Alkali metal oxide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The alkali metals react with oxygen to form several different compounds: suboxides, oxides,
The alkali metals react with oxygen to form several different compounds: suboxides, oxides,
 * Hexarubidium monoxide (Rb6O) h
* Nonarubidium dioxide (Rb9O2)
* Tricaesium monoxide (Cs3O) is a dark green solid.
* Tetracaesium monoxide (Cs4O)
* Heptacaesium monoxide (Cs7O)
* Tricaesium dioxide (Cs3O2)
* Heptacaesium dioxide (Cs7O2)
* Undecacaesium trioxide (Cs11O3)
* Undecacaesium monorubidium trioxide (Cs11RbO3)
* Undecacaesium dirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb2O3)
* Undecacaesium trirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb3O3)
* Hexarubidium monoxide (Rb6O) h
* Nonarubidium dioxide (Rb9O2)
* Tricaesium monoxide (Cs3O) is a dark green solid.
* Tetracaesium monoxide (Cs4O)
* Heptacaesium monoxide (Cs7O)
* Tricaesium dioxide (Cs3O2)
* Heptacaesium dioxide (Cs7O2)
* Undecacaesium trioxide (Cs11O3)
* Undecacaesium monorubidium trioxide (Cs11RbO3)
* Undecacaesium dirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb2O3)
* Undecacaesium trirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb3O3)
 * Lithium oxide (Li2O) is the lightest alkali metal oxide and a white solid. It melts at 1570 °C.
*
* Lithium oxide (Li2O) is the lightest alkali metal oxide and a white solid. It melts at 1570 °C.
*
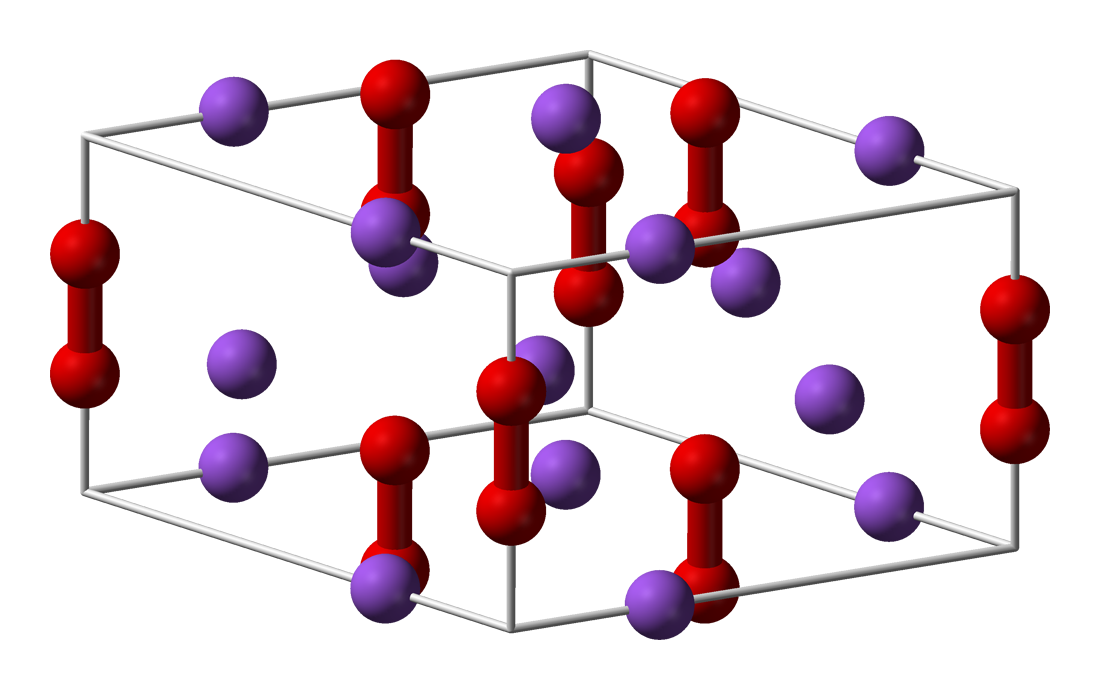 * Lithium peroxide (Li2O2) is a white solid that melts at 195 °C. It reacts with
* Lithium peroxide (Li2O2) is a white solid that melts at 195 °C. It reacts with
 *
*
 The alkali metals react with oxygen to form several different compounds: suboxides, oxides,
The alkali metals react with oxygen to form several different compounds: suboxides, oxides, peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where R = any element. The group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxo group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable.
The most common peroxide is hydrogen ...
s, sesquioxide
A sesquioxide is an oxide of an element (or radical), where the ratio between the number of atoms of that element and the number of atoms of oxygen is 2:3. For example, aluminium oxide and phosphorus(III) oxide are sesquioxides.
Many sesquio ...
s, superoxide
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula . The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of ...
s, and ozonide
Ozonide is the polyatomic anion . Cyclic organic compounds formed by the addition of ozone () to an alkene are also called ozonides.
Ionic ozonides
Inorganic ozonides are dark red salts. The anion has the bent shape of the ozone molecule.
In ...
s. They all react violently with water.
Alkali metal suboxides
 * Hexarubidium monoxide (Rb6O) h
* Nonarubidium dioxide (Rb9O2)
* Tricaesium monoxide (Cs3O) is a dark green solid.
* Tetracaesium monoxide (Cs4O)
* Heptacaesium monoxide (Cs7O)
* Tricaesium dioxide (Cs3O2)
* Heptacaesium dioxide (Cs7O2)
* Undecacaesium trioxide (Cs11O3)
* Undecacaesium monorubidium trioxide (Cs11RbO3)
* Undecacaesium dirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb2O3)
* Undecacaesium trirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb3O3)
* Hexarubidium monoxide (Rb6O) h
* Nonarubidium dioxide (Rb9O2)
* Tricaesium monoxide (Cs3O) is a dark green solid.
* Tetracaesium monoxide (Cs4O)
* Heptacaesium monoxide (Cs7O)
* Tricaesium dioxide (Cs3O2)
* Heptacaesium dioxide (Cs7O2)
* Undecacaesium trioxide (Cs11O3)
* Undecacaesium monorubidium trioxide (Cs11RbO3)
* Undecacaesium dirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb2O3)
* Undecacaesium trirubidium trioxide (Cs11Rb3O3)
Alkali metal oxides
 * Lithium oxide (Li2O) is the lightest alkali metal oxide and a white solid. It melts at 1570 °C.
*
* Lithium oxide (Li2O) is the lightest alkali metal oxide and a white solid. It melts at 1570 °C.
*Sodium oxide
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2 O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such as glass ...
(Na2O) is a white solid that melts at 1132 °C and decomposes at 1950 °C. It is a component of glass
Glass is a non-Crystallinity, crystalline, often transparency and translucency, transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most ...
.
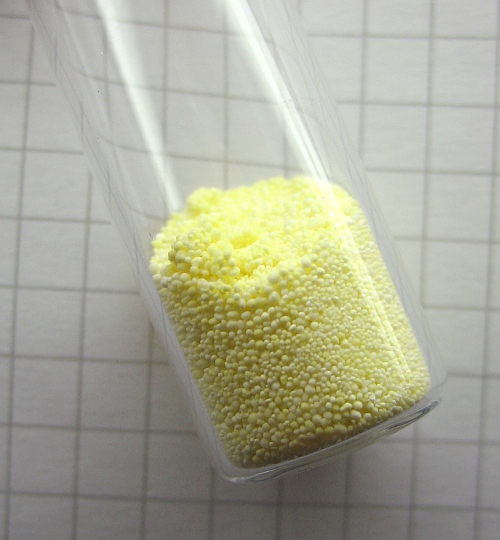
*Potassium oxide
Potassium oxide ( K O) is an ionic compound of potassium and oxygen. It is a base. This pale yellow solid is the simplest oxide of potassium. It is a highly reactive compound that is rarely encountered. Some industrial materials, such as fertili ...
(K2O) is a pale yellow solid that decomposes at 350 °C.
* Rubidium oxide (Rb2O) is a yellow solid that melts at 500 °C.
* Caesium oxide (Cs2O) is a yellow-orange solid that melts at 490 °C.
Alkali metal peroxides
 * Lithium peroxide (Li2O2) is a white solid that melts at 195 °C. It reacts with
* Lithium peroxide (Li2O2) is a white solid that melts at 195 °C. It reacts with carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
to form lithium carbonate
Lithium carbonate is an inorganic compound, the lithium salt of carbonate with the formula . This white salt is widely used in the processing of metal oxides. It is listed on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines because it ...
and oxygen.
*Sodium peroxide
Sodium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2O2. This yellowish solid is the product of sodium ignited in excess oxygen. It is a strong base. This metal peroxide exists in several hydrates and peroxyhydrates including Na2O2·2H2O ...
(Na2O2) is a pale yellow solid that melts at 460 °C and decomposes at 657 °C.
*Potassium peroxide
Potassium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula K2O2. It is formed as potassium reacts with oxygen in the air, along with potassium oxide (K2O) and potassium superoxide (KO2).
Potassium peroxide reacts with water to for ...
(K2O2) is a yellow solid that melts at 490 °C.
* Rubidium peroxide (Rb2O2) is produced when rubidium stands in air.
* Caesium peroxide (Cs2O2) is produced by the decomposition of caesium oxide above 400 °C.
Alkali metal sesquioxides
* Rubidium sesquioxide (Rb4O6)is a black solid. * Caesium sesquioxide (Cs4O6)is a black solid.Alkali metal superoxides
 *
*Lithium superoxide
Lithium superoxide is an unstable inorganic salt with formula Li O2. A radical compound, it can be produced at low temperature in matrix isolation experiments, or in certain nonpolar, non-protic solvents. Lithium superoxide is also a trans ...
(LiO2) has only been isolated in matrix isolation at 15 K.
*Sodium superoxide
Sodium superoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Na O2. This yellow-orange solid is a salt of the superoxide anion. It is an intermediate in the oxidation of sodium by oxygen.
Preparation
NaO2 is prepared by treating sodium peroxide ...
(NaO2) is a yellow-orange solid that melts at 551.7 °C. It is made by the high-pressure oxidation of sodium peroxide.
*Potassium superoxide
Potassium superoxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KO2. It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide anion. It is used as a scrubber, dehumidifier, and g ...
(KO2) is a yellow solid that decomposes at 560 °C. It is used as a CO2 scrubber, H2O dehumidifier, and O2 generator in rebreather
A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen is ...
s, spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth ...
, submarines
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely ...
, and spacesuit
A space suit or spacesuit is a garment worn to keep a human alive in the harsh environment of outer space, vacuum and temperature extremes. Space suits are often worn inside spacecraft as a safety precaution in case of loss of cabin pressure, ...
life support system
A life-support system is the combination of equipment that allows survival in an environment or situation that would not support that life in its absence. It is generally applied to systems supporting human life in situations where the outsid ...
s.
*Rubidium superoxide
Rubidium superoxide or Rubidium hyperoxide is a compound with the formula . In terms of oxidation states, the negatively charged superoxide and positively charged rubidium give it a structural formula of (Rb+)(O2−).
Chemistry
It can be created ...
(RbO2) is produced when rubidium burns in air.
*Caesium superoxide
Caesium superoxide is the superoxide of caesium. It is an orange solid.
Preparation
Burning caesium in excess oxygen will produce caesium superoxide.
:
Properties
Caesium superoxide's crystal structure is same as calcium carbide. It contain ...
(CsO2) is produced when caesium burns in air.
Alkali metal ozonides
*Lithium ozonide
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
(LiO3) is a red solid which is produced from caesium ozonide via an ion-exchange process.
*Sodium ozonide
Sodium ozonide (NaO3) is an oxygen-rich compound of sodium. As an ozonide, it contains the ozonide anion (O3−).
Some experiments report creating sodium ozonide by applying ozone to sodium hydroxide, but the substance was not pure, and the claim ...
(NaO3) is a red solid which is produced from caesium ozonide via an ion-exchange process.
*Potassium ozonide
Potassium ozonide is an oxygen rich compound of potassium. It is an ozonide, meaning it contains the ozonide anion (O3−). In polarized light, it shows pleochroism. Hybrid functional calculations have predicted the compound is an insulator with ...
(KO3) is a dark red solid which is produced when potassium is burned in ozone or exposed to air for years.
*Rubidium ozonide
Rubidium ozonide is an oxygen rich compound of rubidium. It is an ozonide, meaning it contains the ozonide anion (O3−).
It can be created by reacting rubidium superoxide (RbO2) with ozone (O3) in a liquid ammonia solution.
:RbO2 + O3 -> RbO3 + ...
(RbO3) is a dark red solid which is produced when rubidium is burned in ozone.
*Caesium ozonide
Caesium ozonide (CsO3) is an oxygen-rich compound of caesium. It is an ozonide, meaning it contains the ozonide anion (O3−). It can be formed by reacting ozone with caesium superoxide:
:CsO2 + O3 -> CsO3 + O2
The compound will react strongly w ...
(CsO3) is a dark red solid which is produced when caesium is burned in ozone. F. A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson "Advanced Inorganic Chemistry", 5th edition (1988), p.462
References
{{reflist Alkali metals Oxides