Amr Bin Al'aas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
( ar, عمرو بن العاص السهمي; 664) was the Arab commander who led the
 The Muslims pursued the Byzantine army northward and besieged them at Pella, Jordan, Pella for four months. Amr may have retained overall command of the Muslim armies until this point, though other accounts assign command to Khalid or Abu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah. In any case, the Muslims landed a heavy blow against the Byzantines in the ensuing Battle of Fahl in December 634 or January 635. Afterward, Amr and Shurahbil may have been sent to besiege Beisan, which capitulated after minor resistance. The Muslims proceeded to besiege Damascus, where the remnants of the Byzantine army from the battles of Ajnadayn and Fahl had gathered. Amr was positioned at the Bab Tuma gate, the Muslim commanders having each been assigned to block one of the city's entrances. By August–September 635, Damascus surrendered to the Muslims. Amr acquired several residences within the city.
In response to the series of defeats, the Byzantine emperor Heraclius () led a large army in person to confront the Muslims; its rout at the Battle of Yarmouk, in which Amr played a key role by confining the Byzantines between the banks of the Yarmouk River and the Yarmouk's ravine, in August–September 636, paved the way for the rest of Syria's conquest by the Muslims. Following Yarmouk, the Muslims attempted to capture Jerusalem, where Amr had previously sent an advance force. Abu Ubayda led the Siege of Jerusalem (636–637), siege of Jerusalem, in which Amr participated, but the city only surrendered after Caliph Umar arrived in person to conclude a treaty with its defenders. Amr was one of the witnesses of the Treaty of Umar. From Jerusalem, Amr proceeded to besiege and capture the city of Gaza.
The Muslims pursued the Byzantine army northward and besieged them at Pella, Jordan, Pella for four months. Amr may have retained overall command of the Muslim armies until this point, though other accounts assign command to Khalid or Abu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah. In any case, the Muslims landed a heavy blow against the Byzantines in the ensuing Battle of Fahl in December 634 or January 635. Afterward, Amr and Shurahbil may have been sent to besiege Beisan, which capitulated after minor resistance. The Muslims proceeded to besiege Damascus, where the remnants of the Byzantine army from the battles of Ajnadayn and Fahl had gathered. Amr was positioned at the Bab Tuma gate, the Muslim commanders having each been assigned to block one of the city's entrances. By August–September 635, Damascus surrendered to the Muslims. Amr acquired several residences within the city.
In response to the series of defeats, the Byzantine emperor Heraclius () led a large army in person to confront the Muslims; its rout at the Battle of Yarmouk, in which Amr played a key role by confining the Byzantines between the banks of the Yarmouk River and the Yarmouk's ravine, in August–September 636, paved the way for the rest of Syria's conquest by the Muslims. Following Yarmouk, the Muslims attempted to capture Jerusalem, where Amr had previously sent an advance force. Abu Ubayda led the Siege of Jerusalem (636–637), siege of Jerusalem, in which Amr participated, but the city only surrendered after Caliph Umar arrived in person to conclude a treaty with its defenders. Amr was one of the witnesses of the Treaty of Umar. From Jerusalem, Amr proceeded to besiege and capture the city of Gaza.
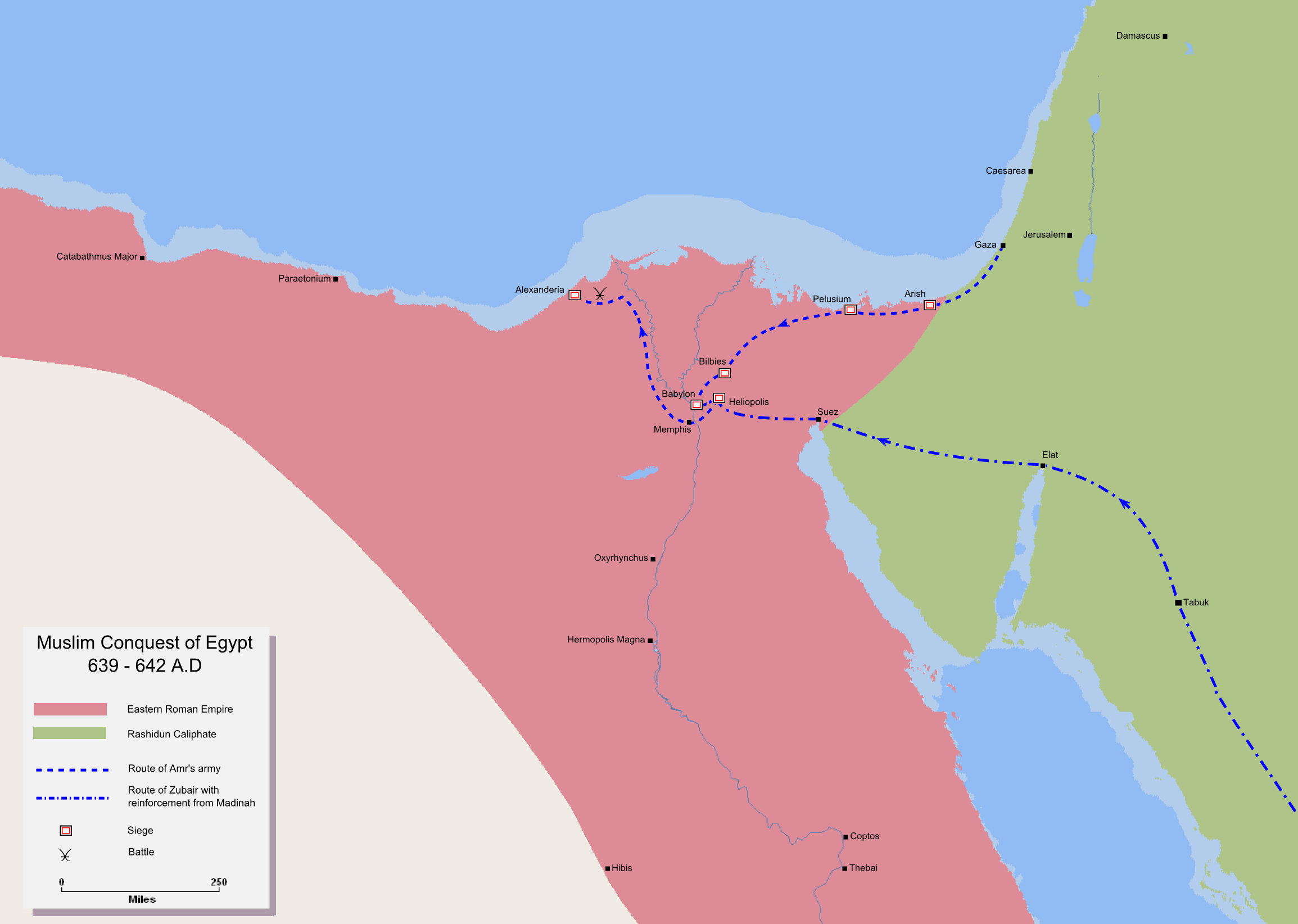 From his base in southern Palestine, Amr launched the conquest of Egypt (Roman province)#Later Roman Egypt (4th–6th centuries), Byzantine Egypt. He had established trading interests there before his conversion to Islam, making him aware of its importance in international trade. The traditional Muslim sources generally hold that Amr undertook the campaign with Caliph Umar's reluctant approval, though a number of accounts hold that he entered the region without Umar's authorization. At the head of 4,000 cavalries and with no siege engines, Amr arrived at the frontier town of al-Arish along the northern Sinai coastline on 12 December 639. He captured the strategic Mediterranean port city of Pelusium (al-Farama) following a month-long siege and moved against Bilbeis, which also fell after a month-long siege.
Amr halted his campaign before the fortified Byzantine stronghold of Babylon Fortress, Babylon, at the head of the Nile Delta, and requested reinforcements from Umar. The latter dispatched al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam, a leading Qurayshite companion of Muhammad, with a 4,000-strong force, which joined Amr's camp in June 640. Amr retained the supreme command of Arab forces in Egypt. In the following month, his army decisively defeated the Byzantines at the Battle of Heliopolis. He captured Memphis, Egypt, Memphis soon after and Siege of Babylon Fortress, besieged Babylon. During the siege, Amr entered truce negotiations with the Alexandria-based Byzantine governor
From his base in southern Palestine, Amr launched the conquest of Egypt (Roman province)#Later Roman Egypt (4th–6th centuries), Byzantine Egypt. He had established trading interests there before his conversion to Islam, making him aware of its importance in international trade. The traditional Muslim sources generally hold that Amr undertook the campaign with Caliph Umar's reluctant approval, though a number of accounts hold that he entered the region without Umar's authorization. At the head of 4,000 cavalries and with no siege engines, Amr arrived at the frontier town of al-Arish along the northern Sinai coastline on 12 December 639. He captured the strategic Mediterranean port city of Pelusium (al-Farama) following a month-long siege and moved against Bilbeis, which also fell after a month-long siege.
Amr halted his campaign before the fortified Byzantine stronghold of Babylon Fortress, Babylon, at the head of the Nile Delta, and requested reinforcements from Umar. The latter dispatched al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam, a leading Qurayshite companion of Muhammad, with a 4,000-strong force, which joined Amr's camp in June 640. Amr retained the supreme command of Arab forces in Egypt. In the following month, his army decisively defeated the Byzantines at the Battle of Heliopolis. He captured Memphis, Egypt, Memphis soon after and Siege of Babylon Fortress, besieged Babylon. During the siege, Amr entered truce negotiations with the Alexandria-based Byzantine governor  In late 641, Amr Siege of Alexandria (641), besieged Alexandria. It fell virtually without resistance after Cyrus, who had since been restored to office, and Amr finalized a treaty in Babylon guaranteeing the security of Egypt's inhabitants and imposing a
In late 641, Amr Siege of Alexandria (641), besieged Alexandria. It fell virtually without resistance after Cyrus, who had since been restored to office, and Amr finalized a treaty in Babylon guaranteeing the security of Egypt's inhabitants and imposing a
 Amr had the original tents of Fustat replaced with mud brick and baked brick dwellings. Documents found in Hermopolis (el-Ashmunein) dating from the 640s confirm official orders to forward building materials to Babylon to construct the new city. The city was organized into allotments over an area stretching along the Nile and inland to the east. The allotments were distributed among the components of Amr's army, with priority given to the Quraysh, the Ansar and Amr's personal guard, the 'Ahl al-Rāya' (People of the Banner), which included several Bali tribesmen as a result of their kinship and marital ties to Amr. An opposing theory holds that Amr did not assign the plots; rather, the tribes staked their own claims and Amr established a commission to resolve the ensuing land disputes. At the center of the new capital Amr built a congregational mosque, later known as the Mosque of Amr ibn al-As; the original structure was frequently redesigned and expanded between its foundation and its final form in 827. Amr had his own dwelling built immediately east of the mosque and it most likely served as his government headquarters.
In the northwestern part of Alexandria, Amr built a hilltop congregational mosque, later called after him, before the Byzantine occupation of 645/46, after which he built a second called the Mosque of Mercy; neither mosque has been presently identified. Adjacent to the congregational mosque, Amr took personal ownership of a fort, which he later donated for government use. This part of the city became the administrative and social core of Arab settlement in Alexandria. Accounts vary as to the number of troops Amr garrisoned in the city, ranging from 1,000 soldiers from the Azd and Banu Fahm tribes to a quarter of the army which was replaced on a rotational basis every six months.
As per the 641 treaty with Cyrus, Amr imposed a poll tax of two gold dinars on non-Muslim adult males. He imposed other measures, sanctioned by Umar, that entailed the inhabitants' regular provision of wheat, honey, oil and vinegar as a subsistence allowance for the Arab troops. He had these goods stored in a distribution warehouse called ''dār al-rizq''. After taking a census of the Muslims, he further ordered that each Muslim be annually supplied by the inhabitants a highly embroidered wool robe (Egyptian robes were prized by the Arabs), a burnous, a turban, a sirwal (trousers) and shoes. In a Greek papyrus dated to 8 January 643 and containing Amr's seal (a fighting bull), Amr (transliterated as "Ambros") requests fodder for his army's animals and bread for his soldiers from an Egyptian village. According to the historian Martin Hinds, there is "no evidence" that Amr "did anything to streamline the cumbersome fiscal system taken over from the Byzantines; rather, the upheavals of conquest can only have made the system more open to abuse than ever".
After entering Alexandria, Amr invited the Pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic patriarch
Amr had the original tents of Fustat replaced with mud brick and baked brick dwellings. Documents found in Hermopolis (el-Ashmunein) dating from the 640s confirm official orders to forward building materials to Babylon to construct the new city. The city was organized into allotments over an area stretching along the Nile and inland to the east. The allotments were distributed among the components of Amr's army, with priority given to the Quraysh, the Ansar and Amr's personal guard, the 'Ahl al-Rāya' (People of the Banner), which included several Bali tribesmen as a result of their kinship and marital ties to Amr. An opposing theory holds that Amr did not assign the plots; rather, the tribes staked their own claims and Amr established a commission to resolve the ensuing land disputes. At the center of the new capital Amr built a congregational mosque, later known as the Mosque of Amr ibn al-As; the original structure was frequently redesigned and expanded between its foundation and its final form in 827. Amr had his own dwelling built immediately east of the mosque and it most likely served as his government headquarters.
In the northwestern part of Alexandria, Amr built a hilltop congregational mosque, later called after him, before the Byzantine occupation of 645/46, after which he built a second called the Mosque of Mercy; neither mosque has been presently identified. Adjacent to the congregational mosque, Amr took personal ownership of a fort, which he later donated for government use. This part of the city became the administrative and social core of Arab settlement in Alexandria. Accounts vary as to the number of troops Amr garrisoned in the city, ranging from 1,000 soldiers from the Azd and Banu Fahm tribes to a quarter of the army which was replaced on a rotational basis every six months.
As per the 641 treaty with Cyrus, Amr imposed a poll tax of two gold dinars on non-Muslim adult males. He imposed other measures, sanctioned by Umar, that entailed the inhabitants' regular provision of wheat, honey, oil and vinegar as a subsistence allowance for the Arab troops. He had these goods stored in a distribution warehouse called ''dār al-rizq''. After taking a census of the Muslims, he further ordered that each Muslim be annually supplied by the inhabitants a highly embroidered wool robe (Egyptian robes were prized by the Arabs), a burnous, a turban, a sirwal (trousers) and shoes. In a Greek papyrus dated to 8 January 643 and containing Amr's seal (a fighting bull), Amr (transliterated as "Ambros") requests fodder for his army's animals and bread for his soldiers from an Egyptian village. According to the historian Martin Hinds, there is "no evidence" that Amr "did anything to streamline the cumbersome fiscal system taken over from the Byzantines; rather, the upheavals of conquest can only have made the system more open to abuse than ever".
After entering Alexandria, Amr invited the Pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic patriarch
 Amr died of natural causes over the age of 90. Accounts vary regarding the date of his death, though the most credible versions place it in 43 Hijri year, AH (663–664 CE). He was buried at the foot of the Mokattam hills to the east of Fustat. Due to the early Muslims' reticence to mark the graves of their dead, Amr's burial place has not been identified. In a testament to the personal wealth that he accrued, at the time of his death he left seventy sacks of gold dinars. His sons Abd Allah and Muhammad refused inheritance of the sums, which were then confiscated by Mu'awiya. Abd Allah succeeded his father as governor for a few weeks until Mu'awiya replaced him with his own brother Utba.
The traditional Egypt-based Arabic and Coptic language, Coptic sources regard Amr positively. The major source of information about the Muslim conquest of Egypt and the province's early Arab military generations, Ibn Abd al-Hakam (d. 871), commends Amr for his leadership of the Egyptian conquest and as the upholder of the interests of Egypt's troops and their families against the central authorities in Medina and later Damascus. The Egyptian Arab tradition holds that Amr was personally praised by Muhammad and was a man of wisdom and piety on his deathbed. The nearly contemporary Coptic historian John of Nikiu (), who was generally critical of Arab rule, said of Amr that he "had no mercy on the Egyptians, and did not observe the covenant they had made with him", but also says of him that: "He exacted the taxes which had been determined upon but he took none of the property of the churches, and he committed no act of spoliation or plunder, and he preserved them throughout all his days." In the words of Kennedy, "Of his [Amr's] competence as a military commander and politician there can be no doubt—the results speak for themselves—but he also has a reputation for straight dealing and justice." Amr's roughly two-year conquest of Egypt was the quickest in the history of the
Amr died of natural causes over the age of 90. Accounts vary regarding the date of his death, though the most credible versions place it in 43 Hijri year, AH (663–664 CE). He was buried at the foot of the Mokattam hills to the east of Fustat. Due to the early Muslims' reticence to mark the graves of their dead, Amr's burial place has not been identified. In a testament to the personal wealth that he accrued, at the time of his death he left seventy sacks of gold dinars. His sons Abd Allah and Muhammad refused inheritance of the sums, which were then confiscated by Mu'awiya. Abd Allah succeeded his father as governor for a few weeks until Mu'awiya replaced him with his own brother Utba.
The traditional Egypt-based Arabic and Coptic language, Coptic sources regard Amr positively. The major source of information about the Muslim conquest of Egypt and the province's early Arab military generations, Ibn Abd al-Hakam (d. 871), commends Amr for his leadership of the Egyptian conquest and as the upholder of the interests of Egypt's troops and their families against the central authorities in Medina and later Damascus. The Egyptian Arab tradition holds that Amr was personally praised by Muhammad and was a man of wisdom and piety on his deathbed. The nearly contemporary Coptic historian John of Nikiu (), who was generally critical of Arab rule, said of Amr that he "had no mercy on the Egyptians, and did not observe the covenant they had made with him", but also says of him that: "He exacted the taxes which had been determined upon but he took none of the property of the churches, and he committed no act of spoliation or plunder, and he preserved them throughout all his days." In the words of Kennedy, "Of his [Amr's] competence as a military commander and politician there can be no doubt—the results speak for themselves—but he also has a reputation for straight dealing and justice." Amr's roughly two-year conquest of Egypt was the quickest in the history of the
Muslim conquest of Egypt
The Muslim conquest of Egypt, led by the army of 'Amr ibn al-'As, took place between 639 and 646 AD and was overseen by the Rashidun Caliphate. It ended the seven-century-long period of Roman Egypt, Roman reign over Egypt that began in 30 BC. ...
and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Quraysh
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qur ...
ite, Amr embraced Islam in and was assigned important roles in the nascent Muslim community by the Islamic prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, di ...
. The first caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
() appointed Amr as a commander of the conquest of Syria. He conquered most of Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, to which he was appointed governor, and led the Arabs to decisive victories over the Byzantines at the battles of Ajnadayn and Yarmouk in 634 and 636.
Amr launched the conquest of Egypt on his own initiative in late 639, defeating the Byzantines in a string of victories ending with the surrender of Alexandria in 641 or 642. It was the swiftest of the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
. This was followed by westward advances by Amr as far as Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
in present-day Libya. In a treaty signed with the Byzantine governor Cyrus
Cyrus (Persian: کوروش) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus t ...
, Amr guaranteed the security of Egypt's population and imposed a poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
on non-Muslim adult males. He maintained the Coptic
Coptic may refer to:
Afro-Asia
* Copts, an ethnoreligious group mainly in the area of modern Egypt but also in Sudan and Libya
* Coptic language, a Northern Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Egypt until at least the 17th century
* Coptic alphabet ...
-dominated bureaucracy and cordial ties with the Coptic patriarch Benjamin
Benjamin ( he, ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel (Jacob's thir ...
. He founded Fustat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by ...
as the provincial capital with the mosque later called after him at its center. Amr ruled relatively independently, acquired significant wealth, and upheld the interests of the Arab conquerors who formed Fustat's garrison in relation to the central authorities in Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
. After gradually diluting Amr's authority, Caliph Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic proph ...
() dismissed him in 646 after accusations of incompetency from his successor Abdallah ibn Sa'd
Abd Allah ibn Sa'd ibn Abi al-Sarh ( ar, عبد الله ابن سعد ابن أبي السرح, ʿAbd Allāh ibn Saʿd ibn Abī al-Sarḥ) was an Arab administrator and commander.
During his time as governor of Egypt (646 CE to 656 CE), Abd A ...
.
After mutineers from Egypt assassinated Uthman, Amr distanced himself from their cause, despite previously instigating opposition against Uthman. In the ensuing First Muslim Civil War
The First Fitna ( ar, فتنة مقتل عثمان, fitnat maqtal ʻUthmān, strife/sedition of the killing of Uthman) was the first civil war in the Islamic community. It led to the overthrow of the Rashidun Caliphate and the establishment of t ...
, Amr joined Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
against Caliph Ali
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. ...
() due to promises of the governorship of Egypt and its tax revenues. Amr served as Mu'awiya's representative in the abortive arbitration talks to end the war. Afterward, he wrested control of Egypt from Ali's loyalists, killing its governor Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr
Muḥammad ibn Abī Bakr ( ar, محمد بن أبي بكر, 631–658), was the youngest son of the first Islamic caliph Abu Bakr. His mother was Asma bint Umais, who was a widow of Ja'far ibn Abi Talib prior to her second marriage with Abu Bakr. ...
, and assumed the governorship instead. Mu'awiya kept him in his post after establishing the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
in 661 and Amr ruled the province until his death.
Early life and military career
Amr ibn al-As was born in . His father,al-As ibn Wa'il Al-As ibn Wa'il ( ar, العاص بن وائل) was the father of the Sahaba 'Amr ibn al-'As and Hisham ibn al-A'as.
He was a part of Hilf al-Fudul.
He was rumored to have had a relationship with Layla bint Harmalah.
Surat al- Kawthar is the ...
, was a wealthy landowner from the Banu Sahm
The Banu Sahm ( ar, بنو سهم) is a clan of the Quraish tribe. They are related to the Banu Jumah, as they both were part of a larger clan descended from the same ancestor, the Banu Husays.
People
* Khunais ibn Hudhaifa
* 'Amr ibn al-'As
* Hi ...
clan of the Quraysh
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qur ...
tribe of Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
. Following the death of al-As in , Amr inherited from him the lucrative estate and vineyards near Ta'if
Taif ( ar, , translit=aṭ-Ṭāʾif, lit=The circulated or encircled, ) is a city and governorate in the Makkan Region of Saudi Arabia. Located at an elevation of in the slopes of the Hijaz Mountains, which themselves are part of the Sarat M ...
. Amr's mother was al-Nabigha bint Harmala from the Banu Jallan clan of the Anaza
Anaza'' or ''anaza'' (sometimes also spelled anza'' or ''anza'') is a term for a short spear or staff which gained ritual significance in the early years of Islam after the Islamic prophet Muhammad planted his spear in the ground to mark th ...
tribe. She had been taken captive and sold, in succession, to several members of the Quraysh, one of whom was Amr's father. As such, Amr had two maternal half-brothers, Amr ibn Atatha of the Banu Adi
Banu Adi ( ar, بنو عدي) was a clan of the Quraysh tribe descended from Adi ibn Ka'b. The Banu Adi were with the Meccans as part of the escort that preceded the Battle of Badr; they did not join Quraysh further.
Notable members
Among the clan ...
and Uqba ibn Nafi
ʿUqba ibn Nāfiʿ ibn ʿAbd al-Qays al-Fihrī al-Qurashī ( ar, عقبة بن نافع بن عبد القيس الفهري القرشي, ʿUqba ibn Nāfiʿ ibn ʿAbd al-Qays al-Fihrī), also simply known as Uqba ibn Nafi, was an Arab general ser ...
of the Banu Fihr, and a half-sister from the Banu Abd Shams
Banu Abd Shams () refers to a clan within the Meccan tribe of Quraysh.
Ancestry
The clan names itself after Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf, the son of Abd Manaf ibn Qusai and brother of Hashim ibn 'Abd Manaf, who was the great-grandfather of the Islam ...
. Amr is physically described in the traditional sources as being short with broad shoulders, having a large head with a wide forehead and wide mouth, long arms and a long beard.
There are conflicting reports about when Amr embraced Islam, with the most credible version placing it in 629/630, not long before the conquest of Mecca
The Conquest of Mecca ( ar, فتح مكة , translit=Fatḥ Makkah) was the capture of the town of Mecca by Muslims led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in December 629 or January 630 AD ( Julian), 10–20 Ramadan, 8 AH. The conquest marked t ...
by Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, di ...
. According to this account, he converted alongside the Qurayshites Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arab military commander. He initially headed campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career in ...
and Uthman ibn Talha
ʿUthmān ibn Ṭalḥa (Arabic: عثمان بن طلحة) was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. His father was Talhah ibn Abi Talhah al-‘Abdari who was killed by Zubayr ibn al-Awwam in the Battle of Uhud. Before the conquest of Mecc ...
. According to Amr's own testimony, transmitted by his fourth-generation descendant Amr ibn Shu'ayb, he converted in Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
in the presence of King Armah
Armah ( gez, አርማህ) or Aṣḥamah ( ar, أَصْحَمَة), commonly known as Najashi ( ar, النَّجَاشِيّ, translit=An-najāshī), was the ruler of the Kingdom of Aksum who reigned from 614–631 CE. He is primarily known th ...
(Najashi) and met Muhammad in Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
upon the latter's return from the Battle of Khaybar
The Battle of Khaybar ( ar, غَزْوَة خَيْبَر, label=Classical Arabic, Arabic) was fought in 628 Common Era, CE between the early Muslims led by Muhammad and Jews living in Khaybar, an oasis located 150 km from Medina in the n ...
in 628. Amr conditioned his conversion on the forgiveness of his past sins and an "active part in affairs", according to a report cited by the historian Ibn Asakir
Ibn Asakir ( ar-at, ابن عساكر, Ibn ‘Asākir; 1105–c. 1176) was a Syrian Sunni Islamic scholar, who was one of the most renowned experts on Hadith and Islamic history in the medieval era. and a disciple of the Sufi mystic Abu al-Najib S ...
(d. 1176).
Indeed, in October 629, Amr was tasked by Muhammad with leading the raid on Dhat al-Salasil, likely located in the northern Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provin ...
(western Arabia), a lucrative opportunity for Amr in view of the potential war spoils. The purpose of the raid is unclear, though the modern historian Fred Donner
Fred McGraw Donner (born 1945) is a scholar of Islam and Peter B. Ritzma Professor of Near Eastern History at the University of Chicago.
speculates that it was to "break up a gathering of hostile tribal groups" possibly backed by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The historian Ibn Hisham
Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Hishām ibn Ayyūb al-Ḥimyarī al-Muʿāfirī al-Baṣrī ( ar, أبو محمد عبدالملك بن هشام ابن أيوب الحميري المعافري البصري; died 7 May 833), or Ibn Hisham, e ...
(d. 833) holds that Amr rallied the nomadic Arabs in the region "to make war on yzantineSyria". The tribal groups targeted in the raid included the Quda'a
The Quda'a ( ar, قضاعة, translit=Quḍāʿa) were a confederation of Arab tribes, including the powerful Kalb and Tanukh, mainly concentrated throughout Syria and northwestern Arabia, from at least the 4th century CE, during Byzantine rule, t ...
in general and the Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
specifically. Amr's paternal grandmother hailed from the Bali, and this may have motivated his appointment to the command by Muhammad as Amr was instructed to recruit tribesmen from the Bali and the other Quda'a tribes of Balqayn Banū al-Qayn () (also spelled Banūʾl Qayn, Balqayn or al-Qayn ibn Jasr) were an Arab tribe that was active between the early Roman Empire, Roman era in the Near East through the early Islamic era (7th–8th centuries CE), as far as the historical ...
and Banu Udhra. Following the raid, a delegation of the Bali embraced Islam. Amr further consecrated ties with the tribe by marrying a Bali woman, with whom he had his son Muhammad.
Muhammad appointed Amr the governor of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
and he remained there until being informed of Muhammad's death in 632. The death of Muhammad prompted several Arab tribes to defect from the nascent Medina-based Muslim polity in the Ridda wars
The Ridda Wars ( ar, حُرُوْبُ الرِّدَّةِ, lit=Apostasy Wars) were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic proph ...
. Muhammad's successor Caliph Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
() appointed Amr to rein in the apostate Quda'a tribes, and among those targeted were the Hejazi branches of the Bali. Amr's campaigns, which were supported by the commander Shurahbil ibn Hasana
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Shuraḥbīl ibn Ḥasana () was one of the earliest Muslim converts, ''sahaba'' (companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad) and a key commander in the Rashidun army during the Muslim conquest of the Levant.
Early life
Shurahbil ...
, succeeded in restoring Medina's authority as far as the northern frontier with Syria.
Governor of Palestine and role in the Syrian conquest
Amr was one of four commanders dispatched by Abu Bakr to conquer Syria in 633. The focus of Amr's campaign wasPalestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, to which he had been appointed governor by Abu Bakr before his departure. As a Qurayshite merchant Amr was likely already well-acquainted with the routes to Gaza, a principle terminal for Meccan caravans. He took the coastal route of the Hejaz, reaching Ayla, a Muslim possession since 630, before breaking west into the Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
desert or possibly the Sinai
Sinai commonly refers to:
* Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Biblical Mount Sinai, the site in the Bible where Moses received the Law of God
Sinai may also refer to:
* Sinai, South Dakota, a place ...
. He arrived near the villages of Dathin and Badan in Gaza's environs where he entered into talks with Gaza's Byzantine commander. After the negotiations broke down, Amr's men bested the Byzantines at the Battle of Dathin
The Battle of Dathin () was a battle during the Arab–Byzantine Wars between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Byzantine Empire in February 634, but became very famous in the literature of the period.
The battle took place following a series of A ...
on 4 February 634 and set up headquarters at Ghamr al-Arabat in the middle of the Wadi Araba. Most accounts hold that Amr's army was 3,000-strong; the Muhajirun (emigrants from Mecca to Medina) and the Ansar (Islam), Ansar (natives of Medina), who together formed the core of the earliest Muslim converts, dominated his forces according to al-Waqidi (d. 823), while the 9th-century historian Ibn A'tham holds that Amr's army consisted of 3,300 Qurayshite and allied horsemen, 1,700 horsemen from the Banu Sulaym and 200 from the South Arabia, Yemenite tribe of Madh'hij. The historian Philip Mayerson considers the troop figures to be "unquestionably exaggerated" but still representing the largest Arab fighting force to have ever been assembled in southern Palestine and the Sinai until then.
Amr conquered the area around Gaza by February or March 634 and proceeded to besiege Caesarea, the capital of Palaestina Prima, Byzantine Palestine, in July. He soon after abandoned the siege upon the approach of a large Byzantine army. After being reinforced by the remainder of the Muslim armies in Syria, including the new arrivals commanded by Khalid ibn al-Walid, Amr, with overall command of the 20,000-strong Muslim forces, routed the Byzantine army at the Battle of Ajnadayn, the first major confrontation between the Muslims and Byzantium, in July–August 634. Amr occupied numerous towns in Palestine, including Bayt Jibrin, Yibna, Imwas, Amwas, Lydda, Jaffa, Nablus and Sebastia, Nablus, Sebastia. Most of these localities surrendered after little resistance due to the flight of Byzantine troops; consequently, there is scant information about them in the traditional accounts of the conquest. Abu Bakr's successor Umar () appointed or confirmed Amr as the commander of the Jund Filastin, military district of Palestine.
 The Muslims pursued the Byzantine army northward and besieged them at Pella, Jordan, Pella for four months. Amr may have retained overall command of the Muslim armies until this point, though other accounts assign command to Khalid or Abu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah. In any case, the Muslims landed a heavy blow against the Byzantines in the ensuing Battle of Fahl in December 634 or January 635. Afterward, Amr and Shurahbil may have been sent to besiege Beisan, which capitulated after minor resistance. The Muslims proceeded to besiege Damascus, where the remnants of the Byzantine army from the battles of Ajnadayn and Fahl had gathered. Amr was positioned at the Bab Tuma gate, the Muslim commanders having each been assigned to block one of the city's entrances. By August–September 635, Damascus surrendered to the Muslims. Amr acquired several residences within the city.
In response to the series of defeats, the Byzantine emperor Heraclius () led a large army in person to confront the Muslims; its rout at the Battle of Yarmouk, in which Amr played a key role by confining the Byzantines between the banks of the Yarmouk River and the Yarmouk's ravine, in August–September 636, paved the way for the rest of Syria's conquest by the Muslims. Following Yarmouk, the Muslims attempted to capture Jerusalem, where Amr had previously sent an advance force. Abu Ubayda led the Siege of Jerusalem (636–637), siege of Jerusalem, in which Amr participated, but the city only surrendered after Caliph Umar arrived in person to conclude a treaty with its defenders. Amr was one of the witnesses of the Treaty of Umar. From Jerusalem, Amr proceeded to besiege and capture the city of Gaza.
The Muslims pursued the Byzantine army northward and besieged them at Pella, Jordan, Pella for four months. Amr may have retained overall command of the Muslim armies until this point, though other accounts assign command to Khalid or Abu Ubayda ibn al-Jarrah. In any case, the Muslims landed a heavy blow against the Byzantines in the ensuing Battle of Fahl in December 634 or January 635. Afterward, Amr and Shurahbil may have been sent to besiege Beisan, which capitulated after minor resistance. The Muslims proceeded to besiege Damascus, where the remnants of the Byzantine army from the battles of Ajnadayn and Fahl had gathered. Amr was positioned at the Bab Tuma gate, the Muslim commanders having each been assigned to block one of the city's entrances. By August–September 635, Damascus surrendered to the Muslims. Amr acquired several residences within the city.
In response to the series of defeats, the Byzantine emperor Heraclius () led a large army in person to confront the Muslims; its rout at the Battle of Yarmouk, in which Amr played a key role by confining the Byzantines between the banks of the Yarmouk River and the Yarmouk's ravine, in August–September 636, paved the way for the rest of Syria's conquest by the Muslims. Following Yarmouk, the Muslims attempted to capture Jerusalem, where Amr had previously sent an advance force. Abu Ubayda led the Siege of Jerusalem (636–637), siege of Jerusalem, in which Amr participated, but the city only surrendered after Caliph Umar arrived in person to conclude a treaty with its defenders. Amr was one of the witnesses of the Treaty of Umar. From Jerusalem, Amr proceeded to besiege and capture the city of Gaza.
First governorship of Egypt
Conquest of Egypt
Cyrus
Cyrus (Persian: کوروش) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus t ...
; Emperor Heraclius opposed the talks and recalled Cyrus to Constantinople. Though strong resistance was put up by Babylon's defenders, their morale was sapped after news of Heraclius' death in February 641. Amr made an agreement with the Byzantine garrison, allowing their peaceful withdrawal toward the provincial capital Alexandria on 9 April 641. Amr then sent his lieutenants to conquer different parts of the country. One of them, Kharija ibn Hudhafa, captured the Fayyum oasis, Oxyrhynchus (Bahnasa), Hermopolis (el-Ashmunein) and Akhmim, all in Middle Egypt, and an unspecified number of villages in Upper Egypt.
poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
on adult males. The date of the city's surrender was likely November 642. Taking advantage of the uncertain political situation in the wake of Umar's death in 644 and the meager Arab military presence in Alexandria, Emperor Constans II () dispatched a naval expedition led by a certain Manuel which occupied the city and killed most of its Arab garrison in 645. Alexandria's elite and most of the inhabitants assisted the Byzantines; medieval Byzantine, Coptic and, to a lesser extent, Muslim sources indicate the city was not firmly in Arab hands during the preceding three years. Byzantine forces pushed deeper into the Nile Delta, but Amr forced them back at the Battle of Nikiou. He besieged and captured Alexandria in the summer of 646; most of the Byzantines, including Manuel, were slain, many of its inhabitants were killed and the city was burned until Amr ordered an end to the onslaught. Afterward, Muslim rule in Alexandria was gradually solidified.
In contrast to the disarray of the Byzantine defense, the Muslim forces under Amr's command were unified and organized; Amr frequently coordinated with Caliph Umar and his own troops for all major military decisions. According to the historian Vassilios Christides, Amr "cautiously counterbalanced the superiority in numbers and equipment of the Byzantine army by applying skillful military tactics" and despite the lack of "definite, prepared, long-term plans ... the Arab army moved with great flexibility as the occasion arose". In the absence of siege engines, Amr oversaw long sieges of heavily fortified Byzantine positions, most prominently Babylon, cut supply lines and engaged in long wars of attrition. He made advantageous use out of the nomads in his ranks, who were seasoned in hit-and-run tactics, and his settled troops, who were generally more acquainted with siege warfare. His cavalry-dominated army moved through Egypt's deserts and oases with relative ease. Moreover, political circumstances became more favorable to Amr with the death of the hawkish Heraclius and his short-term replacement with the more pacifist Heraklonas and Martina (empress), Martina.
Expeditions in Cyrenaica and Tripolitania
After the surrender of Alexandria in 642, Amr marched his army westward, bypassing the fortified Byzantine coastal strongholds of Mersa Matruh, Paraetonium (Marsa Matruh), Apollonia (Cyrenaica), Appolonia Sozusa (Marsa Soussa) and Ptolemais, Cyrenaica, Ptolemais (Tolmeita), capturing Barca (ancient city), Barca and reaching Torca in Cyrenaica. Toward the end of the year, Amr launched a second cavalry assault targetingTripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
. The city was heavily fortified by the Byzantines and contained several naval vessels in its harbor. Due to his lack of siege engines, he employed the lengthy siege tactic used in the Egyptian conquest. After about a month, his troops entered Tripoli through a vulnerable point in its walls and sacked the city. Its fall, which entailed the evacuation by sea of the Byzantine garrison and most of the population, is dated to 642 or 643/44. Though the Arab hold over Cyrenaica and Zawila to the far south remained firm for decades except for a short-lived Byzantine occupation in 690, Tripoli was recaptured by the Byzantines a few years after Amr's entry. The region was definitively conquered by the Arabs during the reign of Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, Abd al-Malik ().
Administration
Amr "regulated the government of the country [Egypt], administration of justice and the imposition of taxes", according to the historian A. J. Wensinck. During his siege of Babylon, Amr had erected an encampment near the fortress. He originally intended for Alexandria to serve as the Arabs' capital in Egypt, but Umar rejected this on the basis that no body of water, i.e. the Nile, should separate the caliph from his army. Instead, following Alexandria's surrender, in 641 or 642, Amr made his encampment near Babylon the permanent amsar, garrison town (''miṣr'') ofFustat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by ...
, the first town founded by the Arabs in Egypt. Its location along the eastern bank of the Nile River and at the head of the Nile Delta and edge of the Eastern Desert strategically positioned it to dominate the Upper and Lower Egypt, Lower halves of Egypt. Fustat's proximity to Babylon, where Amr also established an Arab garrison, afforded the Arab settlers a convenient means to employ and oversee the Copts, Coptic bureaucratic officials who inhabited Babylon and proved critical to running the day-to-day affairs of the Arab government.
 Amr had the original tents of Fustat replaced with mud brick and baked brick dwellings. Documents found in Hermopolis (el-Ashmunein) dating from the 640s confirm official orders to forward building materials to Babylon to construct the new city. The city was organized into allotments over an area stretching along the Nile and inland to the east. The allotments were distributed among the components of Amr's army, with priority given to the Quraysh, the Ansar and Amr's personal guard, the 'Ahl al-Rāya' (People of the Banner), which included several Bali tribesmen as a result of their kinship and marital ties to Amr. An opposing theory holds that Amr did not assign the plots; rather, the tribes staked their own claims and Amr established a commission to resolve the ensuing land disputes. At the center of the new capital Amr built a congregational mosque, later known as the Mosque of Amr ibn al-As; the original structure was frequently redesigned and expanded between its foundation and its final form in 827. Amr had his own dwelling built immediately east of the mosque and it most likely served as his government headquarters.
In the northwestern part of Alexandria, Amr built a hilltop congregational mosque, later called after him, before the Byzantine occupation of 645/46, after which he built a second called the Mosque of Mercy; neither mosque has been presently identified. Adjacent to the congregational mosque, Amr took personal ownership of a fort, which he later donated for government use. This part of the city became the administrative and social core of Arab settlement in Alexandria. Accounts vary as to the number of troops Amr garrisoned in the city, ranging from 1,000 soldiers from the Azd and Banu Fahm tribes to a quarter of the army which was replaced on a rotational basis every six months.
As per the 641 treaty with Cyrus, Amr imposed a poll tax of two gold dinars on non-Muslim adult males. He imposed other measures, sanctioned by Umar, that entailed the inhabitants' regular provision of wheat, honey, oil and vinegar as a subsistence allowance for the Arab troops. He had these goods stored in a distribution warehouse called ''dār al-rizq''. After taking a census of the Muslims, he further ordered that each Muslim be annually supplied by the inhabitants a highly embroidered wool robe (Egyptian robes were prized by the Arabs), a burnous, a turban, a sirwal (trousers) and shoes. In a Greek papyrus dated to 8 January 643 and containing Amr's seal (a fighting bull), Amr (transliterated as "Ambros") requests fodder for his army's animals and bread for his soldiers from an Egyptian village. According to the historian Martin Hinds, there is "no evidence" that Amr "did anything to streamline the cumbersome fiscal system taken over from the Byzantines; rather, the upheavals of conquest can only have made the system more open to abuse than ever".
After entering Alexandria, Amr invited the Pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic patriarch
Amr had the original tents of Fustat replaced with mud brick and baked brick dwellings. Documents found in Hermopolis (el-Ashmunein) dating from the 640s confirm official orders to forward building materials to Babylon to construct the new city. The city was organized into allotments over an area stretching along the Nile and inland to the east. The allotments were distributed among the components of Amr's army, with priority given to the Quraysh, the Ansar and Amr's personal guard, the 'Ahl al-Rāya' (People of the Banner), which included several Bali tribesmen as a result of their kinship and marital ties to Amr. An opposing theory holds that Amr did not assign the plots; rather, the tribes staked their own claims and Amr established a commission to resolve the ensuing land disputes. At the center of the new capital Amr built a congregational mosque, later known as the Mosque of Amr ibn al-As; the original structure was frequently redesigned and expanded between its foundation and its final form in 827. Amr had his own dwelling built immediately east of the mosque and it most likely served as his government headquarters.
In the northwestern part of Alexandria, Amr built a hilltop congregational mosque, later called after him, before the Byzantine occupation of 645/46, after which he built a second called the Mosque of Mercy; neither mosque has been presently identified. Adjacent to the congregational mosque, Amr took personal ownership of a fort, which he later donated for government use. This part of the city became the administrative and social core of Arab settlement in Alexandria. Accounts vary as to the number of troops Amr garrisoned in the city, ranging from 1,000 soldiers from the Azd and Banu Fahm tribes to a quarter of the army which was replaced on a rotational basis every six months.
As per the 641 treaty with Cyrus, Amr imposed a poll tax of two gold dinars on non-Muslim adult males. He imposed other measures, sanctioned by Umar, that entailed the inhabitants' regular provision of wheat, honey, oil and vinegar as a subsistence allowance for the Arab troops. He had these goods stored in a distribution warehouse called ''dār al-rizq''. After taking a census of the Muslims, he further ordered that each Muslim be annually supplied by the inhabitants a highly embroidered wool robe (Egyptian robes were prized by the Arabs), a burnous, a turban, a sirwal (trousers) and shoes. In a Greek papyrus dated to 8 January 643 and containing Amr's seal (a fighting bull), Amr (transliterated as "Ambros") requests fodder for his army's animals and bread for his soldiers from an Egyptian village. According to the historian Martin Hinds, there is "no evidence" that Amr "did anything to streamline the cumbersome fiscal system taken over from the Byzantines; rather, the upheavals of conquest can only have made the system more open to abuse than ever".
After entering Alexandria, Amr invited the Pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic patriarch Benjamin
Benjamin ( he, ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel (Jacob's thir ...
to return to the city after his years of exile under Cyrus. The patriarch maintained close ties with Amr and restored the monasteries of Wadi El Natrun, Wadi el-Natrun, including the Monastery of Saint Macarius the Great, Saint Macarius Monastery, which functions until the present-day. According to the historian Hugh N. Kennedy, "Benjamin played a major role in the survival of the Coptic Church through the transition to Arab rule".
Dismissal and aftermath
Amr acted relatively independent as governor and retained much of the surplus tax revenue of the province for the benefit of its troops despite pressure from Umar to forward proceeds to Medina. He also amassed significant personal wealth in Egypt, part of which was confiscated by Muhammad ibn Maslama on Umar's orders. At a certain point, the Caliph separated Upper Egypt from Amr's administration and appointed Abd Allah ibn Abi Sarh over the region. Umar's successor CaliphUthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic proph ...
() initially kept Amr in his governorship and forged marital links with him by wedding to him his maternal half-sister Umm Kulthum bint Uqba, Umm Kulthum bint Uqba ibn Abi Mu'ayt. Uthman diluted Amr's power in 645/46 by transferring fiscal responsibilities to Ibn Abi Sarh, his own relative, leaving Amr in charge of military affairs. Amr and Ibn Abi Sarh lodged complaints to Uthman each alleging the other of incompetence, prompting Uthman to dismiss Amr entirely and replace him in his duties with Ibn Abi Sarh. Uthman's appointee established an effective fiscal system that largely preserved its Byzantine predecessor. Ibn Abi Sarh reduced the fiscal privileges of Egypt's original Arab military settlers, who had been shown favor by Amr, and secured the remittance of the surplus to Medina. This led to the consternation of the Arab garrisons and the native officials and elite, all of whom were "deprived of the opportunities for self-enrichment which they had hitherto enjoyed", according to Hinds. Open opposition to Ibn Abi Sarh and Uthman began under the leadership of the Qurayshite Muhammad ibn Abi Hudhayfa in 654/55.
Opposition to Uthman
Upon his return to Medina, Amr divorced Umm Kulthum and openly criticized Uthman. The Caliph and Amr engaged in a number of heated public exchanges and, according to a report in the Islamic traditional sources, Amr incited Muhammad's senior companionsAli
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 CE) was the last of four Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. ...
, al-Zubayr and Talha ibn Ubayd Allah, as well as the Hajj pilgrims in Mecca, against Uthman. He lobbied Muhammad's wife A'isha for support and the latter pressed Uthman to reappoint Amr to Egypt citing its garrisons' satisfaction with his rule. In a sermon at the mosque in Medina in June 656 and a letter penned to the Muslim leaders in Syria, Uthman mentioned that he had intended to reappoint Amr but did not follow through as a result of the latter's excessive insult. According to the historian Wilferd Madelung, the insult Uthman cited was likely Amr's public reaction to the Caliph's statement that the mutinous Egyptian troops who had arrived in Medina to protest the Caliph's policies had withdrawn because they were misinformed: "Fear God, Uthman, for you have ridden over abysses and we have ridden over them with you. So repent to God, that we may repent".
After his last exchange with Uthman, Amr retired to his estate in southern Palestine. The estate was called "Ajlan" after one of his ''mawla, mawālī'' (non-Arab, Muslim freedmen) and was located in the vicinity of "al-Sab'", which had conventionally been identified with modern Beersheba, but more likely corresponds with Bayt Jibrin, according to the historian Michael Lecker; the medieval historians al-Baladhuri (d. 892) and Yaqut al-Hamawi (d. 1226) also suggest that Ajlan was located in the area of Bayt Jibrin. Amr had likely become owner of the estate through a caliphal grant, though he possibly could have taken possession of it in the course of his conquest of Palestine and his ownership had been confirmed by the caliphs. He lived on the estate, where he derived agricultural revenue, with his sons Muhammad and Abd Allah ibn Amr ibn al-As, Abd Allah.
At his estate Amr received news of the Siege of Uthman and the Caliph's subsequent assassination by Amr's Egyptian partisans. The roughly 400–600 Egyptian mutineers had protested Uthman's fiscal centralization policies in Medina and accused him of favoring his relatives over the early Muslim converts. The Caliph persuaded them to withdraw, but after they intercepted a letter on their departure ordering Ibn Abi Sarh to punish them, they turned back and assaulted Uthman in his home. In an anecdote cited by al-Baladhuri, Amr is quoted taking partial credit for Uthman's killing. Ali succeeded Uthman, but did not reappoint Amr to his post in Egypt. Amr was one of a number of figures held culpable for Uthman's death by the slain caliph's clan, the Umayyad dynasty, Banu Umayya (Umayyads), most prominently by Uthman's uterine brother and Amr's former brother-in-law al-Walid ibn Uqba. Nonetheless, the governor of Bilad al-Sham, Syria—which included Palestine—the Umayyad Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
, had left Amr on his estate undisturbed. As pressure from the Umayyads increased against him, Amr distanced himself from any role in Uthman's death and wrote Mu'awiya to execute or banish the participating Egyptian troops who had been apprehended when they passed through Mu'awiya's jurisdiction on their way back to Egypt.
Alliance with Mu'awiya
After Ali's victory against al-Zubayr, Talha and A'isha at the Battle of the Camel in Iraq, Mu'awiya, who maintained his opposition to Ali, became the focus of the Caliph's attention. Mu'awiya summoned Amr to discuss an alliance against Ali. In the ensuing negotiations, Amr pressed Mu'awiya for lifetime possession of Egypt, to which Mu'awiya ultimately acceded after being persuaded by his brother Utba ibn Abi Sufyan. The public agreement, composed by Amr's ''mawlā'' Wardan and made in Jerusalem, secured Amr's allegiance to Mu'awiya in return for the latter's assistance in gaining control of Egypt from Ali's governor. According to Madelung, the "alliance between Mu'awiya and Amr b. al-As constituted a formidable political force"; in forging the alliance, Mu'awiya sought to benefit from Amr's political acumen, "practical battle experience and sure judgement of military strategy and tactics", as well as his "expertise" and support base in Egypt. Amr became Mu'awiya's chief adviser. To secure the defense of his Syrian realm from Ali's loyalists in Egypt, Amr counseled Mu'awiya to secure the support of the Judhamite chief in Palestine, Natil ibn Qays, by ignoring his seizure of the district treasury; Natil subsequently joined Mu'awiya's cause. Amr then advised Mu'awiya to lead the Syrian army in person against Ali, who began his march toward Syria in late May 657. When Ali's army set up camp around Siffin, south of the Euphrates town of Raqqa, in early June, Mu'awiya's advance guard led by Abu'l-A'war refused them access to the watering places under their control. After Ali protested, Amr advised Mu'awiya to accept their request as preventing access to water might rally the hitherto demotivated Iraqis to a determined fight against the Syrians. Mu'awiya refused and the Iraqis subsequently defeated the Syrians led by Amr and Abu'l-A'war in a skirmish known as the "Day of the Euphrates". As head of the Syrian cavalry, Amr held the overall field command for Mu'awiya's forces in the ensuing weeks-long Battle of Siffin and on occasion personally participated in direct combat, though without particular distinction. At one point in the battle, he raised a black fabric given to him by Muhammad at the tip of his spear, symbolizing the command role given to him by Muhammad. As the Iraqis gained the battlefield advantage, Amr proposed to Mu'awiya that their men tie leaves from the Qur'an at the tips of their lances in an appeal to Ali's men to settle the conflict peacefully. It served as a successful ruse which ended the fighting as the battle turned in Ali's favor and sowed uncertainty in Ali's ranks. The Caliph heeded the majority will in his army to settle the matter diplomatically; an arbitration was agreed with Amr representing Mu'awiya and Abu Musa al-Ash'ari representing Ali. Amr met with Ali once and the two exchanged insults, but Ali ultimately agreed to Amr's condition that he omit his caliphal title, ''amir al-mu'minin, amīr al-muʾminīn'' (commander of the faithful), from the preliminary arbitration document drafted on 2 August. The omission effectively placed Ali and Mu'awiya on an equal political footing and thereby weakened Ali's leadership position over the Muslim polity. Amr and Abu Musa likely met twice, at Dumat al-Jandal and then Adhruh, to forge an agreement. At Dumat al-Jandal, Amr succeeded in gaining Abu Musa's recognition that Uthman was wrongfully killed, a verdict opposed by Ali and which strengthened Syrian support for Mu'awiya, who had taken up the cause of revenge for the death of his kinsman Uthman. At the last meeting in Adhruh, the office of the caliphate was discussed, but the meeting ended in violence and without agreement; during the brawl, Amr was physically assaulted by a Kufan partisan of Ali, but the latter was fended off by one of Amr's sons. Abu Musa retired to Mecca, while Amr and the Syrians returned to Mu'awiya and recognized him as ''amīr al-muʾminīn'' before formally pledging allegiance to him in April/May 658. As a result, Amr was among those invoked in a ritual curse issued by Ali during the morning prayers and became the subject of derision among the Kufan core of Ali's supporters.Reestablishment in Egypt
As early as 656/57, Amr and Mu'awiya persuaded Ibn Abi Hudhayfa, who had seized control of Egypt after Uthman's assassination, to meet them in al-Arish, where they took him captive in a ruse. Amr and Mu'awiya did not advance further than this point and Ibn Abi Hudhayfa was executed. Ali's second governor in Egypt, Qays ibn Sa'd al-Ansari, was dismissed in late 657 due to concerns that he would defect to Mu'awiya and his next appointee, Malik al-Ashtar, died in Qulzum (Suez) on his way to the province. Al-Ashtar's replacement wasMuhammad ibn Abi Bakr
Muḥammad ibn Abī Bakr ( ar, محمد بن أبي بكر, 631–658), was the youngest son of the first Islamic caliph Abu Bakr. His mother was Asma bint Umais, who was a widow of Ja'far ibn Abi Talib prior to her second marriage with Abu Bakr. ...
, son of the first caliph and a foster son of Ali. Ibn Abi Bakr burned the homes and arrested the families of pro-Uthman mutineers from the Fustat garrison led by Mu'awiya ibn Hudayj al-Kindi and Maslama ibn Mukhallad al-Ansari. The latter two requested intervention by Mu'awiya, who dispatched Amr to Egypt with a 4,000–6,000-strong army. Despite his thirteen-year absence from Egypt, Amr nonetheless mustered the support of Egypt's original Arab military settlers and their sons. In July/August 658, his forces defeated Ali's troops at the Battle of al-Musannah between Heliopolis (Ain Shams) and Fustat. He subsequently captured Fustat. Ibn Hudayj pursued and captured Ibn Abi Bakr and had him executed over the objections of Amr, who had been lobbied by Ibn Abi Bakr's brother Abd al-Rahman ibn Abi Bakr, Abd al-Rahman to spare his life.
As per his agreement with Mu'awiya, Amr was installed as governor of Egypt for life and ruled as a virtual partner rather than a subordinate of Mu'awiya, who had become caliph after Ali's assassination and his son Hasan ibn Ali, al-Hasan's abdication in 661. On 22 January of that year, Amr escaped an assassination attempt by the Kharijite Zadawayh or Amr ibn Bakr, who killed Amr's stand-in for the Friday prayers, Kharija ibn Hudhafa, mistaking the latter for Amr. When the Kharijite was apprehended and brought before him, Amr proclaimed "You wanted me, but God wanted Kharija!" and he personally executed him.
Amr was permitted by the Caliph to retain personally the surplus revenues of the province after the payment of the troops' stipends and other government expenses. He increased the original garrison at Fustat, numbering some 15,000 soldiers, with the Syrian troops he brought with him. According to the historian Clive Foss "Amr ruled the country successfully, and with considerable independence and privilege, until his death".
Death and legacy
 Amr died of natural causes over the age of 90. Accounts vary regarding the date of his death, though the most credible versions place it in 43 Hijri year, AH (663–664 CE). He was buried at the foot of the Mokattam hills to the east of Fustat. Due to the early Muslims' reticence to mark the graves of their dead, Amr's burial place has not been identified. In a testament to the personal wealth that he accrued, at the time of his death he left seventy sacks of gold dinars. His sons Abd Allah and Muhammad refused inheritance of the sums, which were then confiscated by Mu'awiya. Abd Allah succeeded his father as governor for a few weeks until Mu'awiya replaced him with his own brother Utba.
The traditional Egypt-based Arabic and Coptic language, Coptic sources regard Amr positively. The major source of information about the Muslim conquest of Egypt and the province's early Arab military generations, Ibn Abd al-Hakam (d. 871), commends Amr for his leadership of the Egyptian conquest and as the upholder of the interests of Egypt's troops and their families against the central authorities in Medina and later Damascus. The Egyptian Arab tradition holds that Amr was personally praised by Muhammad and was a man of wisdom and piety on his deathbed. The nearly contemporary Coptic historian John of Nikiu (), who was generally critical of Arab rule, said of Amr that he "had no mercy on the Egyptians, and did not observe the covenant they had made with him", but also says of him that: "He exacted the taxes which had been determined upon but he took none of the property of the churches, and he committed no act of spoliation or plunder, and he preserved them throughout all his days." In the words of Kennedy, "Of his [Amr's] competence as a military commander and politician there can be no doubt—the results speak for themselves—but he also has a reputation for straight dealing and justice." Amr's roughly two-year conquest of Egypt was the quickest in the history of the
Amr died of natural causes over the age of 90. Accounts vary regarding the date of his death, though the most credible versions place it in 43 Hijri year, AH (663–664 CE). He was buried at the foot of the Mokattam hills to the east of Fustat. Due to the early Muslims' reticence to mark the graves of their dead, Amr's burial place has not been identified. In a testament to the personal wealth that he accrued, at the time of his death he left seventy sacks of gold dinars. His sons Abd Allah and Muhammad refused inheritance of the sums, which were then confiscated by Mu'awiya. Abd Allah succeeded his father as governor for a few weeks until Mu'awiya replaced him with his own brother Utba.
The traditional Egypt-based Arabic and Coptic language, Coptic sources regard Amr positively. The major source of information about the Muslim conquest of Egypt and the province's early Arab military generations, Ibn Abd al-Hakam (d. 871), commends Amr for his leadership of the Egyptian conquest and as the upholder of the interests of Egypt's troops and their families against the central authorities in Medina and later Damascus. The Egyptian Arab tradition holds that Amr was personally praised by Muhammad and was a man of wisdom and piety on his deathbed. The nearly contemporary Coptic historian John of Nikiu (), who was generally critical of Arab rule, said of Amr that he "had no mercy on the Egyptians, and did not observe the covenant they had made with him", but also says of him that: "He exacted the taxes which had been determined upon but he took none of the property of the churches, and he committed no act of spoliation or plunder, and he preserved them throughout all his days." In the words of Kennedy, "Of his [Amr's] competence as a military commander and politician there can be no doubt—the results speak for themselves—but he also has a reputation for straight dealing and justice." Amr's roughly two-year conquest of Egypt was the quickest in the history of the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
. Though demographically Egypt remained largely non-Arab and non-Muslim for centuries after the conquest, the country has been continuously ruled by Muslims until the present day.
Descendants
Amr's estates in Palestine remained in the possession of his descendants as late as the 10th or 11th centuries. His granddaughter Umm Abd Allah bint Abd Allah married the Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad viceroy of Egypt Abd al-Aziz ibn Marwan (d. 705) and bore his sons Suhayl and Sahl and daughters Sahla and Umm al-Hakam. The estates in Medina that Amr's descendants inherited from him were confiscated by the Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasids after they Abbasid Revolution, took over the Caliphate from the Umayyads in 750. The estates were restored to Amr's family after the intercession of his great-granddaughter Abida al-Hasna bint Shu'ayb ibn Abd Allah, who married the Abbasid prince Abdallah ibn Ubaydallah ibn al-Abbas, al-Husayn ibn Abd Allah ibn Ubayd Allah ibn Abbas (d. 758).Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Amr ibn As 573 births 664 deaths 7th-century Umayyad governors of Egypt Arab people of the Arab–Byzantine wars Banu Sahm Generals of the Rashidun Caliphate Companions of the Prophet Muslim conquest of Egypt People of the First Fitna People of the Muslim conquest of the Levant Rashidun governors of Egypt Umayyad governors of Egypt City founders