tibetan Sakya monk Drogön Chögyal Phagpa
Drogön Chogyal Phagpa (; ; 1235 – 15 December 1280), was the fifth leader of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. He was also the first Imperial Preceptor of the Yuan dynasty, and was concurrently named the director of the Bureau of Buddhist ...
(1235–1280) who converted Kublai Khan, while Altan Khan was a reincarnation of Kublai Khan (1215–1294), the famous ruler of the Mongols and Emperor of China, and that they had come together again to cooperate in propagating the Buddhist religion. While this did not immediately lead to a massive conversion of Mongols to Buddhism (this would only happen in the 1630s), it did lead to the widespread use of Buddhist ideology for the legitimation of power among the Mongol nobility. Last but not least, Yonten Gyatso, the fourth Dalai Lama, was a grandson of Altan Khan.
Khoshut-Gelugpa alliance
Yonten Gyatso (1589–1616), the fourth Dalai Lama and a non-Tibetan, was the grandson of Altan Khan
Altan Khan of the Tümed (1507–1582; mn, ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠨ ᠬᠠᠨ, Алтан хан; Chinese language, Chinese: 阿勒坦汗), whose given name was Anda (Mongolian language, Mongolian: ; Chinese language, Chinese: 俺答), was the leader of ...
. He died in 1616 in his mid-twenties. Some people say he was poisoned but there is no real evidence one way or the other.
Lobsang Gyatso ( Wylie transliteration: Blo-bzang Rgya-mtsho), the Great Fifth Dalai Lama (1617–1682), was the first Dalai Lama to wield effective political power over central Tibet.
The Fifth Dalai Lama's first regent Sonam Rapten is known for unifying the Tibetan heartland under the control of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism, after defeating the rival Kagyu
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineag ...
and Jonang sects and the secular ruler, the Tsangpa prince, in a prolonged civil war. His efforts were in large part successful due to the military aid contributed by Güshi Khan, the Oirat Khoshut leader of the Khoshut Khanate. The positions of the Dalai Lama, Sonam Rapten, and the khans have been subject to various interpretations. Some sources claim the khan appointed Sonam Rapten as ''de facto'' administrator of civil affairs while the Dalai Lama was relegated to religious matters. Other sources claim that Güshi Khan was largely uninvolved in the administration of Tibet and remained in Kokonor after defeating the enemies of the Gelugpa school.
The 5th Dalai Lama and his intimates, especially Sonam Rapten (until his death in 1658), established a civil administration referred to by historians as the ''Lhasa state''. This Tibetan administration is also referred to as the Ganden Phodrang, named after the 5th Dalai Lama's residence in Drepung Monastery.
Sonam Rapten was a fanatical and militant proponent of the Gelugpa. Under his administration, the other schools were persecuted. Jonang sources today claim that the Jonang monasteries were either closed or forcibly converted, and that school remained in hiding until the latter part of the 20th century. However, before leaving Tibet for China in 1652 the Dalai Lama issued a proclamation or decree to Sonam Rapten banning all such sectarian policies that had been implemented by his administration after the 1642 civil war, and ordered their reversal. According to FitzHerbert and, there was an increase in the 5th Dalai Lama's "day-to-day control of ... his government" after the deaths of Sonam Rapten and Güshi Khan in the 1650s.
The 5th Dalai Lama initiated the construction of the Potala Palace in Lhasa in 1645. During the rule of the Great Fifth, two Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
missionaries, the German Johannes Gruber
Johann Grueber (28 October 1623, Linz – 30 September 1680, Sárospatak, Hungary) was an Austrian Jesuit missionary and astronomer in China, and noted explorer.
Life
He joined the Society of Jesus in 1641 and went to China in 1656, where he was ...
and Belgian Albert Dorville
Albert Dorville, (also known as ''Albert Le Comte d’Orville'') (12 August 1621 in Brussels, Belgium – 8 April 1662 in Agra, India) was a Belgian Jesuit priest, missionary in China and cartographer.
Biography
The young Albert, son of nobl ...
, stayed in Lhasa for two months, October and November, 1661 on their way from Peking to Portuguese Goa, in India.[
] In 1652, the 5th Dalai Lama visited the Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Prince ...
of the Qing dynasty. He was not required to kowtow like other visitors, but still had to kneel before the Emperor; and he was later sent an official seal.
The death of the 5th Dalai Lama in 1682 was kept hidden for fifteen years by his assistant confidant, Desi Sangye Gyatso. The 6th Dalai Lama, Tsangyang Gyatso, was enthroned in the Potala on 7 or 8 December 1697. In 1705-6, conflict between the 6th Dalai Lama's regent and the Khoshut Khanate led to the seizure of Lhasa by Lha-bzang Khan, who murdered the regent and deposed the 6th Dalai Lama. A pretender, Yeshe Gyatso, was installed by Lha-bzang until the Dzungar Khanate invaded in 1717 and removed the Khoshut khan and pretender from power. The 7th Dalai Lama was installed but the Dzungars terrorized the people, leading to loss of goodwill from the Tibetans. The Dzungars were ousted in 1720 by the Qing dynasty.
Qing conquest and administrative rule (1720–1912)
The Qing rule over Tibet was established after a Qing expedition force defeated the Dzungars who occupied Tibet in 1720, and lasted until the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. The Qing emperors appointed imperial residents known as the Amban
Amban (Manchu language, Manchu and Mongolian language, Mongol: ''Amban'', Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: ་''am ben'', , Uyghur language, Uighur:''am ben'') is a Manchu language term meaning "high official", corresponding to a number of different ...
s to Tibet, who commanded over 2,000 troops stationed in Lhasa and reported to the Lifan Yuan, a Qing government agency that oversaw the region during this period. During this era, the region was dominated by the Dalai Lamas with the support from the Qing dynasty established by the Manchus in China.

Qing rule

Qing conquest
The Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty sent an expedition army to Tibet in response to the occupation of Tibet by the forces of the Dzungar Khanate, together with Tibetan forces under Polhanas (also spelled Polhaney) of Tsang and Kangchennas (also spelled Gangchenney), the governor of Western Tibet, they expelled the Dzungars from Tibet in 1720. They brought Kelzang Gyatso with them from Kumbum to Lhasa and he was installed as the 7th Dalai Lama. Qing protectorate over Tibet was established at this time, with a garrison at Lhasa, and Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
was annexed to Sichuan. In 1721, the Qing established a government in Lhasa consisting of a council (the '' Kashag'') of three Tibetan ministers, headed by Kangchennas. The Dalai Lama's role at this time was purely symbolic, but still highly influential because of the Mongols' religious beliefs.
After the succession of the Yongzheng Emperor in 1722, a series of reductions of Qing forces in Tibet occurred. However, Lhasa nobility who had been allied with the Dzungars killed Kangchennas and took control of Lhasa in 1727, and Polhanas fled to his native Ngari. Qing troops arrived in Lhasa in September, and punished the anti-Qing faction by executing entire families, including women and children. The Dalai Lama was sent to Lithang
Litang (; ) is in southwest of Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan, China.
Litang is part of Kham in the Tibetan cultural zone, and several famous Buddhist figures were born here, including the 7th Dalai Lama, the 10th Dalai Lama, the ...
Monastery in Kham. The Panchen Lama was brought to Lhasa and was given temporal authority over Tsang and Ngari, creating a territorial division between the two high lamas that was to be a long lasting feature of Chinese policy toward Tibet. Two ''amban
Amban (Manchu language, Manchu and Mongolian language, Mongol: ''Amban'', Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: ་''am ben'', , Uyghur language, Uighur:''am ben'') is a Manchu language term meaning "high official", corresponding to a number of different ...
s'' were established in Lhasa, with increased numbers of Qing troops. Over the 1730s, Qing troops were again reduced, and Polhanas gained more power and authority. The Dalai Lama returned to Lhasa in 1735, temporal power remained with Polhanas. The Qing found Polhanas to be a loyal agent and an effective ruler over a stable Tibet, so he remained dominant until his death in 1747.
At multiple places such as Lhasa, Batang, Dartsendo, Lhari, Chamdo, and Litang, Green Standard Army troops were garrisoned throughout the Dzungar war. Green Standard Army troops and Manchu Bannermen were both part of the Qing force who fought in Tibet in the war against the Dzungars. It was said that the Sichuan commander Yue Zhongqi (a descendant of Yue Fei
Yue Fei ( zh, t=岳飛; March 24, 1103 – January 28, 1142), courtesy name Pengju (), was a Chinese military general who lived during the Song dynasty, Southern Song dynasty and a national hero of China, known for leading Southern Song force ...
) entered Lhasa first when the 2,000 Green Standard soldiers and 1,000 Manchu soldiers of the "Sichuan route" seized Lhasa. According to Mark C. Elliott, after 1728 the Qing used Green Standard Army troops to man the garrison in Lhasa rather than Bannermen. According to Evelyn S. Rawski both Green Standard Army and Bannermen made up the Qing garrison in Tibet. According to Sabine Dabringhaus, Green Standard Chinese soldiers numbering more than 1,300 were stationed by the Qing in Tibet to support the 3,000-strong Tibetan army.
The Qing had made the region of Amdo and Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
into the province of Qinghai in 1724, and incorporated eastern Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
into neighbouring Chinese provinces in 1728.[ Wang Lixiong]
"Reflections on Tibet"
, ''New Left Review'' 14, March–April 2002:'"Tibetan local affairs were left to the willful actions of the Dalai Lama and the shapes ashag members, he said. "The Commissioners were not only unable to take charge, they were also kept uninformed. This reduced the post of the Residential Commissioner in Tibet to name only.' The Qing government sent a resident commissioner (''amban
Amban (Manchu language, Manchu and Mongolian language, Mongol: ''Amban'', Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: ་''am ben'', , Uyghur language, Uighur:''am ben'') is a Manchu language term meaning "high official", corresponding to a number of different ...
'') to Lhasa. Polhanas' son Gyurme Namgyal took over upon his father's death in 1747. The ''ambans'' became convinced that he was going to lead a rebellion, so they killed him. News of the incident leaked out and a riot broke out in the city, the mob avenged the regent's death by killing the ''ambans''. The Dalai Lama stepped in and restored order in Lhasa. The Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
(Yongzheng's successor) sent Qing forces to execute Gyurme Namgyal's family and seven members of the group that killed the ''ambans''. The Emperor re-organized the Tibetan government ('' Kashag'') again, nominally restoring temporal power to the Dalai Lama, but in fact consolidating power in the hands of the (new) ''ambans''.
Expansion of control over Tibet
 The defeat of the 1791 Nepalese invasion increased the Qing's control over Tibet. From that moment, all important matters were to be submitted to the ''ambans''. It strengthened the powers of the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were elevated above the Kashag and the regents in responsibility for Tibetan political affairs. The Dalai and Panchen Lamas were no longer allowed to petition the Qing Emperor directly but could only do so through the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' took control of Tibetan frontier defense and foreign affairs. The ''ambans'' were put in command of the Qing garrison and the Tibetan army (whose strength was set at 3,000 men). Trade was also restricted and travel could be undertaken only with documents issued by the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were to review all judicial decisions. However, according to Warren Smith, these directives were either never fully implemented, or quickly discarded, as the Qing were more interested in a symbolic gesture of authority than actual sovereignty. In 1841, the
The defeat of the 1791 Nepalese invasion increased the Qing's control over Tibet. From that moment, all important matters were to be submitted to the ''ambans''. It strengthened the powers of the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were elevated above the Kashag and the regents in responsibility for Tibetan political affairs. The Dalai and Panchen Lamas were no longer allowed to petition the Qing Emperor directly but could only do so through the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' took control of Tibetan frontier defense and foreign affairs. The ''ambans'' were put in command of the Qing garrison and the Tibetan army (whose strength was set at 3,000 men). Trade was also restricted and travel could be undertaken only with documents issued by the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were to review all judicial decisions. However, according to Warren Smith, these directives were either never fully implemented, or quickly discarded, as the Qing were more interested in a symbolic gesture of authority than actual sovereignty. In 1841, the Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Dogra dynasty attempted to establish their authority on Ü-Tsang but were defeated in the Sino-Sikh War (1841–1842).
In the mid-19th century, arriving with an Amban, a community of Chinese troops from Sichuan who married Tibetan women settled down in the Lubu neighborhood of Lhasa, where their descendants established a community and assimilated into Tibetan culture. Hebalin was the location of where Chinese Muslim troops and their offspring lived, while Lubu was the place where Han Chinese troops and their offspring lived.
European influences in Tibet
 The first Europeans to arrive in Tibet were Portuguese missionaries who first arrived in 1624 led by António de Andrade. They were welcomed by the Tibetans who allowed them to build a church. The 18th century brought more Jesuits and Capuchins from Europe. They gradually met opposition from Tibetan
The first Europeans to arrive in Tibet were Portuguese missionaries who first arrived in 1624 led by António de Andrade. They were welcomed by the Tibetans who allowed them to build a church. The 18th century brought more Jesuits and Capuchins from Europe. They gradually met opposition from Tibetan lama
Lama (; "chief") is a title for a teacher of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. The name is similar to the Sanskrit term ''guru'', meaning "heavy one", endowed with qualities the student will eventually embody. The Tibetan word "lama" means "hi ...
s who finally expelled them from Tibet in 1745. Other visitors included, in 1774 a Scottish nobleman, George Bogle, who came to Shigatse to investigate trade for the British East India Company, introducing the first potatoes into Tibet.
After 1792 Tibet, under Chinese influence, closed its borders to Europeans and during the 19th century only 3 Westerners, the Englishman Thomas Manning Thomas Manning may refer to:
* Thomas Manning (sinologist) (1772–1840), Chinese studies scholar and the first Englishman to enter Lhasa
* Thomas Manning (bishop), Tudor prior and bishop
* Thomas A. Manning (1886–1944), American politician
* Tho ...
and 2 French missionaries Huc and Gabet, reached Lhasa, although a number were able to travel in the Tibetan periphery.
During the 19th century the British Empire was encroaching from northern India into the Himalayas and Afghanistan and the Russian Empire of the tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
s was expanding south into Central Asia. Each power became suspicious of intent in Tibet. But Tibet attracted the attention of many explorers. In 1840, Sándor Kőrösi Csoma arrived in Darjeeling, hoping that he would be able to trace the origin of the Magyar ethnic group, but died before he was able to enter Tibet.
In 1865 Great Britain secretly began mapping Tibet. Trained Indian surveyor-spies disguised as pilgrims or traders, called pundits, counted their strides on their travels across Tibet and took readings at night. Nain Singh, the most famous, measured the longitude, latitude and altitude of Lhasa and traced the Yarlung Tsangpo River.
British invasions of Tibet (1903−1904) and Qing control reasserted
 At the beginning of the 20th century the British and Russian Empires were competing for supremacy in Central Asia. Unable to establish diplomatic contacts with the Tibetan government, and concerned about reports of their dealings with Russia, in 1903–04, a British expedition led by Colonel Francis Younghusband was sent to Lhasa to force a trading agreement and to prevent Tibetans from establishing a relationship with the Russians. In response, the
At the beginning of the 20th century the British and Russian Empires were competing for supremacy in Central Asia. Unable to establish diplomatic contacts with the Tibetan government, and concerned about reports of their dealings with Russia, in 1903–04, a British expedition led by Colonel Francis Younghusband was sent to Lhasa to force a trading agreement and to prevent Tibetans from establishing a relationship with the Russians. In response, the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
foreign ministry asserted that China was sovereign over Tibet, the first clear statement of such a claim. Before the British troops arrived in Lhasa, the 13th Dalai Lama fled to Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
, and then went to Beijing in 1908.
The British invasion was one of the triggers for the 1905 Tibetan Rebellion
Nineteen or 19 may refer to:
* 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20
* one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019
Films
* ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film
* ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film
Musi ...
at Batang monastery, when anti-foreign Tibetan lama
Lama (; "chief") is a title for a teacher of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. The name is similar to the Sanskrit term ''guru'', meaning "heavy one", endowed with qualities the student will eventually embody. The Tibetan word "lama" means "hi ...
s massacred French missionaries, Manchu and Han Qing officials, and Christian converts before the Qing crushed the revolt.
The Anglo-Tibetan Treaty of Lhasa of 1904 was followed by the Sino-British treaty of 1906. Beijing agreed to pay London 2.5 million rupees which Lhasa was forced to agree upon in the Anglo-Tibetan treaty of 1904. In 1907, Britain and Russia agreed that in "conformity with the admitted principle of the suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
of China over Tibet"[Convention Between Great Britain and Russia (1907)]
/ref> both nations "engage not to enter into negotiations with Tibet except through the intermediary of the Chinese Government."[
The Qing government in Beijing then appointed Zhao Erfeng, the Governor of Xining, "Army Commander of Tibet" to reintegrate Tibet into China. He was sent in 1905 (though other sources say this occurred in 1908) on a punitive expedition. His troops destroyed a number of monasteries in ]Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
and Amdo, and a process of sinification of the region was begun. The Dalai Lama once again fled, this time to India, and was once again deposed by the Chinese. The situation was soon to change, however, as, after the fall of the Qing dynasty in October 1911, Zhao's soldiers mutinied and beheaded him. All remaining Qing forces left Tibet after the Xinhai Lhasa turmoil
Xinhai Lhasa turmoil (; ) refers to the ethnic clash in the Lhasa region of Tibet and various mutinies following the Wuchang Uprising. It effectively resulted in the end of Qing rule in Tibet.
Background
The Wuchang Uprising unfolded on October 1 ...
.
''De facto'' independence (1912–1951)
 The Dalai Lama returned to Tibet from India in July 1912 (after the fall of the Qing dynasty), and expelled the ''Amban'' and all Chinese troops. In 1913, the Dalai Lama issued a proclamation that stated that the relationship between the Chinese emperor and Tibet "had been that of patron and priest and had not been based on the subordination of one to the other."
The Dalai Lama returned to Tibet from India in July 1912 (after the fall of the Qing dynasty), and expelled the ''Amban'' and all Chinese troops. In 1913, the Dalai Lama issued a proclamation that stated that the relationship between the Chinese emperor and Tibet "had been that of patron and priest and had not been based on the subordination of one to the other."[Proclamation Issued by H.H. The Dalai Lama XIII]
"We are a small, religious, and independent nation", the proclamation continued.[Tibet during the Republic of China (1912–1949)](_blank)
A book published in 1939 by a Swedish sinologist and linguist about the war in China placed Tibet as part of China. The Chinese government in the 1930s tried to claim superiority. The USA also recognised Tibet as a province of China during this time as seen in the documentary film '' Why We Fight'' #6 '' The Battle of China'' produced by the USA War Department in 1944. Some other authors argue that Tibet was also de jure independent after Tibet-Mongolia Treaty of 1913, before which Mongolia has been recognized by Russia.[Kuzmin, S.L. ''Hidden Tibet: History of Independence and Occupation''. Dharamsala, LTWA, 2011](_blank)
/ref>
Tibet continued in 1913–1949 to have very limited contacts with the rest of the world, although British representatives were stationed in Gyantse, Yatung and Gartok (western Tibet) after the Younghusband Mission. These so-called "Trade Agents" were in effect diplomatic representatives of the British Government of India and in 1936–37 the British also established a permanent mission in Lhasa. This was in response to a Chinese "condolence mission' sent to the Tibetan capital after the demise of the 13th Dalai Lama which remained in Lhasa as, in effect, a Republican Chinese diplomatic post. After 1947 the British mission was transferred to the newly independent Indian government control although the last British representative, Hugh Richardson remained in Lhasa until 1950 serving the Indian government. The British, like the Chinese, encouraged the Tibetans to keep foreigners out of Tibet and no foreigners visited Lhasa between the departure of the Younghusband mission in 1904 and the arrival of a telegraph officer in 1920. Just over 90 European and Japanese visited Lhasa during the years 1920–1950, most of whom were British diplomatic personnel. Very few governments did anything resembling a normal diplomatic recognition of Tibet. In 1914 the Tibetan government signed the Simla Accord with Britain, ceding the several small areas on the southern side of the Himalayan watershed to British India. The Chinese government denounced the agreement as illegal.National Revolutionary Army
The National Revolutionary Army (NRA; ), sometimes shortened to Revolutionary Army () before 1928, and as National Army () after 1928, was the military arm of the Kuomintang (KMT, or the Chinese Nationalist Party) from 1925 until 1947 in China ...
, composed of Muslim and Han soldiers, led by Ma Bufang and Liu Wenhui defeated the Tibetan army in the Sino-Tibetan War when the 13th Dalai Lama tried to seize territory in Qinghai and Xikang. It was also reported that the central government of China encouraged the attack, hoping to solve the "Tibet situation", because the Japanese had just seized Manchuria. They warned the Tibetans not to dare cross the Jinsha river again. A truce was signed, ending the fighting. The Dalai Lama had cabled the British in India for help when his armies were defeated, and started demoting his Generals who had surrendered.
People's Republic of China rule (1950–present)
 In 1949, seeing that the Chinese Communists, with the decisive support from Joseph Stalin, were gaining control of
In 1949, seeing that the Chinese Communists, with the decisive support from Joseph Stalin, were gaining control of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, the Kashag expelled all Chinese connected with the Chinese government, over the protests of both the Kuomintang and the Communists. The People's Republic of China (PRC), founded in October 1949 by the victorious Communists under the leadership of Mao Zedong, lost little time in asserting a new Chinese presence in Tibet. In October 1950, the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
entered the Tibetan area of Chamdo, defeating sporadic resistance from the Tibetan army. In 1951, Tibetan representatives participated in negotiations in Beijing with the Chinese government. This resulted in a ''Seventeen Point Agreement
The Seventeen Point Agreement is a short form of the Agreement of the Central People's Government and the Local Government of Tibet on Measures for the Peaceful Liberation of Tibet, ( zh, 中央人民政府和西藏地方政府关于和平解放 ...
'' which formalized China's sovereignty over Tibet, but was repudiated by the present Tibetan government-in-exile.
From the beginning, it was obvious that incorporating Tibet into Communist China would bring two opposite social systems face-to-face. In Tibet, however, the Chinese Communists opted not to place social reform as an immediate priority. On the contrary, from 1951 to 1959, traditional Tibetan society with its lords and manorial estates continued to function unchanged. Despite the presence of twenty thousand Chinese soldiers in Central Tibet, the Dalai Lama's government was permitted to maintain important symbols from its de facto independence period.
The Communists quickly abolished slavery and serfdom in their traditional forms. They also claim to have reduced taxes, unemployment, and beggary, and to have started work projects. They established secular schools, thereby breaking the educational monopoly of the monasteries, and they constructed running water and electrical systems in Lhasa.
The Tibetan region of Eastern Kham, previously Xikang province, was incorporated in the province of Sichuan. Western Kham was put under the Chamdo Military Committee. In these areas, land reform was implemented. This involved communist agitators designating "landlords"—sometimes arbitrarily chosen—for public humiliation in thamzing
Denunciation rallies, also called struggle sessions, were violent public spectacles in Maoist China where people accused of being "class enemies" were publicly humiliated, accused, beaten and tortured by people with whom they were close. Usually ...
() or " Struggle Sessions", torture, maiming, and even death.
 By 1956 there was unrest in eastern Kham and Amdo, where land reform had been implemented in full. These rebellions eventually spread into western Kham and Ü-Tsang.
In 1956–57, armed Tibetan guerrillas ambushed convoys of the Chinese Peoples Liberation Army. The uprising received extensive assistance from the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), including
By 1956 there was unrest in eastern Kham and Amdo, where land reform had been implemented in full. These rebellions eventually spread into western Kham and Ü-Tsang.
In 1956–57, armed Tibetan guerrillas ambushed convoys of the Chinese Peoples Liberation Army. The uprising received extensive assistance from the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), including military training
Military education and training is a process which intends to establish and improve the capabilities of military personnel in their respective roles. Military training may be voluntary or compulsory duty. It begins with recruit training, proceed ...
, support camps in Nepal, and several airlifts. Meanwhile, in the United States, the American Society for a Free Asia, a CIA-financed front, energetically publicized the cause of Tibetan resistance, with the Dalai Lama's eldest brother, Thubten Norbu
Thubten Jigme Norbu () (August 16, 1922 – September 5, 2008), recognised as the Taktser Rinpoche, was a Tibetan lama, writer, civil rights activist and professor of Tibetan studies and was the eldest brother of the 14th Dalai Lama, Tenzin Gyats ...
, playing an active role in that organization. The Dalai Lama's second-eldest brother, Gyalo Thondup, established an intelligence operation with the CIA as early as 1951. He later upgraded it into a CIA-trained guerrilla unit whose recruits parachuted back into Tibet.
Many Tibetan commandos and agents whom the CIA dropped into the country were chiefs of aristocratic clans or the sons of chiefs. Ninety percent of them were never heard from again, according to a report from the CIA itself, meaning they were most likely captured and killed. Ginsburg and Mathos reached the conclusion, that "As far as can be ascertained, the great bulk of the common people of Lhasa and of the adjoining countryside failed to join in the fighting against the Chinese both when it first began and as it progressed." According to other data, many thousands of common Tibetans participated in the rebellion.Great Chinese Famine
The Great Chinese Famine () was a period between 1959 and 1961 in the history of the People's Republic of China (PRC) characterized by widespread famine. Some scholars have also included the years 1958 or 1962. It is widely regarded as the dead ...
brought about by drought and by the Chinese policies of the Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward (Second Five Year Plan) of the People's Republic of China (PRC) was an economic and social campaign led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1958 to 1962. CCP Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to reconstruc ...
which affected all of China and not only Tibet. The Tenth Panchen Lama
Lobsang Trinley Lhündrub Chökyi Gyaltsen (born Gönbo Cêdän; 19 February 1938 – 28 January 1989) was the tenth Panchen Lama, officially the 10th Panchen Erdeni (), of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. According to Tibetan Buddhism, ...
was a keen observer of Tibet during this period and penned the 70,000 Character Petition to detail the sufferings of the Tibetans and sent it to Zhou Enlai in May 1962.
In 1962, China and India fought a brief war over the disputed Aksai Chin region. Although China won the war, Chinese troops withdrew north of the McMahon Line. In 1965, the area that had been under the control of the Dalai Lama's government from the 1910s to 1959 (Ü-Tsang and western Kham) was renamed the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR). Autonomy provided that the head of government would be an ethnic Tibetan; however, actual power in the TAR is held by the First Secretary of the Tibet Autonomous Regional Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, who has never been a Tibetan. The role of ethnic Tibetans in the higher levels of the TAR Communist Party remains very limited.
The destruction of most of Tibet's more than 6,000 monasteries occurred between 1959 and 1961 by the Chinese Communist Party. During the mid-1960s, the monastic estates were broken up and secular education introduced. During the Cultural Revolution. Red Guards inflicted a campaign of organized vandalism against cultural sites in the entire PRC, including Tibet's Buddhist heritage.
In 1989, the Panchen Lama died of a massive heart attack at the age of 50.
In 1965, the area that had been under the control of the Dalai Lama's government from the 1910s to 1959 (Ü-Tsang and western Kham) was renamed the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR). Autonomy provided that the head of government would be an ethnic Tibetan; however, actual power in the TAR is held by the First Secretary of the Tibet Autonomous Regional Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, who has never been a Tibetan. The role of ethnic Tibetans in the higher levels of the TAR Communist Party remains very limited.
The destruction of most of Tibet's more than 6,000 monasteries occurred between 1959 and 1961 by the Chinese Communist Party. During the mid-1960s, the monastic estates were broken up and secular education introduced. During the Cultural Revolution. Red Guards inflicted a campaign of organized vandalism against cultural sites in the entire PRC, including Tibet's Buddhist heritage.
In 1989, the Panchen Lama died of a massive heart attack at the age of 50.Riots
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted ...
flared up again in 2008. Many ethnic Hans and Huis were attacked in the riot, their shops vandalized or burned. The Chinese government reacted swiftly, imposing curfews and strictly limiting access to Tibetan areas. The international response was likewise immediate and robust, with some leaders condemning the crackdown and large protests and some in support of China's actions.
In 2018, German car manufacturer Mercedes-Benz reverted an advertisement and apologized for 'hurting feelings' of Chinese people by quoting the Dalai Lama.
Tibetans in exile
 Following the Lhasa uprising and the Dalai Lama's flight from Tibet in 1959, the government of India accepted the Tibetan refugees. India designated land for the refugees in the mountainous region of Dharamsala, India, where the Dalai Lama and the Tibetan government-in-exile are now based.
The plight of the Tibetan refugees garnered international attention when the Dalai Lama, spiritual and religious leader of the Tibetan government in exile, won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1989. The Dalai Lama was awarded the Nobel Prize on the basis of his unswerving commitment to peaceful protest against the Chinese occupation of Tibet. He is highly regarded as a result and has since been received by government leaders throughout the world. Among the most recent ceremonies and awards, he was given the Congressional Gold Medal by President Bush in 2007, and in 2006 he was one of only six people to ever receive an honorary Canadian citizenship (see
Following the Lhasa uprising and the Dalai Lama's flight from Tibet in 1959, the government of India accepted the Tibetan refugees. India designated land for the refugees in the mountainous region of Dharamsala, India, where the Dalai Lama and the Tibetan government-in-exile are now based.
The plight of the Tibetan refugees garnered international attention when the Dalai Lama, spiritual and religious leader of the Tibetan government in exile, won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1989. The Dalai Lama was awarded the Nobel Prize on the basis of his unswerving commitment to peaceful protest against the Chinese occupation of Tibet. He is highly regarded as a result and has since been received by government leaders throughout the world. Among the most recent ceremonies and awards, he was given the Congressional Gold Medal by President Bush in 2007, and in 2006 he was one of only six people to ever receive an honorary Canadian citizenship (see Honorary Canadian citizenship
Honorary Canadian citizenship ( French: ''citoyenneté canadienne honoraire'') is an honour bestowed on foreigners of exceptional merit following a joint resolution by both Houses of the Parliament of Canada.
Honorary Canadian citizenship is pu ...
). The PRC consistently protests each official contact with the exiled Tibetan leader.
The community of Tibetans in exile established in Dharamshala and Bylakuppe near Mysore in Karnataka, South India, has expanded since 1959. Tibetans have duplicated Tibetan monasteries
This is the list of Tibetan monasteries of Tibetan Buddhism.
Gallery
File:A grand view of Samye.jpg, Samye Monastery in Dranang
File:Ganden monastery.jpg, Ganden Monastery in Lhasa with some ruins visible from destruction by the Communist Chi ...
in India and these now house tens of thousands of monks. They have also created Tibetan schools and hospitals, and founded the Library of Tibetan Works and Archives
The Library of Tibetan Works and Archives (LTWA) is a Tibetan library in Dharamshala, India. The library was founded by Tenzin Gyatso, the 14th Dalai Lama on 11 June 1970, and is considered one of the most important libraries and institutions of ...
—all aimed at continuing Tibetan tradition and culture. Tibetan festivals such as Lama dances, celebration of Losar (the Tibetan New Year), and the Monlam Prayer Festival, continue in exile.
In 2006, Tenzin Gyatso, the 14th Dalai Lama
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as ...
declared that "Tibet wants autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
, not independence." However, the Chinese distrust him, believing that he has not really given up the quest for Tibetan independence.
Talks between representatives of the Dalai Lama and the Chinese government began again in May, 2008 with little result."Dalai Lama's Envoys To Talk With Chinese. No Conditions Set; Transparency Calls Are Reiterated."
by Peter Wonacott, ''The Wall Street Journal'' May 1, 2008
See also
* 1959 Tibetan uprising
The 1959 Tibetan uprising (also known by other names) began on 10 March 1959, when a revolt erupted in Lhasa, the capital of Tibet, which had been under the effective control of the People's Republic of China since the Seventeen Point Agreemen ...
* 1987–1989 Tibetan unrest
The 1987–1989 Tibetan unrest was a series of protests and demonstrations that called for Tibetan independence. These protests took place between September 1987 and March 1989 in the Tibet Autonomous Region, in the Tibetan regions of Sichuan, and ...
* 2008 Tibetan unrest
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
* History of Central Asia
* History of India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
* History of Ladakh
* History of Tibetan Buddhism
* List of rulers of Tibet
* Patron and priest relationship __NOTOC__
The priest and patron relationship, also written as priest-patron or cho-yon (; ), is the Tibetan political theory that the relationship between Tibet and China referred to a symbiotic link between a spiritual leader and a lay patron, suc ...
* Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa
Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa is a mythical monkey-ancestor of the Tibetan people. With King Gesar and Avalokiteśvara, of whom he is an incarnation, he is one of the most important figures in Tibetan culture. ''Pha'' means "father", ''Trelgen'' ...
* Protests and uprisings in Tibet since 1950 Protests and uprisings in Tibet against the government of the People's Republic of China have occurred since 1950, and include the 1959 uprising, the 2008 uprising, and the subsequent self-immolation protests.
Over the years the Tibetan governme ...
* Sinicization of Tibet
* Tibet
Notes
References
*
*
*
* Second impression, 1993.
*
* In paperback as .
*
* Goldstein, ''A history of modern Tibet'':
**
**
**
* Goldstein, Melvyn C. ''The Snow Lion and the Dragon: China, Tibet, and the Dalai Lama'' (1997) University of California Press.
*
* Grunfeld, A. Tom. ''The Making of Modern Tibet'' (1996) East Gate Book.
*
*
*
* Kuzmin, S.L. ''Hidden Tibet: History of Independence and Occupation'' (2011) Library of Tibetan Works & Archives.
*
*
*
** Volume 1: ''The Early Period: to c. AD 850 The Yarlung Dynasty ''
*
*
*
*
* Powers, John. ''History as Propaganda: Tibetan Exiles versus the People's Republic of China'' (2004) Oxford University Press.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Shirokauer, Conrad. ''A Brief History of Chinese Civilization'' Thompson Higher Education, (c) 2006.
*
*
* - (online version)
* ; first published in French (1962). English translation by J. E. Stapelton Driver. Reprint: Stanford University Press (with minor revisions from 1977 Faber & Faber edition), 1995. (hbk).
*
* Willard J. Peterson, John King Fairbank, Denis C. Twitchett ''The Cambridge history of China: The Ch'ing empire to 1800'' (2002) Cambridge University Press.
*
Further reading
* Tuttle, Gray, and Kurtis R. Schaeffer, eds. ''The Tibetan History Reader'' ( Columbia University Press, 2013), reprints major articles by scholars
* Bell, Charles: Tibet Past & Present. Reprint, New Delhi, 1990 (originally published in Oxford, 1924).
* Bell, Charles: Portrait of the Dalai Lama, Collins, London, 1946.
* Carrington, Michael. Officers Gentlemen and Thieves: The Looting of Monasteries during the 1903/4 Younghusband Mission to Tibet, Modern Asian Studies 37, 1 (2003), pp. 81–109.
* Desideri (1932). ''An Account of Tibet: The Travels of Ippolito Desideri 1712–1727''. Ippolito Desideri. Edited by Filippo De Filippi. Introduction by C. Wessels. Reproduced by Rupa & Co, New Delhi. 2005.
*
*
* Shakabpa, Tsepon Wangchuk Deden (Dbang-phyug-bde-ldan, Zhwa-sgab-pa) (1907/08–1989): One Hundred Thousand Moons: an advanced political history of Tibet. Translated and annotated by Derek F. Maher. 2 Vol., Brill, 2010 (Brill's Tibetan studies library; 23). Leiden, 2010.
*
*
*
*
* McGranahan, C. "Truth, Fear, and Lies: Exile Politics and Arrested Histories of the Tibetan Resistance", ''Cultural Anthropology'', Vol. 20, Issue 4 (2005), pp. 570–600.
* Knaus, J.K. ''Orphans of the Cold War: America and the Tibetan Struggle for Survival'' (New York: Public Affairs, 1999).
* Bageant, J. "War at the Top of the World", ''Military History'', Vol. 20, Issue 6 (2004), pp. 34–80.
External links
"The Early History of Tibet. From Chinese Sources"
S. W. Bushell, ''The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland'', New Series, Vol. 12, No. 4 (Oct., 1880), pp. 435–541, Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland
at Friends of Tibet New Zealand
''Fifty Years after the Asian Relations Conference''
Sharan, 1997, Tibetan Parliamentary and Policy Research Centre
''The Shadow Circus: The CIA in Tibet''
- Documentary website
according to China, at Xinhua
Remembering Tibet as an independent nation
Kuzmin, S.L. Hidden Tibet: History of Independence and Occupation. LTWA, 2011
Old TibetanDocuments Online
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tibet, History
Tibet
Tibet
Tibet
 The Yarlung kings gradually extended their control, and by the early 6th century most of the Tibetan tribes were under its control, when Namri Songtsen (570?–618?/629), the 32nd King of Tibet of the Yarlung Dynasty, gained control of all the area around what is now Lhasa by 630, and conquered Zhangzhung. With this extent of power the Yarlung kingdom turned into the Tibetan Empire.
The government of Namri Songtsen sent two embassies to China in 608 and 609, marking the appearance of Tibet on the international scene. From the 7th century AD Chinese historians referred to Tibet as Tubo (), though four distinct characters were used. The first externally confirmed contact with the Tibetan kingdom in recorded Tibetan history occurred when King
The Yarlung kings gradually extended their control, and by the early 6th century most of the Tibetan tribes were under its control, when Namri Songtsen (570?–618?/629), the 32nd King of Tibet of the Yarlung Dynasty, gained control of all the area around what is now Lhasa by 630, and conquered Zhangzhung. With this extent of power the Yarlung kingdom turned into the Tibetan Empire.
The government of Namri Songtsen sent two embassies to China in 608 and 609, marking the appearance of Tibet on the international scene. From the 7th century AD Chinese historians referred to Tibet as Tubo (), though four distinct characters were used. The first externally confirmed contact with the Tibetan kingdom in recorded Tibetan history occurred when King 
 The Era of Fragmentation was a period of Tibetan history in the 9th and 10th centuries. During this era, the political centralization of the earlier Tibetan Empire collapsed. The period was dominated by rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Upon the death of Langdarma, the last emperor of a unified Tibetan empire, there was a controversy over whether he would be succeeded by his alleged heir Yumtän (''Yum brtan''), or by another son (or nephew) Ösung (''Od-srung'') (either 843–905 or 847–885). A civil war ensued, which effectively ended centralized Tibetan administration until the Sa-skya period. Ösung's allies managed to keep control of Lhasa, and Yumtän was forced to go to Yalung, where he established a separate line of kings. In 910, the tombs of the emperors were defiled.
The son of Ösung was Pälkhortsän (''Dpal 'khor brtsan'') (865–895 or 893–923). The latter apparently maintained control over much of central Tibet for a time, and sired two sons, Trashi Tsentsän (''Bkra shis brtsen brtsan'') and Thrikhyiding (''Khri khyi lding''), also called
The Era of Fragmentation was a period of Tibetan history in the 9th and 10th centuries. During this era, the political centralization of the earlier Tibetan Empire collapsed. The period was dominated by rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Upon the death of Langdarma, the last emperor of a unified Tibetan empire, there was a controversy over whether he would be succeeded by his alleged heir Yumtän (''Yum brtan''), or by another son (or nephew) Ösung (''Od-srung'') (either 843–905 or 847–885). A civil war ensued, which effectively ended centralized Tibetan administration until the Sa-skya period. Ösung's allies managed to keep control of Lhasa, and Yumtän was forced to go to Yalung, where he established a separate line of kings. In 910, the tombs of the emperors were defiled.
The son of Ösung was Pälkhortsän (''Dpal 'khor brtsan'') (865–895 or 893–923). The latter apparently maintained control over much of central Tibet for a time, and sired two sons, Trashi Tsentsän (''Bkra shis brtsen brtsan'') and Thrikhyiding (''Khri khyi lding''), also called  During this era, the region was dominated by the Sakya lama with the Mongols' support, so it is also called the Sakya dynasty. The first documented contact between the Tibetans and the Mongols occurred when the missionary Tsang-pa Dung-khur (''gTsang-pa Dung-khur-ba'') and six disciples met
During this era, the region was dominated by the Sakya lama with the Mongols' support, so it is also called the Sakya dynasty. The first documented contact between the Tibetans and the Mongols occurred when the missionary Tsang-pa Dung-khur (''gTsang-pa Dung-khur-ba'') and six disciples met  The ''Ganden Phodrang'' was the Tibetan government established in 1642 by the
The ''Ganden Phodrang'' was the Tibetan government established in 1642 by the 
 The defeat of the 1791 Nepalese invasion increased the Qing's control over Tibet. From that moment, all important matters were to be submitted to the ''ambans''. It strengthened the powers of the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were elevated above the Kashag and the regents in responsibility for Tibetan political affairs. The Dalai and Panchen Lamas were no longer allowed to petition the Qing Emperor directly but could only do so through the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' took control of Tibetan frontier defense and foreign affairs. The ''ambans'' were put in command of the Qing garrison and the Tibetan army (whose strength was set at 3,000 men). Trade was also restricted and travel could be undertaken only with documents issued by the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were to review all judicial decisions. However, according to Warren Smith, these directives were either never fully implemented, or quickly discarded, as the Qing were more interested in a symbolic gesture of authority than actual sovereignty. In 1841, the
The defeat of the 1791 Nepalese invasion increased the Qing's control over Tibet. From that moment, all important matters were to be submitted to the ''ambans''. It strengthened the powers of the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were elevated above the Kashag and the regents in responsibility for Tibetan political affairs. The Dalai and Panchen Lamas were no longer allowed to petition the Qing Emperor directly but could only do so through the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' took control of Tibetan frontier defense and foreign affairs. The ''ambans'' were put in command of the Qing garrison and the Tibetan army (whose strength was set at 3,000 men). Trade was also restricted and travel could be undertaken only with documents issued by the ''ambans''. The ''ambans'' were to review all judicial decisions. However, according to Warren Smith, these directives were either never fully implemented, or quickly discarded, as the Qing were more interested in a symbolic gesture of authority than actual sovereignty. In 1841, the  The first Europeans to arrive in Tibet were Portuguese missionaries who first arrived in 1624 led by António de Andrade. They were welcomed by the Tibetans who allowed them to build a church. The 18th century brought more Jesuits and Capuchins from Europe. They gradually met opposition from Tibetan
The first Europeans to arrive in Tibet were Portuguese missionaries who first arrived in 1624 led by António de Andrade. They were welcomed by the Tibetans who allowed them to build a church. The 18th century brought more Jesuits and Capuchins from Europe. They gradually met opposition from Tibetan  At the beginning of the 20th century the British and Russian Empires were competing for supremacy in Central Asia. Unable to establish diplomatic contacts with the Tibetan government, and concerned about reports of their dealings with Russia, in 1903–04, a British expedition led by Colonel Francis Younghusband was sent to Lhasa to force a trading agreement and to prevent Tibetans from establishing a relationship with the Russians. In response, the
At the beginning of the 20th century the British and Russian Empires were competing for supremacy in Central Asia. Unable to establish diplomatic contacts with the Tibetan government, and concerned about reports of their dealings with Russia, in 1903–04, a British expedition led by Colonel Francis Younghusband was sent to Lhasa to force a trading agreement and to prevent Tibetans from establishing a relationship with the Russians. In response, the  The Dalai Lama returned to Tibet from India in July 1912 (after the fall of the Qing dynasty), and expelled the ''Amban'' and all Chinese troops. In 1913, the Dalai Lama issued a proclamation that stated that the relationship between the Chinese emperor and Tibet "had been that of patron and priest and had not been based on the subordination of one to the other."Proclamation Issued by H.H. The Dalai Lama XIII
The Dalai Lama returned to Tibet from India in July 1912 (after the fall of the Qing dynasty), and expelled the ''Amban'' and all Chinese troops. In 1913, the Dalai Lama issued a proclamation that stated that the relationship between the Chinese emperor and Tibet "had been that of patron and priest and had not been based on the subordination of one to the other."Proclamation Issued by H.H. The Dalai Lama XIII In 1949, seeing that the Chinese Communists, with the decisive support from Joseph Stalin, were gaining control of
In 1949, seeing that the Chinese Communists, with the decisive support from Joseph Stalin, were gaining control of  By 1956 there was unrest in eastern Kham and Amdo, where land reform had been implemented in full. These rebellions eventually spread into western Kham and Ü-Tsang.
In 1956–57, armed Tibetan guerrillas ambushed convoys of the Chinese Peoples Liberation Army. The uprising received extensive assistance from the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), including
By 1956 there was unrest in eastern Kham and Amdo, where land reform had been implemented in full. These rebellions eventually spread into western Kham and Ü-Tsang.
In 1956–57, armed Tibetan guerrillas ambushed convoys of the Chinese Peoples Liberation Army. The uprising received extensive assistance from the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), including  In 1965, the area that had been under the control of the Dalai Lama's government from the 1910s to 1959 (Ü-Tsang and western Kham) was renamed the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR). Autonomy provided that the head of government would be an ethnic Tibetan; however, actual power in the TAR is held by the First Secretary of the Tibet Autonomous Regional Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, who has never been a Tibetan. The role of ethnic Tibetans in the higher levels of the TAR Communist Party remains very limited.
The destruction of most of Tibet's more than 6,000 monasteries occurred between 1959 and 1961 by the Chinese Communist Party. During the mid-1960s, the monastic estates were broken up and secular education introduced. During the Cultural Revolution. Red Guards inflicted a campaign of organized vandalism against cultural sites in the entire PRC, including Tibet's Buddhist heritage.
In 1989, the Panchen Lama died of a massive heart attack at the age of 50.
The PRC continues to portray its rule over Tibet as an unalloyed improvement, but as some foreign governments continue to make protests about aspects of PRC rule in Tibet as groups such as Human Rights Watch report alleged human rights violations. Most governments, however, recognize the PRC's sovereignty over Tibet today, and none have recognized the Government of Tibet in Exile in India.
In 1965, the area that had been under the control of the Dalai Lama's government from the 1910s to 1959 (Ü-Tsang and western Kham) was renamed the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR). Autonomy provided that the head of government would be an ethnic Tibetan; however, actual power in the TAR is held by the First Secretary of the Tibet Autonomous Regional Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, who has never been a Tibetan. The role of ethnic Tibetans in the higher levels of the TAR Communist Party remains very limited.
The destruction of most of Tibet's more than 6,000 monasteries occurred between 1959 and 1961 by the Chinese Communist Party. During the mid-1960s, the monastic estates were broken up and secular education introduced. During the Cultural Revolution. Red Guards inflicted a campaign of organized vandalism against cultural sites in the entire PRC, including Tibet's Buddhist heritage.
In 1989, the Panchen Lama died of a massive heart attack at the age of 50.
The PRC continues to portray its rule over Tibet as an unalloyed improvement, but as some foreign governments continue to make protests about aspects of PRC rule in Tibet as groups such as Human Rights Watch report alleged human rights violations. Most governments, however, recognize the PRC's sovereignty over Tibet today, and none have recognized the Government of Tibet in Exile in India.
 Following the Lhasa uprising and the Dalai Lama's flight from Tibet in 1959, the government of India accepted the Tibetan refugees. India designated land for the refugees in the mountainous region of Dharamsala, India, where the Dalai Lama and the Tibetan government-in-exile are now based.
The plight of the Tibetan refugees garnered international attention when the Dalai Lama, spiritual and religious leader of the Tibetan government in exile, won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1989. The Dalai Lama was awarded the Nobel Prize on the basis of his unswerving commitment to peaceful protest against the Chinese occupation of Tibet. He is highly regarded as a result and has since been received by government leaders throughout the world. Among the most recent ceremonies and awards, he was given the Congressional Gold Medal by President Bush in 2007, and in 2006 he was one of only six people to ever receive an honorary Canadian citizenship (see
Following the Lhasa uprising and the Dalai Lama's flight from Tibet in 1959, the government of India accepted the Tibetan refugees. India designated land for the refugees in the mountainous region of Dharamsala, India, where the Dalai Lama and the Tibetan government-in-exile are now based.
The plight of the Tibetan refugees garnered international attention when the Dalai Lama, spiritual and religious leader of the Tibetan government in exile, won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1989. The Dalai Lama was awarded the Nobel Prize on the basis of his unswerving commitment to peaceful protest against the Chinese occupation of Tibet. He is highly regarded as a result and has since been received by government leaders throughout the world. Among the most recent ceremonies and awards, he was given the Congressional Gold Medal by President Bush in 2007, and in 2006 he was one of only six people to ever receive an honorary Canadian citizenship (see