Amazonas Basin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
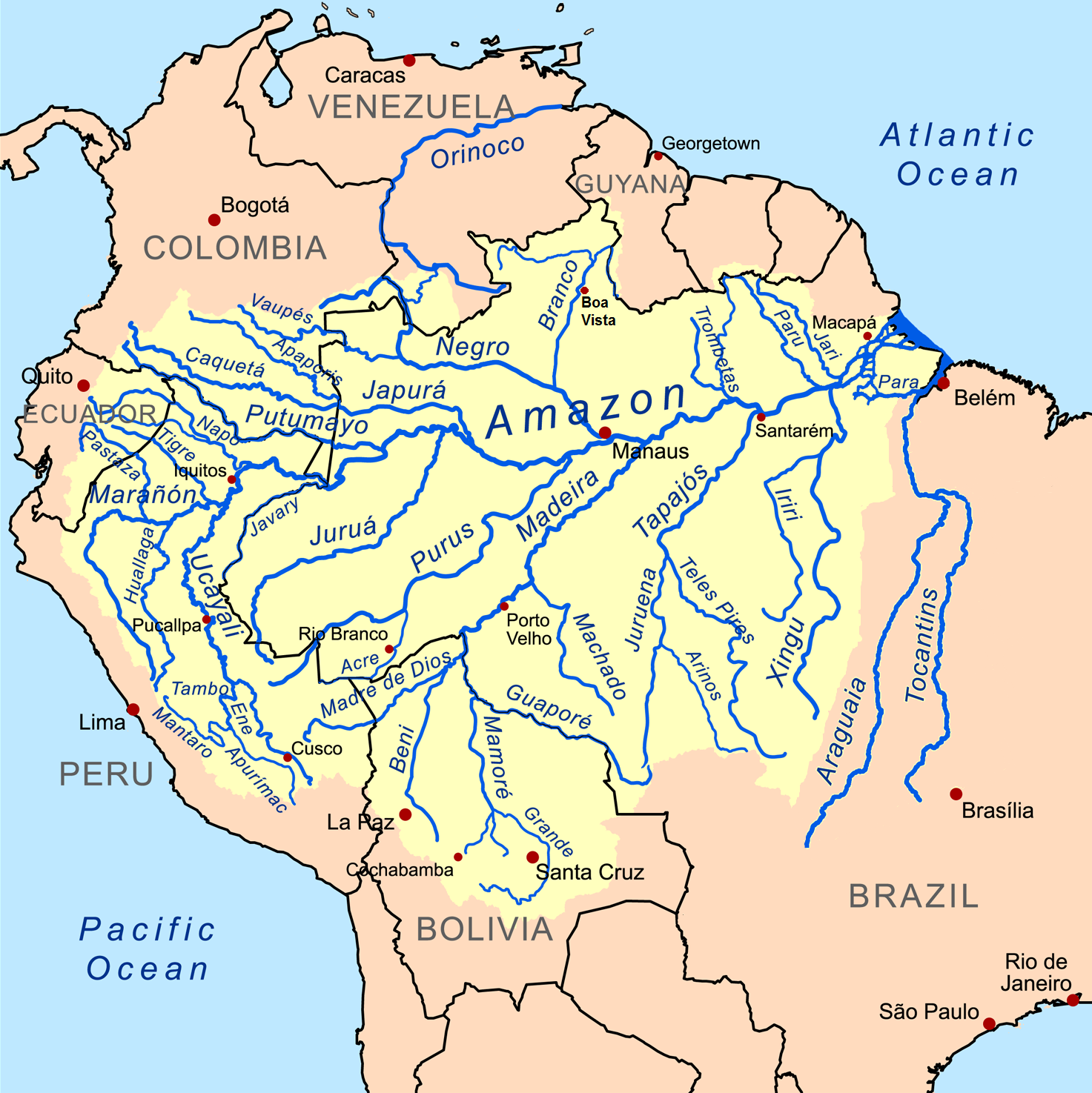
 The Amazon basin is the part of
The Amazon basin is the part of
 Plant growth is quite dense and its variety of animal inhabitants is comparatively high due to the heavy rainfall and the dense and extensive
Plant growth is quite dense and its variety of animal inhabitants is comparatively high due to the heavy rainfall and the dense and extensive
 The Amazon River basin has a low-water season (known popularly as summer), and a wet season (known popularly as winter) during which, the rivers
The Amazon River basin has a low-water season (known popularly as summer), and a wet season (known popularly as winter) during which, the rivers
 Many tribal groups live in the Amazon Basin, often in relative isolation. It is estimated 400 or more tribal groups have lived in the Amazon Basin for hundreds of years with their own culture, language, and lifestyle. Today total population of Amazon basin is 1.5 million distributed. There are an estimated 100 uncontacted tribal groups.
The largest organization fighting for the
Many tribal groups live in the Amazon Basin, often in relative isolation. It is estimated 400 or more tribal groups have lived in the Amazon Basin for hundreds of years with their own culture, language, and lifestyle. Today total population of Amazon basin is 1.5 million distributed. There are an estimated 100 uncontacted tribal groups.
The largest organization fighting for the
"Amazon"
(2015). Center for InterAmerican Studies, University Bielefeld. *
Herndon and Gibbon Lieutenants United States Navy
��An except from the book ''The First North American Explorers of the Amazon Valley'', by historian Normand E. Klare. Actual reports from the explorers are compared with present Amazon basin conditions.
by ''
"The Course of the River of the Amazons, Based on the Account of Christopher d'Acugna"
from 1680 (map {{Coord, 2.3096, S, 54.8881, W, source:wikidata, display=title

 The Amazon basin is the part of
The Amazon basin is the part of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
. The Amazon drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
, Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
, Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
, Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
, Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
, and Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
, as well as the territory of French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
.
Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest
Tropical forests are forested ecoregions with tropical climates – that is, land areas approximately bounded by the Tropic of Cancer, tropics of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing ...
, it is the largest rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
in the world.
Geography
The Amazon River begins in theAndes Mountains
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18°S ...
at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá
Yerupajá is a mountain of the Huayhuash mountain range in west central Peru, part of the Andes. It is located at Áncash, Bolognesi Province, Lauricocha Province. At (other sources: ) it is the second-highest in Peru and the highest in the ...
at .
The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from the Guyana Plateau in the north to the Brazilian Plateau in the south.
With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
, but debate about its exact length continues.
The Amazon system transports the largest volume of water of any river system, accounting for about 20% of the total water carried to the oceans by rivers. Some of the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
s are deforested
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
because of an increase in cattle ranches and soybean fields. The Amazon basin formerly flowed west to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
until the Andes formed, causing the basin to flow eastward towards the Atlantic Ocean.
Politically the basin is divided into Peruvian Amazonia
Peruvian Amazonia (), informally known locally as the Peruvian jungle () or just the jungle (), is the area of the Amazon rainforest in Peru, east of the Andes and Peru's borders with Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, and Bolivia. Peru has the second-l ...
, Amazônia Legal
Brazil's Legal Amazon (abbreviation BLA), in Portuguese Amazônia Legal (), is the largest socio-geographic division in Brazil, containing all nine states in the Amazon basin. The government designated this region in 1948 based on its studies o ...
of Brazil, the Amazon natural region of Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
, Amazonas (Venezuelan state)
Amazonas State (, ) is one of States of Venezuela, the 23 states into which Venezuela is divided. It covers nearly a fifth of the area of Venezuela, but has less than 1% of Venezuela's population.
The state capital is Puerto Ayacucho. The capita ...
, and parts of Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
and Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
.
Plant life
evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has Leaf, foliage that remains green and functional throughout the year. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which lose their foliage completely during the winter or dry season. Consisting of many diffe ...
and coniferous forest
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
s. Little sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
reaches the ground due to the dense roof of canopy by plants. The ground remains dark and damp and only shade-tolerant vegetation will grow here. Orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Eart ...
s and bromeliad
The Bromeliaceae (the bromeliads) are a Family (biology), family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the Tropics, tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and on ...
s exploit trees and other plants to get closer to the sunlight. They grow hanging onto the branches or tree trunks with aerial roots, not as parasites but as epiphyte
An epiphyte is a plant or plant-like organism that grows on the surface of another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphyt ...
s. Species of tropical trees native to the Amazon include Brazil nut
The Brazil nut (''Bertholletia excelsa'') is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and it is also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds. It is one of the largest and longest-lived trees in the Amazon rainforest. ...
, rubber tree and Assai palm.
Wildlife
Mammals
More than 1,400 species ofmammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s are found in the Amazon, the majority of which are species of bat
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out ...
s and rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s. Its larger mammals include the jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large felidae, cat species and the only extant taxon, living member of the genus ''Panthera'' that is native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the biggest cat spe ...
, ocelot
The ocelot (''Leopardus pardalis'') is a medium-sized spotted Felidae, wild cat that reaches at the shoulders and weighs between on average. It is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central America, Central and South America, ...
, capybara
The capybara or greater capybara (''Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris'') is the largest living rodent, native to South America. It is a member of the genus '' Hydrochoerus''. The only other extant member is the lesser capybara (''Hydrochoerus isthmi ...
, puma and South American tapir.
Birds
About 1,500bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
species inhabit the Amazon basin. The biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
of the Amazon and the sheer number of diverse bird species is given by the number of different bird families that reside in these humid forests. An example of such would be the cotinga family, to which the Guianan cock-of-the-rock belong. Birds such as toucan
Toucans (, ) are Neotropical birds in the family Ramphastidae. They are most closely related to the Semnornis, Toucan barbets. They are brightly marked and have large, often colorful Beak, bills. The family includes five genus, genera and over ...
s, and hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With approximately 366 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but most species are found in Cen ...
s are also found here. Macaw
Macaws are a group of Neotropical parrot, New World parrots that are long-tailed and often colorful, in the Tribe (biology), tribe Arini (tribe), Arini. They are popular in aviculture or as companion parrots, although there are conservation con ...
s are famous for duck gathering by the hundreds along the clay cliffs of the Amazon River. In the western Amazon hundreds of macaw
Macaws are a group of Neotropical parrot, New World parrots that are long-tailed and often colorful, in the Tribe (biology), tribe Arini (tribe), Arini. They are popular in aviculture or as companion parrots, although there are conservation con ...
s and other parrot
Parrots (Psittaciformes), also known as psittacines (), are birds with a strong curved beak, upright stance, and clawed feet. They are classified in four families that contain roughly 410 species in 101 genus (biology), genera, found mostly in ...
s descend to exposed river banks to consume clay on an almost daily basis, the exception being rainy days.
Reptiles
The green anaconda inhabits the shallow waters of the Amazon and the emerald tree boa andboa constrictor
The boa constrictor (scientific name also ''Boa constrictor''), also known as the common boa, is a species of large, non-venomous, heavy-bodied snake that is frequently kept and bred in captivity. The boa constrictor is a member of the Family (b ...
live in the Amazonian tree tops.
Many reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
species are illegally collected and exported for the international pet trade. Live animals are the fourth largest commodity in the smuggling industry after drugs, diamonds and weapons.
Amphibians
More than 1,500 species ofamphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s swim and are found in the Amazon. Unlike temperate frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely semiaquatic group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian vertebrates composing the order (biology), order Anura (coming from the Ancient Greek , literally 'without tail'). Frog species with rough ski ...
s which are mostly limited to habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
s near the water, tropical frogs are most abundant in the trees and relatively few are found near bodies of water on the forest floor
The forest floor, also called detritus or wikt:duff#Noun 2, duff, is the part of a forest ecosystem that mediates between the living, aboveground portion of the forest and the mineral soil, principally composed of dead and decaying plant matter ...
. The reason for this occurrence is quite simple: frogs must always keep their skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
moist since almost half of their respiration is carried out through their skin. The high humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
of the rainforest and frequent rainstorm
Rain is a form of precipitation where water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. ...
s gives tropical frogs infinitely more freedom to move into the trees and escape the many predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s of rainforest waters. The differences between temperate and tropical frogs extend beyond their habitat.
Fish
About 2,500fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
species are known from the Amazon basin and it is estimated that more than 1,000 additional undescribed species
In taxonomy, an undescribed taxon is a taxon (for example, a species) that has been discovered, but not yet formally described and named. The various Nomenclature Codes specify the requirements for a new taxon to be validly described and named. U ...
exist. This is more than any other river basin on Earth, and Amazonia is the center of diversity for Neotropical fishes. About 45% (more than 1,000 species) of the known Amazonian fish species are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to the basin. The remarkable species richness can in part be explained by the large differences between the various parts of the Amazon basin, resulting in many fish species that are endemic to small regions. For example, fauna in clearwater rivers differs from fauna in white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
and blackwater river
A blackwater river is a type of River#Classification, river with a slow-moving channel flowing through forested swamps or wetlands. Most major blackwater rivers are in the Amazon Basin and the Southern United States. The term is used in fluvial ...
s, fauna in slow moving sections show distinct differences compared to that in rapids
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep stream gradient, gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Flow, gradient, constriction, and obstacles are four factors that are needed for a rapid t ...
, fauna in small streams differ from that in major rivers, and fauna in shallow sections show distinct differences compared to that in deep parts.Duncan, W.P.; and Fernandes, M.N. (2010). ''Physicochemical characterization of the white, black, and clearwater rivers of the Amazon Basin and its implications on the distribution of freshwater stingrays (Chondrichthyes, Potamotrygonidae).'' PanamJAS 5(3): 454–464. By far the most diverse orders in the Amazon are Characiformes
Characiformes is an order of ray-finned fish, comprising the characins and their allies. Grouped in 18 recognized families, more than 2000 different species are described, including the well-known piranha and tetras.; Buckup P.A.: "Relationsh ...
(43% of total fish species in the Amazon) and Siluriformes (39%), but other groups with many species include Cichlidae
Cichlids ()
are a large, diverse, and widespread family of percomorph fish in the family Cichlidae, order Cichliformes. At least 1,760 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families, with on ...
(6%) and Gymnotiformes (3%).
In addition to major differences in behavior and ecology, Amazonian fish vary extensively in form and size. The largest, the arapaima
The arapaima, pirarucu, or paiche is any large species of bonytongue in the genus ''Arapaima'' native to the Amazon Basin, Amazon and Essequibo River, Essequibo basins of South America. ''Arapaima'' is the type genus of the subfamily Arapaiminae ...
and piraiba can reach or more in length and up to in weight, making them some of the largest strict freshwater fish in the world. The bull shark
The bull shark (''Carcharhinus leucas''), also known as the Zambezi shark (informally zambi) in Africa and Lake Nicaragua shark in Nicaragua, is a species of requiem shark commonly found worldwide in warm, shallow waters along coasts and in riv ...
and common sawfish, which have been recorded far up the Amazon, may reach even greater sizes, but they are euryhaline
Euryhaline organisms are able to adapt to a wide range of salinities. An example of a euryhaline fish is the short-finned molly, '' Poecilia sphenops'', which can live in fresh water, brackish water, or salt water.
The green crab ('' Carcinus m ...
and often seen in marine waters. In contrast to the giants, there are Amazonian fish from several families that are less than long. The smallest are likely the '' Leptophilypnion'' sleeper gobies, which do not surpass and are among the smallest fish in the world.
The Amazon supports very large fisheries, including well-known species of large catfish (such as '' Brachyplatystoma'', which perform long breeding migrations up the Amazon), arapaima
The arapaima, pirarucu, or paiche is any large species of bonytongue in the genus ''Arapaima'' native to the Amazon Basin, Amazon and Essequibo River, Essequibo basins of South America. ''Arapaima'' is the type genus of the subfamily Arapaiminae ...
and tambaqui
The tambaqui (''Colossoma macropomum'') is a large species of freshwater fish in the family Serrasalmidae. It is native to tropical South America, but kept in aquaculture and Introduced species, introduced elsewhere. It is also known by the names ...
, and is also home to many species that are important in the aquarium trade, such as the oscar
Oscar, OSCAR, or The Oscar may refer to:
People and fictional and mythical characters
* Oscar (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters named Oscar, Óscar or Oskar
* Oscar (footballer, born 1954), Brazilian footballer ...
, discus, angelfish, ''Corydoras'' catfish and neon tetra
The neon tetra (''Paracheirodon innesi'') is a freshwater fish of the characin family (family Characidae) of order Characiformes. The type species of its genus, it is native to blackwater and clearwater streams in the Amazon basin of South Am ...
. Although the true danger they represent often is greatly exaggerated, the Amazon basin is home to several feared fish species such as piranha
A piranha (, or ; ) is any of a number of freshwater fish species in the subfamily Serrasalminae, of the family Serrasalmidae, in the order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, floodplains, lakes and reservoirs. Although ...
s (including the famous red-bellied), electric eel
The electric eels are a genus, ''Electrophorus'', of neotropical freshwater fish from South America in the family Gymnotidae, of which they are the only members of the subfamily Electrophorinae. They are known for their electric fish, ability ...
, river stingrays and candiru.
Several cavefish
Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, Troglomorphism, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreat ...
species in the genus '' Phreatobius'' are found in the Amazon, as is the cave-dwelling '' Astroblepus pholeter'' in the far western part of the basin (Andean region). The Tocantins
Tocantins () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is the newest state, formed in 1988 and encompassing what had formerly been the northern two-fifths of the state of Goiás. Tocantins covers and had an estimated population of 1,496,880 in 2014 ...
basin, arguably not part of the Amazon basin, has several other cavefish species. The deeper part of the major Amazonian rivers are always dark and a few species have adaptions similar to cavefish (reduced pigment and eyes). Among these are the knifefish '' Compsaraia'' and '' Orthosternarchus'', some '' Cetopsis'' whale catfish (especially ''C. oliveirai''), some ''Xyliphius
''Xyliphius'' is a genus of banjo catfishes from South America.
This genus appears to be widespread in the Magdalena, Orinoco, Amazon, and Paraguay-Paraná River systems where they are most common in deeper waters.
''Xyliphius'' includes mod ...
'' and ''Micromyzon
''Micromyzon'' is a genus of tiny catfish in the family Aspredinidae native to relatively deep parts of the Amazon and Orinoco basins in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Sou ...
'' banjo catfish, and the loricariid catfish '' Loricaria spinulifera'', ''L. pumila'', '' Peckoltia pankimpuju'', '' Panaque bathyphilus'' and '' Panaqolus nix'' (these five also occur in "normal" forms of shallower waters). The perhaps most unusual habitat used by Amazonian fish is land. The splash tetra is famous for laying its eggs on plants above water, keeping them moist by continuously splashing on them, the South American lungfish
The South American lungfish (''Lepidosiren paradoxa''), also known as the American mud-fish and scaly salamanderfish, is the single species of lungfish found in swamps and slow-moving waters of the Amazon Basin, Amazon, Paraguay River, Paraguay, ...
can survive underground in a mucous cocoon during the dry season, some small rivulid killifish can jump over land between water sources (sometimes moving relatively long distances, even uphill) and may deliberately jump onto land to escape aquatic predators, and an undescribed species
In taxonomy, an undescribed taxon is a taxon (for example, a species) that has been discovered, but not yet formally described and named. The various Nomenclature Codes specify the requirements for a new taxon to be validly described and named. U ...
of worm-like ''Phreatobius'' catfish lives in waterlogged leaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall, or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that has fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituen ...
near (not in) streams.
Some of the major fish groups of the Amazon basin include:
* Order Gymnotiformes: Neotropical electric fishes
* Order Characiformes
Characiformes is an order of ray-finned fish, comprising the characins and their allies. Grouped in 18 recognized families, more than 2000 different species are described, including the well-known piranha and tetras.; Buckup P.A.: "Relationsh ...
: characins, tetras and relatives
* Family Potamotrygonidae
River stingrays or freshwater stingrays are Neotropical freshwater fishes of the family (biology), family Potamotrygonidae in the Order (biology), order Myliobatiformes, one of the four orders of Batoidea, batoids, cartilaginous fishes related to ...
: river stingrays
* Family Arapaimidae: bonytongues
* Family Loricariidae
Loricariidae is the largest family (biology), family of catfish (order Siluriformes), with over 90 genus, genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South A ...
: suckermouth catfishes
* Family Callichthyidae: armored catfishes
* Family Pimelodidae: pimelodid catfishes
* Family Trichomycteridae: pencil catfishes
* Family Auchenipteridae: driftwood catfishes
* Subfamily Cichlinae
The Cichlinae are a subfamily of fishes in the Cichlidae, cichlid family, native to Centra America, Central and South America.
This subfamily consists of approximately 117 described species as of July 2017. Some authors have suggested that the ...
: pike cichlids, peacock cichlids and relatives
* Subfamily Geophaginae: Eartheaters and Neotropical dwarf cichlid
* Subfamily Poeciliinae: guppies and relatives
Insects
More than 90% of the animal species in the Amazon areinsect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s, of which about 40% are beetle
Beetles are insects that form the Taxonomic rank, order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 40 ...
s (Coleoptera constituting almost 25% of all known types of animal life-forms.) Powell (2009)
Whereas all of Europe has some 321 butterfly
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossi ...
species, the Manú National Park in Peru (4,000 hectare-survey) has 2,300 species, while Tambopata National Reserve (5,500 hectare-survey) has at least 1,231 species.
Climate
 The Amazon River basin has a low-water season (known popularly as summer), and a wet season (known popularly as winter) during which, the rivers
The Amazon River basin has a low-water season (known popularly as summer), and a wet season (known popularly as winter) during which, the rivers flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
the adjacent, low-lying forests. The climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
of the basin is generally hot and humid. In some areas, however, the summer months (June–September) can bring cold snaps, fueled by Antarctic winds traveling along the adjacent mountain range. The average annual temperature is around 25-degree and 28
degree Celsius with little to no distinction between summer and winter season.
Human lifestyle
Amazonia is scarcely populated. There are scattered settlements inland, but most of the population lives in a few larger cities on the banks of the Amazon and other major rivers, such as inIquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province, Peru, Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the List of cities in Peru, ninth-most populous city in Peru ...
– Loreto in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, Manaus
Manaus () is the List of capitals of subdivisions of Brazil, capital and largest city of the States of Brazil, Brazilian state of Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas. It is the List of largest cities in Brazil, seventh-largest city in Brazil, w ...
- Amazonas State, and Belém
Belém (; Portuguese for Bethlehem; initially called Nossa Senhora de Belém do Grão-Pará, in English Our Lady of Bethlehem of Great Pará), often called Belém of Pará, is the capital and largest city of the state of Pará in the north of B ...
, Pará
Pará () is a Federative units of Brazil, state of Brazil, located in northern Brazil and traversed by the lower Amazon River. It borders the Brazilian states of Amapá, Maranhão, Tocantins (state), Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Amazonas (Brazilian st ...
. In many regions, the forest has been cleared for soya bean plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
s and ranching
A ranch (from /Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of farm. These terms are most often applied to li ...
(the most extensive non-forest use of the land); some of the inhabitants harvest wild rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
, and Brazilian nuts. This is a form of extractive farms, where the trees are not cut down. These are relatively sustainable operations in contrast to lumbering or agriculture dependent on clearing the rainforest. The people live in thatched houses shaped liked beehives. They also build apartment-like houses called " Maloca", with a steeply slanting roof.
Languages
The most widely spoken languages in the Amazon are Portuguese and Spanish. There are hundreds ofnative languages
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers ...
still spoken in the Amazon, most of which are critically endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
.
Indigenous peoples
 Many tribal groups live in the Amazon Basin, often in relative isolation. It is estimated 400 or more tribal groups have lived in the Amazon Basin for hundreds of years with their own culture, language, and lifestyle. Today total population of Amazon basin is 1.5 million distributed. There are an estimated 100 uncontacted tribal groups.
The largest organization fighting for the
Many tribal groups live in the Amazon Basin, often in relative isolation. It is estimated 400 or more tribal groups have lived in the Amazon Basin for hundreds of years with their own culture, language, and lifestyle. Today total population of Amazon basin is 1.5 million distributed. There are an estimated 100 uncontacted tribal groups.
The largest organization fighting for the indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
in this area is COICA. It is a supra organization encompassing all indigenous rights organizations working in the Amazon basin area, and covers the people living in several countries.
River commerce
The river is the principal path of transportation for people and produce in the regions, with transport ranging from balsaraft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barre ...
s and dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed-out tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (tr ...
s to hand built wooden river craft and modern steel hulled craft.
Agriculture
Seasonal floods excavate and redistribute nutrient-rich silt onto beaches and islands, enabling dry-season riverside agriculture of rice, beans, and corn on the river's shoreline without the addition of fertilizer, with additionalslash and burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a form of shifting cultivation that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. T ...
agriculture on higher floodplains. Fishing provides additional food year-round, and free-range chickens need little or no food beyond what they can forage locally. Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
made largely from forest and shoreline deadfall is produced for use in urban areas. Exploitation of bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are Hunting, hunted for human consumption. Bushmeat represents a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity in poor and rural communities of humid tropical forest regions of the worl ...
, particularly deer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) ...
and turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Crypt ...
s is common.
Extensive deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, particularly in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, is leading to the extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
of known and unknown species, reducing biological diversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distributed evenly on Eart ...
and adversely impacting soil, water, and air quality. A final part of the deforestation process is the large-scale production of charcoal for industrial processes such as steel manufacturing. Soils within the region are generally shallow and cannot be used for more than a few seasons without the addition of imported fertilizers and chemicals.
Global ecological role / Function for climate change
"Over past 20 years (2021), the Brazilian Amazon emitted 13% more CO2 than it absorbed". "Amazon biodiversity also plays a critical role as part of global systems, influencing the globalcarbon cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycl ...
and thus climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, as well as hemispheric hydrological systems, serving as an important anchor for South American climate and rainfall. It also produces 20% oxygen of the Earth."
See also
* Amazon biome * Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization * Amazon Conservation Association * Amazon Conservation Team *Deforestation of the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, spanning an area of 3,000,000 km2 (1,200,000 sq mi), is the world's largest rainforest. It encompasses the largest and most biodiverse tropical rainforest on the planet, representing over half of all rainforests. The ...
* Llanos de Moxos
* Llanos de Moxos (archaeology)
* Ucayali Peneplain
* Pre-Columbian agriculture in the Amazon Basin
References
Further reading
* Acker, Antoine"Amazon"
(2015). Center for InterAmerican Studies, University Bielefeld. *
External links
Herndon and Gibbon Lieutenants United States Navy
��An except from the book ''The First North American Explorers of the Amazon Valley'', by historian Normand E. Klare. Actual reports from the explorers are compared with present Amazon basin conditions.
by ''
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington m ...
''
"The Course of the River of the Amazons, Based on the Account of Christopher d'Acugna"
from 1680 (map {{Coord, 2.3096, S, 54.8881, W, source:wikidata, display=title