Accumbens Nucleus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the
Figure 3: The ventral striatum and self-administration of amphetamine
/ref> Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region ( D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different cognitive functions. As a whole, the nucleus accumbens has a significant role in the cognitive processing of
Figure 1: Glutamatergic afferents to the nucleus accumbens involved in addictive behavior
/ref> The nucleus accumbens receives dopaminergic inputs from the ventral tegmental area, which connect via the mesolimbic pathway. The nucleus accumbens is often described as one part of a cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Dopaminergic inputs from the VTA modulate the activity of
Figure 3: Neural circuits underlying motivated 'wanting' and hedonic 'liking'.
/ref> Addictive drugs have a larger effect on dopamine release in the shell than in the core.
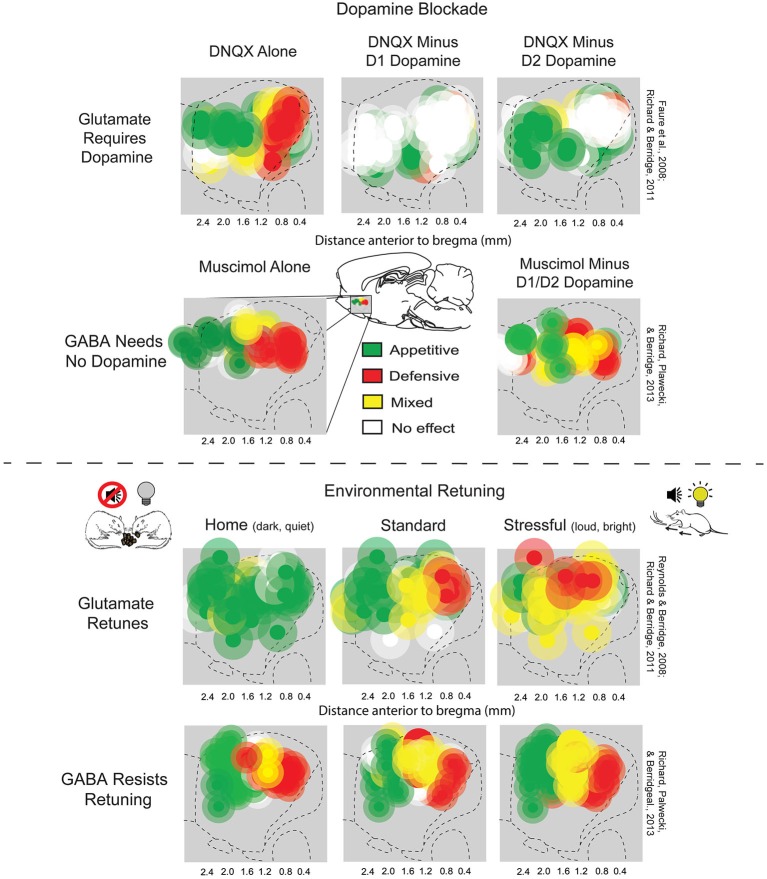 The nucleus accumbens is causally related to the experience of pleasure. Microinjections of μ-opioid agonists, δ-opioid agonists or κ-opioid agonists in the rostrodorsal quadrant of the medial shell enhance "liking", while more caudal injections can inhibit disgust reactions, liking reactions, or both. The regions of the nucleus accumbens that can be ascribed a causal role in the production of pleasure are limited both anatomically and chemically, as besides opioid agonists only endocannabinoids can enhance liking. In the nucleus accumbens as a whole, dopamine, GABA receptor agonist or AMPA antagonists solely modify motivation, while the same is true for opioid and endocannabinoids outside of the hotspot in the medial shell. A rostro-caudal gradient exists for the enhancement of appetitive versus fearful responses, the latter of which is traditionally thought to require only D1 receptor function, and the former of which requires both D1 and D2 function. One interpretation of this finding, the disinhibition hypothesis, posits that inhibition of accumbens MSNs (which are GABAergic) disinhibits downstream structures, enabling the expression of appetitive or consummatory behaviors. The motivational effects of AMPA antagonists, and to a lesser extent GABA agonists, is anatomically flexible. Stressful conditions can expand the fear inducing regions, while a familiar environment can reduce the size of the fear inducing region. Furthermore, cortical input from the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) biases the response towards that of appetitive behavior, and infralimbic input, equivalent to the human subgenual cingulate cortex, suppresses the response regardless of valence.
The nucleus accumbens is neither necessary nor sufficient for instrumental learning, although manipulations can affect performance on instrumental learning tasks. One task where the effect of NAcc lesions is evident is Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (PIT), where a cue paired with a specific or general reward can enhance instrumental responding. Lesions to the core of the NAcc impair performance after devaluation and inhibit the effect of general PIT. On the other hand, lesions to the shell only impair the effect of specific PIT. This distinction is thought to reflect consummatory and appetitive conditioned responses in the NAcc shell and the NAcc core, respectively.
In the dorsal striatum, a dichotomy has been observed between D1-MSNs and D2-MSNs, with the former being reinforcing and enhancing locomotion, and the latter being aversive and reducing locomotion. Such a distinction has been traditionally assumed to apply to the nucleus accumbens as well, but evidence from pharmacological and optogenetics studies is conflicting. Furthermore, a subset of NAcc MSNs express both D1 and D2 MSNs, and pharmacological activation of D1 versus D2 receptors need not necessarily activate the neural populations exactly. While most studies show no effect of selective optogenetic stimulation of D1 or D2 MSNs on locomotor activity, one study has reported a decrease in basal locomotion with D2-MSN stimulation. While two studies have reported reduced reinforcing effects of cocaine with D2-MSN activation, one study has reported no effect. NAcc D2-MSN activation has also been reported to enhance motivation, as assessed by PIT, and D2 receptor activity is necessary for the reinforcing effects of VTA stimulation. A 2018 study reported that D2 MSN activation enhanced motivation via inhibiting the ventral pallidum, thereby disinhibiting the VTA.
The nucleus accumbens is causally related to the experience of pleasure. Microinjections of μ-opioid agonists, δ-opioid agonists or κ-opioid agonists in the rostrodorsal quadrant of the medial shell enhance "liking", while more caudal injections can inhibit disgust reactions, liking reactions, or both. The regions of the nucleus accumbens that can be ascribed a causal role in the production of pleasure are limited both anatomically and chemically, as besides opioid agonists only endocannabinoids can enhance liking. In the nucleus accumbens as a whole, dopamine, GABA receptor agonist or AMPA antagonists solely modify motivation, while the same is true for opioid and endocannabinoids outside of the hotspot in the medial shell. A rostro-caudal gradient exists for the enhancement of appetitive versus fearful responses, the latter of which is traditionally thought to require only D1 receptor function, and the former of which requires both D1 and D2 function. One interpretation of this finding, the disinhibition hypothesis, posits that inhibition of accumbens MSNs (which are GABAergic) disinhibits downstream structures, enabling the expression of appetitive or consummatory behaviors. The motivational effects of AMPA antagonists, and to a lesser extent GABA agonists, is anatomically flexible. Stressful conditions can expand the fear inducing regions, while a familiar environment can reduce the size of the fear inducing region. Furthermore, cortical input from the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) biases the response towards that of appetitive behavior, and infralimbic input, equivalent to the human subgenual cingulate cortex, suppresses the response regardless of valence.
The nucleus accumbens is neither necessary nor sufficient for instrumental learning, although manipulations can affect performance on instrumental learning tasks. One task where the effect of NAcc lesions is evident is Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (PIT), where a cue paired with a specific or general reward can enhance instrumental responding. Lesions to the core of the NAcc impair performance after devaluation and inhibit the effect of general PIT. On the other hand, lesions to the shell only impair the effect of specific PIT. This distinction is thought to reflect consummatory and appetitive conditioned responses in the NAcc shell and the NAcc core, respectively.
In the dorsal striatum, a dichotomy has been observed between D1-MSNs and D2-MSNs, with the former being reinforcing and enhancing locomotion, and the latter being aversive and reducing locomotion. Such a distinction has been traditionally assumed to apply to the nucleus accumbens as well, but evidence from pharmacological and optogenetics studies is conflicting. Furthermore, a subset of NAcc MSNs express both D1 and D2 MSNs, and pharmacological activation of D1 versus D2 receptors need not necessarily activate the neural populations exactly. While most studies show no effect of selective optogenetic stimulation of D1 or D2 MSNs on locomotor activity, one study has reported a decrease in basal locomotion with D2-MSN stimulation. While two studies have reported reduced reinforcing effects of cocaine with D2-MSN activation, one study has reported no effect. NAcc D2-MSN activation has also been reported to enhance motivation, as assessed by PIT, and D2 receptor activity is necessary for the reinforcing effects of VTA stimulation. A 2018 study reported that D2 MSN activation enhanced motivation via inhibiting the ventral pallidum, thereby disinhibiting the VTA.
Image:Dopamine_and_serotonin_pathways.png, Dopamine and serotonin
Image:Nucleus_accumbens_MRI.PNG, MRI coronal slice showing nucleus accumbens outlined in red
Image:Nucleus accumbens sag.jpg, Sagittal MRI slice with highlighting (red) indicating the nucleus accumbens.
File:Nucleus accumbens coronal sections.gif, Nucleus accumbens highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
File:Nucleus accumbens sagittal sections.gif, Nucleus accumbens highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
File:Nucleus accumbens transversal sections.gif, Nucleus accumbens highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
The role of the nucleus accumbens in the reward circuit.
Part of "The Brain From Top to Bottom." at thebrain.mcgill.ca
Nucleus Accumbens – Cell Centered Database
* {{Authority control Limbic system Addiction Basal ganglia
septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Human anatomy
* Interatri ...
") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral
Rostral may refer to:
Anatomy
* Rostral (anatomical term), situated toward the oral or nasal region
* Rostral bone, in ceratopsian dinosaurs
* Rostral organ, of certain fish
* Rostral scale, in snakes and scaled reptiles
Other uses
* Rostral colu ...
to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamate ...
, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons
Dopaminergic cell groups, DA cell groups, or dopaminergic nuclei are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopaminergic neurons or ''dopamine neurons'' were first ident ...
of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A ...
medium spiny neuron
Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), are a special type of GABAergic inhibitory cell representing 95% of neurons within the human striatum, a basal ganglia structure. Medium spiny neurons have two primary ...
s of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle.Figure 3: The ventral striatum and self-administration of amphetamine
/ref> Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region ( D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different cognitive functions. As a whole, the nucleus accumbens has a significant role in the cognitive processing of
motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-dire ...
, aversion
Aversion means opposition or repugnance. The following are different forms of aversion:
* Ambiguity aversion
* Brand aversion
* Dissent aversion in the United States of America
* Endowment effect, also known as divestiture aversion
* Food aversi ...
, reward (i.e., incentive salience
Motivational salience is a cognitive process and a form of attention that ''motivates'' or propels an individual's behavior towards or away from a particular stimulus (psychology), object, perceived event or outcome. Motivational salience regulat ...
, pleasure
Pleasure refers to experience that feels good, that involves the enjoyment of something. It contrasts with pain or suffering, which are forms of feeling bad. It is closely related to value, desire and action: humans and other conscious anima ...
, and positive reinforcement), and reinforcement learning (e.g., Pavlovian-instrumental transfer); hence, it has a significant role in addiction. In addition, part of the nucleus accumbens core is centrally involved in the induction of slow-wave sleep
Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. It usually lasts between 70 and 90 minutes and takes place during the first hours of the night. Initially, SWS consisted of both St ...
. The nucleus accumbens plays a lesser role in processing fear (a form of aversion), impulsivity
In psychology, impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically "poorly conceived, prema ...
, and the placebo effect. It is involved in the encoding of new motor programs as well.
Structure
The nucleus accumbens is an aggregate of neurons which is described as having an outer shell and an inner core.Input
Major glutamatergic inputs to the nucleus accumbens include the prefrontal cortex (particularly the prelimbic cortex and infralimbic cortex),basolateral amygdala
The basolateral amygdala, or basolateral complex, consists of the lateral, basal and accessory-basal nuclei of the amygdala. The lateral nuclei receives the majority of sensory information, which arrives directly from the temporal lobe structures, ...
, ventral hippocampus, thalamic
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, ...
nuclei (specifically the midline thalamic nuclei
The midline nuclear group (or midline thalamic nuclei) is a region of the thalamus consisting of the following nuclei:
* paraventricular nucleus of thalamus (''nucleus paraventricularis thalami'') - not to be confused with paraventricular nucleus ...
and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus
The intralaminar thalamic nuclei (ITN) are collections of neurons in the internal medullary lamina of the thalamus that are generally divided in two groups as follows:Mancall, E., Brock, D. & Gray, H. (2011). Gray's clinical neuroanatomy the anatom ...
), and glutamatergic projections from the ventral tegmental area (VTA).Figure 1: Glutamatergic afferents to the nucleus accumbens involved in addictive behavior
/ref> The nucleus accumbens receives dopaminergic inputs from the ventral tegmental area, which connect via the mesolimbic pathway. The nucleus accumbens is often described as one part of a cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Dopaminergic inputs from the VTA modulate the activity of
GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A ...
neurons within the nucleus accumbens. These neurons are activated directly or indirectly by euphoriant drugs (e.g., amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
, opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term ''opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonis ...
s, etc.) and by participating in rewarding experiences (e.g., sex, music, exercise, etc.).
Another major source of input comes from the CA1 and ventral subiculum of the hippocampus to the dorsomedial area of the nucleus accumbens. Slight depolarizations of cells in the nucleus accumbens correlates with positivity of the neurons of the hippocampus, making them more excitable. The correlated cells of these excited states of the medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens are shared equally between the subiculum and CA1. The subiculum neurons are found to hyperpolarize (increase negativity) while the CA1 neurons "ripple" (fire > 50 Hz) in order to accomplish this priming.
The nucleus accumbens is one of the few regions that receives a high density of histaminergic projections from the tuberomammillary nucleus (the sole source of histamine neurons in the brain).
Output
The output neurons of the nucleus accumbens send axonal projections to the basal ganglia and the ventral analog of theglobus pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
, known as the ventral pallidum (VP). The VP, in turn, projects to the medial dorsal nucleus of the dorsal thalamus, which projects to the prefrontal cortex as well as back to the ventral and to dorsal striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamate ...
. Other efferents from the nucleus accumbens include connections with the tail of the ventral tegmental area The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the ve ...
, substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra app ...
, and the reticular formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation ...
of the pons.
Shell
The nucleus accumbens shell (NAcc shell) is a substructure of the nucleus accumbens. The shell and core together form the entire nucleus accumbens. Location: The shell is the outer region of the nucleus accumbens, and – unlike the core – is considered to be part of the extended amygdala, located at its rostral pole. Cell types: Neurons in the nucleus accumbens are mostlymedium spiny neuron
Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), are a special type of GABAergic inhibitory cell representing 95% of neurons within the human striatum, a basal ganglia structure. Medium spiny neurons have two primary ...
s (MSNs) containing mainly D1-type (i.e., DRD1 and DRD5
Dopamine receptor D5, also known as D1BR, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DRD5'' gene. It belongs to the D1-like receptor family along with the D1 receptor subtype.
Function
D5 receptor is a subtype of the dopamine receptor ...
) or D2-type (i.e., DRD2, DRD3, and DRD4) dopamine receptors. A subpopulation of MSNs contain both D1-type and D2-type receptors, with approximately 40% of striatal MSNs expressing both DRD1 and DRD2 mRNA. These mixed-type NAcc MSNs with both D1-type and D2-type receptors are mostly confined to the NAcc shell. The neurons in the shell, as compared to the core, have a lower density of dendritic spines, less terminal segments, and less branch segments than those in the core. The shell neurons project to the subcommissural part of the ventral pallidum as well as the ventral tegmental area and to extensive areas in the hypothalamus and extended amygdala.
Function: The shell of the nucleus accumbens is involved in the cognitive processing of reward, including subjective "liking" reactions to certain pleasurable stimuli, motivational salience
Motivational salience is a cognitive process and a form of attention that ''motivates'' or propels an individual's behavior towards or away from a particular object, perceived event or outcome. Motivational salience regulates the intensity of be ...
, and positive reinforcement. That NAcc shell has also been shown to mediate specific Pavlovian-instrumental transfer, a phenomenon in which a classically conditioned stimulus modifies operant behavior. A "hedonic hotspot" or pleasure center which is responsible for the pleasurable or "liking" component of some intrinsic rewards is also located in a small compartment within the medial NAcc shell.Figure 3: Neural circuits underlying motivated 'wanting' and hedonic 'liking'.
/ref> Addictive drugs have a larger effect on dopamine release in the shell than in the core.
Core
The nucleus accumbens core (NAcc core) is the inner substructure of the nucleus accumbens. Location: The nucleus accumbens core is part of the ventral striatum, located within the basal ganglia. Cell types: The core of the NAcc is made up mainly of medium spiny neurons containing mainly D1-type or D2-type dopamine receptors. The D1-type medium spiny neurons mediate reward-related cognitive processes, whereas the D2-type medium spiny neurons mediate aversion-related cognition. The neurons in the core, as compared to the neurons in the shell, have an increased density of dendritic spines, branch segments, and terminal segments. From the core, the neurons project to other sub-cortical areas such as the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra. GABA is one of the main neurotransmitters in the NAcc, and GABA receptors are also abundant. Function: The nucleus accumbens core is involved in the cognitive processing of motor function related to reward and reinforcement and the regulation ofslow-wave sleep
Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. It usually lasts between 70 and 90 minutes and takes place during the first hours of the night. Initially, SWS consisted of both St ...
. Specifically, the core encodes new motor programs which facilitate the acquisition of a given reward in the future. The indirect pathway (i.e., D2-type) neurons in the NAcc core which co-express adenosine A2A receptors activation-dependently promote slow-wave sleep. The NAcc core has also been shown to mediate general Pavlovian-instrumental transfer, a phenomenon in which a classically conditioned stimulus modifies operant behavior.
Cell types
Approximately 95% of neurons in the NAcc are GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs) which primarily express either D1-type or D2-type receptors; about 1–2% of the remaining neuronal types are large aspiny cholinergicinterneuron
Interneurons (also called internuncial neurons, relay neurons, association neurons, connector neurons, intermediate neurons or local circuit neurons) are neurons that connect two brain regions, i.e. not direct motor neurons or sensory neurons. I ...
s and another 1–2% are GABAergic interneurons.
Compared to the GABAergic MSNs in the shell, those in the core have an increased density of dendritic spines, branch segments, and terminal segments. From the core, the neurons project to other sub-cortical areas such as the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra. GABA is one of the main neurotransmitters in the NAcc, and GABA receptors are also abundant. These neurons are also the main projection or output neurons of the nucleus accumbens.
Neurochemistry
Some of the neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and hormones that signal through receptors within the nucleus accumbens include:Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
: Dopamine is released into the nucleus accumbens following exposure to rewarding stimuli, including recreational drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
s like substituted amphetamines, cocaine, nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used fo ...
and morphine.
Phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amin ...
and tyramine: Phenethylamine and tyramine are trace amines which are synthesized in neurons that express the aromatic amino acid hydroxylase
Biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAH) are a family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes which includes phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase (), tyrosine 3-hydroxylase (), and tryptophan 5-hydroxylase (). These enzymes primaril ...
(AADC) enzyme, which includes all dopaminergic neurons. Both compounds function as dopaminergic neuromodulators which regulate the reuptake and release of dopamine into the Nacc via interactions with VMAT2 and TAAR1 in the axon terminal of mesolimbic dopamine neurons.
Glucocorticoids and dopamine: Glucocorticoid receptors are the only corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell. L-DOPA, steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
, and specifically glucocorticoids are currently known to be the only known endogenous compounds that can induce psychotic problems, so understanding the hormonal control over dopaminergic projections with regard to glucocorticoid receptors could lead to new treatments for psychotic symptoms. A recent study demonstrated that suppression of the glucocorticoid receptors led to a decrease in the release of dopamine, which may lead to future research involving anti-glucocorticoid drugs to potentially relieve psychotic symptoms.
GABA: A recent study on rats that used GABA agonists and antagonists indicated that GABAA receptors in the NAcc shell have inhibitory control on turning behavior influenced by dopamine, and GABAB receptors have inhibitory control over turning behavior mediated by acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Part ...
.
Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
: Studies have shown that local blockade of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
rgic NMDA receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA rece ...
s in the NAcc core impaired spatial learning. Another study demonstrated that both NMDA and AMPA (both glutamate receptors) play important roles in regulating instrumental learning.
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
(5-HT): Overall, 5-HT synapses are more abundant and have a greater number of synaptic contacts in the NAcc shell than in the core. They are also larger and thicker, and contain more large dense core vesicles than their counterparts in the core.
Function
Reward and reinforcement
The nucleus accumbens, being one part of the reward system, plays an important role in processing rewarding stimuli, reinforcing stimuli (e.g., food and water), and those which are both rewarding and reinforcing (addictive drugs, sex, and exercise). The predominant response of neurons in the nucleus accumbens to the rewardsucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
is inhibition; the opposite is true in response to the administration of aversive quinine. Substantial evidence from pharmacological manipulation also suggests that reducing the excitability of neurons in the nucleus accumbens is rewarding, as, for example, would be true in the case of μ-opioid receptor stimulation. The blood oxygen level dependent signal (BOLD) in the nucleus accumbens is selectively increased during the perception of pleasant, emotionally arousing pictures and during mental imagery of pleasant, emotional scenes. However, as BOLD is thought to be an indirect measure of regional net excitation to inhibition, the extent to which BOLD measures valence dependent processing is unknown. Because of the abundance of NAcc inputs from limbic regions and strong NAcc outputs to motor regions, the nucleus accumbens has been described by Gordon Mogensen as the interface between the limbic and motor system.
 The nucleus accumbens is causally related to the experience of pleasure. Microinjections of μ-opioid agonists, δ-opioid agonists or κ-opioid agonists in the rostrodorsal quadrant of the medial shell enhance "liking", while more caudal injections can inhibit disgust reactions, liking reactions, or both. The regions of the nucleus accumbens that can be ascribed a causal role in the production of pleasure are limited both anatomically and chemically, as besides opioid agonists only endocannabinoids can enhance liking. In the nucleus accumbens as a whole, dopamine, GABA receptor agonist or AMPA antagonists solely modify motivation, while the same is true for opioid and endocannabinoids outside of the hotspot in the medial shell. A rostro-caudal gradient exists for the enhancement of appetitive versus fearful responses, the latter of which is traditionally thought to require only D1 receptor function, and the former of which requires both D1 and D2 function. One interpretation of this finding, the disinhibition hypothesis, posits that inhibition of accumbens MSNs (which are GABAergic) disinhibits downstream structures, enabling the expression of appetitive or consummatory behaviors. The motivational effects of AMPA antagonists, and to a lesser extent GABA agonists, is anatomically flexible. Stressful conditions can expand the fear inducing regions, while a familiar environment can reduce the size of the fear inducing region. Furthermore, cortical input from the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) biases the response towards that of appetitive behavior, and infralimbic input, equivalent to the human subgenual cingulate cortex, suppresses the response regardless of valence.
The nucleus accumbens is neither necessary nor sufficient for instrumental learning, although manipulations can affect performance on instrumental learning tasks. One task where the effect of NAcc lesions is evident is Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (PIT), where a cue paired with a specific or general reward can enhance instrumental responding. Lesions to the core of the NAcc impair performance after devaluation and inhibit the effect of general PIT. On the other hand, lesions to the shell only impair the effect of specific PIT. This distinction is thought to reflect consummatory and appetitive conditioned responses in the NAcc shell and the NAcc core, respectively.
In the dorsal striatum, a dichotomy has been observed between D1-MSNs and D2-MSNs, with the former being reinforcing and enhancing locomotion, and the latter being aversive and reducing locomotion. Such a distinction has been traditionally assumed to apply to the nucleus accumbens as well, but evidence from pharmacological and optogenetics studies is conflicting. Furthermore, a subset of NAcc MSNs express both D1 and D2 MSNs, and pharmacological activation of D1 versus D2 receptors need not necessarily activate the neural populations exactly. While most studies show no effect of selective optogenetic stimulation of D1 or D2 MSNs on locomotor activity, one study has reported a decrease in basal locomotion with D2-MSN stimulation. While two studies have reported reduced reinforcing effects of cocaine with D2-MSN activation, one study has reported no effect. NAcc D2-MSN activation has also been reported to enhance motivation, as assessed by PIT, and D2 receptor activity is necessary for the reinforcing effects of VTA stimulation. A 2018 study reported that D2 MSN activation enhanced motivation via inhibiting the ventral pallidum, thereby disinhibiting the VTA.
The nucleus accumbens is causally related to the experience of pleasure. Microinjections of μ-opioid agonists, δ-opioid agonists or κ-opioid agonists in the rostrodorsal quadrant of the medial shell enhance "liking", while more caudal injections can inhibit disgust reactions, liking reactions, or both. The regions of the nucleus accumbens that can be ascribed a causal role in the production of pleasure are limited both anatomically and chemically, as besides opioid agonists only endocannabinoids can enhance liking. In the nucleus accumbens as a whole, dopamine, GABA receptor agonist or AMPA antagonists solely modify motivation, while the same is true for opioid and endocannabinoids outside of the hotspot in the medial shell. A rostro-caudal gradient exists for the enhancement of appetitive versus fearful responses, the latter of which is traditionally thought to require only D1 receptor function, and the former of which requires both D1 and D2 function. One interpretation of this finding, the disinhibition hypothesis, posits that inhibition of accumbens MSNs (which are GABAergic) disinhibits downstream structures, enabling the expression of appetitive or consummatory behaviors. The motivational effects of AMPA antagonists, and to a lesser extent GABA agonists, is anatomically flexible. Stressful conditions can expand the fear inducing regions, while a familiar environment can reduce the size of the fear inducing region. Furthermore, cortical input from the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) biases the response towards that of appetitive behavior, and infralimbic input, equivalent to the human subgenual cingulate cortex, suppresses the response regardless of valence.
The nucleus accumbens is neither necessary nor sufficient for instrumental learning, although manipulations can affect performance on instrumental learning tasks. One task where the effect of NAcc lesions is evident is Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (PIT), where a cue paired with a specific or general reward can enhance instrumental responding. Lesions to the core of the NAcc impair performance after devaluation and inhibit the effect of general PIT. On the other hand, lesions to the shell only impair the effect of specific PIT. This distinction is thought to reflect consummatory and appetitive conditioned responses in the NAcc shell and the NAcc core, respectively.
In the dorsal striatum, a dichotomy has been observed between D1-MSNs and D2-MSNs, with the former being reinforcing and enhancing locomotion, and the latter being aversive and reducing locomotion. Such a distinction has been traditionally assumed to apply to the nucleus accumbens as well, but evidence from pharmacological and optogenetics studies is conflicting. Furthermore, a subset of NAcc MSNs express both D1 and D2 MSNs, and pharmacological activation of D1 versus D2 receptors need not necessarily activate the neural populations exactly. While most studies show no effect of selective optogenetic stimulation of D1 or D2 MSNs on locomotor activity, one study has reported a decrease in basal locomotion with D2-MSN stimulation. While two studies have reported reduced reinforcing effects of cocaine with D2-MSN activation, one study has reported no effect. NAcc D2-MSN activation has also been reported to enhance motivation, as assessed by PIT, and D2 receptor activity is necessary for the reinforcing effects of VTA stimulation. A 2018 study reported that D2 MSN activation enhanced motivation via inhibiting the ventral pallidum, thereby disinhibiting the VTA.
Maternal behavior
An fMRI study conducted in 2005 found that when mother rats were in the presence of their pups the regions of the brain involved in reinforcement, including the nucleus accumbens, were highly active. Levels of dopamine increase in the nucleus accumbens during maternal behavior, while lesions in this area upset maternal behavior. When women are presented pictures of unrelated infants, fMRIs show increased brain activity in the nucleus accumbens and adjacent caudate nucleus, proportionate to the degree to which the women find these infants "cute".Aversion
Activation of D1-type MSNs in the nucleus accumbens is involved in reward, whereas the activation of D2-type MSNs in the nucleus accumbens promotesaversion
Aversion means opposition or repugnance. The following are different forms of aversion:
* Ambiguity aversion
* Brand aversion
* Dissent aversion in the United States of America
* Endowment effect, also known as divestiture aversion
* Food aversi ...
.
Slow-wave sleep
In late 2017, studies on rodents which utilizedoptogenetic
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by expression of light-sensitive ion channels, pumps or enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individ ...
and chemogenetic methods found that the indirect pathway (i.e., D2-type) medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens core which co-express adenosine A2A receptors and project to the ventral pallidum are involved in the regulation of slow-wave sleep
Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. It usually lasts between 70 and 90 minutes and takes place during the first hours of the night. Initially, SWS consisted of both St ...
. In particular, optogenetic activation of these indirect pathway NAcc core neurons induces slow-wave sleep and chemogenetic activation of the same neurons increases the number and duration of slow-wave sleep episodes. Chemogenetic inhibition of these NAcc core neurons suppresses sleep. In contrast, the D2-type medium spiny neurons in the NAcc shell which express adenosine A2A receptors have no role in regulating slow-wave sleep.
Clinical significance
Addiction
Current models of addiction from chronic drug use involve alterations ingene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
in the mesocorticolimbic projection
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. ...
. The most important transcription factors that produce these alterations are ΔFosB, cyclic adenosine monophosphate ( cAMP) response element binding protein ( CREB), and nuclear factor kappa B ( NFκB). ΔFosB is the most significant gene transcription factor in addiction since its viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
or genetic overexpression in the nucleus accumbens is necessary and sufficient for many of the neural adaptations and behavioral effects (e.g., expression-dependent increases in self-administration
Self-administration is, in its medical sense, the process of a subject administering a pharmacological substance to themself. A clinical example of this is the subcutaneous "self-injection" of insulin by a diabetic patient.
In animal experimentati ...
and reward sensitization) seen in drug addiction. ΔFosB overexpression has been implicated in addictions to alcohol (ethanol), cannabinoids, cocaine, methylphenidate, nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used fo ...
, opioids, phencyclidine, propofol
Propofol, marketed as Diprivan, among other names, is a short-acting medication that results in a decreased level of consciousness and a lack of memory for events. Its uses include the starting and maintenance of general anesthesia, sedation f ...
, and substituted amphetamines, among others. Increases in nucleus accumbens ΔJunD expression can reduce or, with a large increase, even block most of the neural alterations seen in chronic drug abuse (i.e., the alterations mediated by ΔFosB).
ΔFosB also plays an important role in regulating behavioral responses to natural rewards, such as palatable food, sex, and exercise. Natural rewards, like drugs of abuse, induce ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens, and chronic acquisition of these rewards can result in a similar pathological addictive state through ΔFosB overexpression. Consequently, ΔFosB is the key transcription factor involved in addictions to natural rewards as well; in particular, ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens is critical for the reinforcing effects of sexual reward. Research on the interaction between natural and drug rewards suggests that psychostimulants and sexual behavior act on similar biomolecular mechanisms to induce ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens and possess cross-sensitization effects that are mediated through ΔFosB.
Similar to drug rewards, non-drug rewards also increase the level of extracellular dopamine in the NAcc shell. Drug-induced dopamine release in the NAcc shell and NAcc core is usually not prone to habituation (i.e., the development of drug tolerance
Drug tolerance or drug insensitivity is a pharmacological concept describing subjects' reduced reaction to a drug following its repeated use. Increasing its dosage may re-amplify the drug's effects; however, this may accelerate tolerance, further ...
: a decrease in dopamine release from future drug exposure as a result of repeated drug exposure); on the contrary, repeated exposure to drugs that induce dopamine release in the NAcc shell and core typically results in sensitization (i.e., the amount of dopamine that is released in the NAcc from future drug exposure increases as a result of repeated drug exposure). Sensitization of dopamine release in the NAcc shell following repeated drug exposure serves to strengthen stimulus-drug associations (i.e., classical conditioning that occurs when drug use is repeatedly paired with environmental stimuli) and these associations become less prone to extinction (i.e., "unlearning" these classically conditioned associations between drug use and environmental stimuli becomes more difficult). After repeated pairing, these classically conditioned environmental stimuli (e.g., contexts and objects that are frequently paired with drug use) often become drug cue Cue reactivity is a type of learned response which is observed in individuals with an addiction and involves significant physiological and subjective reactions to presentations of drug-related stimuli (i.e., ''drug cues'').
In investigations of th ...
s which function as secondary reinforcer
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher freq ...
s of drug use (i.e., once these associations are established, exposure to a paired environmental stimulus triggers a craving or desire to use the drug which they've become associated with).
In contrast to drugs, the release of dopamine in the NAcc shell by many types of rewarding non-drug stimuli typically undergoes habituation following repeated exposure (i.e., the amount of dopamine that is released from future exposure to a rewarding non-drug stimulus normally decreases as a result of repeated exposure to that stimulus).
Depression
In April 2007, two research teams reported on having inserted electrodes into the nucleus accumbens in order to use deep brain stimulation to treat severe depression. In 2010, experiments reported that deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens was successful in decreasing depression symptoms in 50% of patients who did not respond to other treatments such as electroconvulsive therapy. Nucleus accumbens has also been used as a target to treat small groups of patients with therapy-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder.Ablation
To treat addiction and in an attempt to treat mental illness radiofrequency ablation of the nucleus accumbens has been performed. The results are inconclusive and controversial.Placebo effect
Activation of the NAcc has been shown to occur in the anticipation of effectiveness of a drug when a user is given a placebo, indicating a contributing role of the nucleus accumbens in the placebo effect. *Additional images
See also
* Septal nucleiReferences
External links
The role of the nucleus accumbens in the reward circuit.
Part of "The Brain From Top to Bottom." at thebrain.mcgill.ca
Nucleus Accumbens – Cell Centered Database
* {{Authority control Limbic system Addiction Basal ganglia