Afghan Hindu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hinduism in Afghanistan is practiced by a tiny minority of
/ref>
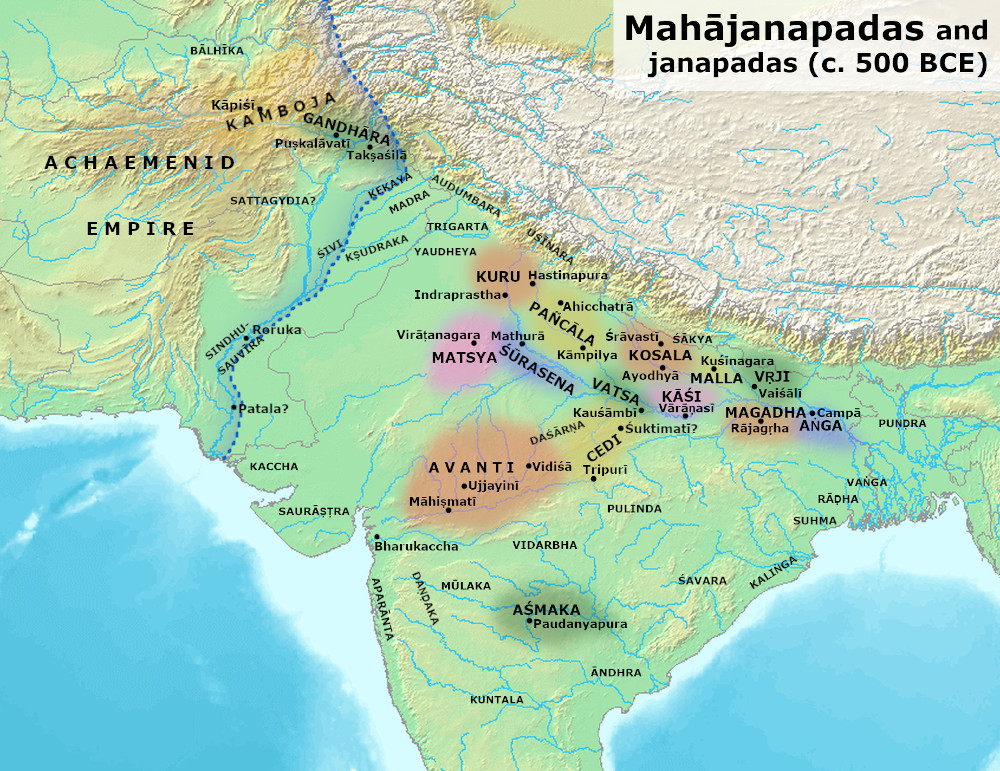


 When
When
Afghans
Afghans ( ps, افغانان, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, افغان ها, translit=afghānhā; Persian: افغانستانی, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry f ...
, believed to be about 30-40 individuals as of 2021, who live mostly in the cities of Kabul and Jalalabad. Afghan Hindus are ethnically Pashtun, Hindkowan
Hindkowans (lit. "Indian-speakers"), also known as the Hindki, is a contemporary designation for speakers of Indo-Aryan languages who live among the neighbouring Pashtuns, particularly the speakers of various Hindko dialects of Lahnda. The o ...
(Hindki), Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, or Sindhi and primarily speak Pashto, Hindko
Hindko (, romanized: , ) is a cover term for a diverse group of Lahnda dialects spoken by several million people of various ethnic backgrounds in several areas in northwestern Pakistan, primarily in the provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Pun ...
, Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, Dari, and Hindustani
Hindustani may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Hindustan (another name of India)
* Hindustani language, an Indo-Aryan language, whose two official norms are Hindi and Urdu
* Fiji Hindi, a variety of Eastern Hindi spoken in Fiji, and ...
( Urdu- Hindi).
Before the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan, the Afghan people were multi-religious. Religious persecution
Religious persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or a group of individuals as a response to their religion, religious beliefs or affiliations or their irreligion, lack thereof. The tendency of societies or groups within soc ...
, discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
, and forced conversion of Hindus perpetrated by Muslims has caused the Afghan Hindus, along with Buddhist and Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
population, to dwindle from Afghanistan.
During the 1970s, the Afghan Hindu population was estimated to number between 80,000 and 280,000, or 0.7% to 2.5% of the national population at the time. However, the population rapidly declined thereafter due to the Afghan wars along with continued persecution, discrimination and forced conversion.
Background
The Indo-Aryan inhabitants of the region, including Pashayi and Nuristanis, were known to be followers of a belief system similar to that of Hinduism.UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Taxila/ref>
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
, the majority ethnic group in Afghanistan (officially, no ethnic census ever made), have a component of Vedic ancestors from the Pakthas
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern p ...
.
Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Vall ...
, a region encompassing the South-east of Afghanistan, was also a center of Hinduism since the time of the Rigveda (), along with Buddhism. Later forms of Hinduism were also prevalent in this south-eastern region of the country during the Turk shahis, with Khair Khaneh
Khair Khaneh is an archaeological site located near Kabul, Afghanistan. A Brahmanical Temple was excavated there in the 1930s by Joseph Hackin. The construction of the Khair Khaneh temple itself is dated to 608-630 CE, at the beginning of the Turk ...
, a Brahmanical temple being excavated in Kabul and a statue of Gardez Ganesha being found in Paktia province. Most of the remains, including marble statuettes, date to the 7th–8th century, during the time of the Turk Shahi. The statue of Ganesha from Gardez is now attributed to the period of Turk Shahis in the 7-8th century CE, rather than to their successors the Hindu Shahis
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details r ...
(9th-10th century) as has also been suggested."It is not therefore possible to attribute these pieces to the Hindu Shahi period. They should be attributed to the Shahi period before the Hindu Shahis originated by the Brahman wazir Kallar, that is, the Turki Shahis." p.405 " According to the above sources, Brahmanism and Buddhism are properly supposed to have coexisted especially during the 7th-8th century A.D. just before the Muslim hegemony. The marble sculptures from eastern Afghanistan should not be attributed to the period of the Hindu Shahis but to that of the Turki Shahis." p.407 in The dating is essentially based on stylistic analysis, as the statue displays great iconographical and stylistic similarities with the works of the Buddhist monastery of Fondukistan, which is also dated to the same period.Hinduism further flourished under the rule of Hindu Shahis
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details r ...
, but went into sharp decline with the advent of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
through the Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
, who defeated the Shahis. Nonetheless, it continued as a significant minority in Afghanistan until the 21st century, when its number of followers fell to a few hundred."Contained within a clay urn were a gold bracteate with the portrait of a ruler, three early drachms of the Turk-Shahis (Type 236, one of which is countermarked), and a countermarked drachm of the Sasanian king Khusro II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (Persian language, New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian Empire, Sasa ...
dating from year 37 of his reign (= 626/7). The two countermarks on Khusro 's drachm prove that the urn could only have been deposited after 689"
History


Prehistory and ancient period (3300–550 BCE)
There is no reliable information on when Hinduism began in Afghanistan but historians suggest that the territory south of the Hindu Kush may have been culturally connected with theIndus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
(3300–2000 BCE) in ancient times.
By roughly 2000–1500 BCE, Indo-Aryan inhabitants of the region (mainly in the eastern and southern parts of present-day Afghanistan) were adherents of Hinduism. Notable among these were the Gandharis and Kambojas. The Pashayi and Nuristanis are present day examples of these Indo-Aryan Vedic people.
Persian, Greek, and Mauryan periods (550–150 BCE)
Most historians maintain that Afghanistan was inhabited by ancient Arians followed by the Achaemenid before the arrival of Alexander the Great and his Greek army in 330 BC. It became part of theSeleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
after the departure of Alexander three years later. In 305 BCE, the Seleucid Empire lost control of the territory south of the Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Kush to the Indian Emperor "Sandrocottus" as a result of the Seleucid-Mauryan War.
Classical period (150 BCE–650 CE)
When the Chinese travelers Faxian, Song Yun, and Xuanzang explored Afghanistan between the 5th and 7th centuries CE, they wrote numerous travelogues in which reliable information on Afghanistan was stored. They stated that Buddhism was practiced in different parts between the Amu Darya (Oxus River) in the north and theIndus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
. However, they did not mention much about Hinduism although Song Yun did state that the Hephthalite
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
rulers did not recognize Buddhism but "preached pseudo gods and killed animals for their meat".
Turk & Kabul Shahi, Zunbil dynasty (650–850 CE)
Before the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan, the territory was a religious sediment of Zoroastrianism, Zunbils, Hinduism and Buddhism. It was inhabited by various peoples, including Persians, Khalaj, Turks, andPashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
. Parts of the territory South of Hindu kush were ruled by the Zunbils, offspring of the southern-Hephthalite. The eastern parts (''Kabulistan'') were controlled by the Turk Shahis.
The Zunbil and Kabul Shahis were connected with the Indian subcontinent through common Buddhism and ''Zun'' religions. The Zunbil kings worshipped a sun god
A solar deity or sun deity is a deity who represents the Sun, or an aspect of it. Such deities are usually associated with power and strength. Solar deities and Sun worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms. The ...
by the name of ''Zun'', from which they derived their name. André Wink writes that "the cult of Zun was primarily Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, not Buddhist or Zoroastrian"; nonetheless he still mentions them having parallels with Tibetan Buddhism and Zoroastrianism in their rituals.André Wink, ''Al-Hind: The Making of the Indo-Islamic World'', Brill 1990. p 118
The Kabul Shahi ruled north of the Zunbil territory, which included Kabulistan and Gandahara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Vall ...
. The Arabs reached Kabul in 653–654 CE when Abdur Rahman bin Samara, along with 6,000 Arab Muslims, penetrated the Zunbil territory and made their way to the shrine of ''Zun'' in Zamindawar, which was believed to be located about south of Musa Qala in today's Helmand Province of Afghanistan. The General of the Arab army "broke of a hand of the idol and plucked out the rubies which were its eyes in order to persuade the Marzbān of Sīstān of the god's worthlessness."
Though the early Arab invaders spread the message of Islam, they were not able to rule for long. Hence, many contemporary ethnic groups in Afghanistan, including the Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
, Kalash, Pashayi, Nuristanis and Hindkowans
Hindkowans (lit. "Indian-speakers"), also known as the Hindki, is a contemporary designation for speakers of Indo-Aryan languages who live among the neighbouring Pashtuns, particularly the speakers of various Hindko dialects of Lahnda. The or ...
continued to practice Hinduism, Buddhism, and Zoroastrianism. The Kabul Shahis decided to build a giant wall around the city to prevent more Arab invasions, and this wall is still visible today.
Hindu Shahi (850–1000 CE)
Willem Vogelsang in his 2002 book writes: "During the 8th and 9th centuries AD the eastern terroritries of modern Afghanistan were still in the hands of non-Muslim rulers. The Muslims tended to regard them as Indians (Hindus), although many of the local rulers and people were apparently of Hunnic or Turkic descent. Yet, the Muslims were right in so far as the non-Muslim population of eastern Afghanistan was, culturally linked to theIndian sub-continent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
. Most of them were either Hindus or Buddhists. "
In 870 AD the Saffarids from medieval Zaranj, located at the Nad-e Ali site of modern-day Iran (not to be confused with the similarly named modern city of Zaranj in Afghanistan), conquered most of Afghanistan, establishing Muslim governors throughout the land. It is reported that Muslims and non-Muslims still lived side by side before the arrival of the Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
in the 10th century.
The first confirmed mention of a ''Hindu'' in Afghanistan appears in the 982 AD Ḥudūd al-ʿĀlam, where it speaks of a king in "Ninhar" ( Nangarhar), who shows a public display of conversion to Islam, even though he had over 30 wives, which are described as "Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Afghan, and Hindu" wives. These names were often used as geographical terms. For example, ''Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
'' (or ''Hindustani
Hindustani may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Hindustan (another name of India)
* Hindustani language, an Indo-Aryan language, whose two official norms are Hindi and Urdu
* Fiji Hindi, a variety of Eastern Hindi spoken in Fiji, and ...
'') has been historically used as a geographical term to describe someone who was native from the region known as Hindustan (Indian subcontinent), and ''Afghan'' as someone who was native from a region called '' Afghanistan''.
Decline (1000–1800 CE)
 When
When Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
Mahmud of Ghazni
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
began crossing the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
into Hindustan (land of Hindus) in the 10th century, the Ghaznavid Muslims began bringing Hindu slaves to what is now Afghanistan. Martin Ewans in his 2002 book writes:
Al-Idirisi testifies that until as late as the 12th century, a contract of investiture for every Shahi king was performed at Kabul and that here he was obliged to agree to certain ancient conditions which completed the contract.Al-Idrisi, p. 67, Maqbul Ahmed; ''Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World'', 1991, p. 127, Andre Wink. The Ghaznavid military incursions assured the domination of Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
in what is now Afghanistan and Pakistan. Various historical sources such as Martin Ewans, E.J. Brill and Farishta have recorded the introduction of Islam to Kabul and other parts of Afghanistan to the conquests of and Mahmud:
Mahmud used his plundered wealth to finance his armies which included mercenaries. The Indian soldiers, presumably Hindus, who were one of the components of the army with their commander called ''sipahsalar
''Ispahsālār'' ( fa, اسپهسالار) or ''sipahsālār'' (; "army commander"), in Arabic rendered as ''isfahsalār'' () or ''iṣbahsalār'' (), was a title used in much of the Islamic world during the 10th–15th centuries, to denote the se ...
-i-Hinduwan'' lived in their quarter of Ghazna practicing their own religion. Indian soldiers under their commander Suvendhray remained loyal to Mahmud. They were also used against a Turkic rebel, with the command given to a Hindu named Tilak according to Baihaki.
In his war on Peshawar and Waihind says al-Utbi, Mahmud acquired 500,000 slaves that included children and girls. Men were sold as slaves to even common merchants. The amount of slaves captured in Nardin plummeted their price and male slaves were even bought by common merchants. After raiding Thanesar, he acquired 200,000 slaves.
The renowned 14th-century Moroccan Muslim scholar Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
remarked that the Hindu Kush meant the "slayer of Indians", because slaves brought from India who had to pass through there died in large numbers due to the extreme cold and quantity of snow.
The Ghaznavid Empire was further expanded by the Ghurids. During the Khalji dynasty
The Khalji or Khilji (Pashto: ; Persian: ) dynasty was a Turco-Afghan dynasty which ruled the Delhi sultanate, covering large parts of the Indian subcontinent for nearly three decades between 1290 and 1320.Mughals followed by the
Suris
Suris is a former commune in the Charente department in southwestern France. On 1 January 2019, it was merged into the new commune Terres-de-Haute-Charente.Durranis.
Modern period
The main ethnic groups in Afghanistan which practice Hinduism today are thePunjabis
The Punjabis ( Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Panjābīs), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. The ...
and Sindhis who are believed to have come along with Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
as merchants to Afghanistan in the 19th century. Till the collapse of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan
The Democratic Republic of Afghanistan (DRA),, renamed the Republic of Afghanistan, in 1987, was the Afghan state during the one-party rule of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) from 1978 to 1992.
The PDPA came to power ...
, there were several thousand Hindus living in the country but today their number is only about 1,000. Most of the others immigrated to India, the European Union, North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
or elsewhere.
Afghan Hindus and Afghan Sikhs often share places of worship. Along with the Sikhs, they are all collectively known as Hindki. Linguistic demographics among the Hindu community are diverse and generally follow regional origins: those hailing from Punjab generally speak Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, Sindhis speak Sindhi, and the northern and southern dialects of Hindko
Hindko (, romanized: , ) is a cover term for a diverse group of Lahnda dialects spoken by several million people of various ethnic backgrounds in several areas in northwestern Pakistan, primarily in the provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Pun ...
. The local Hindu community in Afghanistan is mostly based in the city of Kabul. The 2002 loya jirga had two seats reserved for Hindus and former President Hamid Karzai's economic advisor, Sham Lal Bhatija was an Afghan Hindu.
During the Taliban 1996 to late 2001 rule, Hindus were forced to wear yellow badges in public to identify themselves as non-Muslims. Hindu women were forced to wear burqas, a measure which was claimed to "protect" them from harassment. This was part of the Taliban's plan to segregate "un-Islamic" and "idolatrous" communities from Islamic ones.
The decree was condemned by the Indian and U.S. governments as a violation of religious freedom. Widespread protests against the Taliban regime broke out in Bhopal, India. In the United States, Abraham Foxman, chairman of the Anti-Defamation League
The Anti-Defamation League (ADL), formerly known as the Anti-Defamation League of B'nai B'rith, is an international Jewish non-governmental organization based in the United States specializing in civil rights law. It was founded in late Septe ...
, compared the decree to the practices of Nazi Germany, where Jews were required to wear labels identifying them as such. Several influential lawmakers in the United States wore yellow badges with the inscription "I am a Hindu", on the floor of the Senate during the debate as a demonstration of their solidarity with the Hindu minority in Afghanistan.
Since the 1990s, many Afghan Hindus have fled the country, seeking asylum in countries such as India, Germany and United States.
In July 2013, the Afghan parliament refused to reserve seats for the minority group as a bill reserving seats for the mentioned was voted against. The bill by the then president Hamid Karzai, had tribal people and "women" as "vulnerable groups" who got reservation, but not religious minorities as per the religious equality article in the constitution.
Notable people
* Atma Ram – Afghan Minister and Author. *Celina Jaitley
Celina Jaitly (born 24 November 1981) is an Indian actress who mainly appears in Bollywood films. She won the Miss India in 2001 and was the 4th runner-up at Miss Universe 2001. She made her acting debut with the 2003 thriller '' Janasheen''. ...
– Indian Bollywood actress born to an Indian father, Colonel V. K. Jaitly and an Afghan Hindu mother, Meeta Jaitly, who was also from Kabul and was a nurse in the Indian Army.
* Annet Mahendru – American actress born in Kabul to an Indian father, Ghanshan "Ken" Mahendru whose family had moved from Delhi to Afghanistan for business and a Russian mother, Olga.
Diaspora
As both populations are frequently merged in historic and contemporary estimations, the population ratio between Afghan Sikhs and Hindus is estimated to be 60:40 according to historian Inderjeet Singh. With a wide range of population approximations in the absence of official census data and with much of the community concentrated in the provinces of Kabul, Nangarhar, Ghazni, and Kandahar, the Afghan Hindu population was estimated to be between 80,000 and 280,000 in the 1970s, as per estimates by historian Inderjeet Singh, Ehsan Shayegan with the Porsesh Research and Studies Organisation and Rawail Singh, an Afghan Sikh civil rights activist. In the time of 1980's after the Afghan civil war 1979 the population of Hindus and Sikh fell at a very fast rate due to Taliban's rise to power and religious persecution and discrimination and they migrated from Afghanistan to other countries, The continue rise of Islamization and Taliban insurgency also contributed in the diaspora. The decline was seen mostly inPashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
-dominated areas,due to Pashtunistan and Pashtun nationalism, with the Afghan Hindu population declining to 3,000 by 2009.
As per the 2017 data, more than 99% of Afghan Sikhs and Hindus have left the country in the last 3 decades. Many of Afghan Hindus and Sikhs have been settled in Germany, France, United States, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, India, Belgium, the Netherlands and other nations.
The Afghan Hindu population declined to approximately 50 in 2020. Later, following the Fall of Kabul in 2021, the Government of India evacuated many Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
and Hindus out of the country due to the Taliban takeover
A Offensive (military), military offensive by the Taliban insurgent group and other allied militants led to the fall of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan based in Kabul and marked the end of the nearly 20-year-old War in Afghanistan (2001–20 ...
. As a result, only one Hindu priest remains in the nation today, also acting as Temple guard.
Demographics
Ancient Hindu temples
See also
* Hinduism by country * Religion in Afghanistan *Jainism in Afghanistan Jainism, Jain artwork ruins have been discovered at sites in Afghanistan. According to Pratapaditya Pal, these pieces were found along with coins during road construction projects, and they "almost certainly were imported from India", likely ancient ...
* Sikhism in Afghanistan
* Buddhism in Afghanistan
* Pre-Islamic Hindu and Buddhist heritage of Afghanistan
* Khatri
* Punjabis in Afghanistan
* Hindkowan
Hindkowans (lit. "Indian-speakers"), also known as the Hindki, is a contemporary designation for speakers of Indo-Aryan languages who live among the neighbouring Pashtuns, particularly the speakers of various Hindko dialects of Lahnda. The o ...
* Kalash people
* Burusho people
* Kafiristan
* Hindu Kush
Notes
References
Sources
* * * *External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hinduism In Afghanistan Afghanistan Ancient history of Afghanistan Archaeological sites in Afghanistan History of religion in Afghanistan