Allylic Strain And Hydrogen Bonding on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
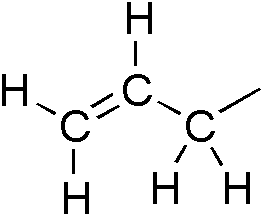 In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a
 A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic
A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic

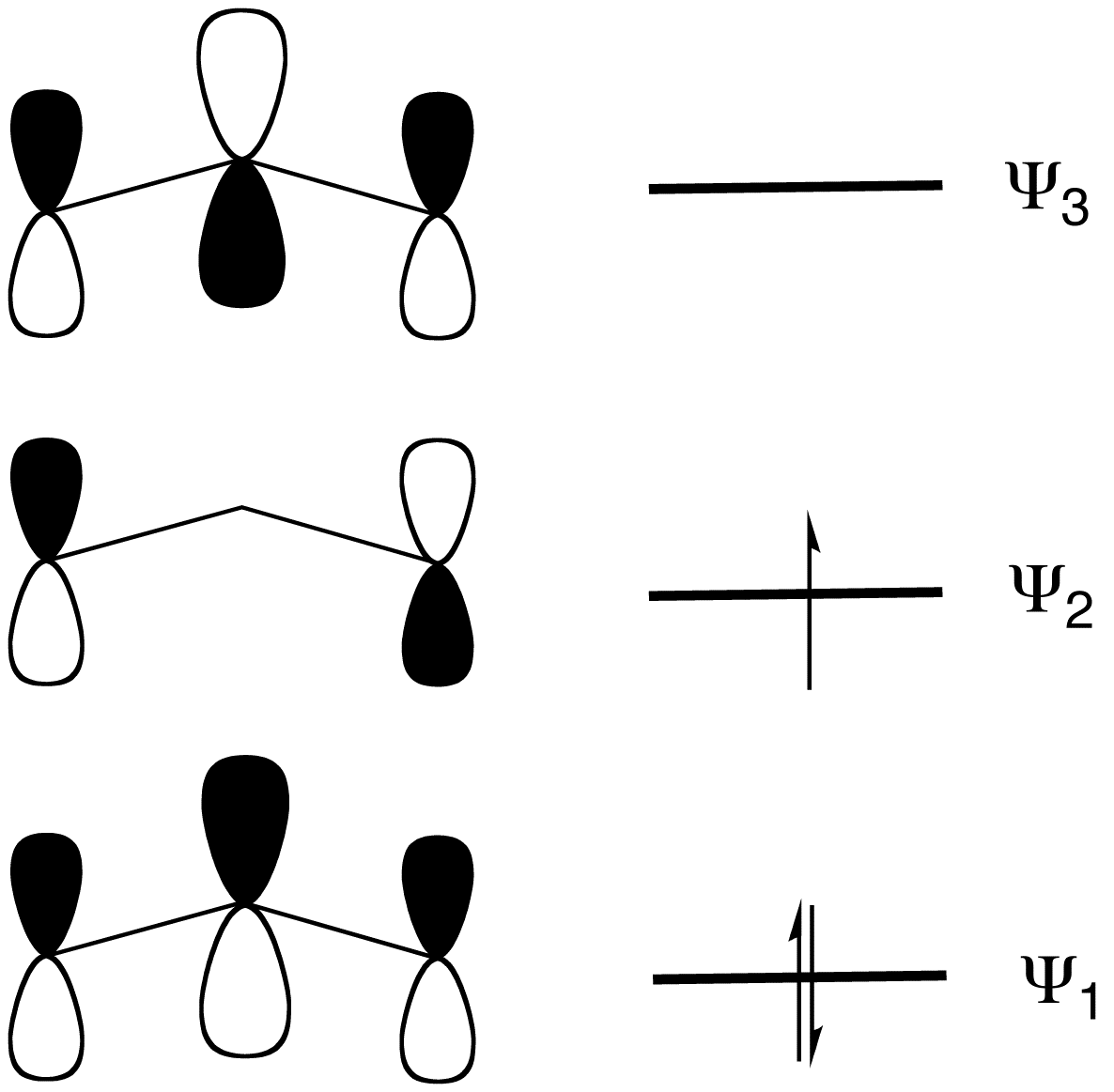
 In terms of MO theory, the MO diagram has three molecular orbitals: the first one bonding, the second one non-bonding, and the higher energy orbital is antibonding.Organic Chemistry 4th Ed. Morisson & Boyd 1988.
:
In terms of MO theory, the MO diagram has three molecular orbitals: the first one bonding, the second one non-bonding, and the higher energy orbital is antibonding.Organic Chemistry 4th Ed. Morisson & Boyd 1988.
:
2CH3-CH=CH2 + 2 NH3 + 3 O2 -> 2CH2=CH-C#N + 6 H2O
An estimated 800,000 tonnes (1997) of allyl chloride is produced by the chlorination of propylene:
:CH3CH=CH2 + Cl2 -> ClCH2CH=CH2 + HCl
It is the precursor to allyl alcohol and
 In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent
A substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. (In organic chemistry and biochemistry, the terms ''substituent'' and ''functional group'', as well as ''side ...
with the structural formula
The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure (determined by structural chemistry methods), showing how the atoms are possibly arranged in the real three-dimensional space. The chemical bondi ...
, where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.
Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (locomotion), the surface over which an organism lo ...
.
Nomenclature
hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive.
Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other reactions that tend to occur with allylic compounds are allylic oxidations, ene reactions, and the Tsuji–Trost reaction. Benzylic groups are related to allyl groups; both show enhanced reactivity.
Pentadienyl group
A group connected to two vinyl groups is said to be doubly allylic. The bond dissociation energy of C−H bonds on a doubly allylic centre is about 10% less than the bond dissociation energy of a C−H bond that is allylic. The weakened C−H bonds reflect the high stability of the resulting pentadienyl radicals. Compounds containing the linkages, e.g. linoleic acid derivatives, are prone to autoxidation, which can lead to polymerization or form semisolids. This reactivity pattern is fundamental to the film-forming behavior of the " drying oils", which are components of oil paints andvarnish
Varnish is a clear transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not a stain. It usually has a yellowish shade from the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmented as desired, and is sold commercially in various ...
es.

Homoallylic
The term homoallylic refers to the position on a carbon skeleton next to an allylic position. In but-3-enyl chloride , the chloride is homoallylic because it is bonded to the homoallylic site.
Bonding
The allyl group is widely encountered in organic chemistry.Jerry March, "Advanced Organic Chemistry" 4th Ed. J. Wiley and Sons, 1992: New York. . Allylicradicals
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
, anions, and cations are often discussed as intermediates in reactions. All feature three contiguous sp²-hybridized carbon centers and all derive stability from resonance.Organic Chemistry John McMurry 2nd ed. 1988 Each species can be presented by two resonance structures with the charge or unpaired electron distributed at both 1,3 positions.
:
Reactions and applications
This heightened reactivity of allylic groups has many practical consequences. Thesulfur vulcanization
Sulfur vulcanization is a chemical process for converting natural rubber or related polymers into materials of varying hardness, elasticity, and mechanical durability by heating them with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds. Sulfur forms cros ...
or various rubbers exploits the conversion of allylic groups into crosslinks. Similarly drying oils such as linseed oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colourless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by ...
crosslink via oxygenation of allylic (or doubly allylic) sites. This crosslinking underpins the properties of paints and the spoilage of foods by rancidification.
The industrial production of acrylonitrile by ammoxidation of propene exploits the easy oxidation of the allylic C−H centers:
:epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin (abbreviated ECH) is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organi ...
.
Allylation
Allylation is the attachment of an allyl group to a substrate, usually another organic compound. Classically, allylation involves the reaction of acarbanion
In organic chemistry, a carbanion is an anion in which carbon is trivalent (forms three bonds) and bears a formal negative charge (in at least one significant resonance form).
Formally, a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid:
:R3C ...
with allyl chloride. Another well-developed process involves addition of allyltrimethylsilane to carbonyls, i.e. carbonyl allylation.
Allylation can be effected also by conjugate addition: the addition of an allyl group to the beta-position of an enone. The Hosomi-Sakurai reaction is a common method for conjugate allylation.

Allyl compounds
Many substituents can be attached to the allyl group to give stable compounds. Commercially important allyl compounds include: * Crotyl alcohol (CH3CH=CH−CH2OH) * Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, central in the biosynthesis of terpenes, a precursor to many natural products, including natural rubber. * Transition-metal allyl complexes, such as allylpalladium chloride dimerSee also
* Allylic strain *Carroll rearrangement The Carroll rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry and involves the transformation of a β- keto allyl ester into a α-allyl-β-ketocarboxylic acid. This organic reaction is accompanied by decarboxylation and the final produc ...
* Allylic palladium complex
* Tsuji–Trost reaction
* Propargylic/Homopropargylic
* Benzylic
* Vinylic
* Acetylenic
* Naloxone
* Allylic rearrangement
References
{{Authority control Alkenyl groups Allyl compounds