The American Theater was a
theater
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actor, actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The p ...
of operations during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
including all
continental American territory, and extending into the ocean.
Owing to North and South America's geographical separation from the central theaters of conflict (in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
,
the Mediterranean and Middle East, and
the Pacific) the threat of an
invasion of the continental U.S. or other areas in the Americas by the
Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
was negligible and the theater saw relatively little conflict.
However, despite the relative unimportance of the American Theater, some battles took place within it, including the
Battle of the River Plate
The Battle of the River Plate was fought in the South Atlantic on 13 December 1939 as the first naval battle of the Second World War. The Kriegsmarine heavy cruiser , commanded by Captain Hans Langsdorff, engaged a Royal Navy squadron, command ...
,
submarine attacks off the East Coast, the
Aleutian Islands campaign, the
Battle of the St. Lawrence, and the attacks on
Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
. Espionage efforts included
Operation Bolívar.
German operations
South America

''See also
Latin America during World War II
During World War II, a number of significant economic, political, and military changes took place in Latin America. The war caused considerable panic in the region over economics as large portions of economy of the region depended on the European ...
''
Battle of the River Plate
The first naval battle during the war was fought on December 13, 1939, off the Atlantic coast of
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
. The German "
pocket battleship
The ''Deutschland'' class was a series of three ''Panzerschiffe'' (armored ships), a form of heavily armed cruiser, built by the ''Reichsmarine'' officially in accordance with restrictions imposed by the Treaty of Versailles. The ships of the c ...
" (acting as a commerce raider) encountered one of the British naval units searching for her. Composed of three
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
cruisers, , , and , the unit was patrolling off the
River Plate estuary of
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
and
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
. In a bloody engagement, ''Admiral Graf Spee'' successfully repulsed the British attacks.
Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
Hans Langsdorff
Hans Wilhelm Langsdorff (20 March 1894 – 20 December 1939) was a German naval officer, most famous for his command of the German pocket battleship ''Admiral Graf Spee'' during the Battle of the River Plate off the coast of Uruguay in 1939. ...
then brought his damaged ship to shelter in neutral Uruguay for repairs. However, British intelligence successfully deceived Langsdorff into believing that a much superior British force had now gathered to wait for him, and he
scuttled
Scuttling is the deliberate sinking of a ship. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self-destruction to prevent the ship from being ...
his ship at
Montevideo
Montevideo () is the capital and largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the city proper has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population) in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern ...
to save his crew's lives before committing suicide. German combat losses were 96 killed or wounded, against 72 British sailors killed and 28 wounded. Two Royal Navy cruisers had been severely damaged.
Submarine warfare
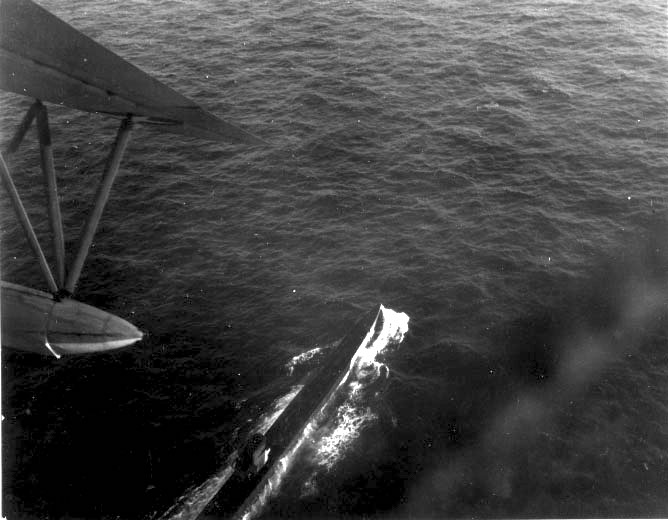

U-boat operations in the region (centered in the
Atlantic Narrows
The Atlantic Narrows is a relatively narrow portion of the Atlantic Ocean between South America and West Africa. More specifically, it lies approximately at the Equator where by definition the North Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic meets the South ...
between
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mau ...
) began in autumn 1940. After negotiations with Brazilian Foreign Minister
Osvaldo Aranha (on behalf of dictator
Getúlio Vargas
Getúlio Dornelles Vargas (; 19 April 1882 – 24 August 1954) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 14th and 17th president of Brazil, from 1930 to 1945 and from 1951 to 1954. Due to his long and controversial tenure as Braz ...
), the
U.S. introduced its
Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ar ...
along Brazil's coast in the second half of 1941. Germany and Italy subsequently extended their submarine attacks to include Brazilian ships wherever they were, and from April 1942 were found in Brazilian waters. On 22 May 1942, the first Brazilian attack (although unsuccessful) was carried out by
Brazilian Air Force
"Wings that protect the country"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march = Hino dos Aviadores
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 22 May (anniver ...
aircraft on the . After a series of attacks on merchant vessels off the Brazilian coast by , Brazil officially entered the war on 22 August 1942, offering an important addition to the Allied strategic position in the South Atlantic. Although the
Brazilian Navy
)
, colors= Blue and white
, colors_label= Colors
, march= " Cisne Branco" ( en, "White Swan") (same name as training ship '' Cisne Branco''
, mascot=
, equipment= 1 multipurpose aircraft carrier7 submarines6 frigates2 corvettes4 amphibious ...
was small, it had modern minelayers suitable for coastal convoy escort and aircraft which needed only small modifications to become suitable for
maritime patrol {{Unreferenced, date=March 2008
Maritime patrol is the task of monitoring areas of water. Generally conducted by military and law enforcement agencies, maritime patrol is usually aimed at identifying human activities.
Maritime patrol refers to ac ...
. During its three years of war, mainly in Caribbean and South Atlantic, alone and in conjunction with the U.S., Brazil escorted 3,167 ships in 614 convoys, totalling 16,500,000 tons, with losses of 0.1%. Brazil saw three of its warships sunk and 486 men
killed in action (332 in the cruiser
''Bahia''); 972
seamen and civilian passengers were also lost aboard the 32 Brazilian merchant vessels attacked by enemy submarines. American and Brazilian air and naval forces worked closely together until the end of the Battle. One example was the sinking of in July 1943, by a coordinated action of Brazilian and American aircraft.
Only in Brazilian waters, eleven other Axis submarines were known sunk between January and September 1943—the Italian and ten German boats: , , , , , , , , , and .
[
By late 1943, the decreasing number of Allied shipping losses in South Atlantic coincided with the increasing elimination of Axis submarines operating there. From then, the battle in the region was lost for Germans, even with the most of remaining submarines in the region receiving official order of withdrawal only in August of the following year, and with (''Baron Jedburgh'') the last Allied merchant ship sunk by a U-boat (''U-532'') there, on 10 March 1945.
]
United States
Duquesne Spy Ring
 Even before the war, a large Nazi spy ring was found operating in the United States. The Duquesne Spy Ring is still the largest espionage case in United States history that ended in convictions. The 33 German agents who formed the Duquesne spy ring were placed in key jobs in the United States to get information that could be used in the event of war and to carry out acts of sabotage. One man opened a restaurant and used his position to get information from his customers; another worked at an airline so he could report Allied ships crossing the
Even before the war, a large Nazi spy ring was found operating in the United States. The Duquesne Spy Ring is still the largest espionage case in United States history that ended in convictions. The 33 German agents who formed the Duquesne spy ring were placed in key jobs in the United States to get information that could be used in the event of war and to carry out acts of sabotage. One man opened a restaurant and used his position to get information from his customers; another worked at an airline so he could report Allied ships crossing the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
; others in the ring worked as deliverymen so they could deliver secret messages alongside normal messages. The ring was led by Captain Fritz Joubert Duquesne, a South African Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this a ...
who spied for Germany in both World Wars and is best known as "The man who killed Kitchener Kitchener may refer to:
People
* Earl Kitchener, a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom
** Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener (1850–1916), British Field Marshal and 1st Earl Kitchener
** Henry Kitchener, 2nd Earl Kitchener (1846–1937) ...
" after he was awarded the Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (german: link=no, Eisernes Kreuz, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, and later in the German Empire (1871–1918) and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). King Frederick William III of Prussia e ...
for his key role in the sabotage and sinking of in 1916.double agent
In the field of counterintelligence, a double agent is an employee of a secret intelligence service for one country, whose primary purpose is to spy on a target organization of another country, but who is now spying on their own country's organ ...
for the United States, was a major factor in the FBI's successful resolution of this case. For nearly two years, Sebold ran a secret radio station in New York for the ring. Sebold provided the FBI with information on what Germany was sending to its spies in the United States while allowing the FBI to control the information that was being transmitted to Germany. On June 29, 1941, six months before the U.S. declared war, the FBI acted. All 33 spies were arrested, found or pled guilty, and sentenced to serve a total of over 300 years in prison.
Operation Pastorius
After declaring war on the United States following the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawa ...
, Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
ordered the remaining German saboteurs to wreak havoc on America. The responsibility for carrying this out was given to German Intelligence (Abwehr
The ''Abwehr'' ( German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', but the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context; ) was the German military-intelligence service for the '' Reichswehr'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' from 1920 to 1944. ...
). In the spring of 1942, nine agents were recruited (one eventually dropping out) and divided into two teams. The first, commanded by George John Dasch, included Ernst Peter Burger, Heinrich Heinck, and Richard Quirin; the second, under command of Edward Kerling, included Hermann Neubauer, Werner Thiel, and Herbert Haupt.
On June 12, 1942, the landed Dasch's team with explosives and plans at Amagansett, New York
Amagansett is a census-designated place that roughly corresponds to the hamlet by the same name in the Town of East Hampton in Suffolk County, New York, United States, on the South Shore of Long Island. As of the 2010 United States Census, ...
. Their mission was to destroy power plants at Niagara Falls and three Aluminum Company of America ( ALCOA) factories in Illinois, Tennessee, and New York. However, Dasch instead turned himself in to the FBI, providing them with a complete list of his team members and an account of the planned missions, which led to their arrests.
On June 17, Kerling's team landed from '' U-584'' at Ponte Vedra Beach
Ponte Vedra Beach is a wealthy unincorporated seaside community and suburb of Jacksonville, Florida in St. Johns County, Florida, United States. Located southeast of downtown Jacksonville and north of St. Augustine, it is part of the Jackson ...
, south-east of Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
. They were ordered to place mines in four areas: the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
in Newark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, most populous City (New Jersey), city in the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat, seat of Essex County, New Jersey, Essex County and the second largest city within the New Yo ...
; canal sluices in both St. Louis, Missouri, and Cincinnati, Ohio
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state lin ...
; and New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
's water supply pipes. The team members made their way to Cincinnati and then split up, two going to Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
, and the others to New York. Dasch's confession led to the arrest of all of the men by July 10.
Because the German agents were captured in civilian clothes (though they had landed in uniforms), they were tried by a military tribunal
Military justice (also military law) is the legal system (bodies of law and procedure) that governs the conduct of the active-duty personnel of the armed forces of a country. In some nation-states, civil law and military law are distinct bodie ...
in Washington D.C., with six of them sentenced to death for spying
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tangibl ...
. President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
approved the sentences. The constitutionality of military tribunals was upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court in '' Ex parte Quirin'' on July 31, and the six men were executed by electrocution at the D.C. jail on August 8. Dasch and Burger were given thirty-year prison sentences because they had turned themselves in to the FBI and provided information about the others. Both were released in 1948 and deported to Germany. Dasch (aka George Davis), who had been a longtime American resident before the war, suffered a difficult life in Germany after his return from U.S. custody because he had betrayed his comrades to the U.S. authorities. As a condition of his deportation, he was not permitted to return to the United States, even though he spent many years writing letters to prominent American authorities (J. Edgar Hoover, President Eisenhower, etc.) seeking permission to return. He eventually moved to Switzerland and wrote a book, titled ''Eight Spies Against America''.
Operation Magpie
In 1944 another attempt at infiltration was made, codenamed Operation Elster ("Magpie"). Elster involved Erich Gimpel and German-American defector William Colepaugh. Their mission's objective was to gather intelligence on a variety of military subjects and transmit it back to Germany by a radio to be constructed by Gimpel. They sailed from Kiel on and landed at Hancock Point, Maine, on November 29, 1944. Both then made their way to New York, but the operation soon collapsed. Colepaugh lost his nerve and turned himself in to the FBI on December 26, confessing the whole plan and naming Gimpel. Gimpel was then arrested four days later in New York. Both men were sentenced to death, but eventually their sentences were commuted. Gimpel spent 10 years in prison, while Colepaugh was released in 1960 and operated a business in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania
King of Prussia (also referred to as KOP) is a census-designated place in Upper Merion Township in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2020 census, its population was 22,028. The community took its unusual name in the 18th c ...
, before he retired to Florida.
Nazi landings in Canada
St. Martins, New Brunswick
One month earlier than the Dasch operation (on May 14, 1942), a solitary Abwehr
The ''Abwehr'' ( German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', but the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context; ) was the German military-intelligence service for the '' Reichswehr'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' from 1920 to 1944. ...
agent, Marius A. Langbein, was landed by a U-boat () near St. Martins, New Brunswick
St. Martins is a community on the Bay of Fundy in Saint John County, New Brunswick, Canada.
The village was founded as Quaco by 1783 by soldiers from the disbanded loyalist King's Orange Rangers. It was incorporated in 1967. Led by shipbuilders ...
, Canada. His mission, codenamed Operation Grete, after the name of the agent's wife, was to observe and report shipping movements at Montreal and Halifax, Nova Scotia (the main departure port for North Atlantic convoys). Langbein, who had lived in Canada before the war, changed his mind and moved to Ottawa, where he lived off his Abwehr funds until he surrendered to the Canadian authorities in December 1944. A jury found Langbein not guilty of spying, since he had never committed any hostile acts against Canada during the war.
New Carlisle, Quebec
 In November 1942, sank two iron ore freighters and damaged another off Bell Island in Conception Bay,
In November 1942, sank two iron ore freighters and damaged another off Bell Island in Conception Bay, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, en route to the Gaspé Peninsula
The Gaspé Peninsula, also known as Gaspesia (; ), is a peninsula along the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River that extends from the Matapedia Valley in Quebec, Canada, into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. It is separated from New Brunswick o ...
where, despite an attack by a Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environ ...
aircraft, it successfully landed a spy, Werner von Janowski, four miles (6.5 km) from New Carlisle, Quebec
New Carlisle, Quebec is a town in the Gaspésie–Îles-de-la-Madeleine region of Quebec, Canada. It best known as the boyhood home of René Lévesque although he was born in Campbellton, New Brunswick. Its population is approximately 1,388, mo ...
, at around 5am on November 9, 1942.
Von Janowski showed up at the New Carlisle Hotel at 06:30 and checked in under the alias of William Brenton. The son of the hotel owner, Earle Annett Jr., grew suspicious of him, because of inconsistencies with the German spy's story. He used an out-of-circulation Canadian note when paying his bill to the owner's son and when he left to wait at the train station the suspicious son of the hotelier followed him.
There Annett grew more suspicious and he alerted a Quebec Provincial Police constable, Alfonse Duchesneau, who quickly boarded the train as it pulled away from the station and began searching for the stranger. Duchesneau located von Janowski, who said he was a radio salesman from Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most pop ...
. He stuck with this story until the policeman asked to search his bags; the stranger then confessed: "That will not be necessary. I am a German officer who serves his country as you do yourself."Abwehr
The ''Abwehr'' ( German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', but the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context; ) was the German military-intelligence service for the '' Reichswehr'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' from 1920 to 1944. ...
, sending false messages to Germany under the joint control of the RCMP
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal and national police service of Canada. As poli ...
and MI5
The Security Service, also known as MI5 ( Military Intelligence, Section 5), is the United Kingdom's domestic counter-intelligence and security agency and is part of its intelligence machinery alongside the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), Go ...
, with spymaster Cyril Mills having been seconded to Canada to assist in the double cross initiative. The effectiveness and honesty of his "turn" is a matter of some dispute. For example, John Cecil Masterman
Sir John Cecil Masterman OBE (12 January 1891 – 6 June 1977) was a noted academic, sportsman and author. His highest-profile role was as Vice-Chancellor of the University of Oxford, but he was also well known as chairman of the Twenty Com ...
wrote in ''The Double Cross System'': "In November, WATCHDOG was landed from a U-boat in Canada together with a wireless set and an extensive questionnaire. This move on the part of the Germans threatened an extension of our activities to other parts of the world, but in fact the case did not develop very satisfactorily... WATCHDOG was closed down in the summer f 1943
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''.
Hist ...
"
German landings in Newfoundland

Weather Station Kurt, Martin Bay
Accurate weather reporting was important to the sea war and on September 18, 1943, sailed from Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland pe ...
, via Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula o ...
, Norway, with a meteorological team led by Professor Kurt Sommermeyer. They landed at Martin Bay, a remote location near the northern tip of Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
on October 22, 1943, and successfully set up an automatic weather station (" Weather Station Kurt" or "''Wetter-Funkgerät Land-26''"), despite the constant risk of Allied air patrols.Canadian War Museum
The Canadian War Museum (french: link=no, Musée canadien de la guerre; CWM) is a national museum on the country's military history in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The museum serves as both an educational facility on Canadian military history, in ad ...
.
U-boat operations
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean was a major strategic battle zone (the "Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blocka ...
") and when Germany declared war on the U.S., the East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. The eastern seaboard contains the ...
offered easy pickings for German U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s (referred to as the "Second Happy Time
The "Second Happy Time" (; officially Operation Paukenschlag ("Operation Drumbeat"), and also known among German submarine commanders as the "American Shooting Season") was a phase in the Battle of the Atlantic during which Axis submarines a ...
"). After a highly successful foray by five Type IX long-range U-boats, the offensive was maximized by the use of short-range Type VII U-boats, with increased fuel stores, replenished from supply U-boats called ''Milchkühe'' (milk cows). From February to May 1942, 348 ships were sunk, for the loss of two U-boats during April and May. U.S. naval commanders were reluctant to introduce the convoy system that had protected trans-Atlantic shipping and, without coastal blackouts, shipping was silhouetted against the bright lights of American towns and cities such as Atlantic City until a dim-out was ordered in May.
The cumulative effect of this campaign was severe; a quarter of all wartime sinkings – 3.1 million tons. There were several reasons for this. The American naval commander, Admiral Ernest King
Ernest Joseph King (23 November 1878 – 25 June 1956) was an American naval officer who served as Commander in Chief, United States Fleet (COMINCH) and Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) during World War II. As COMINCH-CNO, he directed the U ...
, as an apparent anglophobe, was averse to taking British recommendations to introduce convoys, U.S. Coast Guard and Navy patrols were predictable and could be avoided by U-boats, inter-service co-operation was poor, and the U.S. Navy did not possess enough suitable escort vessels (British and Canadian warships were transferred to the U.S. east coast).
U.S. East Coast
Several ships were torpedoed within sight of East Coast cities such as New York and Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
. The only documented World War II sinking of a U-boat close to New England shores occurred on May 5, 1945, when the torpedoed and sank the collier off Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is an American seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Newport County, Rhode Island. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, and northeast of New ...
. When ''Black Point'' was hit, the U.S. Navy immediately chased down the sub and began dropping depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive hydraulic shock. Most depth charges use ...
s. In recent years, ''U-853'' has become a popular dive site. Its intact hull, with open hatches, is located in of water off Block Island
Block Island is an island in the U.S. state of Rhode Island located in Block Island Sound approximately south of the mainland and east of Montauk Point, Long Island, New York, named after Dutch explorer Adriaen Block. It is part of Washin ...
, Rhode Island. A wreck discovered in 1991 off the New Jersey coast was concluded in 1997 to be that of . Previously, ''U-869'' had been thought to have been sunk off Rabat, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
.
U.S. Gulf of Mexico
Once convoys and air cover were introduced in the Atlantic, sinking numbers were reduced and the U-boats shifted to attack shipping in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
. During 1942 and 1943, more than 20 U-boats operated in the Gulf of Mexico. They attacked tankers transporting oil from ports in Texas and Louisiana, successfully sinking 56 vessels. By the end of 1943, the U-boat attacks diminished as the merchant ships began to travel in armed convoys.tanker
Tanker may refer to:
Transportation
* Tanker, a tank crewman (US)
* Tanker (ship), a ship designed to carry bulk liquids
** Chemical tanker, a type of tanker designed to transport chemicals in bulk
** Oil tanker, also known as a petroleum ta ...
''Virginia'' was torpedoed in the mouth of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
by the on May 12, 1942, killing 26 crewmen. There were 14 survivors. Again, when defensive measures were introduced, ship sinkings decreased.
was the only U-boat sunk in the Gulf of Mexico during the war. Once thought to have been sunk by a torpedo dropped from a U.S. Coast Guard Utility Amphibian J4F aircraft on August 1, 1942, ''U-166'' is now believed to have been sunk two days earlier by depth charges from the passenger ship 's naval escort, the U.S. Navy sub-chaser, '' PC-566''. It is thought that the J4F aircraft may have spotted and attacked another German submarine, , which was operating in the area at the same time. ''U-166'' lies in of water within a mile (1,600 m) of her last victim, ''Robert E. Lee''.
Canada
From the start of the war in 1939 until VE Day, several of Canada's Atlantic coast ports became important to the resupply effort for the United Kingdom and later for the Allied land offensive on the Western Front. Halifax and Sydney, Nova Scotia
Sydney is a former city and urban community on the east coast of Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada within the Cape Breton Regional Municipality. Sydney was founded in 1785 by the British, was incorporated as a city in 1904, and disso ...
, became the primary convoy assembly ports, with Halifax being assigned the fast or priority convoys (largely troops and essential material) with the more modern merchant ships, while Sydney was given slow convoys which conveyed bulkier material on older and more vulnerable merchant ships. Both ports were heavily fortified with shore radar emplacements, searchlight batteries, and extensive coastal artillery stations all manned by RCN and Canadian Army regular and reserve personnel. Military intelligence agents enforced strict blackouts throughout the areas and anti-torpedo nets were in place at the harbor entrances, making a direct attack on those facilities unfeasible because it was impossible for Germany to provide air support. Even though no landings of German personnel took place near these ports, there were frequent attacks by U-boats on convoys departing for Europe once these had reached the mouth of the St. Lawrence. Less extensively used, but no less important, was the port of Saint John which also saw matériel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the speci ...
funneled through the port, largely after the United States entered the war in December 1941. The port's location within the protected waters of the Bay of Fundy made it a difficult target for attack. The Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canad ...
mainline from central Canada (which crossed the state of Maine
Maine () is a U.S. state, state in the New England and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and territories of Canad ...
) could be used to transport in aid of the war effort.
Although not crippling to the Canadian war effort, given the country's rail network to the east coast ports, but possibly more destructive to the morale of the Canadian public, was the Battle of the St. Lawrence, when U-boats began to venture upriver and attack domestic coastal shipping along Canada's east coast in the St. Lawrence River and Gulf of St. Lawrence from early 1942 through to the end of the shipping season in late 1944. From a German perspective this area contained most of the military assets in North America that could realistically be targeted for attack, and therefore the St. Lawrence was the only zone that saw consistent warfare—albeit on a limited scale—in North America during World War II. Residents along the Gaspé coast and the St. Lawrence River and Gulf of St. Lawrence were startled at the sight of maritime warfare off their shores, with ships on fire and explosions rattling their communities, while bodies and debris floated ashore. The number of military losses is not known, although loose estimates can be made based on the number of surface units and submarines sunk.
Newfoundland
Five significant attacks on Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
took place in 1942. On 3 March 1942, launched three torpedoes at St. John's; one hit Fort Amherst
Fort Amherst, in Medway, South East England, was constructed in 1756 at the southern end of the Brompton lines of defence to protect the southeastern approaches to Chatham Dockyard and the River Medway against a French invasion. Fort Amherst ...
and two more hit the cliffs of Signal Hill below Cabot Tower
Cabot may refer to:
Businesses
* Cabot Corporation, an American chemicals company
* Cabot Creamery, an American dairy cooperative
Fictional characters
* Alexandra Cabot, in the ''Law & Order'' universe
* Leigh Cabot, from Stephen King's 1983 no ...
. In autumn German U-boats attacked four iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the ...
carriers serving the DOSCO iron mine at Wabana on Bell Island in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
's Conception Bay. The ships SS ''Saganaga'' and SS ''Lord Strathcona'' were sunk by on 5 September 1942, while SS ''Rose Castle'' and ''P.L.M 27'' were sunk by on 2 November with the loss of 69 lives. After the sinkings the submarine fired a torpedo that missed its target, the 3,000-ton collier ''Anna T'', and struck the DOSCO loading pier and exploded. On 14 October 1942, the Newfoundland Railway
The Newfoundland Railway operated on the island of Newfoundland from 1898 to 1988. With a total track length of , it was the longest narrow-gauge railway system in North America.
Early construction
]
In 1880, a committee of the Newfoundland Leg ...
ferry was torpedoed by and sunk in the Cabot Strait
Cabot Strait
(; french: détroit de Cabot, ) is a strait in eastern Canada approximately 110 kilometres wide between Cape Ray, Newfoundland and Cape North, Cape Breton Island.
It is the widest of the three outlets for the Gulf of Saint L ...
south of Port aux Basques
Channel-Port aux Basques is a town at the extreme southwestern tip of Newfoundland fronting on the western end of the Cabot Strait. A Marine Atlantic ferry terminal is located in the town which is the primary entry point onto the island of Newfoun ...
. ''Caribou'' was carrying 45 crew and 206 civilian and military passengers. One hundred thirty-seven lost their lives, many of them Newfoundlanders.
Half a dozen U-boat wrecks lie in waters around Newfoundland and Labrador, destroyed by Canadian patrols.
Caribbean
A German submarine shelled the American Standard Oil
Standard Oil Company, Inc., was an American oil production, transportation, refining, and marketing company that operated from 1870 to 1911. At its height, Standard Oil was the largest petroleum company in the world, and its success made its co- ...
refinery at the San Nicolas harbour and the "Arend"/"Eagle" Maatschappij (from the Dutch/British Shell Co.) near the Oranjestad harbour situated on the Island of Aruba (a Dutch colony) and some ships that were near the entrance to Lake Maracaibo
Lake Maracaibo ( Spanish: Lago de Maracaibo; Anu: Coquivacoa) is a lagoon in northwestern Venezuela, the largest lake in South America and one of the oldest on Earth, formed 36 million years ago in the Andes Mountains. The fault in the northern s ...
on February 16, 1942. Three tankers
Tanker may refer to:
Transportation
* Tanker, a tank crewman (US)
* Tanker (ship), a ship designed to carry bulk liquids
** Chemical tanker, a type of tanker designed to transport chemicals in bulk
** Oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanke ...
, including the Venezuelan ''Monagas'', were sunk. A Venezuelan gunboat, , assisted in rescuing the crews.
A German submarine shelled the island of Mona, some from the main island of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
, on March 2.
Central America
Before 1941, the Central American nations had various diplomatic ties with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, they declared war on the Axis nations. The Central American nations joined the Allied side, broke diplomatic relations with the Axis nations, and initiated persecutions of German and Italian immigrants.
During the course of the war, several merchant ships were sunk in the Caribbean by German submarines, for example the Tela, a Honduran cargo ship sunk by a U-504 submarine in 1942. This led the country to carry out constant air patrols over the coasts under fear of the approach of more German submarines or the general fear of an attack by Germany. Other Central American cargo ships sunk by U-boats are the ''Olancho,'' the ''Comayagua'', and the ''Bluefields'', of Honduran and Nicaraguan origins. Central American volunteers in the United States Army participated in both the European and Asia Pacific theater.
Japanese operations
Aleutian Islands Campaign
 Before Operation MI could be carried out, the Japanese decided to take the Aleutian Islands. On June 3–4, 1942, Japanese planes from two light carriers and struck the U.S. against the city of
Before Operation MI could be carried out, the Japanese decided to take the Aleutian Islands. On June 3–4, 1942, Japanese planes from two light carriers and struck the U.S. against the city of Unalaska, Alaska
Unalaska ( ale, Iluulux̂; russian: Уналашка) is the chief center of population in the Aleutian Islands. The city is in the Aleutians West Census Area, a regional component of the Unorganized Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Unalask ...
, at Dutch Harbor
Dutch Harbor is a harbor on Amaknak Island in Unalaska, Alaska. It was the location of the Battle of Dutch Harbor in June 1942, and was one of the few sites in the United States to be subjected to aerial bombardment by a foreign power during W ...
in the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin, "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, ...
. Originally, the Japanese planned to attack Dutch Harbor simultaneously with its attack on Midway, but the Midway attack was delayed by one day. The attack only did moderate damage on Dutch Harbor, but 43 Americans were killed and 50 others wounded in the attack.
On June 6, two days after the bombing of Dutch Harbor, 500 Japanese marines landed on Kiska
Kiska ( ale, Qisxa, russian: Кыска) is one of the Rat Islands, a group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is about long and varies in width from . It is part of Aleutian Islands Wilderness and as such, special permission is requir ...
, one of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Upon landing, they killed two and captured eight United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
officers
An officer is a person who has a position of authority in a hierarchical organization. The term derives from Old French ''oficier'' "officer, official" (early 14c., Modern French ''officier''), from Medieval Latin ''officiarius'' "an officer," fro ...
, then seized control of American soil for the first time. The next day, a total of 1,140 Japanese infantrymen landed on Attu via Holtz Bay, eventually reaching Massacre Bay and Chichagof Harbor
Chichagof Harbor is an inlet on the northeast coast of the island of Attu in the Aleutian Islands in Alaska.''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary, Third Edition'', p. 243. It is named after Russian Admiral and polar explorer Vasily Chichago ...
. Attu's population at the time consisted of 45 Alaska Native Aleut
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the U ...
s, and two white Americans – Charles Foster Jones, a 60-year-old ham radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communica ...
operator and weather observer, and his 62-year-old wife Etta, a teacher and nurse. The Japanese killed Charles Jones after interrogating him, while Etta Jones and the Aleut population were sent to Japan, where 16 of the Aleuts died and Etta survived the war.
A year after Japan's occupation of Kiska and Attu, U.S. troops invaded Attu on May 11, 1943 and successfully retook the island after three weeks of fighting, killing 2,351 Japanese combatants and taking only 28 as prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
at the cost of 549 lives. Three months later on August 15, U.S. and Canadian forces landed on Kiska expecting the same resistance like Attu; they later found the entire island empty, as most of the Japanese forces secretly evacuated weeks before the landing. In spite of enemy absence on the island, over 313 Allied casualties were sustained nonetheless through car accidents, booby trap
A booby trap is a device or setup that is intended to kill, harm or surprise a human or another animal. It is triggered by the presence or actions of the victim and sometimes has some form of bait designed to lure the victim towards it. The trap m ...
s, landmines
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automati ...
, and friendly fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while e ...
, in which 28 Americans and four Canadians were killed in the exchange of fire between the two forces.
Submarine operations
Several ships were torpedoed within sight of West Coast Californian cities such as Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the wor ...
, Santa Barbara, San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States ...
, and Santa Monica
Santa Monica (; Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 U.S. Census population was 93,076. Santa Monica is a popular resort town, owing to ...
. During 1941 and 1942, more than 10 Japanese submarines operated in the West Coast and Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
. They attacked American, Canadian, and Mexican ships, successfully sinking over 10 vessels including the Soviet Navy submarine ''L-16'' on October 11, 1942.
Bombardment of Ellwood
 The United States continent was first shelled by the Axis on February 23, 1942, when the attacked the
The United States continent was first shelled by the Axis on February 23, 1942, when the attacked the Ellwood Oil Field
Ellwood Oil Field (also spelled "Elwood") and South Ellwood Offshore Oil Field are a pair of adjacent, partially active oil fields adjoining the city of Goleta, California, about west of Santa Barbara, largely in the Santa Barbara Channel. ...
west of Goleta
Goleta or La Goleta may refer to:
* ''Goleta'' (spider), a spider genus
* Goleta, California, United States, a suburban city in Santa Barbara County
* La Goleta, the Spanish and Portuguese name for La Goulette, a municipality and the port of Tu ...
, near Santa Barbara, California
Santa Barbara ( es, Santa Bárbara, meaning "Saint Barbara") is a coastal city in Santa Barbara County, California, of which it is also the county seat. Situated on a south-facing section of coastline, the longest such section on the West Coa ...
. Although only a pumphouse and catwalk at one oil well were damaged, ''I-17'' Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
Nishino Kozo radioed Tokyo that he had left Santa Barbara in flames. No casualties were reported and the total cost of the damage was officially estimated at approximately $500–1,000.
Bombardment of Estevan Point Lighthouse
More than five Japanese submarines operated in Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada� ...
during 1941 and 1942. On June 20, 1942, the , under the command of Yokota Minoru,Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
, but failed to hit its target. Though no casualties were reported, the subsequent decision to turn off the lights of outer stations caused difficulties for coastal shipping activity.
Bombardment of Fort Stevens
In what became the second attack on a continental American military installation during World War II, the , under the command of Tagami Akiji, surfaced near the mouth of the Columbia River in Oregon on the night of June 21 and June 22, 1942, and fired shells toward Fort Stevens. The only damage officially recorded was to a baseball field
A baseball field, also called a ball field or baseball diamond, is the field upon which the game of baseball is played. The term can also be used as a metonym for a baseball park. The term sandlot is sometimes used, although this usually refers ...
's backstop. Probably the most significant damage was a shell that damaged some large phone cables. The Fort Stevens gunners were refused permission to return fire for fear of revealing the guns' location and/or range limitations to the sub. American aircraft on training flights spotted the submarine, which was subsequently attacked by a U.S. bomber, but escaped.
Lookout Air Raids
 The Lookout Air Raids occurred on September 9, 1942. The second location to be subject to
The Lookout Air Raids occurred on September 9, 1942. The second location to be subject to aerial bombing
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offi ...
in the continental United States by a foreign power occurred when an attempt to start a forest fire was made by a Japanese Yokosuka E14Y1 "Glen" seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their tec ...
dropping two incendiary bomb
Incendiary weapons, incendiary devices, incendiary munitions, or incendiary bombs are weapons designed to start fires or destroy sensitive equipment using fire (and sometimes used as anti-personnel weaponry), that use materials such as napalm, ...
s over Mount Emily, near Brookings, Oregon
Brookings is a city in Curry County, Oregon, United States. It was named after John E. Brookings, president of the Brookings Lumber and Box Company, which founded the city in 1908. As of the 2020 census, the population was 6,744.
History
F ...
.
The seaplane, piloted by Nobuo Fujita, had been launched from the Japanese submarine aircraft carrier
A submarine aircraft carrier is a submarine equipped with aircraft for observation or attack missions. These submarines saw their most extensive use during World War II, although their operational significance remained rather small. The most fa ...
''I-25''. No significant damage was officially reported following the attack, nor after a repeat attempt on September 29.
Fire balloon attacks
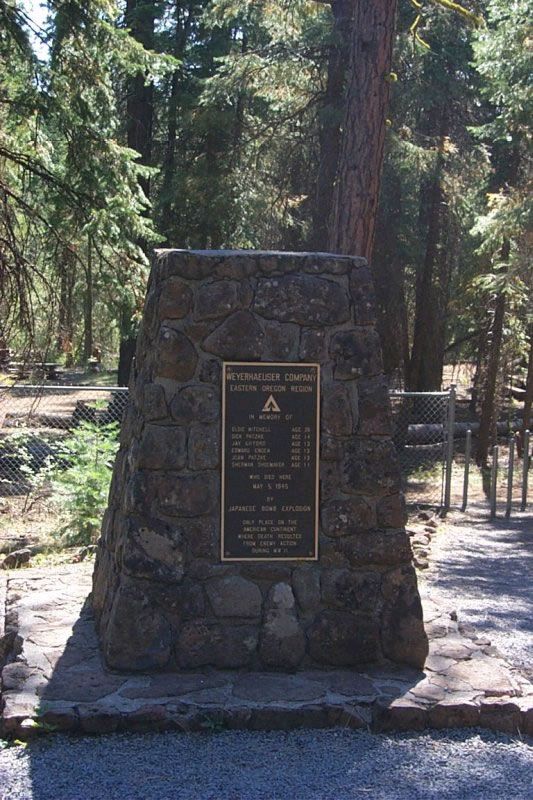 Between November 1944 and April 1945, the Japanese Navy launched over 9,000 fire balloons toward North America. Carried by the recently discovered Pacific jet stream, they were to sail over the Pacific Ocean and land in North America, where the Japanese hoped they would start forest fires and cause other damage. About three hundred were reported as reaching North America, but little damage was caused.
Near Bly, Oregon, six people (five children and a woman) became the only deaths due to an enemy balloon bomb attack in the United States when a balloon bomb exploded.
Between November 1944 and April 1945, the Japanese Navy launched over 9,000 fire balloons toward North America. Carried by the recently discovered Pacific jet stream, they were to sail over the Pacific Ocean and land in North America, where the Japanese hoped they would start forest fires and cause other damage. About three hundred were reported as reaching North America, but little damage was caused.
Near Bly, Oregon, six people (five children and a woman) became the only deaths due to an enemy balloon bomb attack in the United States when a balloon bomb exploded.555th Parachute Infantry Battalion
The 555th Parachute Infantry Battalion, nicknamed The Triple Nickles, was an all-black airborne unit of the United States Army during World War II.
History Activation
The unit was activated as a result of a recommendation made in December 1942 b ...
died while responding to a fire in the Umpqua National Forest
Umpqua National Forest, in southern Oregon's Cascade Range, covers an area of in Douglas, Lane, and Jackson counties, and borders Crater Lake National Park. The four ranger districts for the forest are the Cottage Grove, Diamond Lake, North U ...
near Roseburg, Oregon
Roseburg is a city in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is in the Umpqua River Valley in southern Oregon and is the county seat and most populous city of Douglas County. Founded in 1851, the population was 23,683 at the 2020 census, making it the ...
, on August 6, 1945; other casualties of the 555th were two fractures and 20 other injuries.
Cancelled Axis operations
Germany
In 1940, the German Air Ministry
The Ministry of Aviation (german: Reichsluftfahrtministerium, abbreviated RLM) was a government department during the period of Nazi Germany (1933–45). It is also the original name of the Detlev-Rohwedder-Haus building on the Wilhelmstrasse ...
secretly requested designs from the major German aircraft companies for its ''Amerikabomber
The ''Amerikabomber'' () project was an initiative of the German Ministry of Aviation (''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'') to obtain a long-range strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designe ...
'' program, in which a long-range strategic bomber would strike the continental United States from the Azores
)
, motto=
( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem=( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
(more than away). Planning was complete in 1942 with the submittal of the program to Goering's RLM offices in March 1942, resulting in cogent piston-engined designs from Focke-Wulf
Focke-Wulf Flugzeugbau AG () was a German manufacturer of civil and military aircraft before and during World War II. Many of the company's successful fighter aircraft designs were slight modifications of the Focke-Wulf Fw 190. It is one of the ...
, Heinkel
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with ...
, Junkers
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer. It was founded there in Dessau, ...
and Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG () was a German share-ownership limited, aircraft manufacturing corporation named after its chief designer Willy Messerschmitt from mid-July 1938 onwards, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, in part ...
(who had built the ultra-long-range Messerschmitt Me 261 before WW II), but by mid-1944 the project had been abandoned as too expensive, with a serious increase in the need for defensive fighters, needing to come from Nazi Germany's by-then rapidly diminishing aviation production capacity.
Hitler had ordered that biological warfare should be studied only for the purpose of defending against it. The head of the Science Division of the Wehrmacht, Erich Schumann
Erich Schumann (5 January 1898 – 25 April 1985) was a German physicist who specialized in acoustics and explosives, and had a penchant for music. He was a general officer in the army and a professor at the University of Berlin and the Technic ...
, lobbied for Hitler to be persuaded otherwise: "America must be attacked simultaneously with various human and animal epidemic pathogens, as well as plant pests." The plans were never adopted because they were opposed by Hitler.
Italy
An Italian naval commander Junio Valerio Borghese
Junio Valerio Scipione Ghezzo Marcantonio Maria Borghese (6 June 1906 – 26 August 1974), nicknamed The Black Prince, was an Italian Navy commander during the regime of Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party and a prominent hard-line Fascist ...
devised a plan to attack New York harbor with midget submarines; however, as the tides of war changed against Italy, the plan was postponed and later scrapped.
Japan
Just after the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawa ...
, a force of seven Japanese submarines patrolled the United States West Coast. The Wolfpack made plans to bombard targets in California on Christmas Eve or Christmas Day of 1941. However, the attack was postponed to December 27 in order to avoid attacking during the Christian festival and offending German and Italian allies. Eventually the plan was canceled altogether for fears of American reprisal. In 1946, an unexploded Japanese torpedo was found near the Golden Gate Bridge
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean. The structure links the U.S. city of San Francisco, California—the northern tip of the San Francisco P ...
, and it has been interpreted as evidence of an attack, potentially targeting the bridge itself, in late December of 1941.
The Japanese constructed a plan early in the Pacific War to attack the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a Channel ( ...
, a vital water passage in Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
, used during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
primarily for the Allied supply effort. The Japanese attack was never launched because Japan suffered crippling naval losses at the beginning of conflict with the United States and United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
(See: Aichi M6A
The is a submarine-launched attack floatplane designed for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. It was intended to operate from I-400 class submarines whose original mission was to conduct aerial attacks against the United States.
...
).
The Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor ...
launched Project Z Project Z may refer to:
* Project Z (bomber project), a Japanese project of World War II
* Project Z (band), a band for which Jimmy Herring played
* Project Z, a development of the original Nissan Z-car
* ''Project Z'' (film), a Telugu-language ...
(also called the Z Bombers Project) in 1942, similar to the Nazi German Amerika Bomber project, to design an intercontinental bomber capable of reaching North America. The Project Z plane was to have six engines of 5,000 horsepower each; the Nakajima Aircraft Company
The was a prominent Japanese aircraft manufacturer and aviation engine manufacturer throughout World War II. It continues as the car and aircraft manufacturer Subaru.
History
The Nakajima Aircraft company was Japan's first aircraft manufac ...
quickly began developing engines for the plane, and proposed doubling HA-44 engines (the most powerful engine available in Japan) into a 36-cylinder engine. Designs were presented to the Imperial Japanese Army, including the Nakajima G10N, Kawasaki Ki-91, and Nakajima G5N. None developed beyond prototypes or wind tunnel models, save for the G5N. In 1945, the Z project and other heavy bomber projects were cancelled.
During the final months of World War II, Japan had planned to use bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as ...
as a biological weapon against U.S. civilians in San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
, during Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night
Operation PX, also known as Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night, was a planned Japanese military attack on civilians in the United States using biological weapons, devised during World War II. The proposal was for Imperial Japanese Navy submarine ...
. The plan was set to launch at night on September 22, 1945. However, it was shelved because Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945.
Other alarms
False alarms
These false alarms have generally been attributed to military and civilian inexperience with war and poor radars of the era. Critics have theorized they were a deliberate attempt by the Army to frighten the public in order to stimulate interest in war preparations.[The Virtual Museum of The City of San Francisco The Army Air Forces in World War II; Defense of the Western Hemisphere]
/ref>
Alerts following Pearl Harbor
On December 8, 1941, "rumors of an enemy carrier off the coast led to the closing of schools in Oakland, California
Oakland is the largest city and the county seat of Alameda County, California, United States. A major West Coast of the United States, West Coast port, Oakland is the largest city in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area, the third ...
," a blackout enforced by local wardens and radio silence followed that evening.[ The reports reaching Washington of an attack on San Francisco were regarded as credible.][ The affair was described as a test but Lt. Gen. John L. DeWitt of the ]Western Defense Command
Western Defense Command (WDC) was established on 17 March 1941 as the command formation of the United States Army responsible for coordinating the defense of the Pacific Coast region of the United States during World War II. A second major respo ...
said "Last night there were planes over this community. They were enemy planes! I mean Japanese planes! And they were tracked out to sea. You think it was a hoax? It is damned nonsense for sensible people to assume that the Army and Navy would practice such a hoax on San Francisco."[ Rumors continued on the West Coast in the following days. An alert of a similar nature occurred in the Northeast on December 9.][ "At noon advices were received that hostile planes were only two hours' distance away."][ Although there was no general hysteria, fighter aircraft from ]Mitchel Field
Mitchell may refer to:
People
*Mitchell (surname)
* Mitchell (given name)
Places Australia
* Mitchell, Australian Capital Territory, a light-industrial estate
* Mitchell, New South Wales, a suburb of Bathurst
* Mitchell, Northern Terri ...
on Long Island took the air to intercept the "raiders". Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for ...
had its worst sell off since the Fall of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second Wo ...
, school children in New York City were sent home and several radio stations left the air.[ In Boston police shifted heavy stores of guns and ammunition from storage vaults to stations throughout the city, and industrial establishments were advised to prepare for a raid.][
]
Battle of Los Angeles
The Battle of Los Angeles, also known as "The Great Los Angeles Air Raid", is the name given by contemporary sources to the imaginary enemy attack and subsequent anti-aircraft artillery barrage which took place in 1942 from February 24 and early on February 25 over Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the wor ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
.Secretary of the Navy
The secretary of the Navy (or SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department (component organization) within the United States Department of Defense.
By law, the se ...
Frank Knox
William Franklin Knox (January 1, 1874 – April 28, 1944) was an American politician, newspaper editor and publisher. He was also the Republican vice presidential candidate in 1936, and Secretary of the Navy under Franklin D. Roosevelt duri ...
speaking at a press conference shortly afterward called the incident a "false alarm." Newspapers of the time published a number of sensational reports and speculations of a cover-up to conceal an actual invasion by enemy airplanes. When documenting the incident in 1983, the U.S. Office of Air Force History attributed the event to a case of "war nerves" likely triggered by a lost weather balloon
A weather balloon, also known as sounding balloon, is a balloon (specifically a type of high-altitude balloon) that carries instruments aloft to send back information on atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity and wind speed by means of ...
and exacerbated by stray flares and shell bursts from adjoining batteries.
Minor alerts
1942
In May and June the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Gov ...
underwent a series of alerts:
*May 12: A twenty-five-minute air-raid alert.
*May 27: West Coast defenses put on alert after Army codebreakers
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic sec ...
learned that the Japanese intended a series of hit-and-run attack
Hit-and-run tactics are a tactical doctrine of using short surprise attacks, withdrawing before the enemy can respond in force, and constantly maneuvering to avoid full engagement with the enemy. The purpose is not to decisively defeat the ene ...
s in reprisal for the Doolittle Raid
The Doolittle Raid, also known as the Tokyo Raid, was an air raid on 18 April 1942 by the United States on the Japanese capital Tokyo and other places on Honshu during World War II. It was the first American air operation to strike the Japan ...
.
*May 31: The battleships and USS ''Maryland'' set sail from the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by ...
to form a line of defense against any Japanese attack mounted on San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
.
*June 2: A nine-minute air-raid alert, including at 9:22 pm a radio silence
In telecommunications, radio silence or Emissions Control (EMCON) is a status in which all fixed or mobile radio stations in an area are asked to stop transmitting for safety or security reasons.
The term "radio station" may include anything ca ...
order applied to all radio station
Radio broadcasting is transmission of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radi ...
s from Mexico to Canada.
See also
* American Theater (1914–1918)
*Amerikabomber
The ''Amerikabomber'' () project was an initiative of the German Ministry of Aviation (''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'') to obtain a long-range strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designe ...
*Battle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blocka ...
* (discovered off Massachusetts)
* (destroyed off Rhode Island)
* (destroyed off New Jersey)
*Greenland in World War II
The fall of Denmark in April 1940 left the Danish colony of Greenland an unoccupied territory of an occupied nation, under the possibility of seizure by the United Kingdom, United States or Canada. To forestall this, the United States acted to ...
* List of Japanese spies, 1930–45
*Invasion of the United States
The concept of an invasion of the United States relates to military theory and doctrine which address the feasibility and practicality of a foreign power attacking and successfully invading the United States. The country has been physically invade ...
*Operation Pastorius
Operation Pastorius was a failed German intelligence plan for sabotage inside the United States during World War II. The operation was staged in June, 1942 and was to be directed against strategic American economic targets. The operation was n ...
*Project Z Project Z may refer to:
* Project Z (bomber project), a Japanese project of World War II
* Project Z (band), a band for which Jimmy Herring played
* Project Z, a development of the original Nissan Z-car
* ''Project Z'' (film), a Telugu-language ...
*List of theaters and campaigns of World War II
The List of theatres and campaigns of World War II subdivides military operations of World War II and contemporary wars by war, then by theater and then by campaign.
Pre–World War II
Asia
* Japanese invasion of Manchuria (September 18, 19 ...
Notes
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*Dobbs, Michael. ''Saboteurs: The Nazi Raid on America'' (2004)
*Duffy, J.P. ''Target: America: Hitler's Plan to Attack the United States'', Praeger Publishers; PB: The Lyons Press (A Booklist
''Booklist'' is a publication of the American Library Association that provides critical reviews of books and audiovisual materials for all ages. ''Booklist''s primary audience consists of libraries, educators, and booksellers. The magazine is av ...
br>review
*Gimpel, Erich. ''Agent 146: The True Story of a Nazi Spy in America'' (2003)
*Griehl, Manfred. ''Luftwaffe over America: The Secret Plans to Bomb the United States in World War II'' (2004)
*
*
*Mikesh, Robert C. ''Japan's World War II Balloon Bomb Attacks on North America'', Smithsonian Institution Press, (1973)
*
*O'Donnell, Pierce, ''In Time of War: Hitler's Terrorist Attack on America'' (Operation Pastorius), The New Press, 2005
* Webber, Bert. ''Silent Siege: Japanese Attacks Against North America in World War II'', Ye Galleon Press, Fairfield, Washington (1984). (hardcover). (paperbound).
External links
History.army.mil: Defense of Americas
— publication of the United States Army Center of Military History
The United States Army Center of Military History (CMH) is a directorate within the United States Army Training and Doctrine Command. The Institute of Heraldry remains within the Office of the Administrative Assistant to the Secretary of the A ...
.
History.army.mil: American Theater Army Responses
* ttp://www.history.navy.mil/faqs/faq114-2.htm History.navy.mil: German Sabotage operationsbr>Regiamarina.net: "Planned Italian attack on New York harbor"
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20170911193528/http://alaskainvasion.com/ Alaskainvasion.com: "Red White Black & Blue"– feature documentary about the World War II Battle of Attu in the Aleutians.
Uboat.net: The Battle of the St. Lawrence
{{Authority control
Theaters and campaigns of World War II
Military history of North America
Military history of the Caribbean
Military history of South America
Battle of the Atlantic
.
Military history of Canada during World War II
Military history of Germany during World War II
Military history of Japan during World War II
Military history of the United States during World War II
 ''See also
''See also  U-boat operations in the region (centered in the
U-boat operations in the region (centered in the  Even before the war, a large Nazi spy ring was found operating in the United States. The Duquesne Spy Ring is still the largest espionage case in United States history that ended in convictions. The 33 German agents who formed the Duquesne spy ring were placed in key jobs in the United States to get information that could be used in the event of war and to carry out acts of sabotage. One man opened a restaurant and used his position to get information from his customers; another worked at an airline so he could report Allied ships crossing the
Even before the war, a large Nazi spy ring was found operating in the United States. The Duquesne Spy Ring is still the largest espionage case in United States history that ended in convictions. The 33 German agents who formed the Duquesne spy ring were placed in key jobs in the United States to get information that could be used in the event of war and to carry out acts of sabotage. One man opened a restaurant and used his position to get information from his customers; another worked at an airline so he could report Allied ships crossing the  In November 1942, sank two iron ore freighters and damaged another off Bell Island in Conception Bay,
In November 1942, sank two iron ore freighters and damaged another off Bell Island in Conception Bay, 
 Before Operation MI could be carried out, the Japanese decided to take the Aleutian Islands. On June 3–4, 1942, Japanese planes from two light carriers and struck the U.S. against the city of
Before Operation MI could be carried out, the Japanese decided to take the Aleutian Islands. On June 3–4, 1942, Japanese planes from two light carriers and struck the U.S. against the city of  The United States continent was first shelled by the Axis on February 23, 1942, when the attacked the
The United States continent was first shelled by the Axis on February 23, 1942, when the attacked the  The Lookout Air Raids occurred on September 9, 1942. The second location to be subject to
The Lookout Air Raids occurred on September 9, 1942. The second location to be subject to  Between November 1944 and April 1945, the Japanese Navy launched over 9,000 fire balloons toward North America. Carried by the recently discovered Pacific jet stream, they were to sail over the Pacific Ocean and land in North America, where the Japanese hoped they would start forest fires and cause other damage. About three hundred were reported as reaching North America, but little damage was caused.
Near Bly, Oregon, six people (five children and a woman) became the only deaths due to an enemy balloon bomb attack in the United States when a balloon bomb exploded. The site is marked by a stone monument at the Mitchell Recreation Area in the Fremont-Winema National Forest.
A fire balloon is also considered to be a possible cause of the third fire in the Tillamook Burn in Oregon. One member of the
Between November 1944 and April 1945, the Japanese Navy launched over 9,000 fire balloons toward North America. Carried by the recently discovered Pacific jet stream, they were to sail over the Pacific Ocean and land in North America, where the Japanese hoped they would start forest fires and cause other damage. About three hundred were reported as reaching North America, but little damage was caused.
Near Bly, Oregon, six people (five children and a woman) became the only deaths due to an enemy balloon bomb attack in the United States when a balloon bomb exploded. The site is marked by a stone monument at the Mitchell Recreation Area in the Fremont-Winema National Forest.
A fire balloon is also considered to be a possible cause of the third fire in the Tillamook Burn in Oregon. One member of the