Ancestral Pueblo people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern
 The Ancestral Puebloans were one of four major prehistoric archaeological traditions recognized in the American Southwest, also known as
The Ancestral Puebloans were one of four major prehistoric archaeological traditions recognized in the American Southwest, also known as 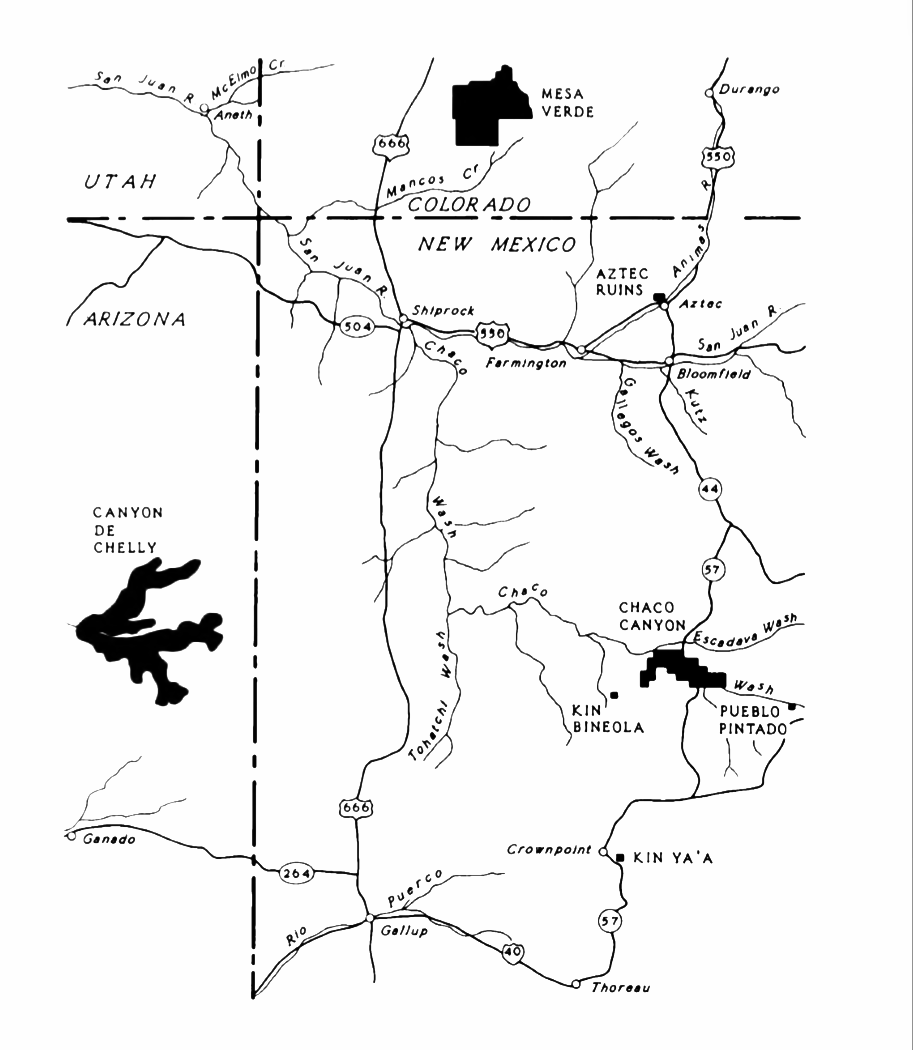
 The Ancestral Puebloan culture is perhaps best known for the stone and earth dwellings its people built along cliff walls, particularly during the Pueblo II and Pueblo III eras, from about 900 to 1350 CE in total. The best-preserved examples of the stone dwellings are now protected within United States'
The Ancestral Puebloan culture is perhaps best known for the stone and earth dwellings its people built along cliff walls, particularly during the Pueblo II and Pueblo III eras, from about 900 to 1350 CE in total. The best-preserved examples of the stone dwellings are now protected within United States'
 Built well before 1492 CE, these towns and villages were located in defensive positions, for example on high, steep mesas such as at Mesa Verde or present-day
Built well before 1492 CE, these towns and villages were located in defensive positions, for example on high, steep mesas such as at Mesa Verde or present-day
 Immense complexes known as "great houses" embodied worship at Chaco. Archaeologists have found musical instruments, jewelry, ceramics, and ceremonial items, indicating people in the Great Houses were elite, wealthier families. They hosted indoor burials, where gifts were interred with the dead, often including bowls of food and turquoise beads.
Over centuries, architectural forms evolved but the complexes kept some core traits, such as their size. They averaged more than 200 rooms each, and some had 700 rooms. Rooms were very large, with higher ceilings than Ancestral Pueblo buildings of earlier periods. They were well-planned: vast sections were built in a single stage.
Immense complexes known as "great houses" embodied worship at Chaco. Archaeologists have found musical instruments, jewelry, ceramics, and ceremonial items, indicating people in the Great Houses were elite, wealthier families. They hosted indoor burials, where gifts were interred with the dead, often including bowls of food and turquoise beads.
Over centuries, architectural forms evolved but the complexes kept some core traits, such as their size. They averaged more than 200 rooms each, and some had 700 rooms. Rooms were very large, with higher ceilings than Ancestral Pueblo buildings of earlier periods. They were well-planned: vast sections were built in a single stage.
 Most houses faced south. Plazas were almost always surrounded by buildings of sealed-off rooms or high walls. There were often four or five stories, with single-story rooms facing the plaza; room blocks were terraced to allow the tallest sections to compose the pueblo's rear edifice. Rooms were often organized into suites, with front rooms larger than rear, interior, and storage rooms or areas.
Ceremonial structures known as kivas were built in proportion to the number of rooms in a pueblo. A small kiva was built for roughly every 29 rooms. Nine complexes each had a Great Kiva, up to in diameter. T-shaped doorways and stone lintels marked all Chacoan kivas.
Although simple and compound walls were often used, great houses usually had
Most houses faced south. Plazas were almost always surrounded by buildings of sealed-off rooms or high walls. There were often four or five stories, with single-story rooms facing the plaza; room blocks were terraced to allow the tallest sections to compose the pueblo's rear edifice. Rooms were often organized into suites, with front rooms larger than rear, interior, and storage rooms or areas.
Ceremonial structures known as kivas were built in proportion to the number of rooms in a pueblo. A small kiva was built for roughly every 29 rooms. Nine complexes each had a Great Kiva, up to in diameter. T-shaped doorways and stone lintels marked all Chacoan kivas.
Although simple and compound walls were often used, great houses usually had
National Park Service. Retrieved 4 June 2012.

 Throughout the southwest Ancestral Puebloan region, the inhabitants built complexes in shallow
Throughout the southwest Ancestral Puebloan region, the inhabitants built complexes in shallow
 The Ancestral Puebloans left their established homes in the 12th and 13th centuries. The main reason is unclear. Factors discussed include global or regional climate change, prolonged drought, environmental degradation such as cyclical periods of
The Ancestral Puebloans left their established homes in the 12th and 13th centuries. The main reason is unclear. Factors discussed include global or regional climate change, prolonged drought, environmental degradation such as cyclical periods of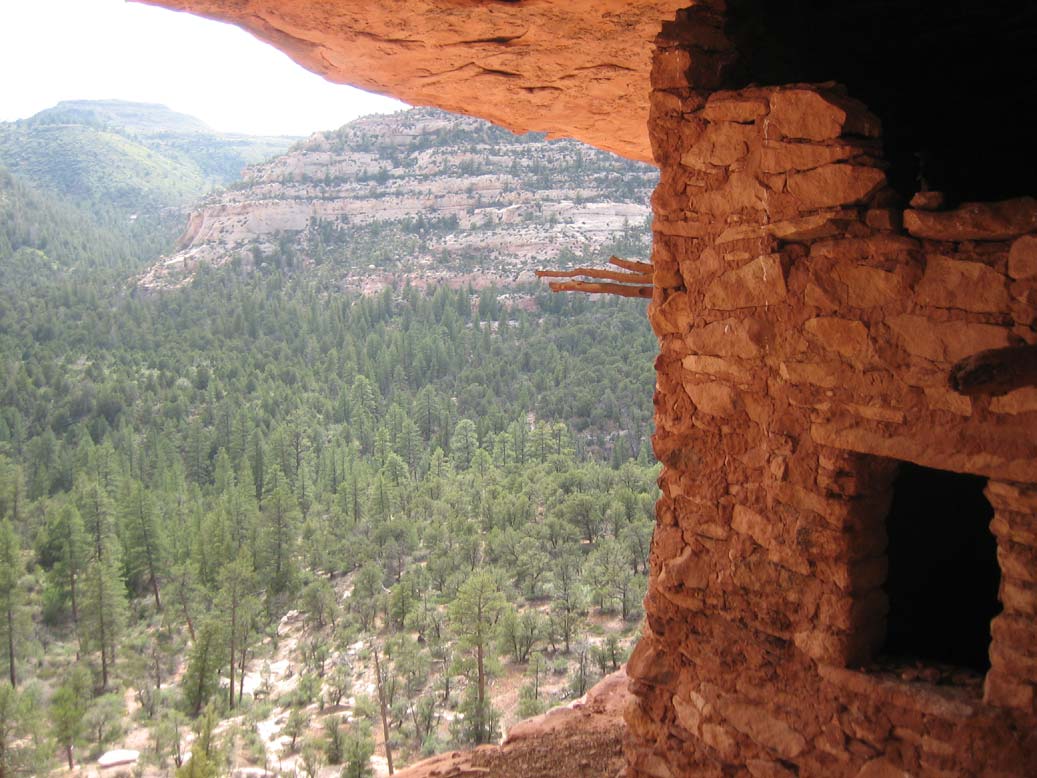  In this later period, the Pueblo II became more self-contained, decreasing trade and interaction with more distant communities. Southwest farmers developed irrigation techniques appropriate to seasonal rainfall, including soil and water control features such as check dams and terraces. The population of the region continued to be mobile, abandoning settlements and fields under adverse conditions. There was also a drop in
In this later period, the Pueblo II became more self-contained, decreasing trade and interaction with more distant communities. Southwest farmers developed irrigation techniques appropriate to seasonal rainfall, including soil and water control features such as check dams and terraces. The population of the region continued to be mobile, abandoning settlements and fields under adverse conditions. There was also a drop in
 Environmental stress may have caused changes in social structure, leading to conflict and warfare. Near
Environmental stress may have caused changes in social structure, leading to conflict and warfare. Near
 Archaeological cultural units such as Ancestral Puebloan, Hohokam, Patayan, or Mogollon are used by archaeologists to define material culture similarities and differences that may identify prehistoric sociocultural units, equivalent to modern societies or peoples. The names and divisions are classification devices based on theoretical perspectives, analytical methods, and data available at the time of analysis and publication. They are subject to change, not only on the basis of new information and discoveries, but also as attitudes and perspectives change within the scientific community. It should not be assumed that an archaeological division or culture unit corresponds to a particular language group or to a socio-political entity such as a tribe.
Current terms and conventions have significant limitations:
* Archaeological research focuses on items left behind during people's activities: fragments of pottery vessels, garbage, human remains, stone tools or evidence left from the construction of dwellings. However, many other aspects of the culture of prehistoric peoples are not tangible. Their beliefs and behavior are difficult to decipher from physical materials, and their languages remain unknown as they had no known
Archaeological cultural units such as Ancestral Puebloan, Hohokam, Patayan, or Mogollon are used by archaeologists to define material culture similarities and differences that may identify prehistoric sociocultural units, equivalent to modern societies or peoples. The names and divisions are classification devices based on theoretical perspectives, analytical methods, and data available at the time of analysis and publication. They are subject to change, not only on the basis of new information and discoveries, but also as attitudes and perspectives change within the scientific community. It should not be assumed that an archaeological division or culture unit corresponds to a particular language group or to a socio-political entity such as a tribe.
Current terms and conventions have significant limitations:
* Archaeological research focuses on items left behind during people's activities: fragments of pottery vessels, garbage, human remains, stone tools or evidence left from the construction of dwellings. However, many other aspects of the culture of prehistoric peoples are not tangible. Their beliefs and behavior are difficult to decipher from physical materials, and their languages remain unknown as they had no known
Bandelier National Monument Virtual Museum Exhibit and Lesson Plans
from
Chaco Culture National Historic Park Virtual Museum Exhibit
from
People of the Colorado PlateauArt by the Ancient Pueblo (Anasazi) at the Brooklyn Museum
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient Pueblo Peoples 01 * Oasisamerica cultures Pre-Columbian cultures Archaeological cultures of North America Native American history of Arizona Native American history of Nevada Native American history of New Mexico Native American history of Utah Post-Archaic period in North America Prehistoric cultures in Colorado Southwest tribes 12th-century BC establishments 13th-century disestablishments in North America Puebloan architecture Puebloan buildings and structures


 The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, northeastern Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, northwestern New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, and southwestern Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition
Oshara Tradition, the northern tradition of the Picosa culture, was a Southwestern Archaic tradition centered in the area now called New Mexico and Colorado. Cynthia Irwin-Williams developed the sequence of Archaic culture for Oshara during he ...
, which developed from the Picosa culture. The people and their archaeological culture are often referred to as ''Anasazi'', meaning "ancient enemies", as they were called by Navajo. Contemporary Puebloan
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zu ...
s object to the use of this term, with some viewing it as derogatory.
The Ancestral Puebloans lived in a range of structures that included small family pit house
A pit-house (or ''pit house'', ''pithouse'') is a house built in the ground and used for shelter. Besides providing shelter from the most extreme of weather conditions, these structures may also be used to store food (just like a pantry, a larder ...
s, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zu ...
, and cliff-sited dwellings for defense. They had a complex network linking hundreds of communities and population centers across the Colorado Plateau. They held a distinct knowledge of celestial sciences that found form in their architecture. The kiva
A kiva is a space used by Puebloans for rites and political meetings, many of them associated with the kachina belief system. Among the modern Hopi and most other Pueblo peoples, "kiva" means a large room that is circular and underground ...
, a congregational space that was used mostly for ceremonies, was an integral part of the community structure.
Archaeologists continue to debate when this distinct culture emerged. The current agreement, based on terminology defined by the Pecos Classification
The Pecos Classification is a chronological division of all known Ancestral Puebloans into periods based on changes in architecture, art, pottery, and cultural remains. The original classification dates back to consensus reached at a 1927 arch� ...
, suggests their emergence around the 12th century BC, during the archaeologically designated Early Basketmaker II Era
The Early Basketmaker II Era (1500 BCE – 50 CE) was the first Post- Archaic cultural period of Ancient Pueblo People. The era began with the cultivation of maize in the northern American southwest, although there was not a dependence upon agric ...
. Beginning with the earliest explorations and excavations, researchers identified Ancestral Puebloans as the forerunners of contemporary Pueblo people
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Z ...
s. Three UNESCO World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
located in the United States are credited to the Pueblos: Mesa Verde National Park
Mesa Verde National Park is an American national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan archaeological sites in the United States.
Established ...
, Chaco Culture National Historical Park
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historic Sites (United States), National Historical Park in the Southwestern United States, American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northw ...
and Taos Pueblo
Taos Pueblo (or Pueblo de Taos) is an ancient pueblo belonging to a Taos-speaking (Tiwa) Native American tribe of Puebloan people. It lies about north of the modern city of Taos, New Mexico. The pueblos are considered to be one of the oldest ...
.
Etymology
''Pueblo'', which means "village" and "people" in Spanish, was a term originating with the Spanish explorers who used it to refer to the people's particular style of dwelling. The Navajo people, who now reside in parts of former Pueblo territory, referred to the ancient people as ', anexonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
meaning "ancestors of our enemies", referring to their competition with the Pueblo peoples. The Navajo now use the term in the sense of referring to "ancient people" or "ancient ones"."Anasazi". ''U*X*L Encyclopedia of Native American Tribes.'' U*X*L. 2008. Retrieved August 14, 2012 from HighBeam Research: http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G2-3048800031.html
Hopi people
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the United ...
use the term ', meaning "ancient people", to describe the Ancestral Puebloans.
Geography
 The Ancestral Puebloans were one of four major prehistoric archaeological traditions recognized in the American Southwest, also known as
The Ancestral Puebloans were one of four major prehistoric archaeological traditions recognized in the American Southwest, also known as Oasisamerica
Oasisamerica is a term that was coined by Paul Kirchhoff (who also coined "Mesoamerica") and published in a 1954 article, and is used by some scholars, primarily Mexican anthropologists, for the broad cultural area defining pre-Columbian sout ...
. The others are the Mogollon, Hohokam, and Patayan
Patayan is a group of prehistoric and historic Native American cultures in parts of modern-day Arizona, west to Lake Cahuilla in California, and in Baja California, from AD 700 to 1550. This included areas along the Gila River, Colorado Riv ...
. In relation to neighboring cultures, the Ancestral Puebloans occupied the northeast quadrant of the area. The Ancestral Puebloan homeland centers on the Colorado Plateau, but extends from central New Mexico on the east to southern Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
on the west.
Areas of southern Nevada, Utah, and Colorado form a loose northern boundary, while the southern edge is defined by the Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
and Little Colorado Rivers in Arizona and the Rio Puerco
The Rio Puerco is a tributary of the Rio Grande in the U.S. state of New Mexico. From its source on the west side of the Nacimiento Mountains, it flows about ,Calculated in Google Earth generally south to join the Rio Grande about south of B ...
and Rio Grande in New Mexico. Structures and other evidence of Ancestral Puebloan culture have been found extending east onto the American Great Plains, in areas near the Cimarron and Pecos Rivers and in the Galisteo Basin
The Galisteo Basin is a surface basin and a closely related groundwater basin in north-central New Mexico. Its primary watercourse is the Galisteo River or Galisteo Creek, a perennial stream, for part of its course, that flows from the ea ...
.

Terrain
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin wo ...
and resources within this large region vary greatly. The plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
regions have high elevations ranging from . Extensive horizontal mesa
A mesa is an isolated, flat-topped elevation, ridge or hill, which is bounded from all sides by steep escarpments and stands distinctly above a surrounding plain. Mesas characteristically consist of flat-lying soft sedimentary rocks capped by a ...
s are capped by sedimentary formations and support woodlands of junipers, pinyon, and ponderosa pines, each favoring different elevations. Wind and water erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
have created steep-walled canyons, and sculpted windows and bridges out of the sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
landscape. In areas where resistant strata (sedimentary rock layers), such as sandstone or limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, overlie more easily eroded strata such as shale, rock overhangs formed. The Ancestral Puebloans favored building under such overhangs for shelters and defensive building sites.
All areas of the Ancestral Puebloan homeland suffered from periods of drought and erosion from wind and water. Summer rains could be unreliable and produced destructive thunderstorms. While the amount of winter snowfall varied greatly, the Ancestral Puebloans depended on the snow for most of their water. Snow melt allowed the germination of seeds, both wild and cultivated, in the spring.
Where sandstone layers overlay shale, snow melt could accumulate and create seeps and springs, which the Ancestral Puebloans used as water sources. Snow also fed the smaller, more predictable tributaries, such as the Chinle, Animas, Jemez, and Taos Rivers. The larger rivers were less directly important to the ancient culture, as smaller streams were more easily diverted or controlled for irrigation.
Cultural characteristics
national parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
, such as Navajo National Monument
Navajo National Monument is a National Monument located within the northwest portion of the Navajo Nation territory in northern Arizona, which was established to preserve three well-preserved cliff dwellings of the Ancestral Puebloan people: Keet ...
, Chaco Culture National Historical Park
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historic Sites (United States), National Historical Park in the Southwestern United States, American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northw ...
, Mesa Verde National Park
Mesa Verde National Park is an American national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan archaeological sites in the United States.
Established ...
, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument
Canyons of the Ancients National Monument is a national monument protecting an archaeologically-significant landscape located in the southwestern region of the U.S. state of Colorado. The monument's are managed by the Bureau of Land Management, ...
, Aztec Ruins National Monument
The Aztec Ruins National Monument in northwestern New Mexico, USA consists of preserved structures constructed by the Pueblo Indians. The national monument lies on the western bank of the Animas River in Aztec, New Mexico, about northeast of ...
, Bandelier National Monument
Bandelier National Monument is a United States National Monument near Los Alamos in Sandoval and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico. The monument preserves the homes and territory of the Ancestral Puebloans of a later era in the Southwest. Most ...
, Hovenweep National Monument
Hovenweep National Monument is located on land in southwestern Colorado and southeastern Utah, between Cortez, Colorado and Blanding, Utah on the Cajon Mesa of the Great Sage Plain. Shallow tributaries run through the wide and deep canyons into t ...
, and Canyon de Chelly National Monument
Canyon de Chelly National Monument ( ) was established on April 1, 1931, as a unit of the National Park Service. Located in northeastern Arizona, it is within the boundaries of the Navajo Nation and lies in the Four Corners region. Reflecting on ...
.
These villages, called ''pueblos
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zu ...
'' by Spanish colonists, were accessible only by rope or through rock climbing. These astonishing building achievements had modest beginnings. The first Ancestral Puebloan homes and villages were based on the pit-house, a common feature in the Basketmaker
Basket weaving (also basketry or basket making) is the process of weaving or sewing pliable materials into three-dimensional artifacts, such as baskets, mats, mesh bags or even furniture. Craftspeople and artists specialized in making baskets ...
periods.
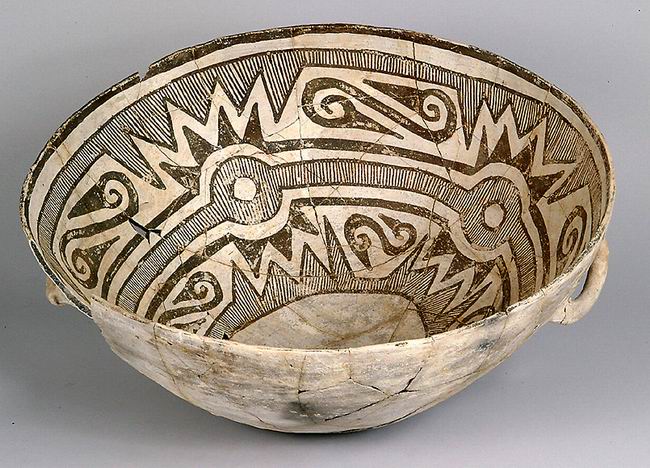
Ancestral Puebloans are also known for their pottery. Local plainware pottery used for cooking or storage was unpainted gray, either smooth or textured. Pottery used for more formal purposes was often more richly adorned. In the northern portion of the Ancestral Pueblo lands, from about 500 to 1300 CE, the pottery styles commonly had black-painted designs on white or light gray backgrounds. Decoration is characterized by fine hatching, and contrasting colors are produced by the use of mineral-based paint on a chalky background.Cordell, p. 98 South of the Anasazi territory, in Mogollon settlements, pottery was more often hand-coiled, scraped, and polished, with red to brown coloring.
Certain tall cylinders were likely ceremonial vessels, while narrow-necked jars, called olla
An olla is a ceramic jar, often unglazed, used for cooking stews or soups, for the storage of water or dry foods, or for other purposes like the irrigation of olive trees. ''Ollas'' have short wide necks and wider bellies, resembling beanpots or ...
s, were often used for liquids. Pottery from the southern regions of Ancestral Pueblo lands has bold, black-line decoration and the use of carbon-based colorants. In northern New Mexico, the local black-on-white pottery tradition, the Rio Grande white wares, continued well after 1300 CE.
Changes in pottery composition, structure, and decoration are signals of social change in the archaeological record. This is particularly true as the peoples of the American Southwest began to leave their historic homes and migrate south. According to archaeologists Patricia Crown and Steadman Upham, the appearance of the bright colors on Salado Polychromes in the 14th century may reflect religious or political alliances on a regional level. Late 14th- and 15th-century pottery from central Arizona, widely traded in the region, has colors and designs which may derive from earlier ware by both Ancestral Pueblo and Mogollon peoples.
The Ancestral Puebloans also excelled at rock art, which included carved petroglyphs
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
and painted pictographs
A pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and g ...
. Ancestral Pueblo peoples painted Barrier Canyon Style pictographs in locations where the images were protected from the sun yet visible to the public. Designs include human-like forms. The so-called "Holy Ghost panel" in the Horseshoe Canyon is considered to be one of the earliest uses of graphical perspective
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection
In three-dimensional geometry, a parallel project ...
where the largest figure appears to take on a three-dimensional representation.
Recent archaeological evidence has established that in at least one great house, Pueblo Bonito, the elite family whose burials associate them with the site practiced matrilineal succession. Room 33 in Pueblo Bonito, the richest burial ever excavated in the Southwest, served as a crypt for one powerful lineage, traced through the female line, for approximately 330 years. While other Ancestral Pueblo burials have not yet been subjected to the same archaeogenomic testing, the survival of matrilineal descent among contemporary Pueblo peoples suggests that this may have been a widespread practice among Ancestral Puebloans.
Architecture
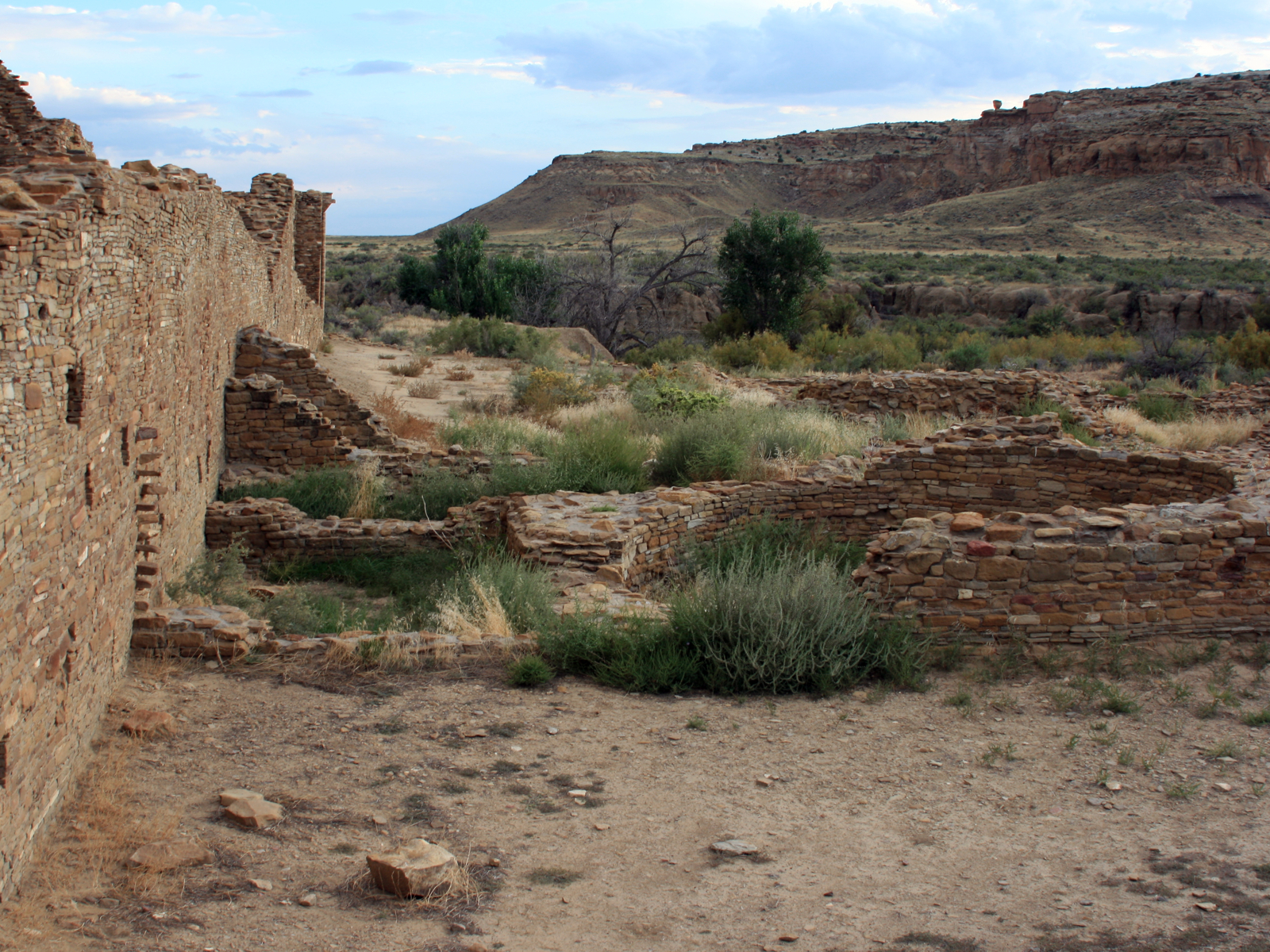
Ancestral Pueblo people in the North American Southwest crafted a unique architecture with planned community spaces. Population centers such asChaco Canyon
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote c ...
(outside Crownpoint, New Mexico
Crownpoint ( nv, ) is a census-designated place (CDP) on the Navajo Nation in McKinley County, New Mexico. The population was 2,500 at the time of the 2010 census. It is located along the Trails of the Ancients Byway, one of the designated New ...
), Mesa Verde
Mesa Verde National Park is an American national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan archaeological sites in the United States.
Established ...
(near Cortez, Colorado
Cortez () is a home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Montezuma County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 8,766 at the 2020 United States Census.
History
In 1886, the town was built ...
), and Bandelier National Monument
Bandelier National Monument is a United States National Monument near Los Alamos in Sandoval and Los Alamos counties, New Mexico. The monument preserves the homes and territory of the Ancestral Puebloans of a later era in the Southwest. Most ...
(near Los Alamos, New Mexico
Los Alamos is an census-designated place in Los Alamos County, New Mexico, United States, that is recognized as the development and creation place of the atomic bomb—the primary objective of the Manhattan Project by Los Alamos National Labo ...
) have brought renown to the Ancestral Pueblo peoples. They consisted of apartment complexes and structures made of stone, adobe mud, and other local material, or were carved into canyon walls. Developed within these cultures, the people also adopted design details from other cultures as far away as contemporary Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.
These buildings were usually multistoried and multipurposed, and surrounded by open plazas and viewshed
A viewshed is the geographical area that is visible from a location. It includes all surrounding points that are in line-of-sight with that location and excludes points that are beyond the horizon or obstructed by terrain and other features (e.g. ...
s. Hundreds to thousands of people lived in these communities. These complexes hosted cultural and civic events and infrastructure that supported a vast outlying region hundreds of miles away linked by transportation roadways.
 Built well before 1492 CE, these towns and villages were located in defensive positions, for example on high, steep mesas such as at Mesa Verde or present-day
Built well before 1492 CE, these towns and villages were located in defensive positions, for example on high, steep mesas such as at Mesa Verde or present-day Acoma Pueblo
Acoma Pueblo (, kjq, Áakʼu) is a Native American pueblo approximately west of Albuquerque, New Mexico, in the United States. Four communities make up the village of Acoma Pueblo: Sky City (Old Acoma), Acomita, Anzac, and McCartys. These co ...
, called the "Sky City", in New Mexico. Before 900 CE and progressing past the 13th century, the population complexes were major cultural centers. In Chaco Canyon, Chacoan developers quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling 15 major complexes. These ranked as the largest buildings in North America until the late 19th century.
Evidence of archaeoastronomy
Archaeoastronomy (also spelled archeoastronomy) is the interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary study of how people in the past "have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cul ...
at Chaco has been proposed, with the Sun Dagger petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, requiring generations of astronomical observations and centuries of skillfully coordinated construction. The Chacoans abandoned the canyon, probably due to climate change beginning with a 50-year drought starting in 1130.
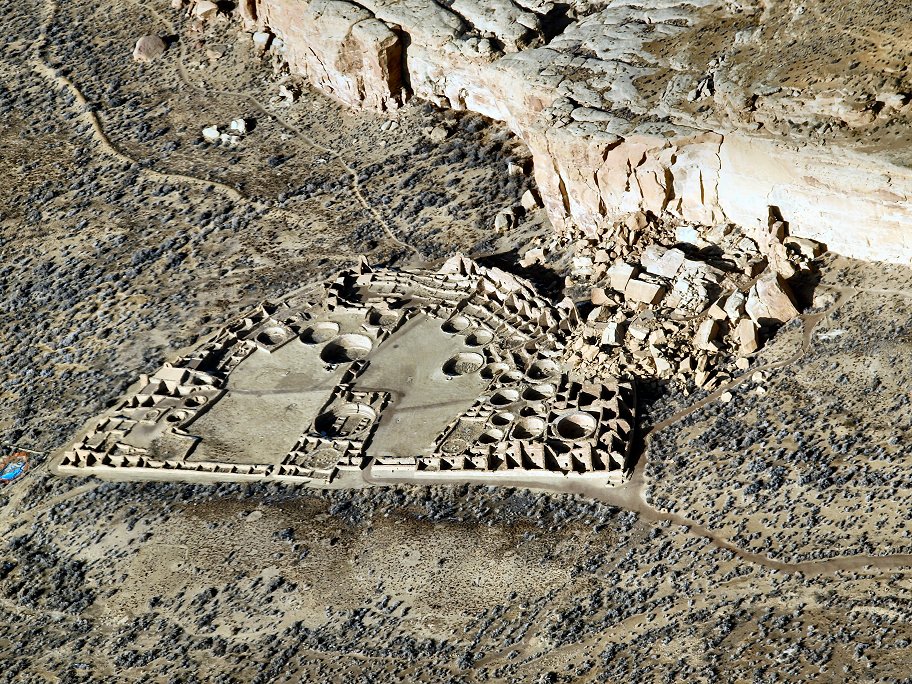
Great Houses
 Immense complexes known as "great houses" embodied worship at Chaco. Archaeologists have found musical instruments, jewelry, ceramics, and ceremonial items, indicating people in the Great Houses were elite, wealthier families. They hosted indoor burials, where gifts were interred with the dead, often including bowls of food and turquoise beads.
Over centuries, architectural forms evolved but the complexes kept some core traits, such as their size. They averaged more than 200 rooms each, and some had 700 rooms. Rooms were very large, with higher ceilings than Ancestral Pueblo buildings of earlier periods. They were well-planned: vast sections were built in a single stage.
Immense complexes known as "great houses" embodied worship at Chaco. Archaeologists have found musical instruments, jewelry, ceramics, and ceremonial items, indicating people in the Great Houses were elite, wealthier families. They hosted indoor burials, where gifts were interred with the dead, often including bowls of food and turquoise beads.
Over centuries, architectural forms evolved but the complexes kept some core traits, such as their size. They averaged more than 200 rooms each, and some had 700 rooms. Rooms were very large, with higher ceilings than Ancestral Pueblo buildings of earlier periods. They were well-planned: vast sections were built in a single stage.
 Most houses faced south. Plazas were almost always surrounded by buildings of sealed-off rooms or high walls. There were often four or five stories, with single-story rooms facing the plaza; room blocks were terraced to allow the tallest sections to compose the pueblo's rear edifice. Rooms were often organized into suites, with front rooms larger than rear, interior, and storage rooms or areas.
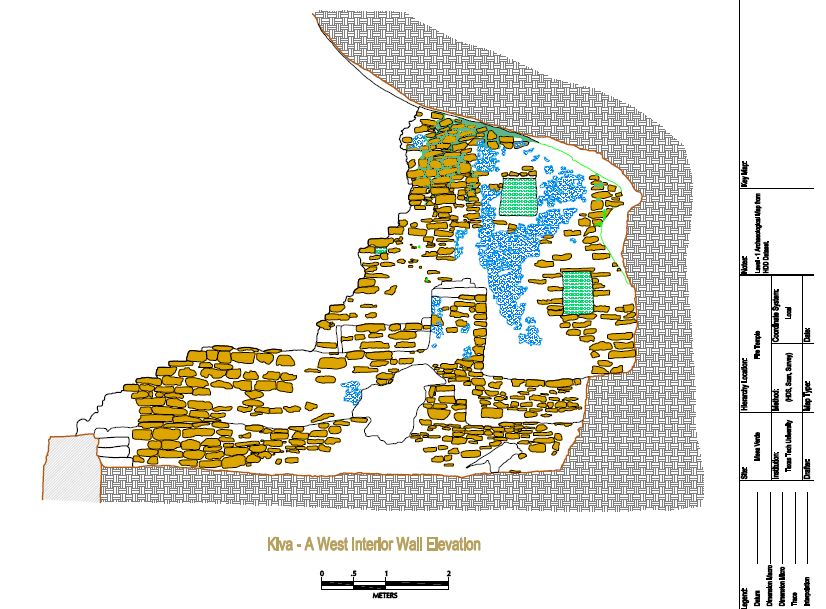
Ceremonial structures known as kivas were built in proportion to the number of rooms in a pueblo. A small kiva was built for roughly every 29 rooms. Nine complexes each had a Great Kiva, up to in diameter. T-shaped doorways and stone lintels marked all Chacoan kivas.
Although simple and compound walls were often used, great houses usually had
Most houses faced south. Plazas were almost always surrounded by buildings of sealed-off rooms or high walls. There were often four or five stories, with single-story rooms facing the plaza; room blocks were terraced to allow the tallest sections to compose the pueblo's rear edifice. Rooms were often organized into suites, with front rooms larger than rear, interior, and storage rooms or areas.
Ceremonial structures known as kivas were built in proportion to the number of rooms in a pueblo. A small kiva was built for roughly every 29 rooms. Nine complexes each had a Great Kiva, up to in diameter. T-shaped doorways and stone lintels marked all Chacoan kivas.
Although simple and compound walls were often used, great houses usually had core-and-veneer
Core-and-veneer, brick and rubble, wall and rubble, ashlar and rubble, and emplekton all refer to a building technique where two parallel walls are constructed and the core between them is filled with rubble or other infill, creating one thick wall ...
walls: rubble
Rubble is broken stone, of irregular size, shape and texture; undressed especially as a filling-in. Rubble naturally found in the soil is known also as 'brash' (compare cornbrash)."Rubble" def. 2., "Brash n. 2. def. 1. ''Oxford English Dictionar ...
filled the gap between parallel load-bearing walls of dressed, flat sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
blocks bound in clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
mortar. Walls were covered in a veneer of small sandstone pieces, which were pressed into a layer of binding mud. These surfacing stones were often arranged in distinctive patterns.
The Chacoan structures together required the wood of 200,000 conifer trees, mostly hauledon footfrom mountain ranges up to away.Kantner, John (2004). "Ancient Puebloan Southwest", pp. 161–166
Ceremonial infrastructure
One of the most notable aspects of Ancestral Puebloan infrastructure is the Chaco Road at Chaco Canyon, a system of roads radiating from many great house sites such as Pueblo Bonito, Chetro Ketl, and Una Vida. They led toward small outlier sites and natural features in the canyon and outside. Through satellite images and ground investigations, archaeologists have found eight main roads that together run for more than 180 miles (300 km), and are more than 30 feet (10 m) wide. These were built by excavating into a smooth, leveled surface in the bedrock or removing vegetation and soil. Large ramps and stairways in the cliff rock connect the roads above the canyon to sites at the bottom. The largest roads, built at the same time as many of the great houses (1000 to 1125 CE), are: the Great North Road, the South Road, theCoyote Canyon Road Coyote Canyon Road is an Ancestral Puebloan road that leads from South Gap in the Chaco Culture National Historical Park to the southwest region of the San Juan Basin. The road is believed to lead to the Grey Ridge community north of Gallup, New Me ...
, the Chacra Face Road, Ahshislepah Road, Mexican Springs Road, the West Road, and the shorter Pintado-Chaco Road. Simple structures like berms and walls are sometimes aligned along the roads. Some tracts of the roads lead to natural features such as springs, lakes, mountain tops, and pinnacles."Chacoan Roads."National Park Service. Retrieved 4 June 2012.
Great North Road
The longest and best-known of these roads is the Great North Road, which originates from different routes close to Pueblo Bonito and Chetro Ketl. These roads converge at Pueblo Alto and from there lead north beyond the canyon limits. Along roadways were only small, isolated structures. Archaeological interpretations of the Chaco road system are divided between an economic purpose and a symbolic, ideological or religious role. The system was discovered in the late 19th century and excavated in the 1970s. By the late 20th century, aerial and satellite photographs helped in the study. Archaeologists suggested that the road's main purpose was to transport local and exotic goods to and from the canyon. The economic purpose of the Chaco road system is shown by the presence of luxury items at Pueblo Bonito and elsewhere in the canyon. Items such asmacaws
Macaws are a group of New World parrots that are long-tailed and often colorful. They are popular in aviculture or as companion parrots, although there are conservation concerns about several species in the wild.
Biology
Of the many differe ...
, turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of year ...
and seashells, which are not part of this environment, and imported vessels distinguished by design, prove that the Chaco traded with distant regions. The widespread use of timber in Chacoan constructions required a large system of easy transportation, as timber was not locally available. Analysis of strontium isotopes shows that much of the timber came from distant mountain ranges.

Cliff communities


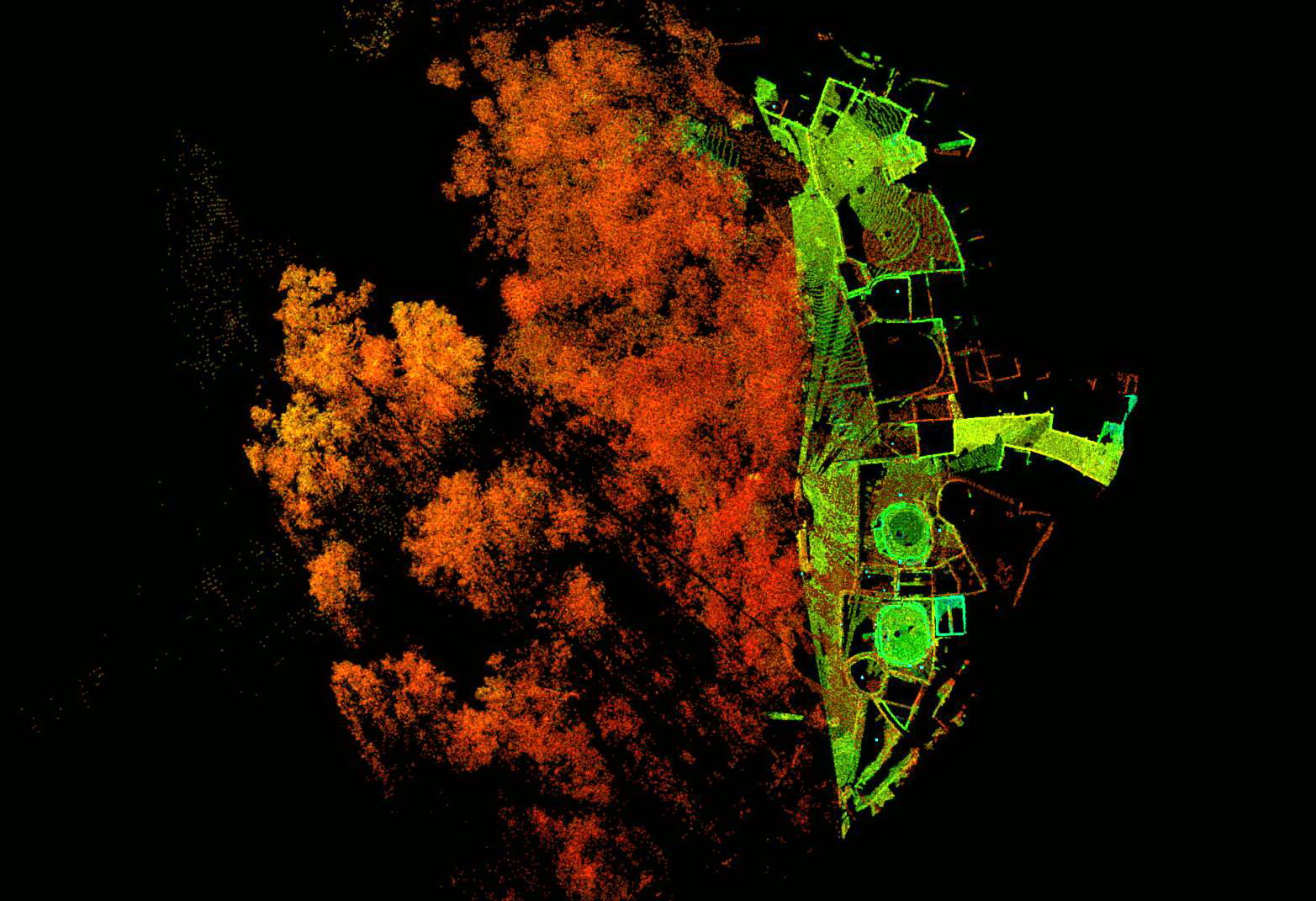
 Throughout the southwest Ancestral Puebloan region, the inhabitants built complexes in shallow
Throughout the southwest Ancestral Puebloan region, the inhabitants built complexes in shallow caves
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
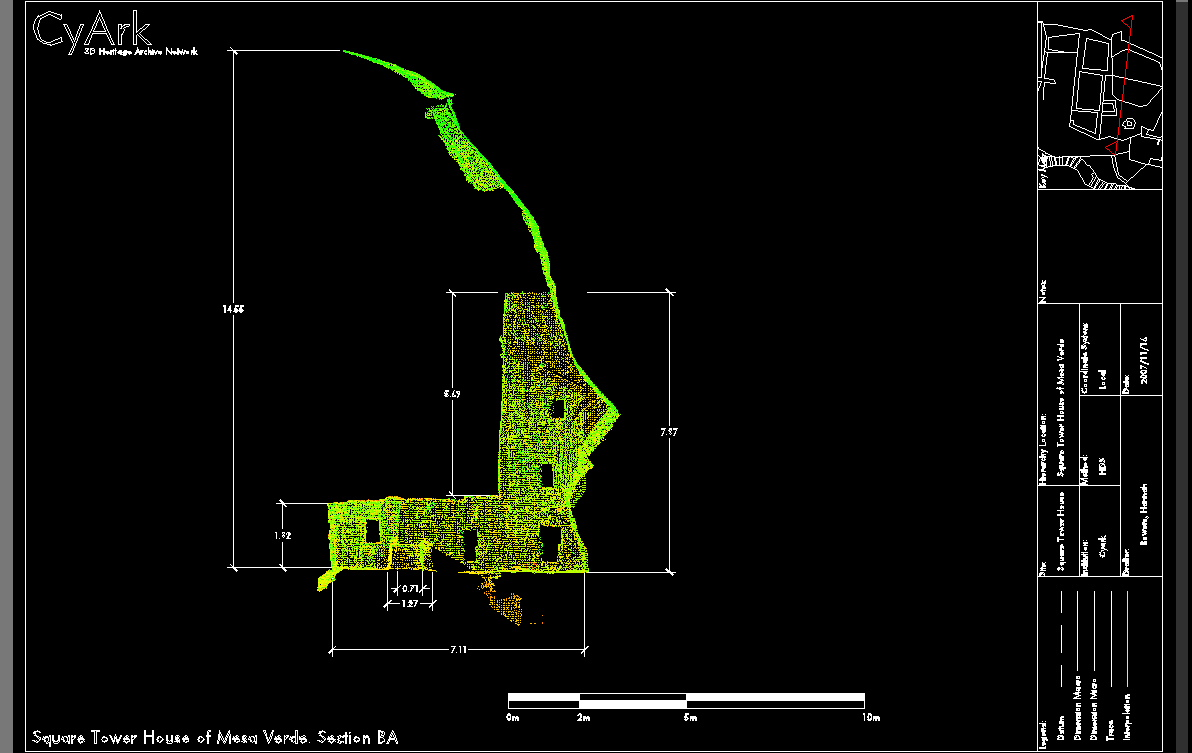
and under rock overhangs in canyon walls. Unlike earlier structures and villages atop mesas, this was a regional 13th-century trend of gathering the growing populations into close, defensible quarters. There were buildings for housing, defense, and storage. These were built mostly of blocks of hard sandstone, held together and plastered with adobe mortar. Constructions had many similarities, but unique forms due to the unique rock topography.
The best-known site is at Mesa Verde, with a large number of well-preserved cliff dwellings. This area included common Pueblo architectural forms, such as kivas, towers, and pit-houses, but the space restrictions of these alcoves resulted in far denser populations. Mug House, a typical cliff dwelling of the period, was home to around 100 people who shared 94 small rooms and eight kivas, built right up against each other and sharing many walls. Builders maximized space use and no area was off-limits.
Not all the people in the region lived in cliff dwellings; many colonized the canyon rims and slopes in multifamily structures that grew to unprecedented size as populations swelled. Decorative motifs for these sandstone/mortar structures, both cliff dwellings and not, included T-shaped windows and doors. This has been taken by some archaeologists, such as Stephen Lekson (1999), as evidence of the continuation of the Chaco Canyon elite system, which had seemingly collapsed a century earlier. Other researchers instead explain these motifs as part a wider Pueblo style or religion.
History
Origins
During the period from 700 to 1130 CE ( Pueblo I and II Eras), the population grew fast due to consistent and regular rainfall which supported agriculture. Studies of skeletal remains show increased fertility rather than decreased mortality. However, this tenfold population increase over a few generations was probably also due to migrations of people from surrounding areas. Innovations such as pottery, food storage, and agriculture enabled this rapid growth. Over several decades, the Ancestral Puebloan culture spread across the landscape. Ancestral Puebloan culture has been divided into three main areas or branches, based on geographical location: *Chaco Canyon
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote c ...
(northwest New Mexico)
* Kayenta
Kayenta ( nv, ) is a U.S. town which is part of the Navajo Nation and is in Navajo County, Arizona, United States. Established November 13, 1986, the Kayenta Township is the only "township" existing under the laws of the Navajo Nation, making it u ...
(northeast Arizona), and
* Northern San Juan (Mesa Verde
Mesa Verde National Park is an American national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan archaeological sites in the United States.
Established ...
and Hovenweep National Monument
Hovenweep National Monument is located on land in southwestern Colorado and southeastern Utah, between Cortez, Colorado and Blanding, Utah on the Cajon Mesa of the Great Sage Plain. Shallow tributaries run through the wide and deep canyons into t ...
) (southwest Colorado and southeastern Utah)
Modern Pueblo oral traditions hold that the Ancestral Puebloans originated from , where they emerged from the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
. For unknown ages, they were led by chiefs and guided by spirits as they completed vast migrations throughout the continent of North America. They settled first in the Ancestral Puebloan areas for a few hundred years before moving to their present locations.
Migration from the homeland
 The Ancestral Puebloans left their established homes in the 12th and 13th centuries. The main reason is unclear. Factors discussed include global or regional climate change, prolonged drought, environmental degradation such as cyclical periods of
The Ancestral Puebloans left their established homes in the 12th and 13th centuries. The main reason is unclear. Factors discussed include global or regional climate change, prolonged drought, environmental degradation such as cyclical periods of topsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs.
Description
Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic matt ...
erosion or deforestation, hostility from new arrivals, religious or cultural change, and influence from Mesoamerican
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Withi ...
cultures. Many of these possibilities are supported by archaeological evidence.
Current scholarly consensus is that Ancestral Puebloans responded to pressure from Numic
Numic is a branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family. It includes seven languages spoken by Native American peoples traditionally living in the Great Basin, Colorado River basin, Snake River basin, and southern Great Plains. The word Numic com ...
-speaking peoples moving onto the Colorado Plateau, as well as climate change that resulted in agricultural failures. The archaeological record indicates that for Ancestral Puebloans to adapt to climatic change by changing residences and locations was not unusual. Early Pueblo I Era sites may have housed up to 600 individuals in a few separate but closely spaced settlement clusters. However, they were generally occupied for 30 years or less. Archaeologist Timothy A. Kohler excavated large Pueblo I sites near Dolores, Colorado
The Town of Dolores is a Statutory Town located in Montezuma County, Colorado, United States. The town population was 885 at the 2020 United States Census.
Description
Dolores (Spanish for "sorrows" and named for the river on which it is loca ...
, and discovered that they were established during periods of above-average rainfall. This allowed crops to be grown without requiring irrigation. At the same time, nearby areas that suffered significantly drier patterns were abandoned.
Ancestral Puebloans attained a cultural "Golden Age" between about 900 and 1150. During this time, generally classed as Pueblo II Era, the climate was relatively warm and rainfall mostly adequate. Communities grew larger and were inhabited for longer. Highly specific local traditions in architecture and pottery emerged, and trade over long distances appears to have been common. Domesticated turkey
The domestic turkey (Meleagris gallopavo domesticus) is a large fowl, one of the two species in the genus '' Meleagris'' and the same species as the wild turkey. Although turkey domestication was thought to have occurred in central Mesoamerica a ...
s appeared.
After around 1130, North America had significant climatic change in the form of a 300-year period of aridity called the Great Drought. This also led to the collapse of the Tiwanaku
Tiwanaku ( es, Tiahuanaco or ) is a Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia near Lake Titicaca, about 70 kilometers from La Paz, and it is one of the largest sites in South America. Surface remains currently cover around 4 square kilo ...
civilization around Lake Titicaca
Lake Titicaca (; es, Lago Titicaca ; qu, Titiqaqa Qucha) is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. By volume of water and by surface area, i ...
in present-day Bolivia. The contemporary Mississippian culture also collapsed during this period. Confirming evidence dated between 1150 and 1350 has been found in excavations of the western regions of the Mississippi Valley
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
, which show long-lasting patterns of warmer, wetter winters and cooler, drier summers.
 In this later period, the Pueblo II became more self-contained, decreasing trade and interaction with more distant communities. Southwest farmers developed irrigation techniques appropriate to seasonal rainfall, including soil and water control features such as check dams and terraces. The population of the region continued to be mobile, abandoning settlements and fields under adverse conditions. There was also a drop in
In this later period, the Pueblo II became more self-contained, decreasing trade and interaction with more distant communities. Southwest farmers developed irrigation techniques appropriate to seasonal rainfall, including soil and water control features such as check dams and terraces. The population of the region continued to be mobile, abandoning settlements and fields under adverse conditions. There was also a drop in water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
due to a different cycle unrelated to rainfall. This forced the abandonment of settlements in the more arid or overfarmed locations.
Evidence suggests a profound change in religion in this period. Chacoan and other structures constructed originally along astronomical alignments, and thought to have served important ceremonial purposes to the culture, were systematically dismantled. Doorways were sealed with rock and mortar. Kiva walls show marks from great fires set within them, which probably required removal of the massive roof – a task which would require significant effort. Habitations were abandoned, and tribes divided and resettled far.
This evidence suggests that the religious structures were abandoned deliberately over time. Pueblo oral history holds that the ancestors had achieved great spiritual power and control over natural forces. They used their power in ways that caused nature to change and caused changes that were never meant to occur. Possibly, the dismantling of their religious structures was an effort to symbolically undo the changes they believed they caused due to their abuse of their spiritual power, and thus make amends with nature.
Most modern Pueblo peoples (whether Keresan
Keres (), also Keresan (), is a Native American language, spoken by the Keres Pueblo people in New Mexico. Depending on the analysis, Keres is considered a small language family or a language isolate with several dialects. The varieties of eac ...
s, Hopi, or Tanoan
Tanoan , also Kiowa–Tanoan or Tanoan–Kiowa, is a family of languages spoken by indigenous peoples in present-day New Mexico, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Most of the languages – Tiwa (Taos, Picuris, Southern Tiwa), Tewa, and Towa – ...
s) assert the Ancestral Puebloans did not "vanish", as is commonly portrayed. They say that the people migrated to areas in the southwest with more favorable rainfall and dependable streams. They merged into the various Pueblo peoples whose descendants still live in Arizona and New Mexico. This perspective was also presented by early 20th-century anthropologists, including Frank Hamilton Cushing
Frank Hamilton Cushing (July 22, 1857 in North East Township, Erie County, Pennsylvania – April 10, 1900 in Washington, D.C.) was an American anthropologist and ethnologist. He made pioneering studies of the Zuni Indians of New Mexico by enter ...
, J. Walter Fewkes
Jesse Walter Fewkes (November 14, 1850 – May 31, 1930) was an American anthropologist, archaeologist, writer, and naturalist.
Biography
Fewkes was born in Newton, Massachusetts on November 14, 1850, and initially trained as a zoologist at ...
, and Alfred V. Kidder.
Many modern Pueblo tribes trace their lineage from specific settlements. For example, the San Ildefonso Pueblo
San Ildefonso Pueblo (Tewa: Pʼohwhogeh Ówîngeh ’òhxʷógè ʔówîŋgè"where the water cuts through"
) is a census-designated place (CDP) in Santa Fe County, New Mexico, United States, and a federally recognized tribe, established c. 13 ...
people believe that their ancestors lived in both the Mesa Verde and the Bandelier areas. Evidence also suggests that a profound change took place in the Ancestral Pueblo area and areas inhabited by their cultural neighbors, the Mogollon. Historian James W. Loewen agrees with this oral tradition in his book, ''Lies Across America: What Our Historic Markers and Monuments Get Wrong'' (1999). No academic consensus exists with the professional archeological and anthropological community on this issue.
Warfare
 Environmental stress may have caused changes in social structure, leading to conflict and warfare. Near
Environmental stress may have caused changes in social structure, leading to conflict and warfare. Near Kayenta, Arizona
Kayenta ( nv, ) is a U.S. town which is part of the Navajo Nation and is in Navajo County, Arizona, United States. Established November 13, 1986, the Kayenta Township is the only "township" existing under the laws of the Navajo Nation, making it ...
, Jonathan Haas of the Field Museum in Chicago has been studying a group of Ancestral Puebloan villages that relocated from the canyons to the high mesa tops during the late 13th century. Haas believes that the reason to move so far from water and arable land was a defense against enemies. He asserts that isolated communities relied on raiding for food and supplies, and that internal conflict and warfare became common in the 13th century.
This conflict may have been aggravated by the influx of less settled peoples, Numic-speakers such as the Utes, Shoshones, and Paiute people
Paiute (; also Piute) refers to three non-contiguous groups of indigenous peoples of the Great Basin. Although their languages are related within the Numic group of Uto-Aztecan languages, these three groups do not form a single set. The term "Paiu ...
, who may have originated in what is today California, and the arrival of the Athabaskan-speaking Diné who migrated from the north during this time and subsequently became the Navajo and Apache tribes most notably. Others suggest that more developed villages, such as that at Chaco Canyon, exhausted their environments, resulting in widespread deforestation and eventually the fall of their civilization through warfare over depleted resources.
A 1997 excavation at Cowboy Wash near Dolores, Colorado
The Town of Dolores is a Statutory Town located in Montezuma County, Colorado, United States. The town population was 885 at the 2020 United States Census.
Description
Dolores (Spanish for "sorrows" and named for the river on which it is loca ...
found remains of at least 24 human skeletons that showed evidence of violence and dismemberment, with strong indications of cannibalism. This modest community appears to have been abandoned during the same time period. Other excavations within the Ancestral Puebloan cultural area have produced varying numbers of unburied, and in some cases dismembered, bodies. In a 2010 paper, Potter and Chuipka argued that evidence at Sacred Ridge site, near Durango, Colorado, is best interpreted as warfare related to competition and ethnic cleansing.
This evidence of warfare, conflict, and cannibalism is hotly debated by some scholars and interest groups. Suggested alternatives include: a community suffering the pressure of starvation or extreme social stress, dismemberment and cannibalism as religious ritual or in response to religious conflict, the influx of outsiders seeking to drive out a settled agricultural community via calculated atrocity, or an invasion of a settled region by nomadic raiders who practiced cannibalism.
Anasazi as a cultural label
The term "Anasazi" was established in archaeological terminology through the Pecos Classification system in 1927. It had been adopted from the Navajo. Archaeologist Linda Cordell discussed the word's etymology and use: Many contemporary Pueblo peoples object to the use of the term Anasazi; controversy exists among them on a native alternative. Some modern descendants of this culture often choose to use the term "Ancestral Pueblo" peoples. Contemporary Hopi use the word in preference to Anasazi.Cultural distinctions
 Archaeological cultural units such as Ancestral Puebloan, Hohokam, Patayan, or Mogollon are used by archaeologists to define material culture similarities and differences that may identify prehistoric sociocultural units, equivalent to modern societies or peoples. The names and divisions are classification devices based on theoretical perspectives, analytical methods, and data available at the time of analysis and publication. They are subject to change, not only on the basis of new information and discoveries, but also as attitudes and perspectives change within the scientific community. It should not be assumed that an archaeological division or culture unit corresponds to a particular language group or to a socio-political entity such as a tribe.
Current terms and conventions have significant limitations:
* Archaeological research focuses on items left behind during people's activities: fragments of pottery vessels, garbage, human remains, stone tools or evidence left from the construction of dwellings. However, many other aspects of the culture of prehistoric peoples are not tangible. Their beliefs and behavior are difficult to decipher from physical materials, and their languages remain unknown as they had no known
Archaeological cultural units such as Ancestral Puebloan, Hohokam, Patayan, or Mogollon are used by archaeologists to define material culture similarities and differences that may identify prehistoric sociocultural units, equivalent to modern societies or peoples. The names and divisions are classification devices based on theoretical perspectives, analytical methods, and data available at the time of analysis and publication. They are subject to change, not only on the basis of new information and discoveries, but also as attitudes and perspectives change within the scientific community. It should not be assumed that an archaeological division or culture unit corresponds to a particular language group or to a socio-political entity such as a tribe.
Current terms and conventions have significant limitations:
* Archaeological research focuses on items left behind during people's activities: fragments of pottery vessels, garbage, human remains, stone tools or evidence left from the construction of dwellings. However, many other aspects of the culture of prehistoric peoples are not tangible. Their beliefs and behavior are difficult to decipher from physical materials, and their languages remain unknown as they had no known writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable fo ...
.
* Cultural divisions are tools of the modern scientist, and so should not be considered similar to divisions or relationships that the ancient residents may have recognized. Modern cultures in this region, many of whom claim some of these ancient people as ancestors, express a striking range of diversity in lifestyles, social organization, language, and religious beliefs. This suggests the ancient people were also more diverse than their material remains may suggest.
* The modern term "style" has a bearing on how material items such as pottery or architecture can be interpreted. Within a people, different means to accomplish the same goal can be adopted by subsets of the larger group. For example, in modern Western cultures, there are alternative styles of clothing that characterize older and younger generations. Some cultural differences may be based on linear traditions, on teaching from one generation or "school" to another. Other varieties in style may have distinguished between arbitrary groups within a culture, perhaps defining status
Status (Latin plural: ''statūs''), is a state, condition, or situation, and may refer to:
* Status (law)
** City status
** Legal status, in law
** Political status, in international law
** Small entity status, in patent law
** Status confere ...
, gender, clan or guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
affiliation, religious belief or cultural alliances. Variations may also simply reflect the different resources available in a given time or area.
Defining cultural groups, such as the Ancestral Puebloans, tends to create an image of territories separated by clear-cut boundaries, like border boundaries separating modern states. These did not exist. Prehistoric people traded, worshipped, collaborated, and fought most often with other nearby groups. Cultural differences should therefore be understood as clinal: "increasing gradually as the distance separating groups also increases".Plog, p. 72.
Departures from the expected pattern may occur because of unidentified social or political situations or because of geographic barriers. In the Southwest, mountain ranges, rivers, and most obviously, the Grand Canyon, can be significant barriers for human communities, likely reducing the frequency of contact with other groups. Current opinion holds that the closer cultural similarity between the Mogollon and Ancestral Puebloans, and their greater differences from the Hohokam and Patayan, is due to both the geography and the variety of climate zones in the Southwest.
See also
*Agriculture in the prehistoric Southwest
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
*Anasazi flute
The Anasazi flute is the name of a prehistoric end-blown flute replicated today from findings at a massive cave in Prayer Rock Valley in Arizona, United States by an archaeological expedition led by Earl H. Morris in 1931. The team excavated 15 c ...
*'' Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed''
*Cynthia Irwin-Williams
Cynthia Irwin-Williams (April 14, 1936 – June 15, 1990) was an archaeologist of the prehistoric American Southwest. She received a B.A. in Anthropology from Radcliffe College in 1957; the next year she received a M.A. in the same field. In 196 ...
* Dinétah
* Gallina
*Indian Mesa
Indian Mesa is a flat top hill whose sides are steep cliffs. Indian Mesa is located within the Lake Pleasant Regional Park grounds by the shores of Lake Pleasant and Agua Fria River in the Bradshaw Mountain Range. Lake Pleasant Regional Park is ...
* Kokopelli
*Matrilocal residence
In social anthropology, matrilocal residence or matrilocality (also uxorilocal residence or uxorilocality) is the societal system in which a married couple resides with or near the wife's parents. Thus, the female offspring of a mother remain ...
*Poqanghoya
The Hopi maintain a complex religious and mythological tradition stretching back over centuries. However, it is difficult to definitively state what all Hopis as a group believe. Like the oral traditions of many other societies, Hopi mythology is ...
*Prehistoric Southwestern cultural divisions
Southwestern archaeology is a branch of archaeology concerned with the Southwestern United States and Northwestern Mexico. This region was first occupied by hunter-gatherers, and thousands of years later by advanced civilizations, such as the Ances ...
* Virgin Anasazi
*Water glyphs
Water glyphs are a recurring type of petroglyph found across the American southwest, but primarily in southern Utah, northern Arizona, and Nevada. The symbols are thought to be of ancient origin (perhaps created by the Ancestral Puebloans) and h ...
* Zuni people
References
Notes Bibliography *Childs, Craig ''House of Rain: Tracking a Vanished Civilization Across the American Southwest''. Little, Brown and Company, February 22, 2007. . *Cordell, Linda S. ''Ancient Pueblo Peoples''. St. Remy Press and Smithsonian Institution, 1994. . * * Fagan, Brian M. "Ancient North America: Tha Archaeology of a Continent (part five)."Thames and Hudson
Thames & Hudson (sometimes T&H for brevity) is a publisher of illustrated books in all visually creative categories: art, architecture, design, photography, fashion, film, and the performing arts. It also publishes books on archaeology, history, ...
, Inc., New York City, 1991. .
*
*
* Jennings, Jesse D. ''Glen Canyon: An Archaeological Summary''. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, Utah, 1966, republished 1998. .
* LeBlanc, Steven A. "Prehistoric Warfare in the American Southwest." 1999, University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, Utah. .
* Plog, Stephen. ''Ancient Peoples of the American Southwest''. Thames and Hudson, London, England, 1997. .
*Roberts, David D. ''In Search of the Old Ones: Exploring the Anasazi World of the Southwest''. Simon & Schuster Adult Publishing Group, 1996. .
*
*
*Great Drought. (2008). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 30, 2008, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/243212/Great-Drought
*
*
External links
Bandelier National Monument Virtual Museum Exhibit and Lesson Plans
from
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propert ...
Chaco Culture National Historic Park Virtual Museum Exhibit
from
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propert ...
People of the Colorado Plateau
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient Pueblo Peoples 01 * Oasisamerica cultures Pre-Columbian cultures Archaeological cultures of North America Native American history of Arizona Native American history of Nevada Native American history of New Mexico Native American history of Utah Post-Archaic period in North America Prehistoric cultures in Colorado Southwest tribes 12th-century BC establishments 13th-century disestablishments in North America Puebloan architecture Puebloan buildings and structures