Altar D on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An altar is a
An altar is a
File:Tel Be'er Sheva Altar 2007041.JPG, Horned altar at Tel Be'er Sheva,
 The word ''altar'', in Greek (''see'': θυσία), appears twenty-four times in the
The word ''altar'', in Greek (''see'': θυσία), appears twenty-four times in the  The area around the altar is seen as endowed with greater holiness, and is usually physically distinguished from the rest of the church, whether by a permanent structure such as an
The area around the altar is seen as endowed with greater holiness, and is usually physically distinguished from the rest of the church, whether by a permanent structure such as an  In the earliest days of the Church, the Eucharist appears to have been celebrated on portable altars set up for the purpose. Some historians hold that, during the persecutions, the
In the earliest days of the Church, the Eucharist appears to have been celebrated on portable altars set up for the purpose. Some historians hold that, during the persecutions, the
 Most
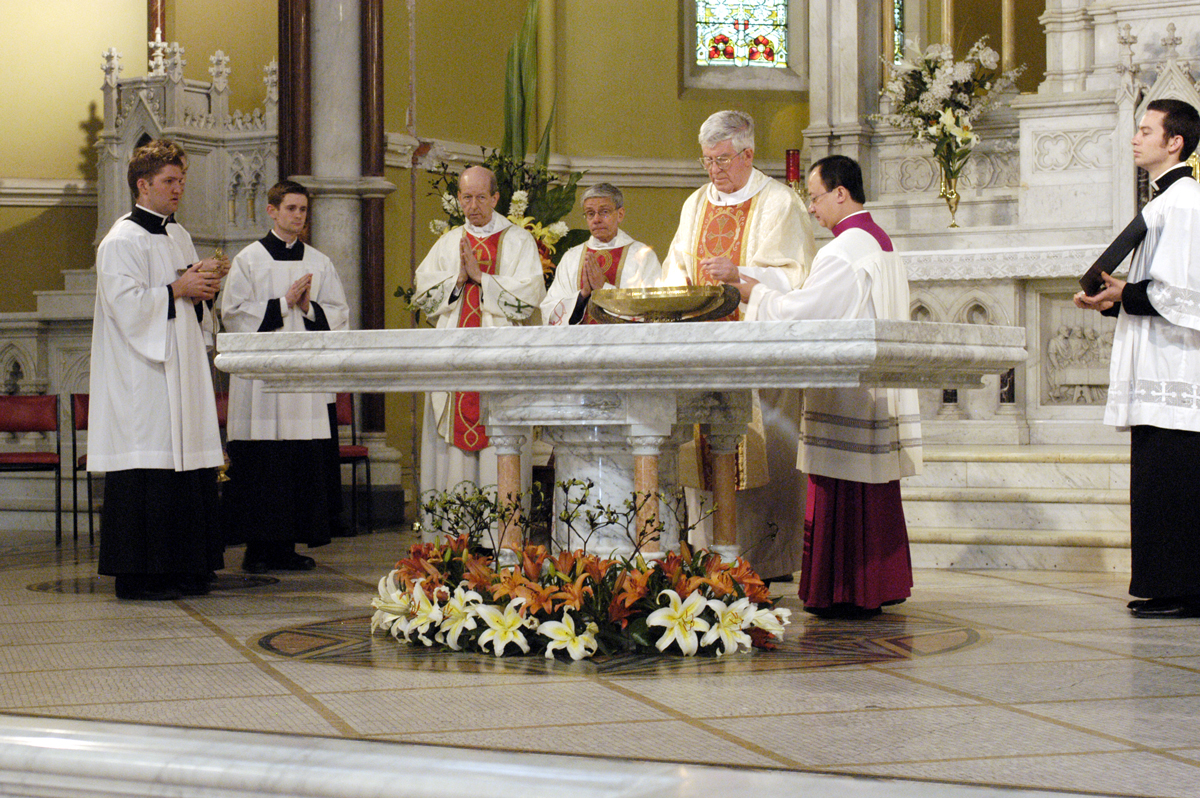
Most  The rules regarding the present-day form of the Roman Rite liturgy declare a free-standing main altar to be "desirable wherever possible". Similarly, in the Anglican Communion, the rubrics of the
The rules regarding the present-day form of the Roman Rite liturgy declare a free-standing main altar to be "desirable wherever possible". Similarly, in the Anglican Communion, the rubrics of the
 The
The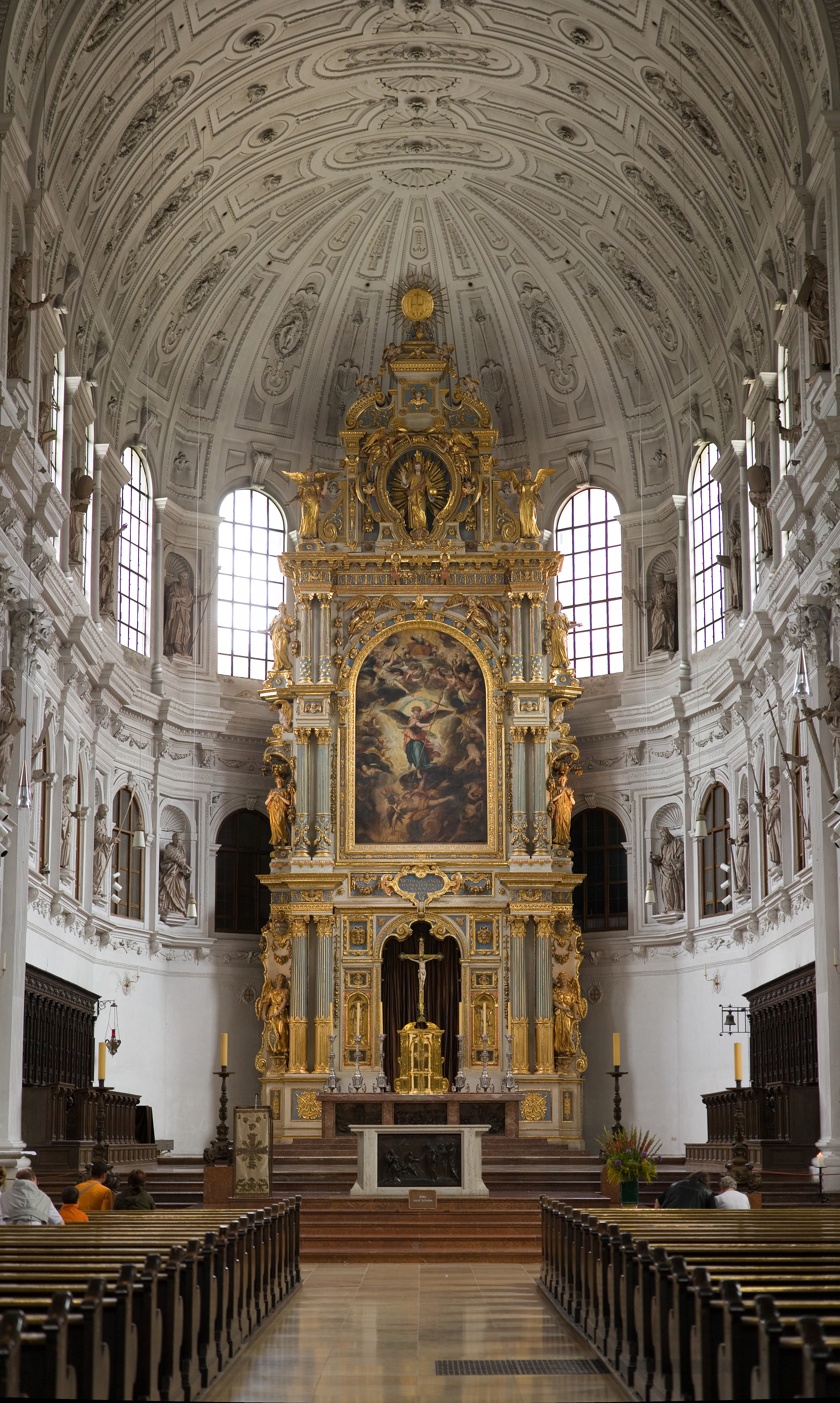  A fixed altar should in general be topped by a slab of natural stone, thus conforming to tradition and to the significance attributed to the altar, but in many places dignified, well-crafted solid wood is permitted; the supports or base of a fixed altar may be of any dignified solid material. A movable altar may be of any noble solid material suitable for liturgical use.
The liturgical norms state:
:It is fitting that the tradition of the Roman liturgy should be preserved of placing relics of martyrs or other saints beneath the altar. However, the following should be noted:
:(a) Relics intended for deposition should be large enough that they can be recognized as parts of human bodies. Hence excessively small relics of one or more saints must not be deposited.
:(b) The greatest care must be taken to determine whether relics intended for deposition are authentic. It is better for an altar to be dedicated without relics than to have relics of doubtful credibility placed beneath it.
:(c) A reliquary must not be placed on the altar, or in the table of the altar; it must be beneath the table of the altar, as the design of the altar may allow.
A fixed altar should in general be topped by a slab of natural stone, thus conforming to tradition and to the significance attributed to the altar, but in many places dignified, well-crafted solid wood is permitted; the supports or base of a fixed altar may be of any dignified solid material. A movable altar may be of any noble solid material suitable for liturgical use.
The liturgical norms state:
:It is fitting that the tradition of the Roman liturgy should be preserved of placing relics of martyrs or other saints beneath the altar. However, the following should be noted:
:(a) Relics intended for deposition should be large enough that they can be recognized as parts of human bodies. Hence excessively small relics of one or more saints must not be deposited.
:(b) The greatest care must be taken to determine whether relics intended for deposition are authentic. It is better for an altar to be dedicated without relics than to have relics of doubtful credibility placed beneath it.
:(c) A reliquary must not be placed on the altar, or in the table of the altar; it must be beneath the table of the altar, as the design of the altar may allow.
 This last norm explicitly excludes the practice customary in recent centuries of inserting relics into a specially created cavity within the table of an altar or
This last norm explicitly excludes the practice customary in recent centuries of inserting relics into a specially created cavity within the table of an altar or
 A wide variety of altars exist in various Protestant denominations. Some Churches, such as the
A wide variety of altars exist in various Protestant denominations. Some Churches, such as the  Some
Some
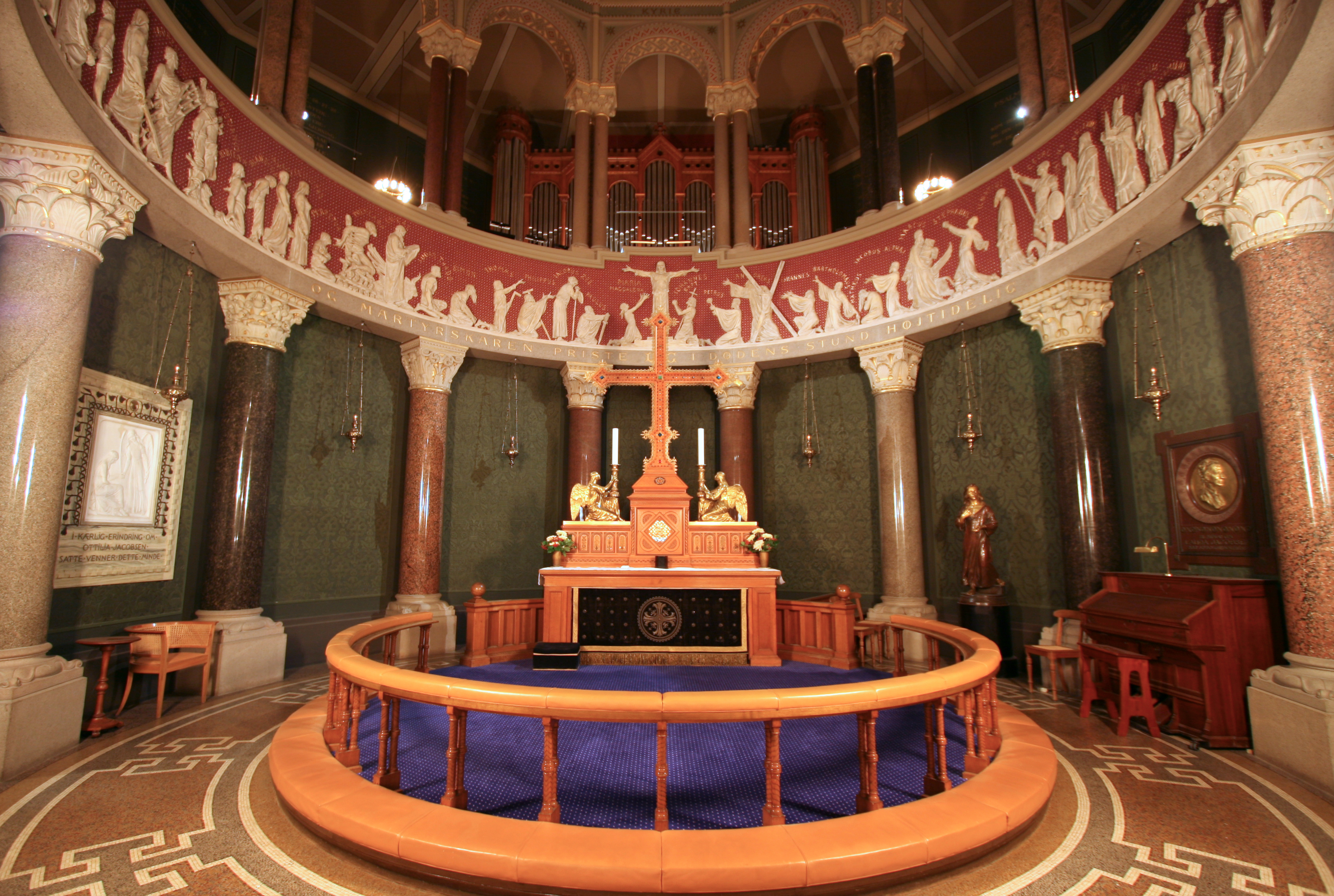
 Altars in the Anglican Communion vary widely. In the
Altars in the Anglican Communion vary widely. In the  Beginning with the Oxford Movement in the 19th century, the appearance of Anglican altars took a dramatic turn in many churches. Candles and, in some cases, tabernacles were re‑introduced. In some churches two candles, on each end of the altar, were used; in other cases six—three on either side of a tabernacle, typically surmounted by a crucifix or some other image of Christ.
Beginning with the Oxford Movement in the 19th century, the appearance of Anglican altars took a dramatic turn in many churches. Candles and, in some cases, tabernacles were re‑introduced. In some churches two candles, on each end of the altar, were used; in other cases six—three on either side of a tabernacle, typically surmounted by a crucifix or some other image of Christ.
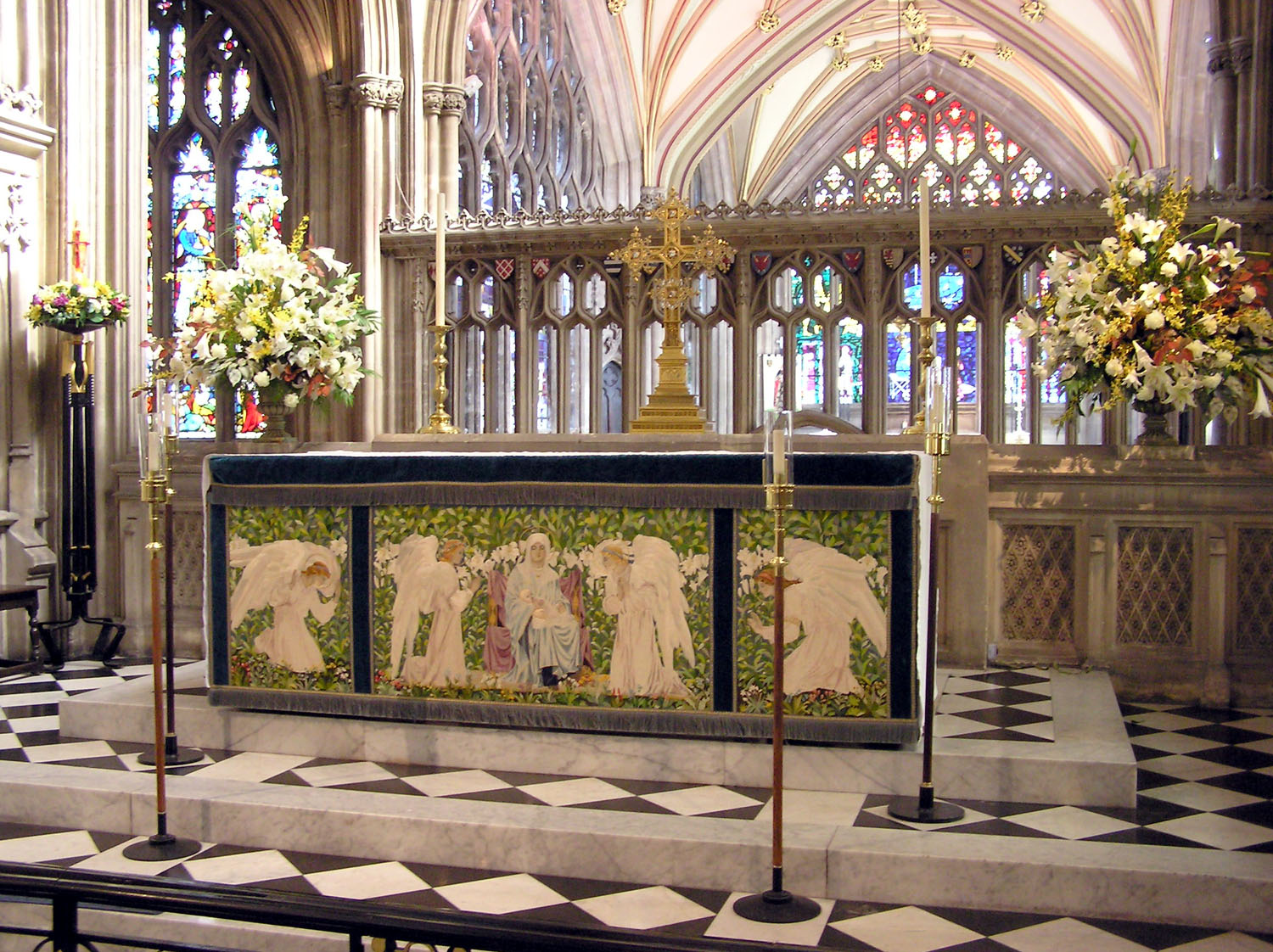
 In Anglican practice, conformity to a given standard depends on the ecclesiastical province and/or the liturgical sensibilities of a given parish. In the ''Parson's Handbook'', an influential manual for priests popular in the early-to-mid-twentieth century, Percy Dearmer recommends that "All altars should be 3 ft. 3 in. high, and ''at least'' deep enough to take a corporal [the square of linen placed underneath the Communion vessels] 20 in. square, with an inch or two to spare." He also recommends that the altar stand upon three steps for each of the three sacred ministers, and that it be decorated with a silk frontal in the liturgical colours, seasonal colour. In some cases, other manuals suggest that a stone be set in the top of wooden altars, in the belief that the custom be maintained of consecrating the bread and wine on a stone surface. In many other Anglican parishes, the custom is considerably less rigorous, especially in those parishes which use free-standing altars. Typically, these altars are made of wood, and may or may not have a solid front, which may or may not be ornamented. In many Anglican parishes, the use of frontals has persisted.
When altars are placed away from the wall of the chancel allowing a westward orientation, only two candles are placed on either end of it, since six would obscure the liturgical action, undermining the intent of a westward orientation (i.e., that it be visible to the congregation). In such an arrangement, a tabernacle may stand to one side of or behind the altar, or an aumbry may be used.
Sensibilities concerning the sanctity of the altar are widespread in Anglicanism. In some parishes, the notion that the surface of the altar should only be touched by those in holy orders is maintained. In others, there is considerably less strictness about the communion table. Nonetheless, the continued popularity of communion rails in Anglican church construction suggests that a sense of the sanctity of the altar and its surrounding area persists. In most cases, moreover, the practice of allowing only those items that have been blessed to be placed on the altar is maintained (that is, the linen cloth, candles, missal, and the Eucharistic vessels).
In Anglican practice, conformity to a given standard depends on the ecclesiastical province and/or the liturgical sensibilities of a given parish. In the ''Parson's Handbook'', an influential manual for priests popular in the early-to-mid-twentieth century, Percy Dearmer recommends that "All altars should be 3 ft. 3 in. high, and ''at least'' deep enough to take a corporal [the square of linen placed underneath the Communion vessels] 20 in. square, with an inch or two to spare." He also recommends that the altar stand upon three steps for each of the three sacred ministers, and that it be decorated with a silk frontal in the liturgical colours, seasonal colour. In some cases, other manuals suggest that a stone be set in the top of wooden altars, in the belief that the custom be maintained of consecrating the bread and wine on a stone surface. In many other Anglican parishes, the custom is considerably less rigorous, especially in those parishes which use free-standing altars. Typically, these altars are made of wood, and may or may not have a solid front, which may or may not be ornamented. In many Anglican parishes, the use of frontals has persisted.
When altars are placed away from the wall of the chancel allowing a westward orientation, only two candles are placed on either end of it, since six would obscure the liturgical action, undermining the intent of a westward orientation (i.e., that it be visible to the congregation). In such an arrangement, a tabernacle may stand to one side of or behind the altar, or an aumbry may be used.
Sensibilities concerning the sanctity of the altar are widespread in Anglicanism. In some parishes, the notion that the surface of the altar should only be touched by those in holy orders is maintained. In others, there is considerably less strictness about the communion table. Nonetheless, the continued popularity of communion rails in Anglican church construction suggests that a sense of the sanctity of the altar and its surrounding area persists. In most cases, moreover, the practice of allowing only those items that have been blessed to be placed on the altar is maintained (that is, the linen cloth, candles, missal, and the Eucharistic vessels).
File:All Saints Bristol 07b altar ciborium.jpg, The altar with ciborium at Church of All Saints, Clifton, All Saints Anglican church, Bristol, England
File:St Barnabas, Calton Avenue, Dulwich, London SE21 - Altar - geograph.org.uk - 1750566.jpg, The Lord's Table in St Barnabas' Church, Dulwich (Diocese of Southwark)
File:StThomas'Bunyip.jpg, Altar in Bunyip, Victoria, Australia
File:Cathedral Altar.JPG, Altar at Grace Cathedral, San Francisco, Grace Cathedral, San Francisco
File:High Altar, Church of the Good Shepherd (Rosemont, Pennsylvania).jpg, Altar at Anglo-Catholic Church of the Good Shepherd (Rosemont, Pennsylvania)
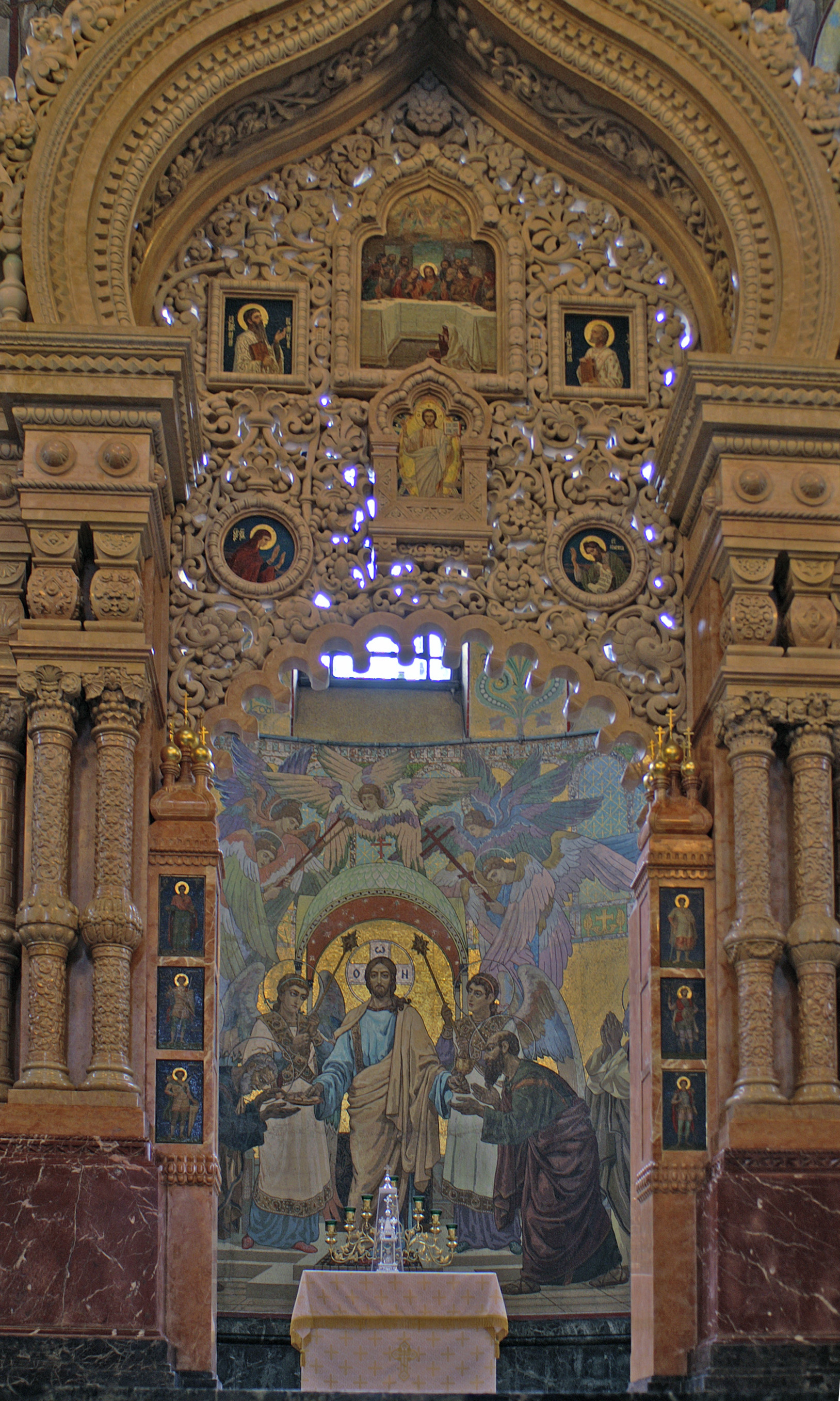 In Greek language, Greek the word () can mean an altar of any religion or, in a broader sense, the area surrounding it; that is to say, the entire sanctuary. In an
In Greek language, Greek the word () can mean an altar of any religion or, in a broader sense, the area surrounding it; that is to say, the entire sanctuary. In an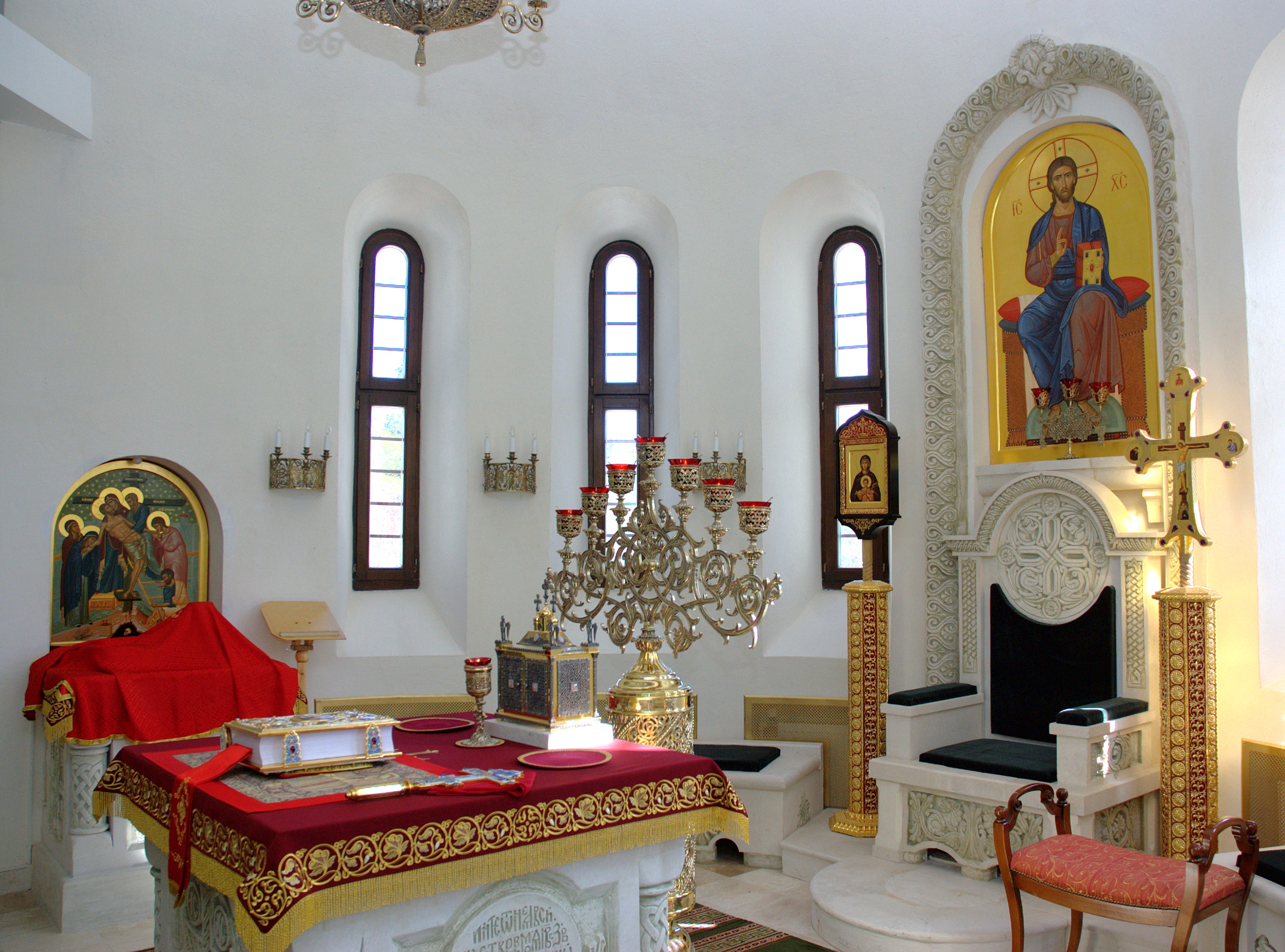  Atop the altar is the Church tabernacle, tabernacle (), a miniature shrine sometimes built in the form of a church, inside of which is a small ark containing the reserved sacrament for use in communing the sick. Also kept on the altar is the Gospel Book. Under the Gospel is kept the '' antimension'', a silken cloth imprinted with an icon of Deposition from the Cross, Christ being prepared for burial, which has a
Atop the altar is the Church tabernacle, tabernacle (), a miniature shrine sometimes built in the form of a church, inside of which is a small ark containing the reserved sacrament for use in communing the sick. Also kept on the altar is the Gospel Book. Under the Gospel is kept the '' antimension'', a silken cloth imprinted with an icon of Deposition from the Cross, Christ being prepared for burial, which has a  The Holy Table is used as the place of offering in the celebration of the
The Holy Table is used as the place of offering in the celebration of the
 In the Armenian Rite the altar is placed against the eastern wall of the church, often in an apse. The shape of the altar is usually rectangular, similar to Latin altars, but is unusual in that it will normally have several steps on top of the table, on which are placed the Church tabernacle, tabernacle, candles, hexapteryga, ceremonial fans, a cross, and the Gospel Book. The altar is often located upon a kind of stage above a row of icons.
In the Armenian Rite the altar is placed against the eastern wall of the church, often in an apse. The shape of the altar is usually rectangular, similar to Latin altars, but is unusual in that it will normally have several steps on top of the table, on which are placed the Church tabernacle, tabernacle, candles, hexapteryga, ceremonial fans, a cross, and the Gospel Book. The altar is often located upon a kind of stage above a row of icons.
 In
In  In South Indian temples, often each god will have his or her own shrine, each contained in a miniature house (specifically, a ''mandir''). These shrines are often scattered around the temple compound, with the three main ones being in the main area. The statue of the god (murti) is placed on a stone pedestal in the shrine, and one or more lamps are hung in the shrine. There is usually a space to put the Puja (Hinduism), puja tray (tray with worship offerings). Directly outside the main shrine there will be a statue of the god's vahana or vehicle. The shrines have curtains hung over the entrances, and wooden doors which are shut when the deities are sleeping. Some South Indian temples have one main altar, with several statues placed upon it.
In South Indian temples, often each god will have his or her own shrine, each contained in a miniature house (specifically, a ''mandir''). These shrines are often scattered around the temple compound, with the three main ones being in the main area. The statue of the god (murti) is placed on a stone pedestal in the shrine, and one or more lamps are hung in the shrine. There is usually a space to put the Puja (Hinduism), puja tray (tray with worship offerings). Directly outside the main shrine there will be a statue of the god's vahana or vehicle. The shrines have curtains hung over the entrances, and wooden doors which are shut when the deities are sleeping. Some South Indian temples have one main altar, with several statues placed upon it.
 North Indian temples generally have one main altar at the front of the temple room. In some temples, the front of the room is separated with walls and several altars are placed in the alcoves. The statues on the altars are usually in pairs, each god with his consort (Radha-Krishna, Sita-Rama, Shiva-Parvati). However, some gods, such as Ganesha and Hanuman, are placed alone. Ritual items such as flowers or lamps may be placed on the altar.
Home shrines can be as simple or as elaborate as the householder can afford. Large, ornate shrines can be purchased in India and countries with large Hindu minorities, like Malaysia and Singapore. They are usually made of wood and have tiled floors for statues to be placed upon. Pictures may be hung on the walls of the shrine. The top of the shrine may have a series of levels, like a gopuram tower on a temple. Each Hindu altar will have at least one oil lamp and may contain a tray with puja equipment as well. Hindus with large houses will set aside one room as their puja room, with the altar at one end of it. Some South Indians also place a shrine with pictures of their departed relatives on the right side of the room, and make offerings to them before making offerings to the gods.
See also: Vedi (altar) and Homa (ritual)
North Indian temples generally have one main altar at the front of the temple room. In some temples, the front of the room is separated with walls and several altars are placed in the alcoves. The statues on the altars are usually in pairs, each god with his consort (Radha-Krishna, Sita-Rama, Shiva-Parvati). However, some gods, such as Ganesha and Hanuman, are placed alone. Ritual items such as flowers or lamps may be placed on the altar.
Home shrines can be as simple or as elaborate as the householder can afford. Large, ornate shrines can be purchased in India and countries with large Hindu minorities, like Malaysia and Singapore. They are usually made of wood and have tiled floors for statues to be placed upon. Pictures may be hung on the walls of the shrine. The top of the shrine may have a series of levels, like a gopuram tower on a temple. Each Hindu altar will have at least one oil lamp and may contain a tray with puja equipment as well. Hindus with large houses will set aside one room as their puja room, with the altar at one end of it. Some South Indians also place a shrine with pictures of their departed relatives on the right side of the room, and make offerings to them before making offerings to the gods.
See also: Vedi (altar) and Homa (ritual)
 In Shinto, altars are found in shrines. Originating in ancient times, are temporarily erected sacred spaces or "altars" used as a locus of worship. A physical area is demarcated with branches of green bamboo or at the four corners, between which are strung sacred border ropes (). In the center of the area a large branch of festooned with sacred emblems () is erected as a ''yorishiro'', a physical representation of the presence of the kami and toward which rites of worship are performed.
In more elaborate cases, a may be constructed by placing a rough straw mat upon the ground, then erecting a ceremonial eight-legged stand () upon the mat, and decorating the stand with a frame festooned with sacred border ropes and sacred border emblems. Finally the branch is erected in the center of this stand as the focus of worship.
In Shinto, altars are found in shrines. Originating in ancient times, are temporarily erected sacred spaces or "altars" used as a locus of worship. A physical area is demarcated with branches of green bamboo or at the four corners, between which are strung sacred border ropes (). In the center of the area a large branch of festooned with sacred emblems () is erected as a ''yorishiro'', a physical representation of the presence of the kami and toward which rites of worship are performed.
In more elaborate cases, a may be constructed by placing a rough straw mat upon the ground, then erecting a ceremonial eight-legged stand () upon the mat, and decorating the stand with a frame festooned with sacred border ropes and sacred border emblems. Finally the branch is erected in the center of this stand as the focus of worship.
 An altar is a
An altar is a table
Table may refer to:
* Table (furniture), a piece of furniture with a flat surface and one or more legs
* Table (landform), a flat area of land
* Table (information), a data arrangement with rows and columns
* Table (database), how the table data ...
or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifice
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly exi ...
s, or for other ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
istic purposes. Altars are found at shrine
A shrine ( la, scrinium "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred or holy sacred space, space dedicated to a specific deity, ancestor worship, ancestor, hero, martyr, saint, Daemon (mythology), daem ...
s, temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
s, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christianity, early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions ot ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, modern paganism
Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, is a term for a religion or family of religions influenced by the various historical pre-Christian beliefs of pre-modern peoples in Europe and adjacent areas of North Afric ...
, and in certain Islamic communities around Caucasia and Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Many historical-medieval faiths also made use of them, including the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
, Greek, and Norse religions.
Etymology
The modernEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
word ''altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
'' was derived from Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
''altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
'', from Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
''alter
Alter may refer to:
* Alter (name), people named Alter
* Alter (automobile)
* Alter (crater), a lunar crater
* Alter Channel, a Greek TV channel
* Archbishop Alter High School, a Roman Catholic high school in Kettering, Ohio
* ALTER, a comman ...
'', taken from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''altare
Altare ( lij, Artâ, pms, Latè, L’Atæ in local dialect) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Savona in the Italian region Liguria, located about west of Genoa and about northwest of Savona. As of 1 January 2009, it had a popula ...
'' ("altar"), probably related to '' adolere'' ("burn"); thus "burning place", influenced by ''altus
Altus or ALTUS may refer to:
Music
*Alto, a musical term meaning second highest musical or vocal type
*Altus (voice type), a vocal type also known as countertenor
Places
* Altus, Arkansas, US
**Altus AVA, a wine-growing region near Altus, Arkans ...
'' ("high"). It displaced the native Old English word '' wēofod''.
Altars in antiquity
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
.
File:3217 - Athens - Sto… of Attalus Museum - Kylix - Photo by Giovanni Dall'Orto, Nov 9 2009.jpg, Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
kylix
In the pottery of ancient Greece, a kylix ( , ; grc, κύλιξ, pl. κύλικες; also spelled cylix; pl.: kylikes , ) is the most common type of wine-drinking cup. It has a broad, relatively shallow, body raised on a stem from a foot ...
showing a hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with ...
offering a sacrifice before an altar, around 480 BC. Ancient Agora Museum of Athens in the Stoa of Attalus
The Stoa of Attalos (also spelled Attalus) was a stoa (covered walkway or portico) in the Agora of Athens, Greece. It was built by and named after King Attalos II of Pergamon, who ruled between 159 BC and 138 BC. The current building was recons ...
File:Berlin - Pergamonmuseum - Altar 02.jpg, The ancient Altar of Pergamon, reconstructed at the Pergamon museum, Berlin.
File:Opferstein Maria Taferl.jpg, The ''Opferstein'' or Sacrifice Rock at Maria Taferl, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. It was used by the ancient Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
to make sacrifices upon and is now located in the plaza of the basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
there.
Judaism
Altars , ''mizbe'ah'' means "a place of slaughter or sacrifice". in theHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
were typically made of earth or unwrought stone. Altars were generally erected in conspicuous places. The first altar recorded in the Hebrew Bible is that erected by ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Noah
Noah ''Nukh''; am, ኖህ, ''Noḥ''; ar, نُوح '; grc, Νῶε ''Nôe'' () is the tenth and last of the pre-Flood patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5– ...
. Altars were erected by Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
, by Isaac
Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the ...
, by Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
, and by Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
.
After the theophany
Theophany (from Ancient Greek , meaning "appearance of a deity") is a personal encounter with a deity, that is an event where the manifestation of a deity occurs in an observable way. Specifically, it "refers to the temporal and spatial manifest ...
on Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai ( he , הר סיני ''Har Sinai''; Aramaic: ܛܘܪܐ ܕܣܝܢܝ ''Ṭūrāʾ Dsyny''), traditionally known as Jabal Musa ( ar, جَبَل مُوسَىٰ, translation: Mount Moses), is a mountain on the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. It is ...
, in the Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
—and afterwards in the Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
—only two altars were used: The Altar of Burnt Offering, and the Altar of Incense, both near where the Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an e ...
was located.
The remains of three rock-hewn altars were discovered in the Land of Israel: one below Tel Zorah, another at the foot of Sebastia (ancient Samaria), and a third near Shiloh.
Christianity
 The word ''altar'', in Greek (''see'': θυσία), appears twenty-four times in the
The word ''altar'', in Greek (''see'': θυσία), appears twenty-four times in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
. In Catholic and Orthodox Christian theology, the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
is a re-presentation, in the literal sense of the one sacrifice of Christ on the cross being made "present again". Hence, the table upon which the Eucharist is consecrated is called an altar.
The altar plays a central role in the celebration of the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
, which takes place at the altar on which the bread and the wine for consecration are placed. Altars occupy a prominent place in most Christian churches, both Eastern and Western branches. Commonly among these churches, altars are placed for permanent use within designated places of communal worship (often called "sanctuaries"). Less often, though nonetheless notable, altars are set in spaces occupied less regularly, such as outdoors in nature, in cemeteries, in mausoleums/crypts, and family dwellings. Personal altars are those placed in a private bedroom, closet, or other space usually occupied by one person. They are used for practices of piety intended for one person (often referred to as a "private devotion"). They are also found in a minority of Protestant worship places; in Reformed
Reform is beneficial change
Reform may also refer to:
Media
* ''Reform'' (album), a 2011 album by Jane Zhang
* Reform (band), a Swedish jazz fusion group
* ''Reform'' (magazine), a Christian magazine
*''Reforme'' ("Reforms"), initial name of the ...
and Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from New Latin language, Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re- ...
churches, a table, often called a "Communion table", serves an analogous function.
 The area around the altar is seen as endowed with greater holiness, and is usually physically distinguished from the rest of the church, whether by a permanent structure such as an
The area around the altar is seen as endowed with greater holiness, and is usually physically distinguished from the rest of the church, whether by a permanent structure such as an iconostasis
In Eastern Christianity, an iconostasis ( gr, εἰκονοστάσιον) is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a Church (building), church. ''Iconostasis'' also refers to a portable icon stand t ...
, a rood screen
The rood screen (also choir screen, chancel screen, or jubé) is a common feature in late medieval church architecture. It is typically an ornate partition between the chancel and nave, of more or less open tracery constructed of wood, stone, or ...
, altar rails
The altar rail (also known as a communion rail or chancel rail) is a low barrier, sometimes ornate and usually made of stone, wood or metal in some combination, delimiting the chancel or the sanctuary and altar in a church, from the nave and oth ...
, a curtain that can be closed at more solemn moments of the liturgy (as in the Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
and Armenian Catholic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, image = St Elie - St Gregory Armenian Catholic Cathedral.jpg
, imagewidth = 260px
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Saint Elias and Saint Gregory the Illuminat ...
), or simply by the general architectural layout. The altar is often on a higher elevation than the rest of the church.
Churches generally have a single altar, although in the Western branches of Christianity, as a result of the former abandonment of concelebration
In Christianity, concelebration (from Lat., ''con'' + ''celebrare'', to celebrate together) is the presiding of a number of presbyters (priests or ministers) at the celebration of the Eucharist with either a presbyter or bishop as the ''principal c ...
of Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
, so that priests always celebrated Mass individually, larger churches have had one or more side chapels, each with its own altar. The main altar was also referred to as the "". Since the revival of concelebration in the West, the Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of the m ...
recommends that in new churches there should be only one altar, "which in the gathering of the faithful will signify the one Christ and the one Eucharist of the Church." This does not exclude altars in distinct side chapels, however, but only separate altars in the main body of the church. But most Western churches of an earlier period, whether Roman Catholic or Anglican, may have a high altar in the main body of the church, with one or more adjoining chapels, each with its own altar, at which the Eucharist may be celebrated on weekdays.
Architecturally, there are two types of altars: Those that are attached to the eastern wall of the chancel, and those that are free-standing and can be walked around, for instance when incensing the altar.
 In the earliest days of the Church, the Eucharist appears to have been celebrated on portable altars set up for the purpose. Some historians hold that, during the persecutions, the
In the earliest days of the Church, the Eucharist appears to have been celebrated on portable altars set up for the purpose. Some historians hold that, during the persecutions, the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
was celebrated among the tombs in the Catacombs of Rome
The Catacombs of Rome ( it, Catacombe di Roma) are ancient catacombs, underground burial places in and around Rome, of which there are at least forty, some rediscovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, either i ...
, using the sarcophagi (see sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek ...
) of martyrs as altars on which to celebrate. Other historians dispute this, but it is thought to be the origin of the tradition of placing relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
beneath the altar.
When Christianity was legalized under Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
and Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan, AD 313, that granted official toleration to C ...
, formal church buildings were built in great numbers, normally with free-standing altars in the middle of the sanctuary, which in all the earliest churches built in Rome was at the west end of the church. "When Christians in fourth-century Rome could first freely begin to build churches, they customarily located the sanctuary towards the west end of the building in imitation of the sanctuary of the Jerusalem Temple. Although in the days of the Jerusalem Temple the High Priest indeed faced east when sacrificing on Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day's ...
, the sanctuary within which he stood was located at the western end of the Temple. The Christian replication of the layout and the orientation of the Jerusalem Temple helped to dramatize the eschatological meaning attached to the sacrificial death of Jesus the High Priest in the Epistle to the Hebrews." The ministers (bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
, priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
s, deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions. Major Christian churches, such as the Catholic Churc ...
s, subdeacon
Subdeacon (or sub-deacon) is a minor order or ministry for men in various branches of Christianity. The subdeacon has a specific liturgical role and is placed between the acolyte (or reader) and the deacon in the order of precedence.
Subdeacons in ...
s, acolytes), celebrated the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
facing east, towards the entrance. Some hold that for the central part of the celebration the congregation faced the same way. After the sixth century the contrary orientation prevailed, with the entrance to the west and the altar at the east end. Then the ministers and congregation all faced east during the whole celebration; and in Western Europe altars began, in the Middle Ages, to be permanently placed against the east wall of the chancel.
In Western Christian churches
 Most
Most rubric
A rubric is a word or section of text that is traditionally written or printed in red ink for emphasis. The word derives from the la, rubrica, meaning red ochre or red chalk, and originates in Medieval illuminated manuscripts from the 13th cent ...
s, even in books of the seventeenth century and later, such as the Pontificale Romanum
The ''Roman Pontifical'', in Latin ''Pontificale Romanum'', is the pontifical as used by the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church. It is the liturgical book that contains the rites and ceremonies usually performed by bishops of the Roman Rite.
The ...
, continued to envisage the altar as free-standing. The rite of the Dedication of the Church continued to presume that the officiating bishop could circle the altar during the consecration of the church and its altar. Despite this, with the increase in the size and importance of the reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for ex ...
, most altars were built against the wall or barely separated from it.
In almost all cases, the eastward orientation for prayer was maintained, whether the altar was at the west end of the church, as in all the earliest churches in Rome, in which case the priest celebrating Mass faced the congregation and the church entrance, or whether it was at the east end of the church, in which case the priest faced the eastern apse and had his back to the congregation. This diversity was recognized in the rubrics of the Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of the m ...
from the 1604 typical edition of Pope Clement VIII
Pope Clement VIII ( la, Clemens VIII; it, Clemente VIII; 24 February 1536 – 3 March 1605), born Ippolito Aldobrandini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 2 February 1592 to his death in March 1605.
Born ...
to the 1962 edition of Pope John XXIII
Pope John XXIII ( la, Ioannes XXIII; it, Giovanni XXIII; born Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli, ; 25 November 18813 June 1963) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death in June 19 ...
: ""
When placed close to a wall or touching it, altars were often surmounted by a reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images.
The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for ex ...
or altarpiece
An altarpiece is an artwork such as a painting, sculpture or relief representing a religious subject made for placing at the back of or behind the altar of a Christian church. Though most commonly used for a single work of art such as a painting o ...
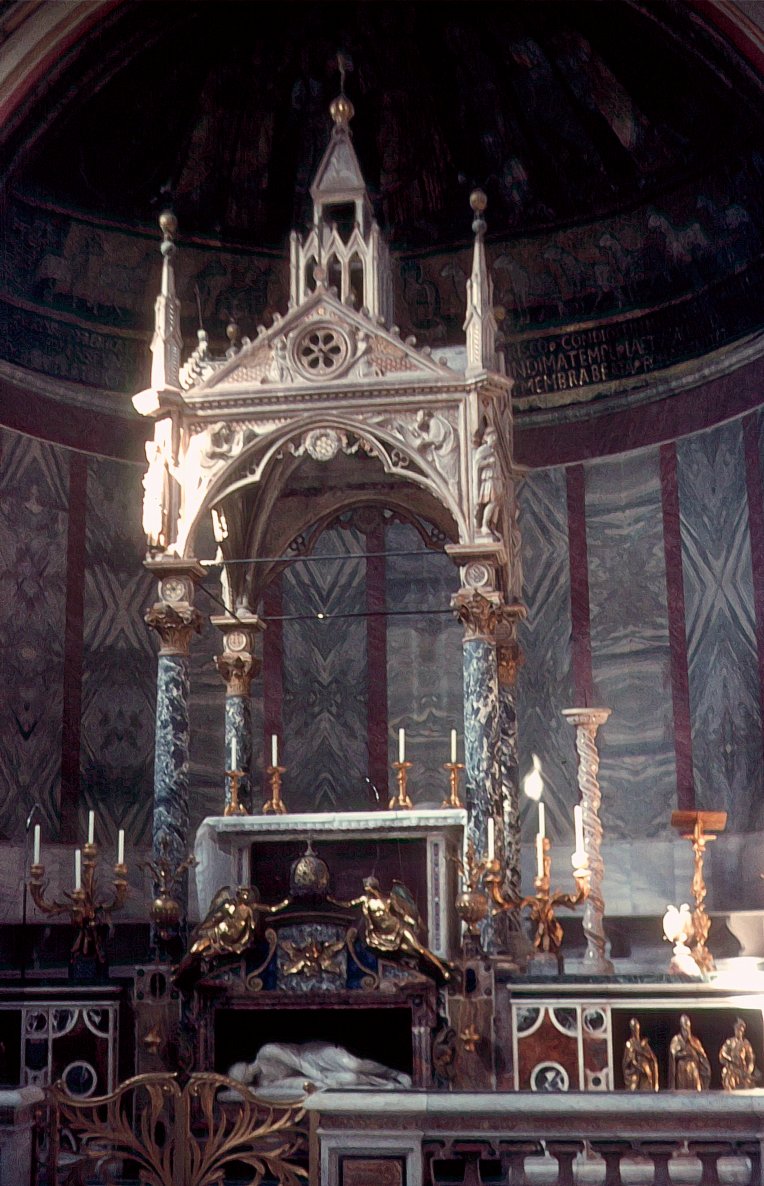
. If free-standing, they could be placed, as also in Eastern Christianity, within a ciborium (sometimes called a baldachin).
 The rules regarding the present-day form of the Roman Rite liturgy declare a free-standing main altar to be "desirable wherever possible". Similarly, in the Anglican Communion, the rubrics of the
The rules regarding the present-day form of the Roman Rite liturgy declare a free-standing main altar to be "desirable wherever possible". Similarly, in the Anglican Communion, the rubrics of the Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
assumed an altar fixed against the wall, until Prayer Book revision in the twentieth century removed language which assumed any particular form of altar.
As well as altars in the structural sense, it became customary in the West to have what in Latin were referred to as (portable altars), more commonly referred to in English as altar stone
An altar stone is a piece of natural stone containing relics in a cavity and intended to serve as the essential part of an altar for the celebration of Mass in the Catholic Church. Consecration by a bishop of the same rite was required. In the Byza ...
s. When travelling, a priest could take one with him and place it on an ordinary table for saying Mass. They were also inserted into the centre of structural altars especially those made of wood. In that case, it was the altar stone that was considered liturgically to be the altar. The Pontificale Romanum contained a rite for blessing at the same time several of these altar stones. In the East the antimension served and continues to serve the same purpose.
The term ''movable altar'' or ''portable altar'' is now used of a full-scale structural altar, with or without an inserted altar stone, that can be moved. ''See also'' General Instruction of the Roman Missal.
Movable altars include the free-standing wooden tables without altar stone, placed in the choir away from the east wall, favoured by churches in the Reformed tradition. Altars that not only can be moved but are repeatedly moved are found in low church traditions that do not focus worship on the Eucharist, celebrating it rarely. Both Catholics and Protestants celebrate the Eucharist at such altars outside of churches and chapels, as outdoors or in an auditorium.
Catholic Church
 The
The Eastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of th ...
each follow their own traditions, which in general correspond to those of similar Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
or Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent o ...
Churches. All Christian Churches see the altar on which the Eucharist is offered as the "table of the Lord" () mentioned by Saint Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
. The rules indicated here are those of the Latin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
.
The Latin Church distinguishes between fixed altars (those attached to the floor) and movable altars (those that can be displaced), and states: "It is desirable that in every church there be a fixed altar, since this more clearly and permanently signifies Christ Jesus, the Living Stone. In other places set aside for sacred celebrations, the altar may be movable."
 A fixed altar should in general be topped by a slab of natural stone, thus conforming to tradition and to the significance attributed to the altar, but in many places dignified, well-crafted solid wood is permitted; the supports or base of a fixed altar may be of any dignified solid material. A movable altar may be of any noble solid material suitable for liturgical use.
The liturgical norms state:
:It is fitting that the tradition of the Roman liturgy should be preserved of placing relics of martyrs or other saints beneath the altar. However, the following should be noted:
:(a) Relics intended for deposition should be large enough that they can be recognized as parts of human bodies. Hence excessively small relics of one or more saints must not be deposited.
:(b) The greatest care must be taken to determine whether relics intended for deposition are authentic. It is better for an altar to be dedicated without relics than to have relics of doubtful credibility placed beneath it.
:(c) A reliquary must not be placed on the altar, or in the table of the altar; it must be beneath the table of the altar, as the design of the altar may allow.
A fixed altar should in general be topped by a slab of natural stone, thus conforming to tradition and to the significance attributed to the altar, but in many places dignified, well-crafted solid wood is permitted; the supports or base of a fixed altar may be of any dignified solid material. A movable altar may be of any noble solid material suitable for liturgical use.
The liturgical norms state:
:It is fitting that the tradition of the Roman liturgy should be preserved of placing relics of martyrs or other saints beneath the altar. However, the following should be noted:
:(a) Relics intended for deposition should be large enough that they can be recognized as parts of human bodies. Hence excessively small relics of one or more saints must not be deposited.
:(b) The greatest care must be taken to determine whether relics intended for deposition are authentic. It is better for an altar to be dedicated without relics than to have relics of doubtful credibility placed beneath it.
:(c) A reliquary must not be placed on the altar, or in the table of the altar; it must be beneath the table of the altar, as the design of the altar may allow.
altar stone
An altar stone is a piece of natural stone containing relics in a cavity and intended to serve as the essential part of an altar for the celebration of Mass in the Catholic Church. Consecration by a bishop of the same rite was required. In the Byza ...
. Placing of relics even in the base of a movable altar is also excluded.
"In building new churches, it is preferable for a single altar to be erected, one that in the gathering of the faithful will signify the one Christ and the one Eucharist of the Church. In already existing churches, however, when the old altar is so positioned that it makes the people's participation difficult but cannot be moved without damage to artistic value, another fixed altar, skillfully made and properly dedicated, should be erected and the sacred rites celebrated on it alone. In order that the attention of the faithful not be distracted from the new altar the old altar should not be decorated in any special way."
The altar, fixed or movable, should as a rule be separate from the wall so as to make it easy to walk around it and to celebrate Mass at it facing the people. It should be positioned so as to be the natural centre of attention of the whole congregation.
The altar should be covered by at least one white cloth, and nothing else should be placed upon the altar table other than what is required for the liturgical celebration. Candlesticks and a crucifix
A crucifix (from Latin ''cruci fixus'' meaning "(one) fixed to a cross") is a cross with an image of Jesus on it, as distinct from a bare cross. The representation of Jesus himself on the cross is referred to in English as the ''corpus'' (Lati ...
, when required, can be either on the altar or near it, and it is desirable that the crucifix remain even outside of liturgical celebrations.
Protestant churches
 A wide variety of altars exist in various Protestant denominations. Some Churches, such as the
A wide variety of altars exist in various Protestant denominations. Some Churches, such as the Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
, have altars very similar to Anglican or Catholic ones keeping with their more sacramental understanding of the Lord's Supper
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
. Calvinist churches from Reformed, Baptist, Congregational, and Non-denominational backgrounds instead have a Communion Table
Communion table or Lord's table are terms used by many Protestant churches—particularly from Reformed, Baptist and low church Anglican and Methodist bodies—for the table used for preparation of Holy Communion (a sacrament also called the '' ...
adorned with a linen cloth, as well as an open Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
and a pair of candlesticks; it is not referred to as an altar because they do not see Holy Communion
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
as sacrificial in any way. Such a table may be temporary: Moved into place only when there is a Communion Service. Some nondenominational churches have no altar or communion table, even if they retain the practice of the " altar call" that originated in the Methodist Church
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related Christian denomination, denominations of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John W ...
.
 Some
Some Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
and other evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide Interdenominationalism, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "bor ...
churches practice what is referred to as an '' altar call'', whereby those who wish to make a new spiritual commitment to Jesus Christ are invited to come forward publicly.
It is so named because the supplicants, at the end of the sermon
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. El ...
, kneel at the altar rails
The altar rail (also known as a communion rail or chancel rail) is a low barrier, sometimes ornate and usually made of stone, wood or metal in some combination, delimiting the chancel or the sanctuary and altar in a church, from the nave and oth ...
, which are located around the altar within chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse.
Ove ...
.
Those that come forward will often recite a sinner's prayer
The Sinner's prayer (also called the Consecration prayer and Salvation prayer) is an evangelicalism, evangelical Christian term referring to any prayer of repentance, prayed by individuals who feel convinced of the presence of sin in their liv ...
, which, in evangelical understanding, if truly heart-felt indicates that they are now "saved". They may also be offered religious literature, counselling or other assistance. Many times it is said that those who come forth are going to " be saved". This is a ritual in which the supplicant makes a prayer of penitence (asking for his sins to be forgiven) and faith (called in evangelical Christianity "accepting Jesus Christ as their personal Lord and Saviour").
=Lutheran churches
= Altars inLutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
churches are often similar to those in Roman Catholic and Anglican churches. Lutherans believe that the altar represents Christ and should only be used to consecrate and distribute the Eucharist. Lutheran altars are commonly made out of granite, but other materials are also used. A crucifix is to be put above the altar. Sometimes relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
s are also placed around the altar.
=Anglican churches
= Altars in the Anglican Communion vary widely. In the
Altars in the Anglican Communion vary widely. In the Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
, the basis of doctrine and practice for the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
, there is no use of the specific word ''altar''; the item in question is called the Communion table, ''Lord's Table'' or ''Holy Table''. This remains the official terminology, though common usage may call the communion table an altar.
At the time of the Reformation, altars were fixed against the east end of the church, and the priests would celebrate the Mass standing at the front of the altar. Beginning with the rubric
A rubric is a word or section of text that is traditionally written or printed in red ink for emphasis. The word derives from the la, rubrica, meaning red ochre or red chalk, and originates in Medieval illuminated manuscripts from the 13th cent ...
s of the Book of Common Prayer (1552), Second Prayer Book of Edward VI published in 1552, and through the Book of Common Prayer (1662), 1662 ''Book of Common Prayer'' (which prevailed for almost 300 years and is still in occasional use), the priest is directed to stand "at the north syde of the Table". This was variously interpreted over the years to mean the north side of the front of a fixed communion table, the north end of a fixed table (i.e., facing south), the north side of a free-standing table (presumably facing those intending to receive the Elements who would be sitting in the quire stalls opposite), or at the north end of a free-standing table lengthwise in the chancel, facing a congregation seated in the nave.
Often, where a celebrant chose to situate himself was meant to convey his churchmanship (that is, more Reformed or more Catholic). The use of candles or church tabernacle, tabernacles was banned by canon law, with the only appointed adornment being a white linen cloth.
 Beginning with the Oxford Movement in the 19th century, the appearance of Anglican altars took a dramatic turn in many churches. Candles and, in some cases, tabernacles were re‑introduced. In some churches two candles, on each end of the altar, were used; in other cases six—three on either side of a tabernacle, typically surmounted by a crucifix or some other image of Christ.
Beginning with the Oxford Movement in the 19th century, the appearance of Anglican altars took a dramatic turn in many churches. Candles and, in some cases, tabernacles were re‑introduced. In some churches two candles, on each end of the altar, were used; in other cases six—three on either side of a tabernacle, typically surmounted by a crucifix or some other image of Christ.
 In Anglican practice, conformity to a given standard depends on the ecclesiastical province and/or the liturgical sensibilities of a given parish. In the ''Parson's Handbook'', an influential manual for priests popular in the early-to-mid-twentieth century, Percy Dearmer recommends that "All altars should be 3 ft. 3 in. high, and ''at least'' deep enough to take a corporal [the square of linen placed underneath the Communion vessels] 20 in. square, with an inch or two to spare." He also recommends that the altar stand upon three steps for each of the three sacred ministers, and that it be decorated with a silk frontal in the liturgical colours, seasonal colour. In some cases, other manuals suggest that a stone be set in the top of wooden altars, in the belief that the custom be maintained of consecrating the bread and wine on a stone surface. In many other Anglican parishes, the custom is considerably less rigorous, especially in those parishes which use free-standing altars. Typically, these altars are made of wood, and may or may not have a solid front, which may or may not be ornamented. In many Anglican parishes, the use of frontals has persisted.
When altars are placed away from the wall of the chancel allowing a westward orientation, only two candles are placed on either end of it, since six would obscure the liturgical action, undermining the intent of a westward orientation (i.e., that it be visible to the congregation). In such an arrangement, a tabernacle may stand to one side of or behind the altar, or an aumbry may be used.
Sensibilities concerning the sanctity of the altar are widespread in Anglicanism. In some parishes, the notion that the surface of the altar should only be touched by those in holy orders is maintained. In others, there is considerably less strictness about the communion table. Nonetheless, the continued popularity of communion rails in Anglican church construction suggests that a sense of the sanctity of the altar and its surrounding area persists. In most cases, moreover, the practice of allowing only those items that have been blessed to be placed on the altar is maintained (that is, the linen cloth, candles, missal, and the Eucharistic vessels).
In Anglican practice, conformity to a given standard depends on the ecclesiastical province and/or the liturgical sensibilities of a given parish. In the ''Parson's Handbook'', an influential manual for priests popular in the early-to-mid-twentieth century, Percy Dearmer recommends that "All altars should be 3 ft. 3 in. high, and ''at least'' deep enough to take a corporal [the square of linen placed underneath the Communion vessels] 20 in. square, with an inch or two to spare." He also recommends that the altar stand upon three steps for each of the three sacred ministers, and that it be decorated with a silk frontal in the liturgical colours, seasonal colour. In some cases, other manuals suggest that a stone be set in the top of wooden altars, in the belief that the custom be maintained of consecrating the bread and wine on a stone surface. In many other Anglican parishes, the custom is considerably less rigorous, especially in those parishes which use free-standing altars. Typically, these altars are made of wood, and may or may not have a solid front, which may or may not be ornamented. In many Anglican parishes, the use of frontals has persisted.
When altars are placed away from the wall of the chancel allowing a westward orientation, only two candles are placed on either end of it, since six would obscure the liturgical action, undermining the intent of a westward orientation (i.e., that it be visible to the congregation). In such an arrangement, a tabernacle may stand to one side of or behind the altar, or an aumbry may be used.
Sensibilities concerning the sanctity of the altar are widespread in Anglicanism. In some parishes, the notion that the surface of the altar should only be touched by those in holy orders is maintained. In others, there is considerably less strictness about the communion table. Nonetheless, the continued popularity of communion rails in Anglican church construction suggests that a sense of the sanctity of the altar and its surrounding area persists. In most cases, moreover, the practice of allowing only those items that have been blessed to be placed on the altar is maintained (that is, the linen cloth, candles, missal, and the Eucharistic vessels).
Eastern Christian Rites
Byzantine Rite
 In Greek language, Greek the word () can mean an altar of any religion or, in a broader sense, the area surrounding it; that is to say, the entire sanctuary. In an
In Greek language, Greek the word () can mean an altar of any religion or, in a broader sense, the area surrounding it; that is to say, the entire sanctuary. In an Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
or a Byzantine Rite Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic church this sanctuary includes both the area behind the iconostasis
In Eastern Christianity, an iconostasis ( gr, εἰκονοστάσιον) is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a Church (building), church. ''Iconostasis'' also refers to a portable icon stand t ...
, and the soleas (the elevated projection in front of the iconostasis), and the Ambon (liturgy), ambo. It is also called the βῆμα (Bema#Christianity, bema). When one enters the sanctuary, one is said to be going into the or . The altar itself in such a church may be referred to as either the ''Holy Table'' (Greek ) or the ''Throne'' (Church Slavonic language, chu ).
For both Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Eastern Catholics, the Holy Table (altar) is normally free-standing, although in very small sanctuaries it might be placed flush against the back wall for reasons of space. They are typically about one meter high, and although they may be made of stone they are generally built out of wood. The exact dimensions may vary, but it is generally square in Floor plan, plan and in reasonable proportion to the size of the sanctuary. It has five legs: one at each corner plus a central pillar for supporting the relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
which are placed in it at its consecration.
A plain linen covering (Greek: , Slavonic: ) is bound to the Holy Table with cords; this cover is never removed after the altar is consecrated, and is considered to be the "baptismal garment" of the altar. The linen covering symbolizes the Epitaphios (liturgical), winding sheet in which the body of Christ was wrapped when he was laid in the Holy Sepulchre, tomb. Since the altar is never seen uncovered thereafter, the table tends to be constructed more with sturdiness than aesthetics in mind. Above this first cover is a second ornamented altar cloth (), often in a brocade of a liturgical color that may change with the liturgical year, ecclesiastical season. This outer covering usually comes all the way to the floor and represents the glory of God's Throne. In many churches it is the custom for a dust cover to be placed on the Holy Table between services. This is often a simple red cloth, though it may be made of richer stuff. Sometimes it covers only the Gospel Book or the front half of the Holy Table, but it may be large enough to cover the entire Holy Table and everything on it, including candlesticks and the seven-branch candelabra.
 Atop the altar is the Church tabernacle, tabernacle (), a miniature shrine sometimes built in the form of a church, inside of which is a small ark containing the reserved sacrament for use in communing the sick. Also kept on the altar is the Gospel Book. Under the Gospel is kept the '' antimension'', a silken cloth imprinted with an icon of Deposition from the Cross, Christ being prepared for burial, which has a
Atop the altar is the Church tabernacle, tabernacle (), a miniature shrine sometimes built in the form of a church, inside of which is a small ark containing the reserved sacrament for use in communing the sick. Also kept on the altar is the Gospel Book. Under the Gospel is kept the '' antimension'', a silken cloth imprinted with an icon of Deposition from the Cross, Christ being prepared for burial, which has a relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
sewn into it and bears the signature of the bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
. Another, simpler cloth, the , is wrapped around the antimension to protect it, and symbolizes the "napkin" that was tied around the face of Jesus when he was laid in the tomb (forming a companion to the ). The Divine Liturgy must be served on an antimension even if the altar has been consecrated and contains relics. When not in use, the antimension is left in place in the center of the Holy Table and is not removed except for necessity.
The Holy Table may only be touched by ordained members of the higher clergy
and nothing which is not itself consecrated or an object of veneration should be placed on it. Objects may also be placed on the altar as part of the process for setting them aside for sacred use. For example, icons are usually blessed by laying them on the Holy Table for a period of time or for a certain number of Divine Liturgies before sprinkling them with holy water, and placing them where they will be veneration, venerated. The Epitaphios (liturgical), Epitaphios on Good Friday, and the Cross on the Feasts of the Cross, are also placed on the Holy Table before they are taken to the center of the church to be venerated by the faithful.
In place of the outer covering, some altars have a permanent solid cover which may be highly ornamented, richly carved, or even plated in precious metals. A smaller brocade cover is used on top of this if it is desired that the altar decoration reflect the liturgical season.
Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
, where bread and wine are offered to God the Father and the Holy Spirit is invoked to make his Son Jesus Christ present in the Gifts. It is also the place where the presiding clergy stand at any service, even where no Eucharist is being celebrated and no offering is made other than prayer. When the priest reads the Gospel during Matins (or All-Night Vigil) on Sunday, he reads it standing in front of the Holy Table, because it represents the Tomb of Christ, and the Gospel lessons for Sunday Matins are always one of the Resurrection appearances of Jesus.
On the northern side of the sanctuary stands another, smaller altar, known as the Table of Oblation ( or ) at which the Liturgy of Preparation takes place. On it the bread and wine are prepared before the Divine Liturgy. The Prothesis symbolizes the cave of Bethlehem and also the Holy Sepulchre#Modern arrangement of the church, Anointing Stone at which the Body of Christ was prepared after the Deposition from the Cross. The Table of Oblation is also blessed, sprinkled with holy water and vested at the consecration of a church, but there are no relics placed in it. Nothing other than the sacred vessels, veils, etc. which are used in the Liturgy of Preparation may be placed on the Table of Oblation. The Epitaphios and Cross are also placed on the Table of Oblation before the priest and deacon solemnly transfer them to the Holy Table. In addition to the higher clergy, subdeacon
Subdeacon (or sub-deacon) is a minor order or ministry for men in various branches of Christianity. The subdeacon has a specific liturgical role and is placed between the acolyte (or reader) and the deacon in the order of precedence.
Subdeacons in ...
s are permitted to touch the Table of Oblation, but no one of lesser rank may do so. The ''Table of Oblation'' is the place where the deacon will consume the remaining Gifts (Eucharist, Body and Blood of Christ) after the Divine Liturgy and perform the ablution in Christianity, ablutions.
Syro-Maronite Church
The Syriac Maronite Church, along with the other Syriac Churches, has freestanding altars in most cases so the priests and deacons can circumambulate the altar during processions and incensations. Traditionally the Maronite liturgy was offered with the priest and people oriented to the East but because of modern latinizations it is common to find Maronite liturgies offered with the priest facing against the people from the opposite side of the altar, in imitation of modern practices in the Latin Church.Oriental Rites
Armenian Rite
 In the Armenian Rite the altar is placed against the eastern wall of the church, often in an apse. The shape of the altar is usually rectangular, similar to Latin altars, but is unusual in that it will normally have several steps on top of the table, on which are placed the Church tabernacle, tabernacle, candles, hexapteryga, ceremonial fans, a cross, and the Gospel Book. The altar is often located upon a kind of stage above a row of icons.
In the Armenian Rite the altar is placed against the eastern wall of the church, often in an apse. The shape of the altar is usually rectangular, similar to Latin altars, but is unusual in that it will normally have several steps on top of the table, on which are placed the Church tabernacle, tabernacle, candles, hexapteryga, ceremonial fans, a cross, and the Gospel Book. The altar is often located upon a kind of stage above a row of icons.
Alexandrian Rite
Altars in the Alexandrian (Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic Orthodox Church) tradition must have a square face upon which to offer the sacrifice. As the standard Coptic liturgy requires the priest to encircle the altar, it is never attached to any wall. Most Coptic altars are located under a baldachin.Ethiopic Rite
In Ethiopian Orthodox Church tradition an icon is placed upon but towards the rear of the altar. It is away from the wall as in the Coptic tradition.West Syriac Rite
In the West Syriac Tradition, churches have altars in the eastern part of the sanctuary.East Syriac
Altars of East Syriac Rite are similar in appearance to Armenian altars only they are not placed on a stage.Indian Rites
Altars are often heavily decorated in the Indian tradition.War altar
A war altar was a mobile altar on whichMass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
was celebrated before a battle. The ultimate example is the carroccio of the medieval Italy, Italian city states, which was a four-wheeled mobile shrine pulled by oxen and sporting a flagpole and a bell. The carroccio also served as the army standard.
Altar stones were used by army chaplains of the Latin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
in the period leading up to the 20th century.
Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, altars generally contain pictures or statues of gods and goddesses. Large, ornate altars are found in Hindu temples while smaller altars are found in homes and sometimes also in Hindu-run shops and restaurants. The word for temple is (), the altar as hypostasis (philosophy), hypostatised temple.
 In South Indian temples, often each god will have his or her own shrine, each contained in a miniature house (specifically, a ''mandir''). These shrines are often scattered around the temple compound, with the three main ones being in the main area. The statue of the god (murti) is placed on a stone pedestal in the shrine, and one or more lamps are hung in the shrine. There is usually a space to put the Puja (Hinduism), puja tray (tray with worship offerings). Directly outside the main shrine there will be a statue of the god's vahana or vehicle. The shrines have curtains hung over the entrances, and wooden doors which are shut when the deities are sleeping. Some South Indian temples have one main altar, with several statues placed upon it.
In South Indian temples, often each god will have his or her own shrine, each contained in a miniature house (specifically, a ''mandir''). These shrines are often scattered around the temple compound, with the three main ones being in the main area. The statue of the god (murti) is placed on a stone pedestal in the shrine, and one or more lamps are hung in the shrine. There is usually a space to put the Puja (Hinduism), puja tray (tray with worship offerings). Directly outside the main shrine there will be a statue of the god's vahana or vehicle. The shrines have curtains hung over the entrances, and wooden doors which are shut when the deities are sleeping. Some South Indian temples have one main altar, with several statues placed upon it.
 North Indian temples generally have one main altar at the front of the temple room. In some temples, the front of the room is separated with walls and several altars are placed in the alcoves. The statues on the altars are usually in pairs, each god with his consort (Radha-Krishna, Sita-Rama, Shiva-Parvati). However, some gods, such as Ganesha and Hanuman, are placed alone. Ritual items such as flowers or lamps may be placed on the altar.
Home shrines can be as simple or as elaborate as the householder can afford. Large, ornate shrines can be purchased in India and countries with large Hindu minorities, like Malaysia and Singapore. They are usually made of wood and have tiled floors for statues to be placed upon. Pictures may be hung on the walls of the shrine. The top of the shrine may have a series of levels, like a gopuram tower on a temple. Each Hindu altar will have at least one oil lamp and may contain a tray with puja equipment as well. Hindus with large houses will set aside one room as their puja room, with the altar at one end of it. Some South Indians also place a shrine with pictures of their departed relatives on the right side of the room, and make offerings to them before making offerings to the gods.
See also: Vedi (altar) and Homa (ritual)
North Indian temples generally have one main altar at the front of the temple room. In some temples, the front of the room is separated with walls and several altars are placed in the alcoves. The statues on the altars are usually in pairs, each god with his consort (Radha-Krishna, Sita-Rama, Shiva-Parvati). However, some gods, such as Ganesha and Hanuman, are placed alone. Ritual items such as flowers or lamps may be placed on the altar.
Home shrines can be as simple or as elaborate as the householder can afford. Large, ornate shrines can be purchased in India and countries with large Hindu minorities, like Malaysia and Singapore. They are usually made of wood and have tiled floors for statues to be placed upon. Pictures may be hung on the walls of the shrine. The top of the shrine may have a series of levels, like a gopuram tower on a temple. Each Hindu altar will have at least one oil lamp and may contain a tray with puja equipment as well. Hindus with large houses will set aside one room as their puja room, with the altar at one end of it. Some South Indians also place a shrine with pictures of their departed relatives on the right side of the room, and make offerings to them before making offerings to the gods.
See also: Vedi (altar) and Homa (ritual)
Taoism
Taoist altars are erected to honor traditional deities and the spirits of ancestors. Taoist altars may be erected in temples or in private homes. Strict traditions and different sects describe the items offered and the ritual involved in the temples, but folk custom in the homes is much freer. Imperial dynasties built huge altars called () to perform various sacrifice, offering ceremonies called (). The Temple of Heaven in Beijing is one of those. Nearly all forms of Chinese traditional religion involve ()--bowing towards an altar, with a stick of incense in one's hand. (Some schools prescribe the use of three sticks of incense in the hand at one time.) This may be done at home, or in a temple, or outdoors; by an ordinary person, or a professional (such as a Taoist priest); and the altar may feature any number of deities or ancestral tablets. is usually done in accordance with certain dates of the lunar/solar calendar (see Chinese calendar). At certain dates, food may be set out as asacrifice
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly exi ...
to the gods or spirits of the departed. (See, for example, Qingming Festival and Ghost Festival.) This may include rice, slaughtered pigs and ducks, or fruit. Another form of sacrifice involves the burning of Hell Bank Notes, on the assumption that images thus consumed by the fire will reappear—not as a mere image, but as the actual item—in the spirit world, and be available for the departed spirit to use. In Taoist folk religion, sometimes chickens, pigs' feet, and pig heads are given as offerings. But in orthodox Daoist practice, offerings should essentially be incense, candles and vegetarian offerings.
Buddhism
In Buddhist-following cultures, structures such as , butsudan, or spirit houses are found in temples or homes. In Japan, the butsudan is a wooden cabinet with doors that enclose and protect a religious image of the Gautama Buddha, Buddha or the Bodhisattvas (typically in the form of a statue) or a mandala scroll, installed in the highest place of honor and centered. The doors are opened to display the image during religious observances. A butsudan usually contains subsidiary religious items—called ''butsugu''—such as candlesticks, incense burners, bells, and platforms for placing offerings such as fruit. Some sects place ''ihai'', memorial tablets for deceased relatives, within or near the butsudan. Butsudans are often decorated with flowers. The shrine is placed in the temple or home as a place of worship to the Buddha, the Law of the Universe, etc. Scrolls (''honzon'') or statues are placed in the butsudan and prayed to morning and evening. Zen Buddhism, Zen Buddhists also meditation, meditate before the butsudan. The original design for the butsudan began in India, where people built altars as an offering-place to the Buddha. When Buddhism came to China and Korea statues of the Buddha were placed on pedestals or platforms. The Chinese and Koreans built walls and doors around the statues to shield them from the weather and also adapted elements of their respective indigenous religions. They could then safely offer their prayers, incense, etc. to the statue or scroll without it falling and breaking.Shinto
 In Shinto, altars are found in shrines. Originating in ancient times, are temporarily erected sacred spaces or "altars" used as a locus of worship. A physical area is demarcated with branches of green bamboo or at the four corners, between which are strung sacred border ropes (). In the center of the area a large branch of festooned with sacred emblems () is erected as a ''yorishiro'', a physical representation of the presence of the kami and toward which rites of worship are performed.
In more elaborate cases, a may be constructed by placing a rough straw mat upon the ground, then erecting a ceremonial eight-legged stand () upon the mat, and decorating the stand with a frame festooned with sacred border ropes and sacred border emblems. Finally the branch is erected in the center of this stand as the focus of worship.
In Shinto, altars are found in shrines. Originating in ancient times, are temporarily erected sacred spaces or "altars" used as a locus of worship. A physical area is demarcated with branches of green bamboo or at the four corners, between which are strung sacred border ropes (). In the center of the area a large branch of festooned with sacred emblems () is erected as a ''yorishiro'', a physical representation of the presence of the kami and toward which rites of worship are performed.
In more elaborate cases, a may be constructed by placing a rough straw mat upon the ground, then erecting a ceremonial eight-legged stand () upon the mat, and decorating the stand with a frame festooned with sacred border ropes and sacred border emblems. Finally the branch is erected in the center of this stand as the focus of worship.
Norse paganism
A basic altar, called a , was used for sacrifice in Norse paganism. The was constructed of piled stones, possibly in a wood (hearg, harrow), and would be used in sacrifices and perhaps other ceremonies as well. A possible use of the during a sacrifice would be to place upon it a bowl of the blood of an animal sacrificed to a Norse deity (e.g. a goat for Thor, a sow for Freyja, a boar for Freyr), then dipping a bundle of fir twigs into it and sprinkling the participants with the blood. This would consecrate the attendees to the ceremony, such as a wedding.Asatru
In Nordic Modern Pagan practice, altars may be set up in the home or in wooded areas in imitation of the hörgr of ancient times. They may be dedicated to Thor, Odin, or other Nordic deities.Neopaganism
In neopaganism there is a wide variety of ritual practice, running the gamut from a very eclectic syncretism to strict polytheistic reconstructionism. Many of these groups make use of altars. Some are constructed merely of rough-hewn or stacked stone, and some are made of fine wood or other finished material.Wicca
Neo-Druidism
Modern Neo-Druidism may also make use of altars, often erected in Grove (nature), groves. Though little is known of the specific religious beliefs and practices presided over by the ancient Druids, modern people who identify themselves as Druids are free to incorporate their imagination in developing ceremonies and the use of ritual objects in keeping with their belief system. The "Order of Common Worship" of the Reformed Druids of North America' ''Liturgy of the Druids'' calls for a fire to be started "in or near the altar" and makes use of various objects such as a chalice, staves, and a plant offering. If no altar is used, the objects may be placed on the ground.High places
High places are elevated areas on which altars have been erected for worship in the belief that, as they were nearer heaven than the plains and valleys, they are more favourable places for prayer. High places were prevalent in almost all ancient cultures as centers of cultic worship. High places in Israelite (Hebrew: ''Bamah'', or ''Bama'') or Canaanite culture were open-air shrines, usually erected on an elevated site. Prior to the conquest of Canaan by the Israelites in the the high places served as shrines of the Canaanite fertility deities, the Baals (Lords) and the Asherah, Asherot (Semitic goddesses). In addition to an altar, ''matzevot'' (stone pillars representing the presence of the divine) were erected. The practice of worship on these spots became frequent among the Hebrews, though after the temple was built it was forbidden. Such worship was with difficulty abolished, though denounced time after time by the prophets as an affront to God. A closely related example is a "backyard" altar, so to speak. Before there was a set temple and an established altar people built their own altars. After the temple was built use of these altars was forbidden. Unlike the case of high places, "backyard" altar worship was quickly eradicated. In following years, the practice drastically decreased in popularity.See also
*Altar candle *Altar cards *Altar Crucifix *Altars in Latin America *Altars in Roman Catholicism *Analogion *Ara Pacis *Back-choir *Cathedral diagram *Credence table *Dambana *Double Altar *Ofrenda *Predella *Prothesis (altar), Prothesis *Sacrament *Sacred architecture *Winged altarFootnotes
References
Sources
* *Further reading
*External links
* * * * * * {{Authority control Altars, Ceremonial magic Tables (furniture) Eucharistic objects Objects used in Hindu worship Shinto religious objects