Aircraft First Flown In 1945 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to
 A
A
 The forerunner of the fixed-wing aircraft is the
The forerunner of the fixed-wing aircraft is the 
 Rotorcraft, or rotary-wing aircraft, use a spinning
Rotorcraft, or rotary-wing aircraft, use a spinning
 * A ''
* A ''
16 August 2016, London 'Daily Telegraph' via Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 22 November 2016."Airlander 10, the world's largest aircraft, takes off for the first time," 19 August 2016, CBS News (TV) retrieved 22 November 2016.Kottasova, Ivan
"The world's largest aircraft crashes after 2nd test flight"
, 24 August 2016, ''CNN Tech'' on
16 May 2016, Fox News. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Rumbaugh, Andrea
"World's biggest airplane lands at Bush airport,"
Updated 18 November 2016, ''Houston Chronicle'' / Chron.com. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Lewis, Danny
"The World's Largest Aircraft Might Lose its Title to a Blimp,"
18 September 2015, ''Smart News'', Smithsonian.com,
Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved 22 November 2016. The aircraft was destroyed during the
28 July 2013,
"Wide-Body Transports"
, in Chapter 13, "Jet Transports," in Part II, "The Jet Age," in ''Quest for Performance: The Evolution of Modern Aircraft'', NASA SP-468, 1985, Scientific and Technical Information Branch,
29 April 2008, ''
Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2 December 2016. Prior to the X-43A, the fastest recorded powered airplane flight (and still the record for the fastest manned, powered airplane / fastest manned, non-spacecraft aircraft) was of the North American X-15A-2, rocket-powered airplane at Mach 6.72, or , on 3 October 1967. On one flight it reached an altitude of .Jackson, Doug
"Ask Us – Aircraft Speed Records,"
22 April 2001, Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved 22 November 2016."Fastest speed in a non-spacecraft aircraft,"
Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2 December 2016.Bergqvist, Pia
"Fastest Airplanes: Top Performers in Their Class,"
17 September 2014, '' Flying''. Retrieved 3 December 2016 The fastest known, production aircraft (other than rockets and missiles) currently or formerly operational (as of 2016) are: * The fastest fixed-wing aircraft, and fastest glider, is the
"Speed Regimes: Hypersonic Re-Entry,"
Glenn Research Center,
display notes, 29 May 2015,
"SR-71 Blackbird: Gone but not forgotten,"
26 January 2016, 9th Reconnaissance Wing Public Affairs, U.S. Air Force. Retrieved 2 December 2016"Absolute speed record still stands 40 years later," 27 July 2016 ''General Aviation News''. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Woolen, Angela
"SR-71 pilots, crew relive absolute speed record,"
9 August 2016, 78th Air Base Wing Public Affairs, United States Air Force. Retrieved 2 December 2016 :Note: Some sources refer to the above-mentioned X-15 as the "fastest military airplane" because it was partly a project of the U.S. Navy and Air Force; however, the X-15 was not used in non-experimental actual military operations. * The fastest current military aircraft are the Soviet/Russian
"The 9 fastest piloted planes in the world,"
18 September 2015, ''Business Insider''. Retrieved 3 December 2016"Fast and furious — the world's fastest military aircraft,"
''Airforce Technology''. Retrieved 3 December 2016The Five Fastest Military Jets Ever Made","
2016, Bloomberg. Retrieved 3 December 2016 * The fastest civilian airplane ever built, and fastest passenger airliner ever built: the briefly operated
Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2 December. 2016. * The fastest civilian airplane currently flying: the
15 April 2013, ''Wichita Business Journal''. Retrieved 22 November 2016. * The fastest airliner currently flying is the
Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved 22 November 2016. Before them, the
 Gliders are heavier-than-air aircraft that do not employ propulsion once airborne. Take-off may be by launching forward and downward from a high location, or by pulling into the air on a tow-line, either by a ground-based winch or vehicle, or by a powered "tug" aircraft. For a glider to maintain its forward air speed and lift, it must descend in relation to the air (but not necessarily in relation to the ground). Many gliders can "soar", ''i.e.'', gain height from updrafts such as thermal currents. The first practical, controllable example was designed and built by the British scientist and pioneer
Gliders are heavier-than-air aircraft that do not employ propulsion once airborne. Take-off may be by launching forward and downward from a high location, or by pulling into the air on a tow-line, either by a ground-based winch or vehicle, or by a powered "tug" aircraft. For a glider to maintain its forward air speed and lift, it must descend in relation to the air (but not necessarily in relation to the ground). Many gliders can "soar", ''i.e.'', gain height from updrafts such as thermal currents. The first practical, controllable example was designed and built by the British scientist and pioneer


in ''Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge'' (PHAK),
 Heavier-than-air types are characterised by one or more wings and a central
Heavier-than-air types are characterised by one or more wings and a central
in ''Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge'' (PHAK),
Glenn Research Center,
Glenn Research Center,
Glenn Research Center,
 The range is the distance an aircraft can fly between
The range is the distance an aircraft can fly between
 Flight dynamics is the science of air vehicle orientation and control in three dimensions. The three critical flight dynamics parameters are the
Flight dynamics is the science of air vehicle orientation and control in three dimensions. The three critical flight dynamics parameters are the
 An aircraft that is unstable tends to diverge from its intended flight path and so is difficult to fly. A very stable aircraft tends to stay on its flight path and is difficult to maneuver. Therefore, it is important for any design to achieve the desired degree of stability. Since the widespread use of digital computers, it is increasingly common for designs to be inherently unstable and rely on computerised control systems to provide artificial stability.
A fixed wing is typically unstable in pitch, roll, and yaw. Pitch and yaw stabilities of conventional fixed wing designs require horizontal and vertical stabilisers,Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 194. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', p. 10 (27th revised edition) which act similarly to the feathers on an arrow. These stabilizing surfaces allow equilibrium of aerodynamic forces and to stabilise the
An aircraft that is unstable tends to diverge from its intended flight path and so is difficult to fly. A very stable aircraft tends to stay on its flight path and is difficult to maneuver. Therefore, it is important for any design to achieve the desired degree of stability. Since the widespread use of digital computers, it is increasingly common for designs to be inherently unstable and rely on computerised control systems to provide artificial stability.
A fixed wing is typically unstable in pitch, roll, and yaw. Pitch and yaw stabilities of conventional fixed wing designs require horizontal and vertical stabilisers,Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 194. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', p. 10 (27th revised edition) which act similarly to the feathers on an arrow. These stabilizing surfaces allow equilibrium of aerodynamic forces and to stabilise the
 A military aircraft is any aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat:
* Combat aircraft are aircraft designed to destroy enemy equipment using its own armament. Combat aircraft divide broadly into
A military aircraft is any aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat:
* Combat aircraft are aircraft designed to destroy enemy equipment using its own armament. Combat aircraft divide broadly into
 Civil aircraft divide into ''commercial'' and ''general'' types, however there are some overlaps.
Civil aircraft divide into ''commercial'' and ''general'' types, however there are some overlaps.

The Evolution of Modern Aircraft (NASA)
Smithsonian Air and Space Museum
- online collection with a particular focus on history of aircraft and spacecraft
Amazing Early Flying Machines
slideshow by ''
Airliners.net
Aviation Dictionary
- free aviation terms, phrases and jargons
''New Scientist''s aviation page
{{Authority control
 An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbin ...
, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and ...
s. Common examples of aircraft include airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad ...
s, helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribu ...
s, airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
s (including blimp
A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships (e.g. Zeppelins), blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas (usually helium, rather than hy ...
s), gliders, paramotors
Powered paragliding, also known as paramotoring or PPG, is a form of ultralight aviation where the pilot wears a back-pack motor (a paramotor) which provides enough thrust to take off using a paraglider. It can be launched in still air, and on ...
, and hot air balloon
A hot air balloon is a lighter-than-air aircraft consisting of a bag, called an envelope, which contains heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule), which carries p ...
s.
The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical Society identifies ...
.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators, because they a ...
, but unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller ...
s may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion
A powered aircraft is an aircraft that uses onboard propulsion with mechanical power generated by an aircraft engine of some kind.
Aircraft propulsion nearly always uses either a type of propeller, or a form of jet propulsion. Other potential ...
, usage and others.
History
Flying model craft and stories of mannedflight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be a ...
go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air balloons developed in the 18th century. Each of the two World Wars
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
led to great technical advances. Consequently, the history of aircraft can be divided into five eras:
* Pioneers of flight, from the earliest experiments to 1914.
* First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, 1914 to 1918.
* Aviation between the World Wars
Sometimes dubbed the Golden Age of Aviation, the period in the history of aviation between the end of World War I (1918) and the beginning of World War II (1939) was characterised by a progressive change from the slow wood-and-fabric biplanes of ...
, 1918 to 1939.
* Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, 1939 to 1945.
* Postwar era
In Western world, Western usage, the phrase post-war era (or postwar era) usually refers to the time since the end of World War II. More broadly, a post-war period (or postwar period) is the interval immediately following the end of a war. A po ...
, also called the Jet Age
The Jet Age is a period in the history of aviation defined by the advent of aircraft powered by jet turbine engines, and by the social change this brought about.
Jet airliners were able to fly much higher, faster, and farther than older pisto ...
, 1945 to the present day.
Methods of lift
Lighter than air – aerostats

Aerostat
An aerostat (, via French) is a lighter-than-air aircraft that gains its lift through the use of a buoyant gas. Aerostats include unpowered balloons and powered airships. A balloon may be free-flying or tethered. The average density of the cra ...
s use buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the p ...
to float in the air in much the same way that ships float on the water. They are characterized by one or more large cells or canopies, filled with a relatively low-density gas such as helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
, or hot air
''Hot Air'' is a conservative American political blog. It is written by the pseudonymous Allahpundit, Ed Morrissey, John Sexton, and Jazz Shaw.
Hot Air was founded by Michelle Malkin, a conservative author and blogger, in 2006, taking over '' ...
, which is less dense than the surrounding air. When the weight of this is added to the weight of the aircraft structure, it adds up to the same weight as the air that the craft displaces.
Small hot-air balloons, called sky lantern
A sky lantern (), also known as Kǒngmíng lantern (), or Chinese lantern, is a small hot air balloon made of paper, with an opening at the bottom where a small fire is suspended.
In Asia and elsewhere around the world, sky lanterns have bee ...
s, were first invented in ancient China prior to the 3rd century BC and used primarily in cultural celebrations, and were only the second type of aircraft to fly, the first being kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. ...
s, which were first invented in ancient China over two thousand years ago. (See Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
)
 A
A balloon
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, and air. For special tasks, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light so ...
was originally any aerostat, while the term airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
was used for large, powered aircraft designs — usually fixed-wing. In 1919, Frederick Handley Page
Sir Frederick Handley Page, CBE, FRAeS (15 November 1885 – 21 April 1962) was an English industrialist who was a pioneer in the aircraft industry and became known as the father of the heavy bomber.
His company Handley Page Limited was ...
was reported as referring to "ships of the air," with smaller passenger types as "Air yachts." In the 1930s, large intercontinental flying boats were also sometimes referred to as "ships of the air" or "flying-ships". — though none had yet been built. The advent of powered balloons, called dirigible balloons, and later of rigid hulls allowing a great increase in size, began to change the way these words were used. Huge powered aerostats, characterized by a rigid outer framework and separate aerodynamic skin surrounding the gas bags, were produced, the Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp ...
s being the largest and most famous. There were still no fixed-wing aircraft or non-rigid balloons large enough to be called airships, so "airship" came to be synonymous with these aircraft. Then several accidents, such as the Hindenburg disaster
The ''Hindenburg'' disaster was an airship accident that occurred on May 6, 1937, in Manchester Township, New Jersey, United States. The German passenger airship LZ 129 ''Hindenburg'' caught fire and was destroyed during its attemp ...
in 1937, led to the demise of these airships. Nowadays a "balloon" is an unpowered aerostat and an "airship" is a powered one.
A powered, steerable aerostat is called a ''dirigible
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
''. Sometimes this term is applied only to non-rigid balloons, and sometimes ''dirigible balloon'' is regarded as the definition of an airship (which may then be rigid or non-rigid). Non-rigid dirigibles are characterized by a moderately aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
gasbag with stabilizing fins at the back. These soon became known as ''blimp
A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships (e.g. Zeppelins), blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas (usually helium, rather than hy ...
s''. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, this shape was widely adopted for tethered balloons
A tether is a cord, fixture, or flexible attachment that characteristically anchors something movable to something fixed; it also maybe used to connect two movable objects, such as an item being towed by its tow.
Applications for tethers includ ...
; in windy weather, this both reduces the strain on the tether and stabilizes the balloon. The nickname ''blimp'' was adopted along with the shape. In modern times, any small dirigible or airship is called a blimp, though a blimp may be unpowered as well as powered.
Heavier-than-air – aerodynes
Heavier-than-air aircraft, such asairplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad ...
s, must find some way to push air or gas downwards so that a reaction occurs (by Newton's laws of motion) to push the aircraft upwards. This dynamic movement through the air is the origin of the term. There are two ways to produce dynamic upthrust — aerodynamic lift
A fluid flowing around an object exerts a force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direc ...
, and powered lift
A powered lift aircraft takes off and lands vertically under engine power but uses a fixed wing for horizontal flight. Like helicopters, these aircraft do not need a long runway to take off and land, but they have a speed and performance similar ...
in the form of engine thrust.
Aerodynamic lift involving wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expres ...
s is the most common, with fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinc ...
being kept in the air by the forward movement of wings, and rotorcraft
A rotorcraft or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings or rotor blades, which generate lift by rotating around a vertical mast. Several rotor blades mounted on a single mast are referred to as a rotor. The Internati ...
by spinning wing-shaped rotors sometimes called "rotary wings." A wing is a flat, horizontal surface, usually shaped in cross-section as an aerofoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbine.
...
. To fly, air must flow over the wing and generate lift
Lift or LIFT may refer to:
Physical devices
* Elevator, or lift, a device used for raising and lowering people or goods
** Paternoster lift, a type of lift using a continuous chain of cars which do not stop
** Patient lift, or Hoyer lift, mobil ...
. A ''flexible wing'' is a wing made of fabric or thin sheet material, often stretched over a rigid frame. A ''kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. ...
'' is tethered to the ground and relies on the speed of the wind over its wings, which may be flexible or rigid, fixed, or rotary.
With powered lift, the aircraft directs its engine thrust vertically downward. V/STOL
A vertical and/or short take-off and landing (V/STOL) aircraft is an airplane able to take-off or land vertically or on short runways. Vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft are a subset of V/STOL craft that do not require runways at al ...
aircraft, such as the Harrier jump jet
The Harrier, informally referred to as the Harrier jump jet, is a family of jet-powered attack aircraft capable of vertical/short takeoff and landing operations (V/STOL). Named after a bird of prey, it was originally developed by British ma ...
and Lockheed Martin F-35B take off and land vertically using powered lift and transfer to aerodynamic lift in steady flight.
A pure rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
is not usually regarded as an aerodyne because it does not depend on the air for its lift (and can even fly into space); however, many aerodynamic lift vehicles have been powered or assisted by rocket motors. Rocket-powered missiles that obtain aerodynamic lift at very high speed due to airflow over their bodies are a marginal case.
Fixed-wing
 The forerunner of the fixed-wing aircraft is the
The forerunner of the fixed-wing aircraft is the kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. ...
. Whereas a fixed-wing aircraft relies on its forward speed to create airflow over the wings, a kite is tethered to the ground and relies on the wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
blowing over its wings to provide lift. Kites were the first kind of aircraft to fly and were invented in China around 500 BC. Much aerodynamic research was done with kites before test aircraft, wind tunnel
Wind tunnels are large tubes with air blowing through them which are used to replicate the interaction between air and an object flying through the air or moving along the ground. Researchers use wind tunnels to learn more about how an aircraft ...
s, and computer modelling programs became available.
The first heavier-than-air craft capable of controlled free-flight were gliders. A glider designed by George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific aeri ...
carried out the first true manned, controlled flight in 1853.
The practical, powered, fixed-wing aircraft (the airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad ...
or aeroplane) was invented by Wilbur and Orville Wright. Besides the method of propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
, fixed-wing aircraft are in general characterized by their wing configuration
The wing configuration of a fixed-wing aircraft (including both glider (aircraft), gliders and powered aeroplanes) is its arrangement of lifting and related surfaces.
Aircraft designs are often classified by their wing configuration. For examp ...
. The most important wing characteristics are:
* Number of wings — monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple planes.
A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing confi ...
, biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While ...
, etc.
* Wing support — Braced or cantilever, rigid, or flexible.
* Wing planform — including aspect ratio, angle of sweep
Sweep or swept may refer to:
Cleaning
* Sweep, the action of using a brush to clean
* Chimney sweep, a worker who clears ash and soot from chimneys
* Street sweeper, a person's occupation, or a machine that cleans streets
* Swept quartz, a cleani ...
, and any variations along the span (including the important class of delta wing
A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ).
Although long studied, it did not find significant applications until the Jet Age, when it proved suitabl ...
s).
* Location of the horizontal stabilizer, if any.
* Dihedral angle
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes or half-planes. In chemistry, it is the clockwise angle between half-planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry, it is defined as the uni ...
— positive, zero, or negative (anhedral).
A variable geometry aircraft can change its wing configuration during flight.
A ''flying wing
A flying wing is a tailless fixed-wing aircraft that has no definite fuselage, with its crew, payload, fuel, and equipment housed inside the main wing structure. A flying wing may have various small protuberances such as pods, nacelles, blis ...
'' has no fuselage, though it may have small blisters or pods. The opposite of this is a ''lifting body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage wi ...
'', which has no wings, though it may have small stabilizing and control surfaces.
Wing-in-ground-effect
A ground-effect vehicle (GEV), also called a wing-in-ground-effect (WIG), ground-effect craft, wingship, flarecraft or ekranoplan (russian: экранопла́н – "screenglider"), is a vehicle that is able to move over the surface by gainin ...
vehicles are generally not considered aircraft. They "fly" efficiently close to the surface of the ground or water, like conventional aircraft during takeoff. An example is the Russian ekranoplan nicknamed the "Caspian Sea Monster
The KM (Korabl Maket) (Russian: Корабль-Макет, literally "Ship-maquette" or "Model-Ship"), known colloquially as the Caspian Sea Monster, was an experimental ground effect vehicle developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s by the C ...
". Man-powered aircraft also rely on ground effect to remain airborne with minimal pilot power, but this is only because they are so underpowered—in fact, the airframe is capable of flying higher.

Rotorcraft
 Rotorcraft, or rotary-wing aircraft, use a spinning
Rotorcraft, or rotary-wing aircraft, use a spinning rotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
with aerofoil cross-section blades (a ''rotary wing'') to provide lift. Types include helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribu ...
s, autogyro
An autogyro (from Greek and , "self-turning"), also known as a ''gyroplane'', is a type of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift. Forward thrust is provided independently, by an engine-driven propeller. Whi ...
s, and various hybrids such as gyrodyne
A gyrodyne is a type of VTOL aircraft with a helicopter rotor-like system that is driven by its engine for takeoff and landing only, and includes one or more conventional propeller (aircraft), propeller or jet engines to provide forward thrust d ...
s and compound rotorcraft.
''Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
s'' have a rotor turned by an engine-driven shaft. The rotor pushes air downward to create lift. By tilting the rotor forward, the downward flow is tilted backward, producing thrust for forward flight. Some helicopters have more than one rotor and a few have rotors turned by gas jets at the tips. Some have a tail rotor
The tail rotor is a smaller rotor mounted vertically or near-vertically at the tail of a traditional single-rotor helicopter, where it rotates to generate a propeller-like horizontal thrust in the same direction as the main rotor's rotation. The ...
to counteract the rotation of the main rotor, and to aid directional control.
''Autogyro
An autogyro (from Greek and , "self-turning"), also known as a ''gyroplane'', is a type of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift. Forward thrust is provided independently, by an engine-driven propeller. Whi ...
s'' have unpowered rotors, with a separate power plant to provide thrust. The rotor is tilted backward. As the autogyro moves forward, air blows upward across the rotor, making it spin. This spinning increases the speed of airflow over the rotor, to provide lift. Rotor kite
A rotor kite or gyrokite is an unpowered, rotary-wing aircraft. Like an autogyro or helicopter, it relies on lift created by one or more sets of rotors in order to fly. Unlike a helicopter, gyrokites and rotor kites do not have an engine poweri ...
s are unpowered autogyros, which are towed to give them forward speed or tethered to a static anchor in high-wind for kited flight.
''Cyclogyro
The cyclogyro, or cyclocopter, is an aircraft configuration that uses a horizontal-axis cyclorotor as a rotor wing to provide lift and sometimes also propulsion and control. In principle, the cyclogyro is capable of vertical take off and land ...
s'' rotate their wings about a horizontal axis.
''Compound rotorcraft'' have wings that provide some or all of the lift in forward flight. They are nowadays classified as ''powered lift
A powered lift aircraft takes off and lands vertically under engine power but uses a fixed wing for horizontal flight. Like helicopters, these aircraft do not need a long runway to take off and land, but they have a speed and performance similar ...
'' types and not as rotorcraft. ''Tiltrotor
A tiltrotor is an aircraft which generates lift and propulsion by way of one or more powered rotors (sometimes called ''proprotors'') mounted on rotating shafts or nacelles usually at the ends of a fixed wing. Almost all tiltrotors use a trans ...
'' aircraft (such as the Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey
The Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey is an American multi-mission, tiltrotor military aircraft with both vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities. It is designed to combine the functionality of a convention ...
), tiltwing
A tiltwing aircraft features a wing that is horizontal for conventional forward flight and rotates up for vertical takeoff and landing. It is similar to the tiltrotor design where only the propeller and engine rotate. Tiltwing aircraft are typical ...
, tail-sitter
A tail-sitter, or tailsitter, is a type of VTOL aircraft that takes off and lands on its tail, then tilts horizontally for forward flight.
Originating in the 1920s with the inventor Nikola Tesla, the first aircraft to adopt a tail-sitter configur ...
, and coleopter
A coleopter is a type of VTOL aircraft design that uses a ducted fan as the primary fuselage of the entire aircraft. Generally they appear to be a large barrel-like extension at the rear, with a small cockpit area suspended above it. Coleopters ...
aircraft have their rotors/propellers
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
horizontal for vertical flight and vertical for forward flight.
Other methods of lift
 * A ''
* A ''lifting body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage wi ...
'' is an aircraft body shaped to produce lift. If there are any wings, they are too small to provide significant lift and are used only for stability and control. Lifting bodies are not efficient: they suffer from high drag, and must also travel at high speed to generate enough lift to fly. Many of the research prototypes, such as the Martin Marietta X-24
The Martin Marietta X-24 was an American experimental aircraft developed from a joint United States Air Force-NASA program named PILOT (1963–1975). It was designed and built to test lifting body concepts, experimenting with the concept of u ...
, which led up to the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
, were lifting bodies, though the Space Shuttle is not, and some supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
missile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket i ...
s obtain lift from the airflow over a tubular body.
* ''Powered lift
A powered lift aircraft takes off and lands vertically under engine power but uses a fixed wing for horizontal flight. Like helicopters, these aircraft do not need a long runway to take off and land, but they have a speed and performance similar ...
'' types rely on engine-derived lift for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-win ...
). Most types transition to fixed-wing lift for horizontal flight. Classes of powered lift types include VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-win ...
jet aircraft (such as the Harrier jump jet
The Harrier, informally referred to as the Harrier jump jet, is a family of jet-powered attack aircraft capable of vertical/short takeoff and landing operations (V/STOL). Named after a bird of prey, it was originally developed by British ma ...
) and tiltrotor
A tiltrotor is an aircraft which generates lift and propulsion by way of one or more powered rotors (sometimes called ''proprotors'') mounted on rotating shafts or nacelles usually at the ends of a fixed wing. Almost all tiltrotors use a trans ...
s, such as the Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey
The Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey is an American multi-mission, tiltrotor military aircraft with both vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities. It is designed to combine the functionality of a convention ...
, among others. A few experimental designs rely entirely on engine thrust to provide lift throughout the whole flight, including personal fan-lift hover platforms and jetpacks. VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-win ...
research designs include the Rolls-Royce Thrust Measuring Rig
The Rolls-Royce Thrust Measuring Rig (TMR), was a pioneering vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft developed by Rolls-Royce in the 1950s. It has the distinction of being "the first jet-lift aircraft to fly anywhere in the world".
The ...
.
* The ''Flettner airplane
A Flettner airplane is a type of rotor airplane which uses a Flettner rotor to provide lift. The rotor comprises a spinning cylinder with circular end plates and, in an aircraft, spins about a spanwise horizontal axis. When the aircraft moves ...
'' uses a rotating cylinder in place of a fixed wing, obtaining lift from the Magnus effect
The Magnus effect is an observable phenomenon commonly associated with a spinning object moving through a fluid. The path of the spinning object is deflected in a manner not present when the object is not spinning. The deflection can be expl ...
.
* The ''ornithopter
An ornithopter (from Greek ''ornis, ornith-'' "bird" and ''pteron'' "wing") is an aircraft that flies by flapping its wings. Designers sought to imitate the flapping-wing flight of birds, bats, and insects. Though machines may differ in form, th ...
'' obtains thrust by flapping its wings.
Size and speed extremes
Size
The smallest aircraft are toys/recreational items, and nano aircraft. The largest aircraft by dimensions and volume (as of 2016) is the long BritishAirlander 10
The Hybrid Air Vehicles Airlander 10, originally developed as the HAV 304, is a hybrid airship designed and built by British manufacturer Hybrid Air Vehicles (HAV). Comprising a helium airship with auxiliary wing and tail surfaces, it flies u ...
, a hybrid blimp, with helicopter and fixed-wing features, and reportedly capable of speeds up to , and an airborne endurance of two weeks with a payload of up to ."World's largest aircraft the Airlander makes maiden flight in UK,"16 August 2016, London 'Daily Telegraph' via Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 22 November 2016."Airlander 10, the world's largest aircraft, takes off for the first time," 19 August 2016, CBS News (TV) retrieved 22 November 2016.Kottasova, Ivan
"The world's largest aircraft crashes after 2nd test flight"
, 24 August 2016, ''CNN Tech'' on
CNN
CNN (Cable News Network) is a multinational cable news channel headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news channel, and presently owned by ...
, the Cable News Network. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
The largest aircraft by weight and largest regular fixed-wing aircraft ever built, , was the Antonov An-225 ''Mriya''. That Ukrainian-built six-engine Russian transport of the 1980s is long, with an wingspan. It holds the world payload record, after transporting of goods, and has recently flown loads commercially. With a maximum loaded weight of , it was also the heaviest aircraft built to date. It could cruise at ."Watch the world's biggest plane land in Australia,"16 May 2016, Fox News. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Rumbaugh, Andrea
"World's biggest airplane lands at Bush airport,"
Updated 18 November 2016, ''Houston Chronicle'' / Chron.com. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Lewis, Danny
"The World's Largest Aircraft Might Lose its Title to a Blimp,"
18 September 2015, ''Smart News'', Smithsonian.com,
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
, Washington, D.C.. Retrieved 22 November 2016."Ask Us – Largest Plane in the World,"Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved 22 November 2016. The aircraft was destroyed during the
Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatist forces in Donbas, Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since Feb ...
.
The largest military airplanes are the Ukrainian Antonov An-124 ''Ruslan'' (world's second-largest airplane, also used as a civilian transport),"World's Second Largest Aircraft,"28 July 2013,
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
. Retrieved 22 November 2016. and American Lockheed C-5 Galaxy
The Lockheed C-5 Galaxy is a large military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed, and now maintained and upgraded by its successor, Lockheed Martin. It provides the United States Air Force (USAF) with a heavy intercontinental-rang ...
transport, weighing, loaded, over .Loftin, Laurence K., Jr."Wide-Body Transports"
, in Chapter 13, "Jet Transports," in Part II, "The Jet Age," in ''Quest for Performance: The Evolution of Modern Aircraft'', NASA SP-468, 1985, Scientific and Technical Information Branch,
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
, Washington, D.C., Updated: 6 August 2004. Retrieved 22 November 2016. The 8-engine, piston/propeller Hughes H-4 ''Hercules'' "Spruce Goose" — an American World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
wooden flying boat transport with a greater wingspan (94m/260ft) than any current aircraft and a tail height equal to the tallest (Airbus A380-800 at 24.1m/78ft) — flew only one short hop in the late 1940s and never flew out of ground effect.
The largest civilian airplanes, apart from the above-noted An-225 and An-124, are the Airbus Beluga
The Airbus A300-600ST (Super Transporter), or Beluga, is a version of the standard A300-600 wide-body airliner modified to carry aircraft parts and outsize cargo. It received the official name of ''Super Transporter'' early on; however, the nam ...
cargo transport derivative of the Airbus A300
The Airbus A300 is a wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Airbus.
In September 1967, aircraft manufacturers in the United Kingdom, France, and West Germany signed a memorandum of understanding to develop a large airliner.
West G ...
jet airliner, the Boeing Dreamlifter cargo transport derivative of the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, t ...
jet airliner/transport (the 747-200B was, at its creation in the 1960s, the heaviest aircraft ever built, with a maximum weight of over ), and the double-decker Airbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a large wide-body airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and only full-length double-deck jet airliner.
Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was annou ...
"super-jumbo" jet airliner (the world's largest passenger airliner)."Airbus reviews A380 schedule,"29 April 2008, ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Speeds
The fastest recorded powered aircraft flight and fastest recorded aircraft flight of an air-breathing powered aircraft was of theNASA X-43
The NASA X-43 was an experimental unmanned hypersonic aircraft with multiple planned scale variations meant to test various aspects of hypersonic flight. It was part of the X-plane series and specifically of NASA's Hyper-X program. It set seve ...
A ''Pegasus'', a scramjet
A scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully ...
-powered, hypersonic
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds 5 times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above.
The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since in ...
, lifting body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage wi ...
experimental research aircraft, at Mach 9.6, exactly . The X-43A set that new mark, and broke its own world record of Mach 6.3, exactly , set in March 2004, on its third and final flight on 16 November 2004."Hypersonic X-43A Takes Flight.htm,"NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
retrieved November 2016."Fastest aircraft, air-breathing engine,"Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2 December 2016. Prior to the X-43A, the fastest recorded powered airplane flight (and still the record for the fastest manned, powered airplane / fastest manned, non-spacecraft aircraft) was of the North American X-15A-2, rocket-powered airplane at Mach 6.72, or , on 3 October 1967. On one flight it reached an altitude of .Jackson, Doug
"Ask Us – Aircraft Speed Records,"
22 April 2001, Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved 22 November 2016."Fastest speed in a non-spacecraft aircraft,"
Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2 December 2016.Bergqvist, Pia
"Fastest Airplanes: Top Performers in Their Class,"
17 September 2014, '' Flying''. Retrieved 3 December 2016 The fastest known, production aircraft (other than rockets and missiles) currently or formerly operational (as of 2016) are: * The fastest fixed-wing aircraft, and fastest glider, is the
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
, a rocket-glider hybrid, which has re-entered the atmosphere as a fixed-wing glider at more than Mach 25, equal to .Benson, Tom, ed."Speed Regimes: Hypersonic Re-Entry,"
Glenn Research Center,
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
* The fastest military airplane ever built: Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, a U.S. reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmisher ...
jet fixed-wing aircraft, known to fly beyond Mach 3.3, equal to . On 28 July 1976, an SR-71 set the record for the fastest and highest-flying operational aircraft with an absolute speed record of and an absolute altitude record of . At its retirement in January 1990, it was the fastest air-breathing aircraft / fastest jet aircraft in the world, a record still standing ."Lockheed SR-71A,"display notes, 29 May 2015,
National Museum of the United States Air Force
The National Museum of the United States Air Force (formerly the United States Air Force Museum) is the official museum of the United States Air Force located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, northeast of Dayton, Ohio. The NMUSAF is the ...
retrieved 2 December 2016Trujillo, Staff Sgt. Robert M"SR-71 Blackbird: Gone but not forgotten,"
26 January 2016, 9th Reconnaissance Wing Public Affairs, U.S. Air Force. Retrieved 2 December 2016"Absolute speed record still stands 40 years later," 27 July 2016 ''General Aviation News''. Retrieved 22 November 2016.Woolen, Angela
"SR-71 pilots, crew relive absolute speed record,"
9 August 2016, 78th Air Base Wing Public Affairs, United States Air Force. Retrieved 2 December 2016 :Note: Some sources refer to the above-mentioned X-15 as the "fastest military airplane" because it was partly a project of the U.S. Navy and Air Force; however, the X-15 was not used in non-experimental actual military operations. * The fastest current military aircraft are the Soviet/Russian
Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-25; NATO reporting name: Foxbat) is a supersonic interceptor and reconnaissance aircraft that is among the fastest military aircraft to enter service. Designed by the ...
— capable of Mach 3.2, equal to , at the expense of engine damage, or Mach 2.83, equal to , normally — and the Russian Mikoyan MiG-31
The Mikoyan MiG-31 (russian: link=no, Микоян МиГ-31; NATO reporting name: Foxhound) is a supersonic interceptor aircraft that was developed for use by the Soviet Air Forces. The aircraft was designed by the Mikoyan design bureau as a ...
E (also capable of Mach 2.83 normally). Both are fighter-interceptor jet airplanes, in active operations as of 2016.
Bender, Jeremy and Amanda Macias"The 9 fastest piloted planes in the world,"
18 September 2015, ''Business Insider''. Retrieved 3 December 2016"Fast and furious — the world's fastest military aircraft,"
''Airforce Technology''. Retrieved 3 December 2016The Five Fastest Military Jets Ever Made","
2016, Bloomberg. Retrieved 3 December 2016 * The fastest civilian airplane ever built, and fastest passenger airliner ever built: the briefly operated
Tupolev Tu-144
The Tupolev Tu-144 (russian: Tyполев Ту-144; NATO reporting name: Charger) is a Soviet supersonic passenger airliner designed by Tupolev in operation from 1968 to 1999.
The Tu-144 was the world's first commercial supersonic transport ai ...
supersonic jet airliner (Mach 2.35, 1,600 mph, 2,587 km/h), which was believed to cruise at about Mach 2.2. The Tu-144 (officially operated from 1968 to 1978, ending after two crashes of the small fleet) was outlived by its rival, the ''Concorde
The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde () is a retired Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation (later Aérospatiale) and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC).
Studies started in 1954, and France an ...
'' (Mach 2.23), a French/British supersonic airliner, known to cruise at Mach 2.02 (1.450 mph, 2,333 kmh at cruising altitude), operating from 1976 until the small Concorde fleet was grounded permanently in 2003, following the crash of one in the early 2000s."Fastest aircraft, airliner,"Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2 December. 2016. * The fastest civilian airplane currently flying: the
Cessna Citation X
The Cessna Citation X is an American business jet produced by Cessna and part of the Citation family.
Announced at the October 1990 NBAA convention, the Model 750 made its maiden flight on December 21, 1993, received its type certification on ...
, an American business jet, capable of Mach 0.935, or . Its rival, the American Gulfstream G650
The Gulfstream G650 is a large business jet produced by Gulfstream Aerospace.
business jet, can reach Mach 0.925, or "Cessna rolls out first production unit of new Citation X,"15 April 2013, ''Wichita Business Journal''. Retrieved 22 November 2016. * The fastest airliner currently flying is the
Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, t ...
, quoted as being capable of cruising over Mach 0.885, . Previously, the fastest were the troubled, short-lived Russian (Soviet Union) Tupolev Tu-144
The Tupolev Tu-144 (russian: Tyполев Ту-144; NATO reporting name: Charger) is a Soviet supersonic passenger airliner designed by Tupolev in operation from 1968 to 1999.
The Tu-144 was the world's first commercial supersonic transport ai ...
SST (Mach 2.35; equal to ) and the French/British ''Concorde'', with a maximum speed of Mach 2.23 or and a normal cruising speed of Mach 2 or ."Ask Us – Fastest Airliner and Area Rule,"Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved 22 November 2016. Before them, the
Convair 990 Coronado
The Convair 990 Coronado is an American narrow-body four-engined jet airliner produced between 1961 and 1963 by the Convair division of American company General Dynamics. It was a stretched version of its earlier Convair 880 produced in respon ...
jet airliner of the 1960s flew at over .Propulsion
Unpowered aircraft
George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific aeri ...
, whom many recognise as the first aeronautical engineer. Common examples of gliders are sailplanes
A glider or sailplane is a type of glider aircraft used in the leisure activity and sport of gliding (also called soaring). This unpowered aircraft can use naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere to gain altitude. Sailplan ...
, hang gliders
Hang gliding is an air sport or recreational activity in which a pilot flies a light, non-motorised foot-launched heavier-than-air aircraft called a hang glider. Most modern hang gliders are made of an aluminium alloy or composite frame covered ...
and paragliders
Paragliding is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying paragliders: lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched Glider (aircraft), glider aircraft with no rigid primary structure. The pilot sits in a :wikt:harness, harness o ...
.
Balloons
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the per ...
drift with the wind, though normally the pilot can control the altitude, either by heating the air or by releasing ballast, giving some directional control (since the wind direction changes with altitude). A wing-shaped hybrid balloon can glide directionally when rising or falling; but a spherically shaped balloon does not have such directional control.
Kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. ...
s are aircraft that are tethered to the ground or other object (fixed or mobile) that maintains tension in the tether or kite line
In kiting, a line is the string made of cotton, nylon, silk or wire, which connects the kite to the person operating it or an anchor. Kites have a set of wings, a set of anchors, and a set of lines coupling the wings with the anchors. Kite lines p ...
; they rely on virtual or real wind blowing over and under them to generate lift and drag. Kytoon
A kytoon or kite balloon is a tethered aircraft which obtains some of its lift dynamically as a heavier-than-air kite and the rest aerostatically as a lighter-than-air balloon. The word is a portmanteau of kite and balloon.
The primary advantage ...
s are balloon-kite hybrids that are shaped and tethered to obtain kiting deflections, and can be lighter-than-air, neutrally buoyant, or heavier-than-air.
Powered aircraft
Powered aircraft have one or more onboard sources of mechanical power, typicallyaircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many ...
s although rubber and manpower have also been used. Most aircraft engines are either lightweight reciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common featu ...
s or gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directi ...
s. Engine fuel is stored in tanks, usually in the wings but larger aircraft also have additional fuel tank
A fuel tank (also called a petrol tank or gas tank) is a safe container for flammable fluids. Though any storage tank for fuel may be so called, the term is typically applied to part of an engine system in which the fuel is stored and propel ...
s in the fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft t ...
.
Propeller aircraft

Propeller aircraft
A powered aircraft is an aircraft that uses onboard propulsion with mechanical power generated by an aircraft engine of some kind.
Aircraft propulsion nearly always uses either a type of propeller, or a form of jet propulsion. Other potential ...
use one or more propellers
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
(airscrews) to create thrust in a forward direction. The propeller is usually mounted in front of the power source in ''tractor configuration
In aviation, the term tractor configuration refers to an aircraft constructed in the standard configuration with its engine mounted with the propeller in front of it so that the aircraft is "pulled" through the air. Oppositely, the pusher c ...
'' but can be mounted behind in ''pusher configuration
In an aircraft with a pusher configuration (as opposed to a tractor configuration), the propeller(s) are mounted behind their respective engine(s). Since a pusher propeller is mounted behind the engine, the drive shaft is in compression in nor ...
''. Variations of propeller layout include ''contra-rotating propellers
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers, also referred to as CRP, coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propell ...
'' and ''ducted fan
In aeronautics, a ducted fan is a thrust-generating mechanical fan or propeller mounted within a cylindrical duct or shroud. Other terms include ducted propeller or shrouded propeller. When used in vertical takeoff and landing
(VTOL) applicatio ...
s''.
Many kinds of power plant have been used to drive propellers. Early airships used man power or steam engines. The more practical internal combustion piston engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
was used for virtually all fixed-wing aircraft until World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and is still used in many smaller aircraft. Some types use turbine engines to drive a propeller in the form of a turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel ...
or propfan
A propfan, also called an open rotor engine, or unducted fan (as opposed to a ducted fan), is a type of aircraft engine related in concept to both the turboprop and turbofan, but distinct from both. The design is intended to offer the speed an ...
. Human-powered flight
A human-powered aircraft (HPA) is an aircraft belonging to the class of vehicles known as human-powered transport.
Human-powered aircraft have been successfully flown over considerable distances. However, they are still primarily constructed a ...
has been achieved, but has not become a practical means of transport. Unmanned aircraft and models have also used power sources such as electric motors
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force ...
and rubber bands.
Jet aircraft

Jet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by jet engines.
Whereas the engines in propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much lower speeds and altitudes, je ...
use airbreathing jet engine
An airbreathing jet engine (or ''ducted jet engine'') is a jet engine that ejects a propelling (reaction) jet of hot exhaust gases after first taking in atmospheric air, followed by compression, heating and expansion back to atmospheric pressure ...
s, which take in air, burn fuel with it in a combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Interna ...
, and accelerate the exhaust rearwards to provide thrust.
Different jet engine configurations include the turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and ...
and turbofan
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft engine, aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the ''turbo'' portion refers to a gas turbine engine which ac ...
, sometimes with the addition of an afterburner
An afterburner (or reheat in British English) is an additional combustion component used on some jet engines, mostly those on military supersonic aircraft. Its purpose is to increase thrust, usually for supersonic flight, takeoff, and comba ...
. Those with no rotating turbomachinery include the pulsejet
300px, Diagram of a pulsejet
A pulsejet engine (or pulse jet) is a type of jet engine in which combustion occurs in pulses. A pulsejet engine can be made with few or no moving parts, and is capable of running statically (i.e. it does not need ...
and ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an ass ...
. These mechanically simple engines produce no thrust when stationary, so the aircraft must be launched to flying speed using a catapult, like the V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buz ...
, or a rocket, for example. Other engine types include the motorjet
A motorjet is a rudimentary type of jet engine which is sometimes referred to as ''thermojet'', a term now commonly used to describe a particular and completely unrelated pulsejet design.
Design
At the heart the motorjet is an ordinary pis ...
and the dual-cycle Pratt & Whitney J58
The Pratt & Whitney J58 (company designation JT11D-20) is an American jet engine that powered the Lockheed A-12, and subsequently the YF-12 and the SR-71 aircraft. It was an afterburning turbojet engine with a unique compressor bleed to the a ...
.
Compared to engines using propellers, jet engines can provide much higher thrust, higher speeds and, above about , greater efficiency. They are also much more fuel-efficient than rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
s. As a consequence nearly all large, high-speed or high-altitude aircraft use jet engines.
Rotorcraft
Some rotorcraft, such ashelicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribu ...
s, have a powered rotary wing or ''rotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
'', where the rotor disc can be angled slightly forward so that a proportion of its lift is directed forwards. The rotor may, like a propeller, be powered by a variety of methods such as a piston engine or turbine. Experiments have also used jet nozzles at the rotor blade tips.
Other types of powered aircraft
* ''Rocket-powered aircraft
A rocket-powered aircraft or rocket plane is an aircraft that uses a rocket engine for propulsion, sometimes in addition to airbreathing jet engines. Rocket planes can achieve much higher speeds than similarly sized jet aircraft, but typicall ...
'' have occasionally been experimented with, and the Messerschmitt Me 163 ''Komet'' fighter even saw action in the Second World War. Since then, they have been restricted to research aircraft, such as the North American X-15
The North American X-15 is a hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft. It was operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as part of the X-plane series of experimental aircraft. The X-15 set speed an ...
, which traveled up into space where air-breathing engines cannot work (rockets carry their own oxidant). Rockets have more often been used as a supplement to the main power plant, typically for the rocket-assisted take off
JATO (acronym for jet-assisted take-off) is a type of assisted take-off for helping overloaded aircraft into the air by providing additional thrust in the form of small rockets. The term ''JATO'' is used interchangeably with the (more specific ...
of heavily loaded aircraft, but also to provide high-speed dash capability in some hybrid designs such as the Saunders-Roe SR.53
The Saunders-Roe SR.53 was a British prototype interceptor aircraft of mixed jet and rocket propulsion developed for the Royal Air Force (RAF) by Saunders-Roe in the early 1950s. As envisaged, the SR.53 would have been used as an interceptor a ...
.
* The ''ornithopter
An ornithopter (from Greek ''ornis, ornith-'' "bird" and ''pteron'' "wing") is an aircraft that flies by flapping its wings. Designers sought to imitate the flapping-wing flight of birds, bats, and insects. Though machines may differ in form, th ...
'' obtains thrust by flapping its wings. It has found practical use in a model hawk used to freeze prey animals into stillness so that they can be captured, and in toy birds.
Design and construction
Aircraft are designed according to many factors such as customer and manufacturer demand,safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to risk management, the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are ...
protocols and physical and economic constraints. For many types of aircraft the design process is regulated by national airworthiness authorities.
The key parts of an aircraft are generally divided into three categories:
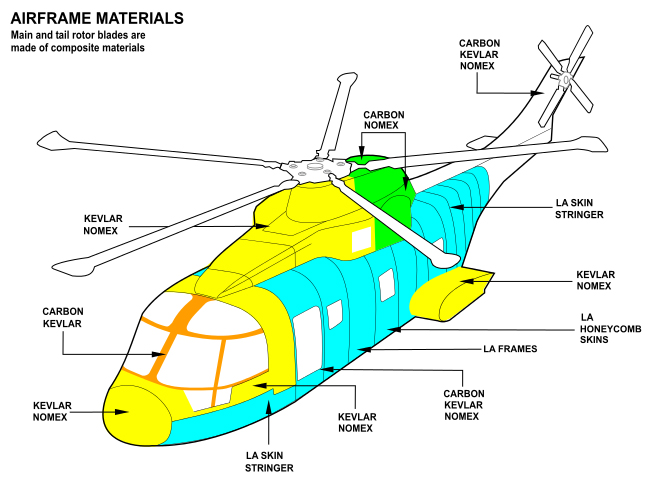
* The ''structure'' ("airframe
The mechanical structure of an aircraft is known as the airframe. This structure is typically considered to include the fuselage, undercarriage, empennage and wings, and excludes the propulsion system.
Airframe design is a field of aerospa ...
"Gove, P.B., editor: ''Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged,'' 1993, Merriam-Webster, Springfield, Mass., USACrane, D., editor: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms,'' Third Edition, ASA (Aviation Supplies & Academics), Newcastle, Washington, USA''2012 Federal Aviation Regulations for Aviation Maintenance Technicians,'' 2012, Federal Aviation Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation Gunston, Bill, editor: ''Jane's Aerospace Dictionary'' 1980, Jane's, London / New York / Sydney) comprises the main load-bearing elements and associated equipment, as well as flight controls.
* The ''propulsion system'' ("powerplant
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
""Glossary"in ''Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge'' (PHAK),
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ...
, Washington, D.C., retrieved September 12, 2022) (if it is powered) comprises the power source and associated equipment, as described above.
* The ''avionics
Avionics (a blend word, blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, ...
'' comprise the electrical and electronic control, navigation and communication systems.Wragg, David W. editor: ''A Dictionary of Aviation,'' 1974, Frederick Fell, New York
Structure
The approach to structural design varies widely between different types of aircraft. Some, such as paragliders, comprise only flexible materials that act in tension and rely on aerodynamic pressure to hold their shape. Aballoon
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, and air. For special tasks, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light so ...
similarly relies on internal gas pressure, but may have a rigid basket or gondola slung below it to carry its payload. Early aircraft, including airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
s, often employed flexible doped aircraft fabric covering
Aircraft fabric covering is a term used for both the material used and the process of covering aircraft open structures. It is also used for reinforcing closed plywood structures. The de Havilland Mosquito is an example of this technique, as ar ...
to give a reasonably smooth aeroshell stretched over a rigid frame. Later aircraft employed semi-monocoque
Monocoque ( ), also called structural skin, is a structural system in which loads are supported by an object's external skin, in a manner similar to an egg shell. The word ''monocoque'' is a French term for "single shell".
First used for boats, ...
techniques, where the skin of the aircraft is stiff enough to share much of the flight loads. In a true monocoque design there is no internal structure left. With the recent emphasis on sustainability hemp has picked up some attention, having a way smaller carbon foot print and 10 times stronger than steel, hemp could become the standard of manufacturing in the future.
The key structural parts of an aircraft depend on what type it is.
Aerostats
Lighter-than-air types are characterised by one or more gasbags, typically with a supporting structure of flexible cables or a rigid framework called its hull. Other elements such as engines or a gondola may also be attached to the supporting structure.Aerodynes
 Heavier-than-air types are characterised by one or more wings and a central
Heavier-than-air types are characterised by one or more wings and a central fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft t ...
. The fuselage typically also carries a tail or empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third ed ...
for stability and control, and an undercarriage for takeoff and landing. Engines may be located on the fuselage or wings. On a fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinc ...
the wings are rigidly attached to the fuselage, while on a rotorcraft
A rotorcraft or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings or rotor blades, which generate lift by rotating around a vertical mast. Several rotor blades mounted on a single mast are referred to as a rotor. The Internati ...
the wings are attached to a rotating vertical shaft. Smaller designs sometimes use flexible materials for part or all of the structure, held in place either by a rigid frame or by air pressure. The fixed parts of the structure comprise the airframe
The mechanical structure of an aircraft is known as the airframe. This structure is typically considered to include the fuselage, undercarriage, empennage and wings, and excludes the propulsion system.
Airframe design is a field of aerospa ...
.
Power
The source of motive power for an aircraft is normally called the ''powerplant
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
,'' and includes engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gen ...
or motor
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power g ...
, propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
or rotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
, (if any), jet nozzle
A propelling nozzle is a nozzle that converts the internal energy of a working gas into propulsive force; it is the nozzle, which forms a jet, that separates a gas turbine, or gas generator, from a jet engine.
Propelling nozzles accelerate the av ...
s and thrust reverser
Thrust reversal, also called reverse thrust, is the temporary diversion of an aircraft engine's thrust for it to act against the forward travel of the aircraft, providing deceleration. Thrust reverser systems are featured on many jet aircraft ...
s (if any), and accessories essential to the functioning of the engine or motor (e.g.: starter, ignition system
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ig ...
, intake system, exhaust system
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system ...
, fuel system, lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology.
Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubric ...
system, engine cooling system
Internal combustion engine cooling uses either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from an internal combustion engine. For small or special purpose engines, cooling using air from the atmosphere makes for a lightweight and relatively simple sys ...
, and engine controls
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ...
)."Glossary"in ''Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge'' (PHAK),
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ...
, Washington, D.C., retrieved September 12, 2022
Powered aircraft are typically powered by internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
s (piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
"Internal Combustion Engine,"Glenn Research Center,
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
(NASA), retrieved September 12, 2022 or turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating e ...
"Engines,"Glenn Research Center,
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
(NASA), retrieved September 12, 2022) burning fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ...
-- typically gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
(avgas
Avgas (aviation gasoline, also known as aviation spirit in the UK) is an aviation fuel used in aircraft with spark-ignited internal combustion engines. ''Avgas'' is distinguished from conventional gasoline (petrol) used in motor vehicles, w ...
) or jet fuel
Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel (ATF, also abbreviated avtur) is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial a ...
. A very few are powered by rocket power, ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an ass ...
propulsion, or by electric motors
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force ...
, or by internal combustion engines of other types, or using other fuels. A very few have been powered, for short flights, by human muscle energy (e.g.: Gossamer Condor
The MacCready ''Gossamer Condor'' was the first human-powered aircraft capable of controlled and sustained flight; as such, it won the Kremer prize in 1977. Its design was led by Paul MacCready of AeroVironment, Inc.
Design and development
...
).Bryan, C.D.B.: ''The National Air and Space Museum,'' 1979 / 1984, Abrams, New YorkTaylor, Michael J.H., editor: ''Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation,'' 1989 ed., Portland House / Random House, New York"Electrified Aircraft Propulsion" (EAP)Glenn Research Center,
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding th ...
(NASA), retrieved September 12, 2022
Avionics
The avionics comprise any ''electronic''aircraft flight control system
A conventional Fixed-wing aircraft, fixed-wing aircraft flight control system consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction ...
s and related equipment, including electronic cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, usually near the front of an aircraft or spacecraft, from which a Pilot in command, pilot controls the aircraft.
The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the ...
instrumentation, navigation, radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
, monitoring, and communications system
A communications system or communication system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperati ...
s.Wragg, David W. editor: ''A Dictionary of Aviation,'' 1974, Frederick Fell, New York
Flight characteristics
Flight envelope
The flight envelope of an aircraft refers to its approved design capabilities in terms ofairspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are:
* Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system;
* Calibrated a ...
, load factor and altitude. The term can also refer to other assessments of aircraft performance such as maneuverability. When an aircraft is abused, for instance by diving it at too-high a speed, it is said to be flown ''outside the envelope'', something considered foolhardy since it has been taken beyond the design limits which have been established by the manufacturer. Going beyond the envelope may have a known outcome such as flutter or entry to a non-recoverable spin (possible reasons for the boundary).
Range
 The range is the distance an aircraft can fly between
The range is the distance an aircraft can fly between takeoff
Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle leaves the ground and becomes airborne. For aircraft traveling vertically, this is known as liftoff.
For aircraft that take off horizontally, this usually involves starting with a t ...
and landing
Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or ...
, as limited by the time it can remain airborne.
For a powered aircraft the time limit is determined by the fuel load and rate of consumption.
For an unpowered aircraft, the maximum flight time is limited by factors such as weather conditions and pilot endurance. Many aircraft types are restricted to daylight hours, while balloons are limited by their supply of lifting gas. The range can be seen as the average ground speed multiplied by the maximum time in the air.
The Airbus A350-900ULR is now the longest range airliner.
Flight dynamics
 Flight dynamics is the science of air vehicle orientation and control in three dimensions. The three critical flight dynamics parameters are the
Flight dynamics is the science of air vehicle orientation and control in three dimensions. The three critical flight dynamics parameters are the angles of rotation
In mathematics, the angle of rotation is a measurement of the amount, of namely angle, that a figure is rotated about a fixed point, often the center of a circle. A clockwise rotation is considered a negative rotation, so that, for instance ...
around three axes which pass through the vehicle's center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the distributed mass sums to zero. Thi ...
, known as '' pitch'', ''roll
Roll or Rolls may refer to:
Movement about the longitudinal axis
* Roll angle (or roll rotation), one of the 3 angular degrees of freedom of any stiff body (for example a vehicle), describing motion about the longitudinal axis
** Roll (aviation), ...
,'' and '' yaw''.
* Roll is a rotation about the longitudinal axis (equivalent to the rolling or heeling of a ship) giving an up-down movement of the wing tips measured by the roll or bank angle.
* Pitch is a rotation about the sideways horizontal axis giving an up-down movement of the aircraft nose measured by the angle of attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is m ...
.
* Yaw is a rotation about the vertical axis giving a side-to-side movement of the nose known as sideslip.
Flight dynamics is concerned with the stability and control of an aircraft's rotation about each of these axes.
Stability
flight dynamics
Flight dynamics in aviation and spacecraft, is the study of the performance, stability, and control of vehicles flying through the air or in outer space. It is concerned with how forces acting on the vehicle determine its velocity and attitude w ...
of pitch and yaw. They are usually mounted on the tail section (empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third ed ...
), although in the canard layout, the main aft wing replaces the canard foreplane as pitch stabilizer. Tandem wing QAC Quickie Q2
A tandem wing is a wing configuration in which a flying craft or animal has two or more sets of wings set one behind another. All the wings contribute to lift.
The tandem wing is distinct from the biplane in which the wings are ...
and tailless aircraft
In aeronautics, a tailless aircraft is an aircraft with no other horizontal aerodynamic surface besides its main wing. It may still have a fuselage, vertical tail fin (vertical stabilizer), and/or vertical rudder.
Theoretical advantages of the ...
rely on the same general rule to achieve stability, the aft surface being the stabilising one.
A rotary wing is typically unstable in yaw, requiring a vertical stabiliser.
A balloon is typically very stable in pitch and roll due to the way the payload is slung underneath the center of lift.
Control
Flight control surfaces
Aircraft flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude.
Development of an effective set of flight control surfaces was a critical advance in the development of aircraft. Ea ...
enable the pilot to control an aircraft's flight attitude and are usually part of the wing or mounted on, or integral with, the associated stabilizing surface. Their development was a critical advance in the history of aircraft, which had until that point been uncontrollable in flight.
Aerospace engineers develop control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial c ...
s for a vehicle's orientation (attitude) about its center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may ...
. The control systems include actuators, which exert forces in various directions, and generate rotational forces or moments about the aerodynamic center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magnit ...
of the aircraft, and thus rotate the aircraft in pitch, roll, or yaw. For example, a pitching moment
In aerodynamics, the pitching moment on an airfoil is the moment (or torque) produced by the aerodynamic force on the airfoil if that aerodynamic force is considered to be applied, not at the center of pressure, but at the aerodynamic center o ...
is a vertical force applied at a distance forward or aft from the aerodynamic center of the aircraft, causing the aircraft to pitch up or down. Control systems are also sometimes used to increase or decrease drag, for example to slow the aircraft to a safe speed for landing.
The two main aerodynamic forces acting on any aircraft are lift supporting it in the air and drag opposing its motion. Control surfaces or other techniques may also be used to affect these forces directly, without inducing any rotation.
Impacts of aircraft use
Aircraft permit long distance, high speedtravel
Travel is the movement of people between distant geographical locations. Travel can be done by foot, bicycle, automobile, train, boat, bus, airplane, ship or other means, with or without luggage, and can be one way or round trip. Travel c ...
and may be a more fuel efficient
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, wh ...
mode of transportation in some circumstances. Aircraft have environmental and climate impacts beyond fuel efficiency considerations, however. They are also relatively noisy compared to other forms of travel and high altitude aircraft generate contrail
Contrails (; short for "condensation trails") or vapor trails are line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft engine exhaust or changes in air pressure, typically at aircraft cruising altitudes several miles above the Earth's surface. Contrails ar ...
s, which experimental evidence suggests may alter weather patterns.
Uses for aircraft
Aircraft are produced in several different types optimized for various uses;military aircraft
A military aircraft is any fixed-wing or rotary-wing aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat:
* Combat aircraft are designed to destroy enemy equipm ...
, which includes not just combat types but many types of supporting aircraft, and civil aircraft
Civil aviation is one of two major categories of flying, representing all non-military and non-state aviation, both private and commercial. Most of the countries in the world are members of the International Civil Aviation Organization and work ...
, which include all non-military types, experimental and model.
Military
 A military aircraft is any aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat:
* Combat aircraft are aircraft designed to destroy enemy equipment using its own armament. Combat aircraft divide broadly into
A military aircraft is any aircraft that is operated by a legal or insurrectionary armed service of any type. Military aircraft can be either combat or non-combat:
* Combat aircraft are aircraft designed to destroy enemy equipment using its own armament. Combat aircraft divide broadly into fighters
Fighter(s) or The Fighter(s) may refer to:
Combat and warfare
* Combatant, an individual legally entitled to engage in hostilities during an international armed conflict
* Fighter aircraft, a warplane designed to destroy or damage enemy warplan ...
and bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
s, with several in-between types, such as fighter-bomber
A fighter-bomber is a fighter aircraft that has been modified, or used primarily, as a light bomber or attack aircraft. It differs from bomber and attack aircraft primarily in its origins, as a fighter that has been adapted into other roles, wh ...
s and attack aircraft
An attack aircraft, strike aircraft, or attack bomber is a tactical military aircraft that has a primary role of carrying out airstrikes with greater precision than bombers, and is prepared to encounter strong low-level air defenses while pre ...
, including attack helicopter
An attack helicopter is an armed helicopter with the primary role of an attack aircraft, with the offensive capability of engaging ground targets such as enemy infantry, military vehicles and fortifications. Due to their heavy armament they ...
s.
* Non-combat aircraft are not designed for combat as their primary function, but may carry weapons for self-defense. Non-combat roles include search and rescue, reconnaissance, observation, transport, training, and aerial refueling
Aerial refueling, also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft a ...
. These aircraft are often variants of civil aircraft.
Most military aircraft are powered heavier-than-air types. Other types, such as gliders and balloons, have also been used as military aircraft; for example, balloons were used for observation during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
and World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and military glider
Military gliders (an offshoot of common gliders) have been used by the militaries of various countries for carrying troops (glider infantry) and heavy equipment to a combat zone, mainly during the Second World War. These engineless aircraft were ...
s were used during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
to land troops.
Civil
 Civil aircraft divide into ''commercial'' and ''general'' types, however there are some overlaps.
Civil aircraft divide into ''commercial'' and ''general'' types, however there are some overlaps.
Commercial aircraft
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ai ...
include types designed for scheduled and charter airline flights, carrying passengers, mail
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letter (message), letters, and parcel (package), parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid ...
and other cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
. The larger passenger-carrying types are the airliners, the largest of which are wide-body aircraft
A wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is . In the typical wide-body economy cabin ...
. Some of the smaller types are also used in general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
, and some of the larger types are used as VIP aircraft.
General aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
is a catch-all covering other kinds of private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
(where the pilot is not paid for time or expenses) and commercial use, and involving a wide range of aircraft types such as business jets (bizjets), trainers
Sneakers (also called trainers, athletic shoes, tennis shoes, gym shoes, kicks, sport shoes, flats, running shoes, or runners) are shoes primarily designed for sports or other forms of physical exercise, but which are now also widely used f ...
, homebuilt
Homebuilt machines are machines built outside of specialised workshops or factories. This can include different things such as kit cars or homebuilt computers, but normally it pertains to homebuilt aircraft, also known as amateur-built aircraft or ...
, gliders, warbird
A warbird is any vintage military aircraft now operated by civilian organizations and individuals, or in some instances, by historic arms of military forces, such as the Battle of Britain Memorial Flight, the RAAF Museum Historic Flight, or the ...
s and hot air balloon
A hot air balloon is a lighter-than-air aircraft consisting of a bag, called an envelope, which contains heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule), which carries p ...
s to name a few. The vast majority of aircraft today are general aviation types.
Experimental
An experimental aircraft is one that has not been fully proven in flight, or that carries a Special Airworthiness Certificate, called an Experimental Certificate in United States parlance. This often implies that the aircraft is testing new aerospace technologies, though the term also refers to amateur-built and kit-built aircraft, many of which are based on proven designs.
Model
A model aircraft is a small unmanned type made to fly for fun, for static display, for aerodynamic research or for other purposes. Ascale model
A scale model is a physical model which is geometrically similar to an object (known as the prototype). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small prototypes ...
is a replica of some larger design.
See also
Lists
*Early flying machines
Early flying machines include all forms of aircraft studied or constructed before the development of the modern aeroplane by 1910. The story of modern flight begins more than a century before the first successful manned aeroplane, and the ear ...
* Flight altitude record
This listing of flight altitude records are the records set for the highest aeronautical flights conducted in the atmosphere, set since the age of ballooning.
Some, but not all of the records were certified by the non-profit international avia ...
* List of aircraft
The lists of aircraft are sorted in alphabetical order.
Further reading
The following reference sources, among many others, have been used to compile this list:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* ...
* List of civil aircraft
List of civil aircraft is a list of articles on civilian aircraft with descriptions, which excludes aircraft operated by military organizations in civil markings, warbirds, warbirds used for racing, replica warbirds and research aircraft.
A ABC ...
* List of fighter aircraft
This is a list of military aircraft that are primarily designed for air-to-air combat and thus does not include aircraft intended for other roles where they have some secondary air-to-air capability, such as with many ground attack aircraft. The l ...
* List of individual aircraft
This is a list of individual aircraft which are notable in their own right.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Individual Aircraft, List Of
Individual aircraft
Lists of aircraft ...
* List of large aircraft
This is a list of large aircraft, including three types: fixed wing, rotary wing, and airships.
The US Federal Aviation Administration defines a large aircraft as any aircraft with a certificated maximum takeoff weight of more than
The Euro ...
* List of aviation, aerospace and aeronautical terms
Topics
*Aircraft hijacking
Aircraft hijacking (also known as airplane hijacking, skyjacking, plane hijacking, plane jacking, air robbery, air piracy, or aircraft piracy, with the last term used within the special aircraft jurisdiction of the United States) is the unlawfu ...
* Aircraft spotting
Aircraft spotting, or plane spotting is a hobby of tracking the movement of aircraft, which is often accomplished by photography. Besides monitoring aircraft, plane spotting enthusiasts (who are usually called plane spotters) also record informa ...
* Air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
* Airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface ...
* Flying car
A flying car or roadable aircraft is a type of vehicle which can function both as a road vehicle and as an aircraft. As used here, this includes vehicles which drive as motorcycles when on the road. The term "flying car" is also sometimes u ...
* Personal air vehicle
A personal air vehicle (PAV) is a proposed type of aircraft providing on-demand aviation services.
The emergence of this alternative to traditional ground transport methods has been enabled by unmanned aerial vehicle technologies and electric pr ...
* Powered parachute
A powered parachute, often abbreviated PPC, and also called a motorized parachute or paraplane, is a type of aircraft that consists of a parafoil with a motor and wheels.
The FAA defines a powered parachute as ''a powered aircraft a flexible o ...
* Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, p ...
* Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes ten ...
References
*External links
History
The Evolution of Modern Aircraft (NASA)
Smithsonian Air and Space Museum
- online collection with a particular focus on history of aircraft and spacecraft
Amazing Early Flying Machines
slideshow by ''
Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energ ...
'' magazine
Information
Airliners.net
Aviation Dictionary
- free aviation terms, phrases and jargons
''New Scientist''s aviation page
{{Authority control