Alberto Del Bono (1856–1932) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alberto del Bono ( Parma, 21 September 1856 – Rome, 26 July 1932) was an Italian admiral and politician.
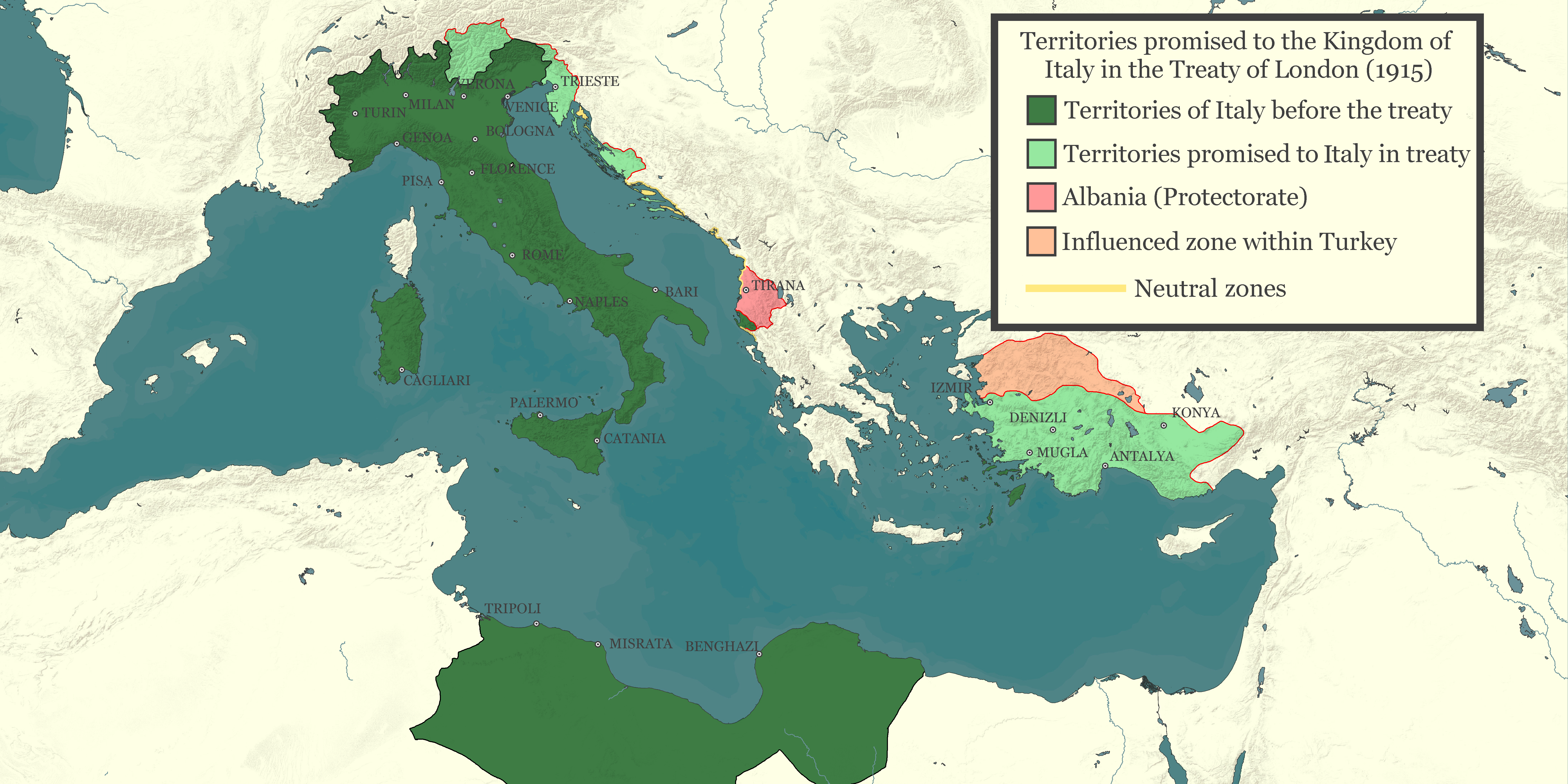 As minister Del Bono was also involved in the political and military decisions that determined the borders and power relations in the eastern Mediterranean. He was suspicious of French backing for the new Kingdom of Yugoslavia, convinced that France’ project to establish a base at
As minister Del Bono was also involved in the political and military decisions that determined the borders and power relations in the eastern Mediterranean. He was suspicious of French backing for the new Kingdom of Yugoslavia, convinced that France’ project to establish a base at
Naval career
He attended the naval schools of Naples and Genoa. Graduating in 1873 he entered the navy and was promoted on multiple occasions. Commander of the cruiser ''Ettore Fieramosca
Ettore Fieramosca (born Ferramosca) (Capua, 1476 – Valladolid, 20 January 1515) was an Italian condottiero and nobleman during the Italian Wars. His father was Rainaldo, baron of Rocca d'Evandro, and it is thought that his mother was a noble wo ...
'' from 18 December 1906 to 13 April 1908, he then assumed command of the battleship '' Regina Elena'' on 21 September 1908. In December of that year he distinguished himself in the relief efforts following the Messina earthquake
The 1908 Messina earthquake (also known as the 1908 Messina and Reggio earthquake) occurred on 28 December in Sicily and Calabria, southern Italy with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The epicente ...
, and around this time became acquainted with Umberto Cagni, commander of the battleship '' Napoli'' and Paolo Thaon di Revel, commander of the '' Vittorio Emanuele.''
Promoted rear admiral on 19 February 1911, he was a member of the Superior Navy Council from 16 March to 6 September 1911. Hewas then appointed commander of the Royal Naval Academy of Livorno on 6 September 1911, a position he held until 14 April 1914 during which he took part in the invasion of Libya with the naval training division composed of the cruisers '' Flavio Gioia'' (his flagship), '' Amerigo Vespucci'' and '' Etna''.
Political career
Promoted vice admiral in 1914, he was vice-president of the Superior Council of the Navy from 14 April 1914 to 11 January 1915 and commander in chief of the Upper Tyrrhenian Sea (La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest city ...
) since 1914, then general secretary of the Ministry of the Navy. He served as Minister of the Navy in the Boselli and Orlando governments and was appointed senator of the Kingdom of Italy.
After the defeat of Caporetto and the advance of Austrian troops to the Piave, Del Bono urged the Supreme Command and Prime Minister Orlando not to abandon Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, but at the same time he worked with Paolo Thaon Di Revel to prepare a plan for large-scale flooding of the areas between the Adige and the Brenta and construct a defensive line on the right of the Po. At the end of 1917, a marine regiment and a marine artillery group were established while armed pontoons, light vessels and reconnaissance seaplanes were massed on the lower Piave and in the lagoon of Venice.
 As minister Del Bono was also involved in the political and military decisions that determined the borders and power relations in the eastern Mediterranean. He was suspicious of French backing for the new Kingdom of Yugoslavia, convinced that France’ project to establish a base at
As minister Del Bono was also involved in the political and military decisions that determined the borders and power relations in the eastern Mediterranean. He was suspicious of French backing for the new Kingdom of Yugoslavia, convinced that France’ project to establish a base at Fiume
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
was intended to push Italy out of the upper Adriatic.
Del Bono was also at odds with both France and Britain over Italy's role in the peace settlement with the Ottoman Empire. In the Treaty of London (1915) and in the Agreement of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne London and Paris had agreed that Italy should occupy extensive territories in Anatolia following the Ottoman defeat. However in the event Britain and France were determined mainly to se use their own advantage in the region, and supported the Greek Occupation of Smyrna. Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino urged del Bono to send Italian warships into the Aegean Sea, but the British and French manoeuvred to keep Italy out of an active role, and the Italian crews in Rhodes were debilitated by the Spanish flu.
During his period in office Italy had to manage the reconstitution of its merchant marine, 57.5% of which had been sunk in the First World War with the loss of many trained and experienced seamen. Del Bono's solution was to bring all the nautical technical schools under the control of his ministry.
In the postwar debates about the future size and profile of the Italian navy, Del Bono supported building more battleships and declared his intention to complete the construction of the ''Caracciolo Caracciolo () is an Italian surname most associated with the noble House of Carácciolo from the Kingdom of Naples.
Other people with the name include:
* Alberto Caracciolo, Argentinian musician
* Andrea Caracciolo, Italian footballer
* Battiste ...
'', though he did not give much consideration to the future role of aircraft carriers and naval aviation.
Later life
From 1919 to 1921 he was commander of the Lower Tyrrhenian Sea ( Naples) and president of the Superior Council of the Navy; After leaving active service in 1921 he worked in the steel industry as manager of the Metallurgica Bresciana company (formerly Tempini) finally becoming president of Aero Espresso Italiana. Alberto del Bono died in Rome on July 26, 1932.Honours
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:del Bono, Alberto 1856 births 1932 deaths Italian admirals 19th-century Italian politicians 20th-century Italian politicians Members of the Senate of the Kingdom of Italy Ministers of the navy of Italy