Altishahr on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Altishahr (, , ;
4 n.10
/ref> The ''Altishahr'' term was used by Turkic-speaking inhabitants of the Tarim Basin in the 18th and 19th century, and adopted by some Western sources in the 19th century. Other local words for the region included Dorben Shahr ('Four Cities') and Yeti Shahr ('Seven Cities'). Another Western term for the same region is Kashgaria.
 In the 18th century, prior to the Qing conquest of Xinjiang in 1759, the oasis towns around the Tarim did not have a single political structure governing them, and Altishahr referred to the region in general rather than any cities in particular. Bellér-Hann 2008
In the 18th century, prior to the Qing conquest of Xinjiang in 1759, the oasis towns around the Tarim did not have a single political structure governing them, and Altishahr referred to the region in general rather than any cities in particular. Bellér-Hann 2008
39 nn.7 & 8
/ref> Foreign visitors to the region would attempt to identify the cities, offering various lists. According to Albert von Le Coq, the 'Six Cities' (''Altishahr'') referred to (1)

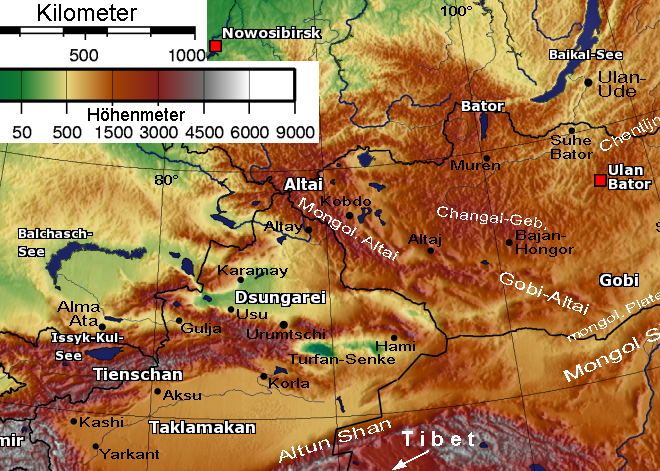 Altishahr refers to the
Altishahr refers to the
p. 2.Martin 1847
p. 21.''The Encyclopædia Britannica: A Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, and General Literature, Volume 23'' 1852
p. 681. although both were under control of the
Modular History: Identity Maintenance before Uyghur Nationalism
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Regions of China History of Xinjiang
romanized
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and ...
: ''Altä-şähär'' or ''Alti-şähär''), also known as Kashgaria, is a historical name for the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
region used in the 18th and 19th centuries. The term means 'Six Cities' in Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
, referring to oasis towns along the rim of the Tarim, including Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
, in what is now southern Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
Etymology
The name Altishahr is derived from the Turkic word ''alti'' ('six') and Persian word ''shahr'' ('city'). Newby 20054 n.10
/ref> The ''Altishahr'' term was used by Turkic-speaking inhabitants of the Tarim Basin in the 18th and 19th century, and adopted by some Western sources in the 19th century. Other local words for the region included Dorben Shahr ('Four Cities') and Yeti Shahr ('Seven Cities'). Another Western term for the same region is Kashgaria.
Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
sources refer to the region primarily as Nanlu, or the 'Southern Circuit'. Other Qing terms for the region include Huijiang (, the 'Muslim Frontier'), Huibu (, the 'Muslim Region'), Bacheng (the 'Eight Cities'), or Nanjiang
Nanjiang County () is a county in the northeast of Sichuan Province, China, bordering Shaanxi province to the north. It is under the administration of Bazhong
Bazhong () is a prefecture-level city in north-eastern Sichuan province, China. Its pop ...
('Southern Frontier').
Onomatology
 In the 18th century, prior to the Qing conquest of Xinjiang in 1759, the oasis towns around the Tarim did not have a single political structure governing them, and Altishahr referred to the region in general rather than any cities in particular. Bellér-Hann 2008
In the 18th century, prior to the Qing conquest of Xinjiang in 1759, the oasis towns around the Tarim did not have a single political structure governing them, and Altishahr referred to the region in general rather than any cities in particular. Bellér-Hann 200839 nn.7 & 8
/ref> Foreign visitors to the region would attempt to identify the cities, offering various lists. According to Albert von Le Coq, the 'Six Cities' (''Altishahr'') referred to (1)
Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
; (2) Maralbexi (Maralbashi, Bachu); (3) Aksu (Aqsu), alternatively Kargilik (Yecheng); (4) Yengisar (Yengi Hisar); (5) Yarkant (Yarkand, Shache); and (6) Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
. W. Barthold
Vasily Vladimirovich Bartold (russian: Васи́лий Влади́мирович Барто́льд.; 1869–1930), who published in the West under his German baptism name, Wilhelm Barthold, was a Russian orientalist who specialized in the his ...
later replaced Yengisar with Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t=庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
(Kuqa). According to Aurel Stein
Sir Marc Aurel Stein,
( hu, Stein Márk Aurél; 26 November 1862 – 26 October 1943) was a Hungarian-born British archaeologist, primarily known for his explorations and archaeological discoveries in Central Asia. He was also a professor at ...
, in the early 20th century, Qing administrators used the term to describe the oasis towns around Khotan, including Khotan itself, along with (2) Yurungqash, (3) Karakax (Qaraqash, Moyu), (4) Qira (Chira, Cele), (5) Keriya (Yutian), and a sixth undocumented place.
The term ' Seven Cities' may have been used after Yaqub Beg
Muhammad Yaqub Bek (محمد یعقوب بیگ; uz, Яъқуб-бек, ''Ya’qub-bek''; ; 182030 May 1877) was a Khanate of Kokand, Khoqandi ruler of Yettishar (Kashgaria) during his invasion of Xinjiang from 1865 to 1877. He held the title o ...
captured Turpan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the cit ...
(Turfan), and referred to (1) Kashgar; (2) Yarkant; (3) Khotan; (4) Uqturpan
Uqturpan County, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency or Uchturpan County (SASM/GNC romanization#Uyghur, transliterated from ; ), also Wushi County (), is a county in the Xinjiang, Xinjian ...
(Uch Turfan); (5) Aksu; (6) Kucha; and (7) Turpan.
The term 'Eight Cities' (, ''Şäkiz Şähār'') may have been a Turkic translation of the Qing Chinese term ''Nanlu Bajiang'' (literally 'Eight Cities of the Southern Circuit'), referring to (1) Kashgar, (2) Yengisar (3) Yarkant and (4) Khotan in the west and (5) Uqturpan, (6) Aksu, (7) Karasahr
Karasahr or Karashar ( ug, قاراشەھەر, Qarasheher, 6=Қарашәһәр), which was originally known, in the Tocharian languages as ''Ārśi'' (or Arshi) and Agni or the Chinese derivative Yanqi ( zh, s=焉耆, p=Yānqí, w=Yen-ch'i), is an ...
(Qarashahr, Yanqi), and (8) Turpan in the east.
Geography and relation to Xinjiang

 Altishahr refers to the
Altishahr refers to the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
of Southern Xinjiang
Southern Xinjiang or Nanjiang () is the southern half of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China. Its historical name was Altishahr ({{zh, c=回部, p=Huíbù), which also includes some territories in modern-day Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, ...
, which was historically, geographically, and ethnically distinct from the Junggar Basin
The Junggar Basin () is one of the largest sedimentary basins in Northwest China. It is located in Xinjiang, and enclosed by the Tarbagatai Mountains of Kazakhstan in the northwest, the Altai Mountains of Mongolia in the northeast, and the Heaven ...
of Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian language, Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang" ...
. At the time of the Qing conquest in 1759, Dzungaria was inhabited by Oirats
Oirats ( mn, Ойрад, ''Oirad'', or , Oird; xal-RU, Өөрд; zh, 瓦剌; in the past, also Eleuths) are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
Histor ...
, steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
-dwelling, nomadic Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
who practiced Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
. In contrast, the Tarim Basin was inhabited by sedentary
Sedentary lifestyle is a lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while engaged in an activity like soci ...
, oasis-dwelling, Turkic-speaking Muslim farmers, now known as the Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghur ...
. The two regions were governed as separate circuits before the region became independent. Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
was made into a single province in 1884.
History
Until the 8th century AD, much of the Tarim Basin was inhabited byTocharians
The Tocharians, or Tokharians ( US: or ; UK: ), were speakers of Tocharian languages, Indo-European languages known from around 7600 documents from around 400 to 1200 AD, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China). ...
who spoke an Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
and built city states in the oases along the rim of the Taklamakan Desert
The Taklimakan or Taklamakan Desert (; zh, s=塔克拉玛干沙漠, p=Tǎkèlāmǎgān Shāmò, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Такәламаган Шамә; ug, تەكلىماكان قۇملۇقى, Täklimakan qumluqi; also spelled Taklimakan and Te ...
. The collapse of the Uyghur Khanate in modern Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
and settlement of Uyghur diaspora in the Tarim led to the prevalence of the Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
. During the reign of the Karakhanids
The Kara-Khanid Khanate (; ), also known as the Karakhanids, Qarakhanids, Ilek Khanids or the Afrasiabids (), was a Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia in the 9th through the early 13th century. The dynastic names of Karakhanids and Ilek ...
much of the region converted to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
. From the 13th to the 16th centuries, the western Tarim was part of the larger Muslim Turkic-Mongol Chaghatay
Chagatai (چغتای, ''Čaġatāy''), also known as ''Turki'', Eastern Turkic, or Chagatai Turkic (''Čaġatāy türkīsi''), is an extinct Turkic literary language that was once widely spoken across Central Asia and remained the shared literar ...
, Timurid Timurid refers to those descended from Timur (Tamerlane), a 14th-century conqueror:
* Timurid dynasty, a dynasty of Turco-Mongol lineage descended from Timur who established empires in Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
** Timurid Empire of C ...
and Eastern Chagatai Empires.
In the 17th century, the local Yarkent Khanate
The Yarkent Khanate, also known as the Yarkand Khanate and the Kashghar Khanate, was a Sunni Muslim Turkic state ruled by the Mongol descendants of Chagatai Khan. It was founded by Sultan Said Khan in 1514 as a western offshoot of Moghulistan, i ...
ruled Altishahr until its conquest
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
by the Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
Dzungar
Dzungar may refer to:
*Dzungar people, Oirat tribes in the Dzungar Khanate
*Dzungar Khanate, a historical empire
* Jungar Banner, an administrative division of China
*Junggar Basin
The Junggar Basin () is one of the largest sedimentary basins in ...
s from the Dzungarian Basin to the north. In the 1750s, the region was acquired by the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
in its conquest of the Dzungar Khanate
The Dzungar Khanate, also written as the Zunghar Khanate, was an Inner Asian khanate of Oirat Mongol origin. At its greatest extent, it covered an area from southern Siberia in the north to present-day Kyrgyzstan in the south, and from t ...
. The Qing initially administered the Dzungaria and Altishahar separately as the Northern and Southern Circuits of Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
, respectively,Michell 1870p. 2.Martin 1847
p. 21.
p. 681.
General of Ili
The General of Ili ( Officially ), also known in western sources as the Kuldya Military Governor, was a position created during the reign of the Qing Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735-1799) to "pacify" Dzungaria (now part of Xinjiang) and suppress uprising ...
. The Southern Circuit (''Tianshan Nanlu'') was also known as ''Huibu'' (, 'Muslim Region'), ''Huijiang'' (, 'Muslim Frontier'), Chinese Turkestan, Kashgaria, Little Bukharia, and East Turkestan
East Turkestan ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان, Sherqiy Türkistan, bold=no; zh, s=东突厥斯坦; also spelled East Turkistan), is a loosely-defined geographical and historical region in the western provinces of the People's Republic of ...
. After quelling the Dungan Revolt in the late 19th century, the Qing combined the two circuits into the newly created Xinjiang Province
Xinjiang Province is a historical administrative area of Northwest China, between 1884 and 1955.
Periods during which various boundaries of Xinjiang Province have been defined include:
* Xinjiang Province (Qing) (1884–1912).
* Xinjiang Provin ...
in 1884. Xinjiang has since been used by the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
and People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and Southern Xinjiang replaced Altishahr as place name for the region.
See also
*Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
* Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian language, Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang" ...
* East Turkestan
East Turkestan ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان, Sherqiy Türkistan, bold=no; zh, s=东突厥斯坦; also spelled East Turkistan), is a loosely-defined geographical and historical region in the western provinces of the People's Republic of ...
* Taklamakan Desert
The Taklimakan or Taklamakan Desert (; zh, s=塔克拉玛干沙漠, p=Tǎkèlāmǎgān Shāmò, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Такәламаган Шамә; ug, تەكلىماكان قۇملۇقى, Täklimakan qumluqi; also spelled Taklimakan and Te ...
* Yettishar
Yettishar ( Uyghur: يەتتىشەر دۆلەتى; ; meaning "Seven Cities" or "Heptapolis"), commonly known as Kashgaria, was a short-lived Sunni Muslim Turkic state that existed in Xinjiang between 1865 and 1877 during the Dungan Revolt agai ...
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * *Further reading
Modular History: Identity Maintenance before Uyghur Nationalism
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Regions of China History of Xinjiang