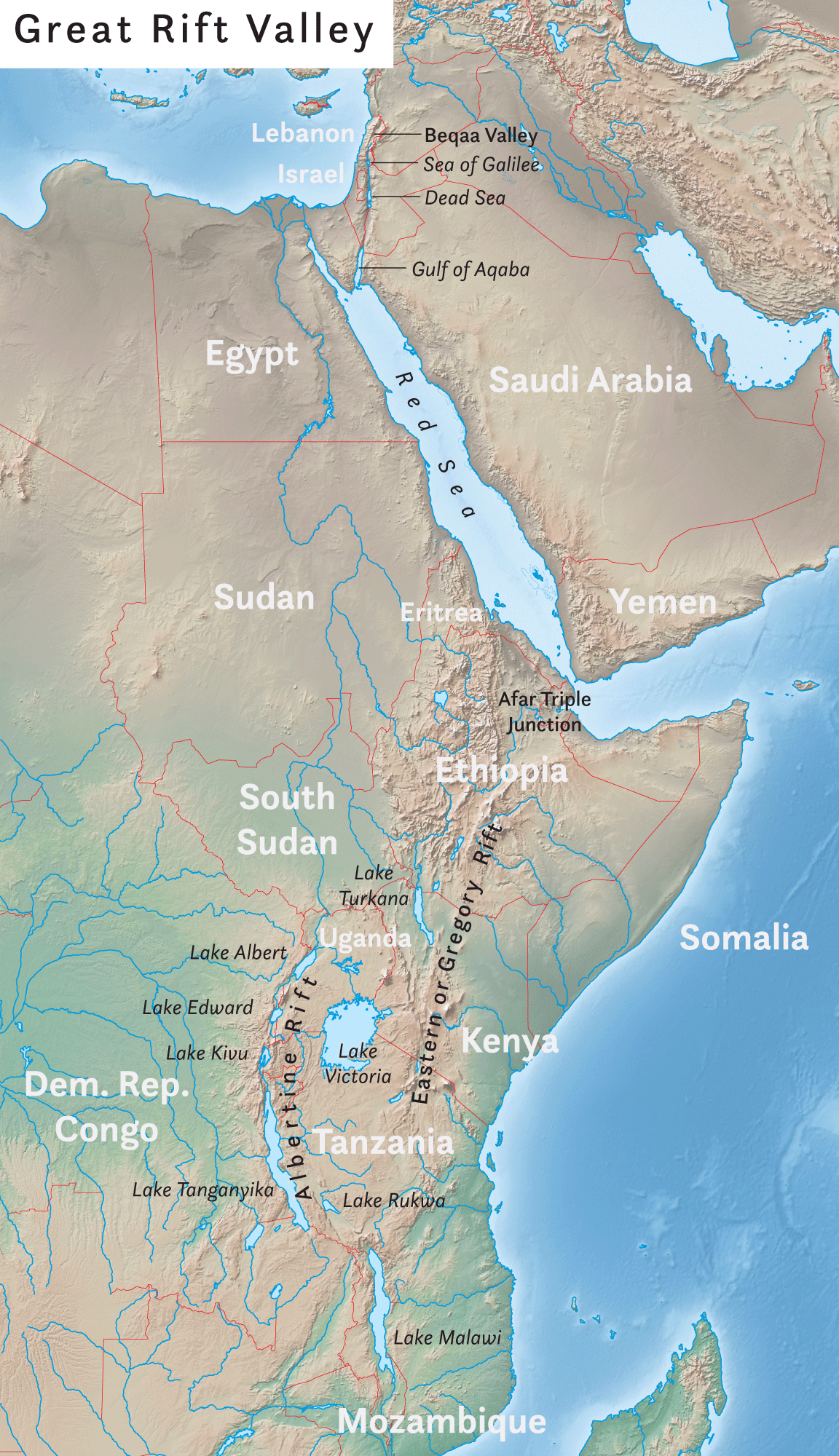
African Rift Lake on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the
The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the
 The
The
 South of the Ethiopian highlands, the rift valley splits into two major troughs. The Eastern Rift is home to the
South of the Ethiopian highlands, the rift valley splits into two major troughs. The Eastern Rift is home to the

 The lakes of the Western or
The lakes of the Western or
Lakes of the African Rift Valley
Africa Rift Valley Pictures From Helicopter by Michael Poliza
{{Regions of Africa Freshwater ecoregions

 The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the
The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a ...
valley that runs through eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
from Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
in the north to Malawi
Malawi (; or aláwi Tumbuka: ''Malaŵi''), officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast ...
in the south, and includes the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in the ...
in the south. These include some of the world's oldest lakes, deepest lakes, largest lakes by area, and largest lakes by volume. Many are freshwater ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of l ...
s of great biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, while others are alkaline "soda lakes" supporting highly specialised organisms.
The Rift Valley lakes are well known for the evolution of at least 800 cichlid
Cichlids are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses ( Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted this ...
fish species that live in their waters. More species are expected to be discovered.
The World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor ...
has designated these lakes as one of its Global 200
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature ( WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or w ...
priority ecoregions for conservation.
Geology
Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is the fifth largest fre ...
and Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika () is an African Great Lake. It is the second-oldest freshwater lake in the world, the second-largest by volume, and the second-deepest, in all cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. It is the world's longest freshwater lake. ...
have formed in the various valleys of the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a ...
zone.
Ecology
Lake Kivu's "still waters ... hide another face: dissolved within are billions of cubic meters of flammable methane and more still of carbon dioxide, the result of volcanic gases seeping in."Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes national park
 The
The Ethiopian Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley of Ethiopia, (or Main Ethiopian Rift or Ethiopian Rift Valley) is a branch of the East African Rift that runs through Ethiopia in a southwest direction from the Afar Triple Junction. In the past, it was seen as part of a "G ...
lakes are the northernmost of the African Rift Valley lakes. In central Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, the Main Ethiopian Rift
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
, also known as the Great Rift Valley, splits the Ethiopian highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
into northern and southern halves, and the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes occupy the floor of the rift valley between the two highlands. Most of the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes do not have an outlet, and most are alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a base (chemistry), basic, ionic compound, ionic salt (chemistry), salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as ...
. Although the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes are of great importance to Ethiopia's economy, as well as being essential to the survival of the local people, there were no intensive and extensive limnological
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems.
The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristic ...
studies undertaken of these lakes until recently.
The major ones are
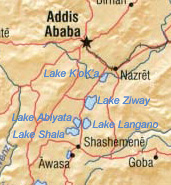
* Lake Abaya
Lake Abaya (Amharic: አባያ ሐይቅ) is a lake in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. It is located in the Main Ethiopian Rift, east of the Guge Mountains.
The town of Arba Minch lies on its southwestern s ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth ), the largest Ethiopian Rift Valley lake by surface area
* Lake Chamo
Lake Chamo ( Amharic: ቻሞ ሐይቅ) is a lake in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of southern Ethiopia. Located in the Main Ethiopian Rift, it is at an elevation of 1,110 meters. The Chamo lake is just to the south of ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth )
* Lake Zway
Hora-Dambal also known as Lake Zway or Dambal ( Oromo: ''Hora Dambal'', Amharic: ዟይ ሐይቅ) is one of the freshwater Rift Valley lakes of Ethiopia. It is located about 100 miles south of Addis Ababa, on the border between the Oromia and S ...
or Dambal (areal extent , elevation , maximum depth )
* Lake Shala
Lake Shala (also spelled Shalla) is an alkaline lake located in the Ethiopian Rift Valley, in the Abijatta-Shalla National Park.
Overview
The lake is 28 kilometers long and 12 wide,''Statistical Abstract of Ethiopia for 1967/68'' with a surface ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth ), the deepest Ethiopian Rift Valley lake and the largest by water volume
* Koka Reservoir
The Koka Reservoir ( om, Haroo Qooqaa) is a reservoir in south-central Ethiopia. It was created by the construction of the Koka Dam across the Awash River. The reservoir has an area of 180 square kilometers.
Geography
Located in the East(Baha) Sh ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth not listed)
* Lake Langano
Lake Langano ( Oromo: ''Hora Langaanoo'', Amharic: ላንጋኖ ሐይቅ) is a lake in the Oromia Region of Ethiopia, exactly 200 kilometers by road south of the capital, Addis Ababa, on the border between the East Shewa Zone and Arsi Zones. It i ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth )
* Lake Abijatta
Lake Abijatta is an alkaline lake in Ethiopia. It lies in the Main Ethiopian Rift valley south of Addis Ababa, in the Abijatta-Shalla National Park.
Overview
According to the ''Statistical Abstract of Ethiopia for 1967/68'', the lake is 17 kilo ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth )
* Lake Awasa
Lake Hawassa or Awasa, is an endorheic basin in Sidama Region of Ethiopia, located in the Main Ethiopian Rift south of Addis Ababa, the capital city of the country. According to the ''Statistical Abstract of Ethiopia for 1967/68'', the lake is 1 ...
(areal extent , elevation , maximum depth )
Lake Tana
Lake Tana ( am, ጣና ሐይቅ, T’ana ḥāyik’i; previously Tsana) is the largest lake in Ethiopia and the source of the Blue Nile. Located in Amhara Region in the north-western Ethiopian Highlands, the lake is approximately long and wid ...
, the source of the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile (; ) is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the water ...
, lies in the Ethiopian highlands north of the Rift Valley; however, it is not a Rift Valley lake.
Eastern Rift Valley lakes
Kenyan Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues no ...
lakes, while most of the Central African Rift Valley lakes lie in the Western Rift. This area includes the Gregory Rift
The Gregory Rift is the eastern branch of the East African Rift fracture system. The rift is being caused by the separation of the Somali plate from the Nubian plate, driven by a thermal plume. Although the term is sometimes used in the narrow s ...
in Kenya and Tanzania.
Kenya
The Kenyan section of the Rift Valley is home to eight lakes, of which three are freshwater and the rest alkaline. Of the latter, the shallow soda lakes of the Eastern Rift Valley have crystallised salt turning the shores white and are famous for the large flocks offlamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes are a type of Wader, wading bird in the Family (biology), family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas ...
that feed on crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s.
* Lake Baringo
Lake Baringo is, after Lake Turkana, the most northern of the Kenyan Rift Valley lakes, with a surface area of and an elevation of . The lake is fed by several rivers: the Molo, Perkerra and Ol Arabel. It has no obvious outlet; the waters ar ...
: second largest of the Kenyan Rift Valley lakes.
** , elevation , freshwater
* Lake Bogoria
Lake Bogoria (formerly Lake Hannington) is a saline, alkaline lake that lies in a volcanic region in a half-graben basin south of Lake Baringo, Kenya, a little north of the equator. Lake Bogoria, like Lake Nakuru, Lake Elementeita, and Lake Maga ...
: shallow soda lake, a national preserve.
** , elevation
* Lake Elmenteita
Lake Elmenteita is a soda lake, in the Great Rift Valley, about 120 km northwest of Nairobi, Kenya.
Geography
Elmenteita is derived from the Maasai word , meaning "dust place", a reference to the dryness and dustiness of the area, espec ...
: shallow soda lake.
* Lake Logipi
Lake Logipi is a saline, alkaline lake that lies at the northern end of the arid Suguta Valley in the northern Kenya Rift. It is separated from Lake Turkana by the Barrier Volcano, Barrier volcanic complex, a group of young volcanoes that last eru ...
: a shallow hot-spring fed soda lake in the Suguta
The Suguta Valley, also known as the Suguta Mud Flats, is an arid part of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya (Africa), directly south of Lake Turkana.
Location
The Suguta valley today is one of the driest parts of Kenya, with annual rainfall below . ...
Valley just south of Lake Turkana. Formerly Lake Suguta
Lake Suguta is a former lake in Africa. It formed in the Suguta Valley, which is part of the East African Rift, south of Lake Turkana during the Holocene African humid period.
The lake existed a number of times during history, most recently du ...
* Lake Magadi
Lake Magadi is the southernmost lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, lying in a catchment of faulted volcanic rocks, north of Tanzania's Lake Natron. During the dry season, it is 80% covered by soda and is well known for its wading birds, including f ...
: shallow soda lake near the southern border with Tanzania.
* Lake Naivasha
Lake Naivasha is a freshwater lake in Kenya, outside the town of Naivasha in Nakuru County, which lies north west of Nairobi. It is part of the Great Rift Valley. The name derives from the local Maasai name ''Nai'posha'', meaning "rough wate ...
:
** although it varies somewhat with rainfall, elevation , freshwater
* Lake Nakuru
Lake Nakuru is one of the Rift Valley lakes at an elevation of above sea level. It lies to the south of Nakuru, in the rift valley of Kenya and is protected by Lake Nakuru National Park.
The lake's abundance of algae used to attract a vast qu ...
: shallow soda lake, has been a national park since 1968.
** , elevation
* Lake Turkana
Lake Turkana (), formerly known as Lake Rudolf, is a lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya, with its far northern end crossing into Ethiopia. It is the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. B ...
: the largest of the Kenyan lakes, on the border of Kenya and Ethiopia.
** , elevation , freshwater
Tanzania
All the lakes in the Tanzanian section of this group are alkaline: *Lake Eyasi
Lake Eyasi (formerly german: Njarasasee, "Njarasa Lake", and ''Hohenlohesee'', "Hohenlohe Lake") is a lake located in Karatu District of Arusha Region in north Tanzania. Lake Eyasi is the largest body of water in Arusha region. It is a seasonal ...
: shallow soda lake
* Lake Makati: shallow soda lake
* Lake Manyara
Lake Manyara is a lake located in Monduli District of Arusha Region, Tanzania and is the seventh-largest lake of Tanzania by surface area, at . It is a shallow, alkaline lake in the Natron-Manyara-Balangida branch of the East African Rift. The n ...
: shallow soda lake
* Lake Natron
Lake Natron is a salt or alkaline lake located in north Ngorongoro District of Arusha Region in Tanzania. It is in the Gregory Rift, which is the eastern branch of the East African Rift. The lake is within the Lake Natron Basin, a Ramsar Site ...
: shallow soda lake that has been categorised by the World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wo ...
as being in the East African halophytics
Lake Natron is a salt or alkaline lake located in north Ngorongoro District of Arusha Region in Tanzania. It is in the Gregory Rift, which is the eastern branch of the East African Rift. The lake is within the Lake Natron Basin, a Ramsar Site ...
ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of l ...
.
Western or Albertine Rift Valley lakes
 The lakes of the Western or
The lakes of the Western or Albertine Rift
The Albertine Rift is the western branch of the East African Rift, covering parts of Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania.
It extends from the northern end of Lake Albert to the southern end of Lake Tan ...
, with Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after ...
, include the largest, deepest, and oldest of the Rift Valley Lakes. They are also referred to as the Central African lakes. Lakes Albert, Victoria, and Edward are part of the Nile River
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
basin.
Lake Victoria (elevation ), with an area of , is the largest lake in Africa. It is not in the rift valley, instead occupying a depression between the eastern and western rifts formed by the uplift of the rifts to either side. Lakes Victoria, Tanganyika, and Malawi are sometimes collectively known as the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in the ...
.
The Western Rift Valley lakes are fresh water and home to an extraordinary number of species. Approximately 1,500 cichlid
Cichlids are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses ( Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted this ...
fish (Cichlidae) species live in the lakes. In addition to the cichlids, populations of Clariidae, Claroteidae
The Claroteidae are a family of catfish (order Siluriformes) found in Africa. This family was separated from Bagridae. However, the monophyly of the family is sometimes contested.
The 12 genera contain 86 known species of claroteids in two subfa ...
, Mochokidae
The Mochokidae are a family of catfishes ( order Siluriformes) that are known as the squeakers and upside-down catfish (although not all species swim upside-down). There are nine genera and about 200 species of mochokids. All the mochokids are fr ...
, Poeciliidae
The Poeciliidae are a family of freshwater fishes of the order Cyprinodontiformes, the tooth-carps, and include well-known live-bearing aquarium fish, such as the guppy, molly, platy, and swordtail. The original distribution of the family was t ...
, Mastacembelidae
The Mastacembelidae are a family of fishes, known as the spiny eels. The Mastacembelids are part of the Order Synbranchiformes, the swamp eels, which are part of the Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes).
In an evaluation of the family in 2004, the ...
, Centropomidae
''Centropomus'' is a genus of predominantly marine fish comprising the family Centropomidae. The type species is ''Centropomus undecimalis'', the common snook. Commonly known as snooks or ''róbalos'', the ''Centropomus'' species are native to t ...
, Cyprinidae
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest verte ...
, Clupeidae
Clupeidae is a family of ray-finned fishes, comprising, for instance, the herrings, shads, sardines, hilsa, and menhadens. The clupeoids include many of the most important food fishes in the world, and are also commonly caught for production of ...
and other fish families are found in these lakes. They are also important habitats for a number of amphibia
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbore ...
n species, including ''Amietophrynus kisoloensis
''Sclerophrys kisoloensis'' is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in southwestern Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, northeastern Zambia, western Tanzania, and (pending confirmation) northern Mal ...
'', '' Bufo keringyagae'', '' Cardioglossa cyaneospila'', and ''Nectophryne batesii
''Nectophryne'', or African tree toads, is a small genus of true toads
A true toad is any member of the family Bufonidae, in the order Anura (frogs and toads). This is the only family of anurans in which all members are known as toads, altho ...
''.
* Lake Albert (, elevation ) is the northernmost lake in the western rift.
* Lake Edward
Lake Edward (locally Rwitanzigye or Rweru) is one of the smaller African Great Lakes. It is located in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift, on the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Uganda, w ...
(, elevation ) drains north into Lake Albert
* Lake Kivu
Lake Kivu is one of the African Great Lakes. It lies on the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda, and is in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift. Lake Kivu empties into the Ruzizi River, which ...
(, elevation ) empties into Lake Tanganyika via the Ruzizi River
The Ruzizi (also sometimes spelled Rusizi) is a river, long, that flows from Lake Kivu to Lake Tanganyika in Central Africa, descending from about to about above sea level over its length. The steepest gradients occur over the first , where hy ...
.
* Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika () is an African Great Lake. It is the second-oldest freshwater lake in the world, the second-largest by volume, and the second-deepest, in all cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. It is the world's longest freshwater lake. ...
(, elevation ) is the largest and deepest of the Rift Valley lakes (more than ), and is the second deepest fresh water lake on the planet (after Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
). Below roughly 200 meters depth, its water is anoxic
The term anoxia means a total depletion in the level of oxygen, an extreme form of hypoxia or "low oxygen". The terms anoxia and hypoxia are used in various contexts:
* Anoxic waters, sea water, fresh water or groundwater that are depleted of diss ...
and devoid of life besides anoxic bacteria. It is very sensitive to climate. It is part of the Congo River
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
basin, feeding into the River Congo
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
via the Lukuga River
The Lukuga River is a tributary of the Lualaba River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) that drains Lake Tanganyika. It is unusual in that its flow varies not just seasonally but also due to longer term climate fluctuations.
Location
...
.
Southern Rift Valley lakes (Tanzania and Malawi)
The Southern Rift Valley lakes are like the Western Rift Valley lakes in that, with one exception, they are freshwater lakes. *Lake Rukwa
Lake Rukwa is an endorheic lake located the Rukwa Valley of Rukwa Region, Songwe Region and Katavi Region in southwestern Tanzania. The lake is the third largest inland body of water in the country.
Geography
The alkaline Lake Rukwa lies midway ...
(about but quite variable) in Tanzania is the alkaline exception, lying south-east of Tanganyika, and has no outlet.
* Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is the fifth largest fre ...
(, elevation ), the second largest and second deepest of the Rift Valley lakes at over , is drained by the Shire River
The Shire is the largest river in Malawi. It is the only outlet of Lake Malawi and flows into the Zambezi River in Mozambique. Its length is . The upper Shire River issues from Lake Malawi and runs approximately before it enters shallow Lake Malo ...
, a tributary of the Zambezi River
The Zambezi River (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than hal ...
. Also known as Lake Nyasa.
* Lake Malombe
Lake Malombe is a lake in southern part of Malawi, on the Shire River, in the Southern Region, Malawi, Southern Region. It is located at around , about south of much larger Lake Malawi. It has an area of about . In recent years the number of fishe ...
() is on the Shire River
The Shire is the largest river in Malawi. It is the only outlet of Lake Malawi and flows into the Zambezi River in Mozambique. Its length is . The upper Shire River issues from Lake Malawi and runs approximately before it enters shallow Lake Malo ...
.
* Lake Chilwa
Lake Chilwa is the second-largest lake in Malawi after Lake Malawi. It is in eastern Zomba District, near the border with Mozambique. Approximately 60 km long and 40 km wide, the lake is surrounded by extensive wetlands. There is an islan ...
(, elevation ) has no outlet but extensive wetlands. It is the southernmost of the Rift Valley lakes.
Other lakes of the Great Rift Valley
*Lake Mweru
Lake Mweru (also spelled ''Mwelu'', ''Mwero'') is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up of the total length of th ...
( elevation 922 m) lies in the Lake Mweru-Luapula graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic contex ...
, which is a branch off the Albertine rift.
* Lake Mweru Wantipa
Lake Mweru Wantipa or Mweru-wa-Ntipa meaning "muddy lake" (also called 'Mweru Marsh') is a lake and Zambezian flooded grasslands, swamp system in the Northern Province, Zambia, Northern Province of Zambia. It has been regarded in the past as somet ...
(, elevation ) is a marshy lake between lakes Tanganyika
Tanganyika may refer to:
Places
* Tanganyika Territory (1916–1961), a former British territory which preceded the sovereign state
* Tanganyika (1961–1964), a sovereign state, comprising the mainland part of present-day Tanzania
* Tanzania Main ...
and Mweru, and is endorheic
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
but may overflow into Lake Mweru at times of very high flood.
References
External links
Lakes of the African Rift Valley
Africa Rift Valley Pictures From Helicopter by Michael Poliza
{{Regions of Africa Freshwater ecoregions
Rift Valley lakes
The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the East African Rift valley that runs through eastern Africa from Ethiopia in the north to Malawi in the south, and includes the African Great Lakes in the south. These include some of the world's ...