|
Aviation Between The World Wars
Sometimes dubbed the Golden Age of Aviation, the period in the history of aviation between the end of World War I (1918) and the beginning of World War II (1939) was characterised by a progressive change from the slow wood-and-fabric biplanes of World War I to fast, streamlined metal monoplanes, creating a revolution in both commercial and military aviation. By the outbreak of World War II in 1939 the biplane was all but obsolete. This revolution was made possible by the continuing development of lightweight aero engines of increasing power. The jet engine also began development during the 1930s but would not see operational use until later. During this period civil aviation became widespread and many daring and dramatic feats took place such as round-the-world flights, air races and barnstorming displays. Many commercial airlines were started during this period. Long-distance flights for the luxury traveller became possible for the first time; the early services used airsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
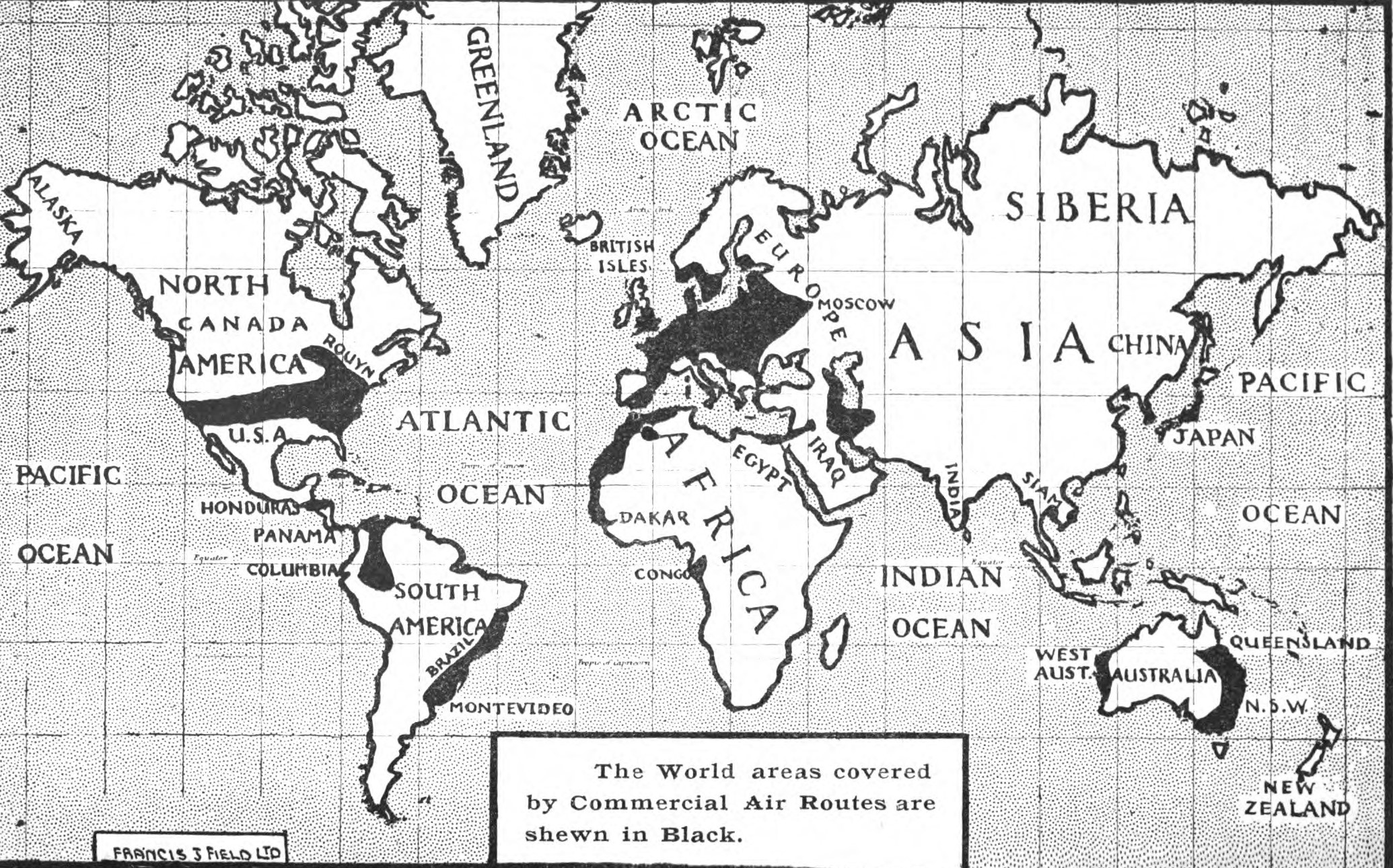
The World Areas Covered By Commercial Air Routes
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. Many variants of the Spitfire were built, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon engined Mk 24 using several wing configurations and guns. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts; around 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world. The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing with innovative sunken rivets (designed by Beverley Shenstone) to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire State", the nickname of the state of New York. The building has a roof height of and stands a total of tall, including its antenna. The Empire State Building was the world's tallest building until the World Trade Center was constructed in 1970; following the collapse of the World Trade Center in 2001, the Empire State Building was New York City's tallest building until it was surpassed in 2012. , the building is the seventh-tallest building in New York City, the ninth-tallest completed skyscraper in the United States, the 54th-tallest in the world, and the sixth-tallest freestanding structure in the Americas. The site of the Empire State Building, in Midtown South on the west side of Fifth Avenue between West 33rd and 34th Streets, was developed in 1893 as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets. The key performance features of a fighter include not only its firepower but also its high speed and maneuverability relative to the target aircraft. The success or failure of a combatant's efforts to gain air superiority hinges on several factors including the skill of its pilots, the tactical soundness of its doctrine for deploying its fighters, and the numbers and performance of those fighters. Many modern fighter aircraft also have secondary capabilities such as ground attack and some types, such as fighter-bombers, are designed from the outset for dual roles. Other fighter designs are highly specialized while still filling the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
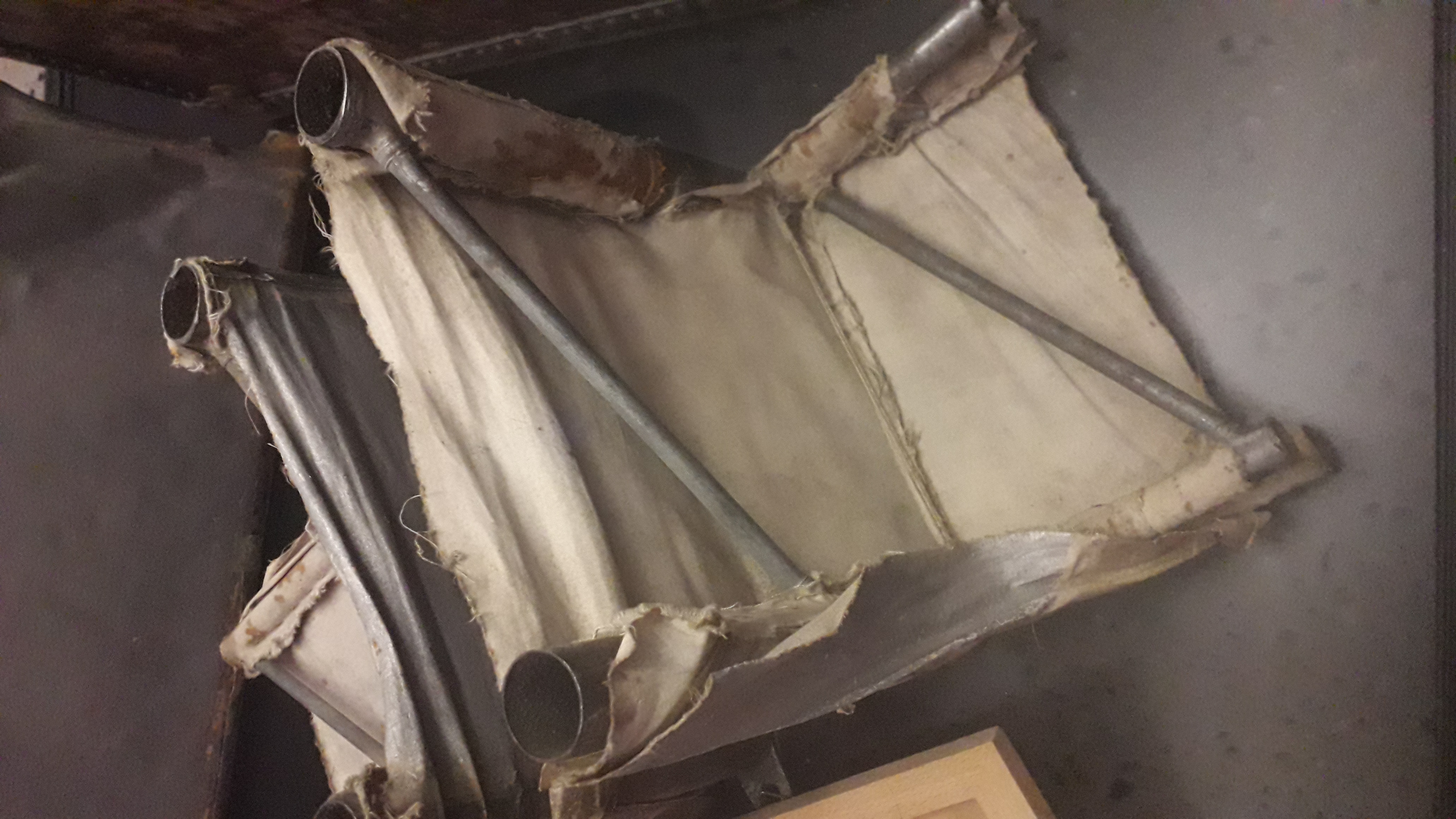
F9C Sparrowhawk
The Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk is a light 1930s biplane fighter aircraft that was carried by the United States Navy airships and . It is an example of a parasite fighter, a small airplane designed to be deployed from a larger aircraft such as an airship or bomber. Design and development On 20 August 1929, off New Jersey, a Vought UO-1 biplane A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While ... hooked to the bottom of the Navy airship for a second time in the US, and was carried by the larger craft. After matching its speed to that of the dirigible, the biplane flew close underneath the Los Angeles. A large hook mounted above the top wing of the biplane was caught by a U-shaped yoke mounted below the Los Angeles, which then carried the biplane for 3 or 4 minutes. The pilot of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
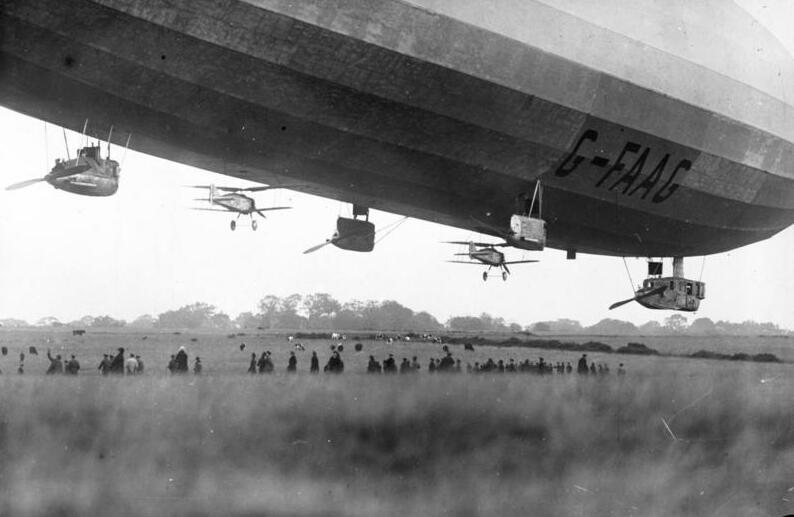
Airborne Aircraft Carrier
An airborne aircraft carrier is a type of mother ship aircraft which can carry, launch, retrieve and support other smaller parasite aircraft. The only dedicated examples to have been built were airships, although existing heavier-than-air aircraft have been modified for use in similar roles, and airborne aircraft carriers of various types appear in fiction, such as ''Cloudbase'' in Gerry Anderson's ''Captain Scarlet and the Mysterons'', the Helicarrier from Marvel Comics, the ''Valiant'' from series 3 of ''Doctor Who,'' and an unnamed one in ''Sky Captain and the World of Tomorrow''. Airship projects In July 1917, experiments were made with aircraft slung under HM Airship No. 23, in hopes that they could defend the airship. First an unmanned, then a manned, Sopwith Camel fighters were launched successfully. The experiment was successfully completed with two other manned Camels. The British Imperial Airship Scheme of 1924 initially envisaged an airship that could carry five fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Magnetic North Pole. The North Pole is by definition the northernmost point on the Earth, lying antipodally to the South Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° North, as well as the direction of true north. At the North Pole all directions point south; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the North Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, counterclockwise is east and clockwise is west. The North Pole is at the center of the Northern Hemisphere. The nearest land is usually said to be Kaffeklubben Island, off the northern coast of Greenland about away, though some perhaps semi-permanent gravel banks lie slightly clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norge (airship)
The ''Norge'' was a semi-rigid Italian-built airship that carried out the first verified trip of any kind to the North Pole, an overflight on 12 May 1926. It was also the first aircraft to fly over the polar ice cap between Europe and America. The expedition was the brainchild of polar explorer and expedition leader Roald Amundsen, the airship's designer and pilot Umberto Nobile and American adventurer and explorer Lincoln Ellsworth who, along with the Aero Club of Norway, financed the trip, which was known as the Amundsen-Ellsworth 1926 Transpolar Flight. Design and development ''Norge'' was the first N-class semi-rigid airship designed by Umberto Nobile, and its construction started in 1923. As part of the selling contract s the ''Norge''it was refitted for Arctic conditions. The pressurised envelope was reinforced with metal frames at the nose and tail, with a flexible tubular metal keel connecting the two. This was covered with fabric and used as storage and crew space. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R34 (airship)
The R.33 class of British rigid airships were built for the Royal Naval Air Service during the First World War, but were not completed until after the end of hostilities, by which time the RNAS had become part of the Royal Air Force. The lead ship, R.33, served successfully for ten years and survived one of the most alarming and heroic incidents in airship history when she was torn from her mooring mast in a gale. She was called a "Pulham Pig" by the locals, as the blimps based there had been, and is immortalised in the village sign for Pulham St Mary. The only other airship in the class, R.34, became the first aircraft to make an east to west transatlantic flight in July 1919 and, with the return flight, made the first two-way crossing. It was decommissioned two years later, after being damaged during a storm. The crew nicknamed her "Tiny". Design and development Substantially larger than the preceding R31 class, the R.33 class was in the design stage in 1916 when the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)








