Abdulaziz Raheem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
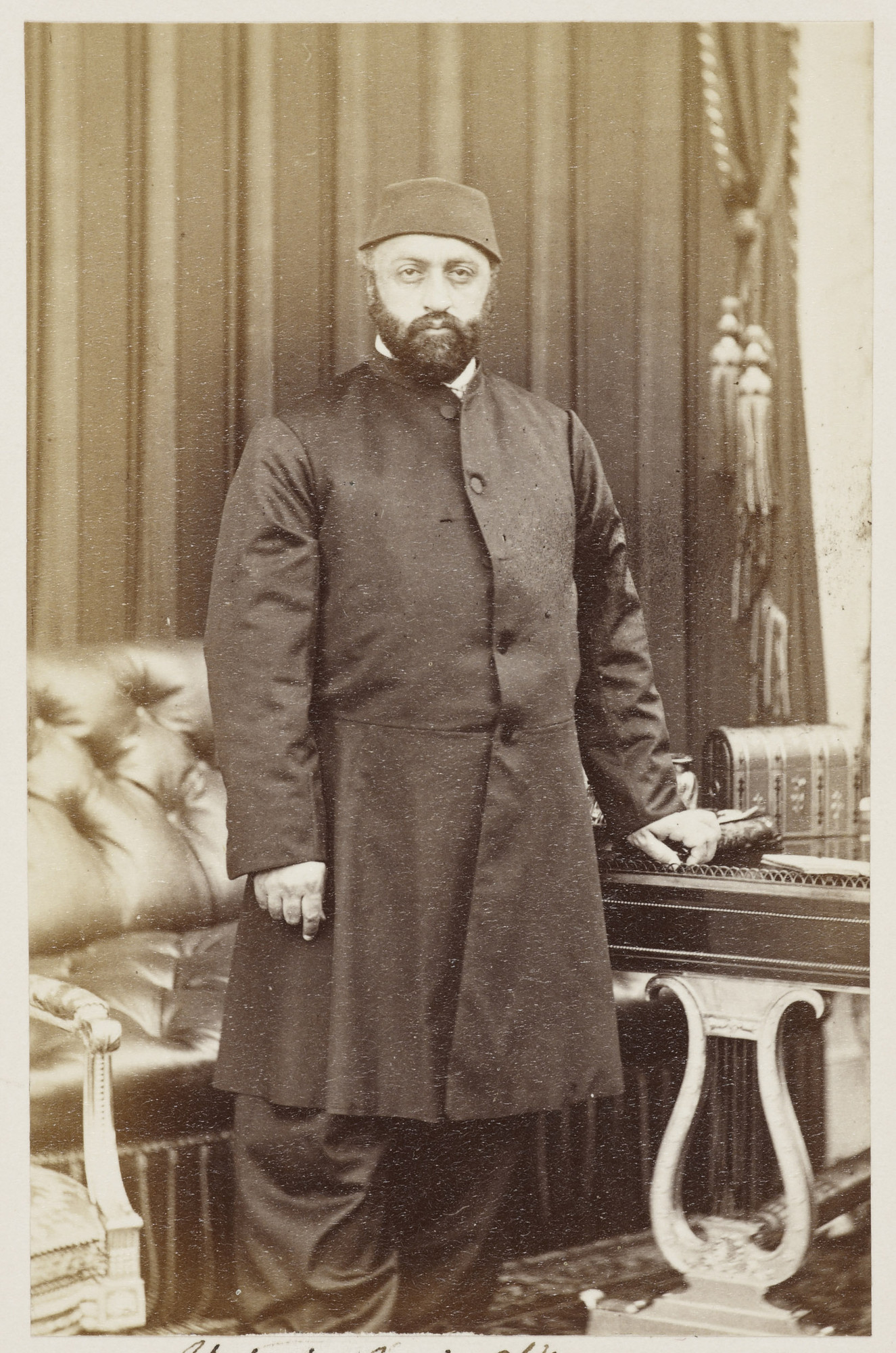
Abdulaziz ( ota, ØđØĻØŊ اŲØđØēŲØē, ĘŋAbdÞ'l-ĘŋAzÃŪz; tr, AbdÞlaziz; 8 February 18304 June 1876) was the 32nd
 His parents were Mahmud II and Pertevniyal Sultan , originally named Besime, a Circassian. In 1868 Pertevniyal was residing at Dolmabahçe Palace. That year Abdulaziz took the visiting
His parents were Mahmud II and Pertevniyal Sultan , originally named Besime, a Circassian. In 1868 Pertevniyal was residing at Dolmabahçe Palace. That year Abdulaziz took the visiting
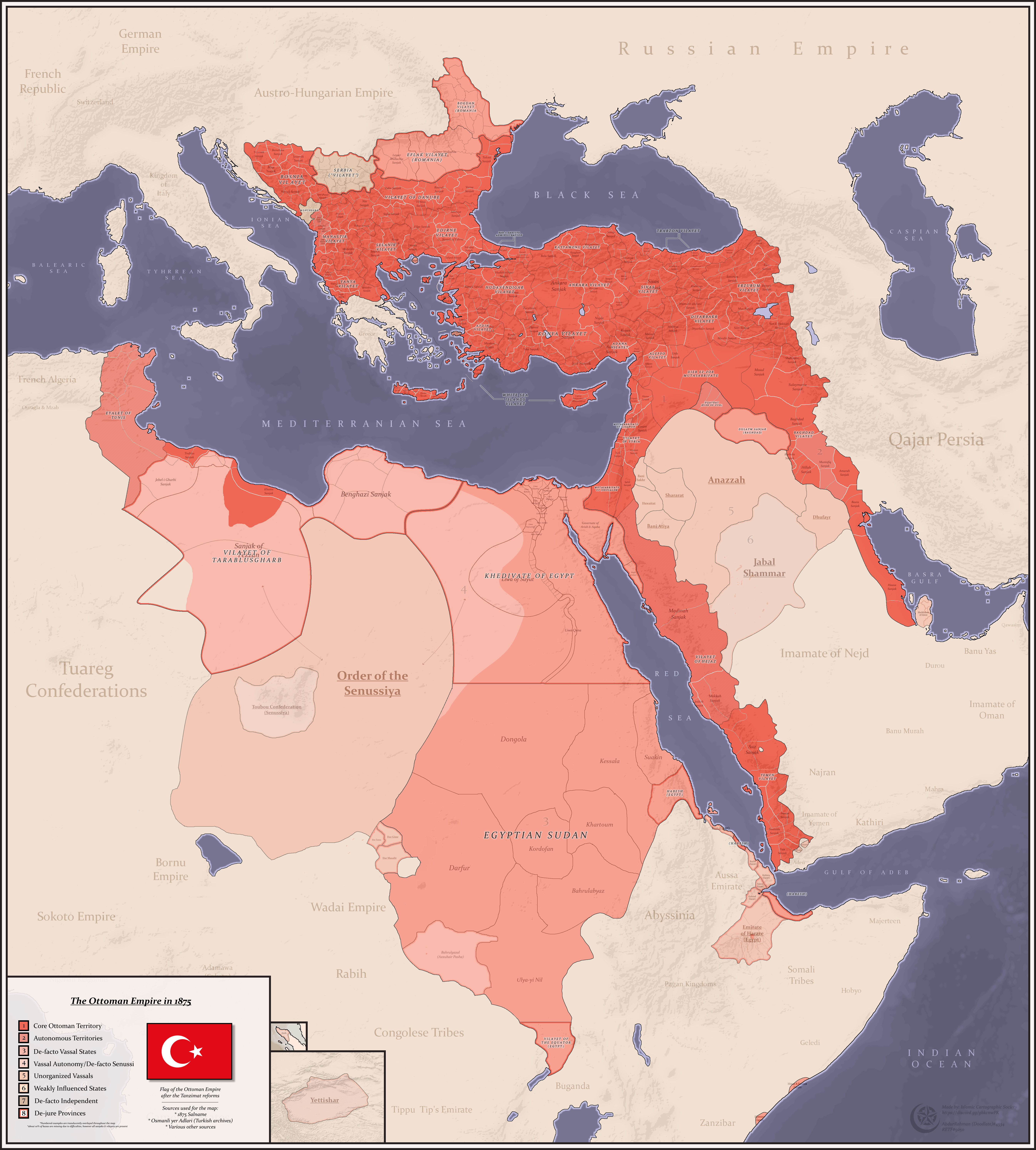
 Between 1861 and 1871, the
Between 1861 and 1871, the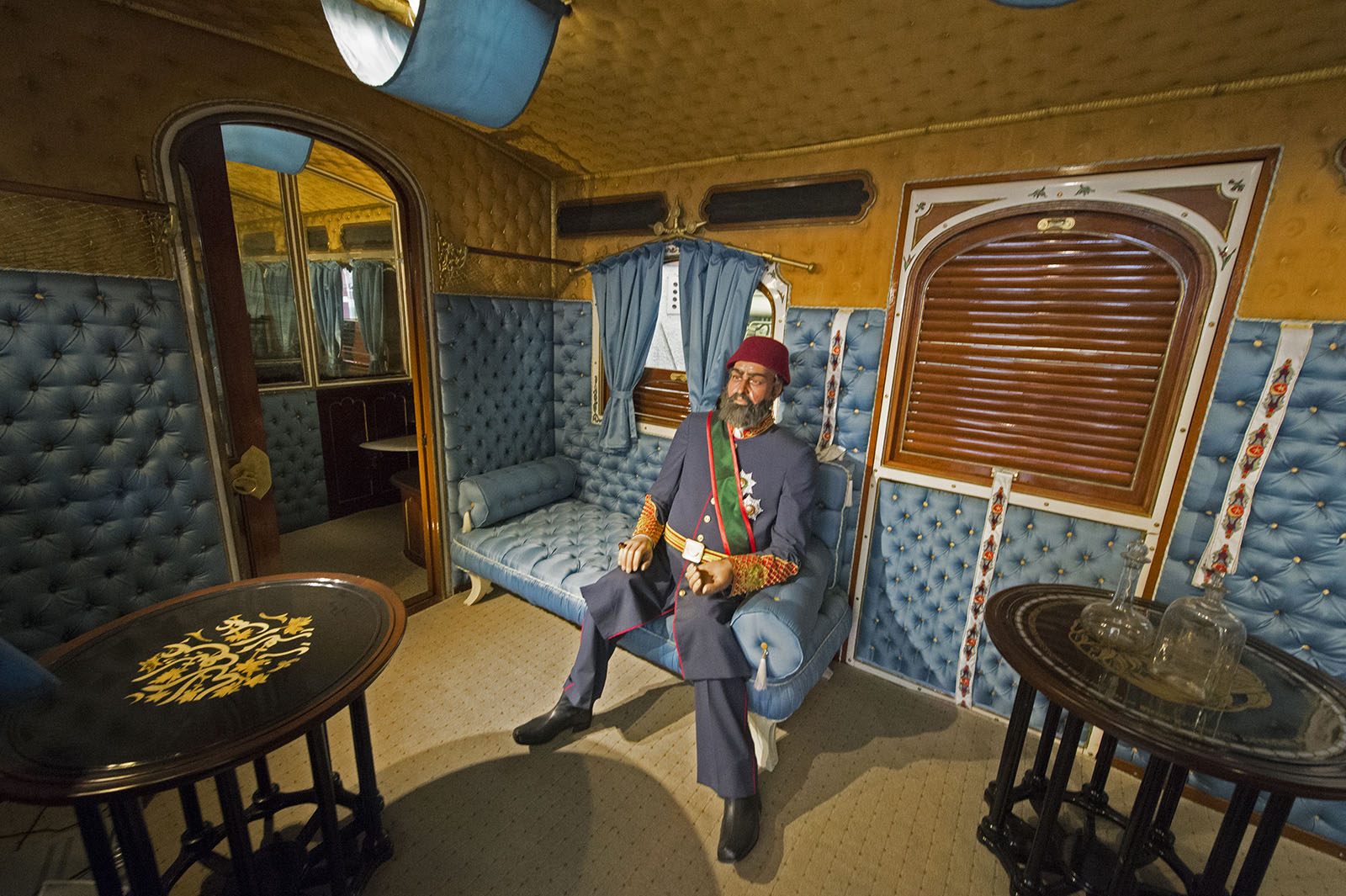  Also in 1867, Abdulaziz became the first Ottoman
Also in 1867, Abdulaziz became the first Ottoman

 Abdulaziz's death at ÃÄąraÄan Palace in Istanbul a few days later was documented as a suicide.
Following Sultan Abdulaziz's dethronement, he was taken into a room at Topkapi Palace. This room happened to be the same room that Sultan Selim III was murdered in. The room caused him to be concerned for his life and he subsequently requested to be moved to
Abdulaziz's death at ÃÄąraÄan Palace in Istanbul a few days later was documented as a suicide.
Following Sultan Abdulaziz's dethronement, he was taken into a room at Topkapi Palace. This room happened to be the same room that Sultan Selim III was murdered in. The room caused him to be concerned for his life and he subsequently requested to be moved to 
 Several physicians were allowed to examine his body. Among which "Dr. Marco, Nouri, A. Sotto, Physician attached to the Imperial and Royal Embassy of AustriaâHungary; Dr. Spagnolo, Marc Markel, Jatropoulo, Abdinour, Servet, J. de Castro, A. Marroin, Julius Millingen, C. Caratheodori; E. D. Dickson, Physician of the British Embassy; Dr. O. Vitalis, Physician of the Sanitary Board; Dr. E. Spadare, J. Nouridjian, Miltiadi Bey, Mustafa, Mehmed" certified that the death had been "caused by the loss of blood produced by the wounds of the bloodâvessels at the joints of the arms" and that "the direction and nature of the wounds, together with the instrument which is said to have produced them, lead us to conclude that suicide had been committed". One of those physicians also stated that "His skin was very pale, and entirely free from bruises, marks or spots of any kind whatever. There was no lividity of the lips indicating suffocation nor any sign of pressure having been applied to the throat".
Several physicians were allowed to examine his body. Among which "Dr. Marco, Nouri, A. Sotto, Physician attached to the Imperial and Royal Embassy of AustriaâHungary; Dr. Spagnolo, Marc Markel, Jatropoulo, Abdinour, Servet, J. de Castro, A. Marroin, Julius Millingen, C. Caratheodori; E. D. Dickson, Physician of the British Embassy; Dr. O. Vitalis, Physician of the Sanitary Board; Dr. E. Spadare, J. Nouridjian, Miltiadi Bey, Mustafa, Mehmed" certified that the death had been "caused by the loss of blood produced by the wounds of the bloodâvessels at the joints of the arms" and that "the direction and nature of the wounds, together with the instrument which is said to have produced them, lead us to conclude that suicide had been committed". One of those physicians also stated that "His skin was very pale, and entirely free from bruises, marks or spots of any kind whatever. There was no lividity of the lips indicating suffocation nor any sign of pressure having been applied to the throat".
 * Abdulaziz gave special emphasis on modernizing the Ottoman Navy. In 1875, the Ottoman Navy had 21 battleships and 173 warships of other types, ranking as the third largest navy in the world after the British and French navies. His passion for the Navy, ships and sea can be observed in the wall paintings and pictures of the
* Abdulaziz gave special emphasis on modernizing the Ottoman Navy. In 1875, the Ottoman Navy had 21 battleships and 173 warships of other types, ranking as the third largest navy in the world after the British and French navies. His passion for the Navy, ships and sea can be observed in the wall paintings and pictures of the
- Trains and Railways of Turkey The railway was extended to Gebze, which opened on 1 January 1873. In August 1873 the railway reached Izmit. Another railway extension was built in 1871 to serve a populated area along
Sultan
Sultan (; ar, ØģŲطاŲ ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
of the Ottoman Empire and reigned from 25 June 1861 to 30 May 1876, when he was overthrown in a government coup. He was a son of Sultan Mahmud II and succeeded his brother Abdulmejid I in 1861.
Born at EyÞp Palace, Constantinople (present-day Istanbul), on 8 February 1830, Abdulaziz received an Ottoman education but was nevertheless an ardent admirer of the material progress that was being achieved in the West. He was the first Ottoman Sultan who travelled to Western Europe, visiting a number of important European capitals including Paris, London, and Vienna in the summer of 1867.
Apart from his passion for the Ottoman Navy, which had the world's third largest fleet in 1875 (after the British and French navies), the Sultan took an interest in documenting the Ottoman Empire. He was also interested in literature and was a talented classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" also ...
composer. Some of his compositions, together with those of the other members of the Ottoman dynasty, have been collected in the album ''European Music at the Ottoman Court'' by the London Academy of Ottoman Court Music. He was deposed on the grounds of having mismanaged the Ottoman economy on 30 May 1876, and was found dead six days later in mysterious circumstances.
Early life
EugÃĐnie de Montijo
''DoÃąa'' MarÃa Eugenia Ignacia Agustina de Palafox y Kirkpatrick, 19th Countess of Teba, 16th Marchioness of Ardales (5 May 1826 â 11 July 1920), known as EugÃĐnie de Montijo (), was Empress of the French from her marriage to Emperor Napo ...
, Empress of France, to see his mother. Pertevniyal considered the presence of a foreign woman within her private quarters of the seraglio to be an insult. She reportedly slapped EugÃĐnie across the face, which almost caused an international incident. According to another account, Pertevniyal was outraged by the forwardness of EugÃĐnie in taking the arm of one of her sons while he gave a tour of the palace garden, and she gave the Empress a slap on the stomach as a possibly more subtly intended reminder that they were not in France.
The Pertevniyal Valide Sultan Mosque was built under the patronage of his mother. The construction work began in November 1869 and the mosque was finished in 1871.
His paternal grandparents were Sultan Abdul Hamid I and Sultana NakÅidil Sultan. Several accounts identify his paternal grandmother with AimÃĐe du Buc de RivÃĐry, a cousin of Empress JosÃĐphine. Pertevniyal was a sister of Khushiyar Qadin, third wife of Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt. Khushiyar and Ibrahim were the parents of Isma'il Pasha.
Reign

 Between 1861 and 1871, the
Between 1861 and 1871, the Tanzimat
The Tanzimat (; ota, ØŠŲØļŲŲ
ا؊, translit=TanzimÄt, lit=Reorganization, ''see'' nizÄm) was a period of reform in the Ottoman Empire that began with the GÞlhane Hatt-Äą Åerif in 1839 and ended with the First Constitutional Era in 1876. ...
reforms which began during the reign of his brother Abdulmejid I were continued under the leadership of his chief ministers, Mehmed Fuad Pasha and Mehmed Emin Ãli Pasha
Mehmed Emin Ãli Pasha, also spelled as Mehmed Emin Aali (March 5, 1815 â September 7, 1871) was a prominent Ottoman statesman during the Tanzimat period, best known as the architect of the Ottoman Reform Edict of 1856, and for his role in ...
. New administrative districts (''vilayets'') were set up in 1864 and a Council of State was established in 1868. Public education was organized on the French model and Istanbul University
, image = Istanbul_University_logo.svg
, image_size = 200px
, latin_name = Universitas Istanbulensis
, motto = tr, Tarihten GeleceÄe Bilim KÃķprÞsÞ
, mottoeng = Science Bridge from Past to the Future
, established = 1453 1846 1933
...
was reorganised as a modern institution in 1861. He was also integral in establishing the first Ottoman civil code.
Abdulaziz cultivated good relations with France and the United Kingdom. In 1867 he was the first Ottoman sultan to visit Western Europe; his trip included a visit to the Exposition Universelle (1867) in Paris and a trip to the United Kingdom, where he was made a Knight of the Garter by Queen Victoria and shown a Royal Navy Fleet Review with Ismail Pasha. He travelled by a private rail car, which today can be found in the Rahmi M. Koç Museum in Istanbul. His fellow Knights of the Garter created in 1867 were Charles Gordon-Lennox, 6th Duke of Richmond, Charles Manners, 6th Duke of Rutland, Henry Somerset, 8th Duke of Beaufort
Henry Charles FitzRoy Somerset, 8th Duke of Beaufort KG, PC, DL (1 February 1824 â 30 April 1899), styled Earl of Glamorgan until 1835 and Marquess of Worcester from 1835 to 1853, was a British peer, soldier, and Conservative Party politi ...
, Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn
Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn (Arthur William Patrick Albert; 1 May 185016 January 1942), was the seventh child and third son of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He served as Gov ...
(a son of Queen Victoria), Franz Joseph I of Austria and Alexander II of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, ÐÐŧÐĩКŅаĖÐ―ÐīŅ II ÐÐļКÐūÐŧаĖÐĩÐēÐļŅ, AleksÃĄndr II NikolÃĄyevich, p=ÉlĘēÉŠËksandr ftÉËroj nĘēÉŠkÉËlajÉŠvĘēÉŠtÉ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Gra ...
.
 Also in 1867, Abdulaziz became the first Ottoman
Also in 1867, Abdulaziz became the first Ottoman Sultan
Sultan (; ar, ØģŲطاŲ ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
to formally recognize the title of Khedive
Khedive (, ota, ØŪØŊÛŲ, hÄądiv; ar, ØŪØŊŲŲŲ, khudaywÄŦ) was an honorific title of Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan"Kh ...
(Viceroy) to be used by the Vali (Governor) of the Ottoman Eyalet of Egypt and Sudan (1517â1867), which thus became the autonomous Ottoman Khedivate of Egypt and Sudan (1867â1914). Muhammad Ali Pasha and his descendants had been the governors (Vali) of Ottoman Egypt and Sudan since 1805, but were willing to use the higher title of Khedive, which was unrecognized by the Ottoman government until 1867. In return, the first Khedive, Ismail Pasha, had agreed a year earlier (in 1866) to increase the annual tax revenues which Egypt and Sudan would provide for the Ottoman treasury. Between 1854 and 1894, the revenues from Egypt and Sudan were often declared as a surety
In finance, a surety , surety bond or guaranty involves a promise by one party to assume responsibility for the debt obligation of a borrower if that borrower defaults. Usually, a surety bond or surety is a promise by a surety or guarantor to pay ...
by the Ottoman government for borrowing loans from British and French banks. After the Ottoman government declared a sovereign default on its foreign debt repayments on 30 October 1875, which triggered the Great Eastern Crisis
The Great Eastern Crisis of 1875â78 began in the Ottoman Empire's territories on the Balkan peninsula in 1875, with the outbreak of several uprisings and wars that resulted in the intervention of international powers, and was ended with the T ...
in the empire's Balkan provinces that led to the devastating Russo-Turkish War (1877â78) and the establishment of the Ottoman Public Debt Administration in 1881, the importance for Britain of the sureties regarding the Ottoman revenues from Egypt and Sudan increased. Combined with the much more important Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, ŲŲŲŲاØĐŲ ŲąŲØģŲŲŲŲŲŲØģŲ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
which was opened in 1869, these sureties were influential in the British government's decision to occupy Egypt and Sudan in 1882, with the pretext of helping the Ottoman-Egyptian government to put down the ĘŧUrabi revolt (1879â1882). Egypt and Sudan (together with Cyprus) nominally remained Ottoman territories until 5 November 1914, when the British Empire declared war against the Ottoman Empire during World War I.
In 1869, Abdulaziz received visits from EugÃĐnie de Montijo
''DoÃąa'' MarÃa Eugenia Ignacia Agustina de Palafox y Kirkpatrick, 19th Countess of Teba, 16th Marchioness of Ardales (5 May 1826 â 11 July 1920), known as EugÃĐnie de Montijo (), was Empress of the French from her marriage to Emperor Napo ...
, Empress consort of Napoleon III of France and other foreign monarchs on their way to the opening of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, ŲŲŲŲاØĐŲ ŲąŲØģŲŲŲŲŲŲØģŲ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
. The Prince of Wales, the future Edward VII, twice visited Istanbul.
By 1871, both Mehmed Fuad Pasha and Mehmed Emin Ãli Pasha
Mehmed Emin Ãli Pasha, also spelled as Mehmed Emin Aali (March 5, 1815 â September 7, 1871) was a prominent Ottoman statesman during the Tanzimat period, best known as the architect of the Ottoman Reform Edict of 1856, and for his role in ...
were dead. The Second French Empire, his Western European model, had been defeated in the Franco-Prussian War by the North German Confederation under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia. Abdulaziz turned to the Russian Empire for friendship, as unrest in the Balkan provinces continued. In 1875, the Herzegovinian rebellion was the beginning of further unrest in the Balkan provinces. In 1876, the April Uprising saw insurrection spreading among the Bulgarians. Ill feeling mounted against Russia for its encouragement of the rebellions.
While no one event led to his being deposed, the crop failure of 1873 and his lavish expenditures on the Ottoman Navy and on new palaces which he had built, along with mounting public debt, helped to create an atmosphere conducive to his being overthrown. Abdulaziz was deposed by his ministers on 30 May 1876.
Death
 Abdulaziz's death at ÃÄąraÄan Palace in Istanbul a few days later was documented as a suicide.
Following Sultan Abdulaziz's dethronement, he was taken into a room at Topkapi Palace. This room happened to be the same room that Sultan Selim III was murdered in. The room caused him to be concerned for his life and he subsequently requested to be moved to
Abdulaziz's death at ÃÄąraÄan Palace in Istanbul a few days later was documented as a suicide.
Following Sultan Abdulaziz's dethronement, he was taken into a room at Topkapi Palace. This room happened to be the same room that Sultan Selim III was murdered in. The room caused him to be concerned for his life and he subsequently requested to be moved to Beylerbeyi Palace
The Beylerbeyi Palace ( tr, Beylerbeyi SarayÄą, literally meaning ''the palace of the bey of beys'') is located in the Beylerbeyi neighbourhood of ÃskÞdar district in Istanbul, Turkey, at the Asian side of the Bosphorus. An Imperial Ottoma ...
. His request was denied for the palace was considered inconvenient for his situation and he was moved to Feriye Palace instead. He nevertheless had grown increasingly nervous and paranoid about his security. In the morning of 5 June, Abdulaziz asked for a pair of scissors to trim his beard. Shortly after this, he was found dead in a pool of blood flowing from two wounds in his arms.

Conspiracy Theories
There are several sources claiming the death of Abdulaziz was due to an assassination. Islamic nationalist author Necip FazÄąl KÄąsakÞrek claimed that it was a clandestine operation carried out by the British. Another similar claim is based on the book ''The Memoirs of Sultan Abdulhamid II''. In the book, which turned out to be a fraud, Abdulhamid II claims that Sultan Murad V had begun to show signs of paranoia, madness, and continuous fainting and vomiting until the day of his coronation, and he even threw himself into a pool yelling at his guards to protect his life. High-ranking politicians of the time were afraid the public would become outraged and revolt to bring Abdulaziz back to power. Thus, they arranged the assassination of Abdulaziz by cutting his wrists and announced that "he committed suicide". This book of memoir was commonly referred to as a first-hand testimony of the assassination of Abdulaziz. Yet it was proven, later on, that Abdulhamid II never wrote nor dictated such a document.Achievements
 * Abdulaziz gave special emphasis on modernizing the Ottoman Navy. In 1875, the Ottoman Navy had 21 battleships and 173 warships of other types, ranking as the third largest navy in the world after the British and French navies. His passion for the Navy, ships and sea can be observed in the wall paintings and pictures of the
* Abdulaziz gave special emphasis on modernizing the Ottoman Navy. In 1875, the Ottoman Navy had 21 battleships and 173 warships of other types, ranking as the third largest navy in the world after the British and French navies. His passion for the Navy, ships and sea can be observed in the wall paintings and pictures of the Beylerbeyi Palace
The Beylerbeyi Palace ( tr, Beylerbeyi SarayÄą, literally meaning ''the palace of the bey of beys'') is located in the Beylerbeyi neighbourhood of ÃskÞdar district in Istanbul, Turkey, at the Asian side of the Bosphorus. An Imperial Ottoma ...
on the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, ÎÏÏÏÎŋÏÎŋÏ ; tr, Ä°stanbul BoÄazÄą 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''BoÄaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
in Istanbul, which was constructed during his reign. However, the large budget for modernizing and expanding the Navy (combined with a severe drought in 1873 and incidents of flooding in 1874 which damaged Ottoman agriculture and reduced the government's tax revenues) contributed to the financial difficulties which caused the Porte
Porte may refer to:
* Sublime Porte, the central government of the Ottoman empire
* Porte, Piedmont, a municipality in the Piedmont region of Italy
* John Cyril Porte, British/Irish aviator
* Richie Porte, Australian professional cyclist who compe ...
to declare a sovereign default with the "Ramazan Kanunnamesi" on 30 October 1875. The subsequent decision to increase agricultural taxes for paying the Ottoman public debt
The Ottoman public debt was a term which dated back to 24 August 1855,< ...
to foreign creditors (mainly British and French banks) triggered the Great Eastern Crisis
The Great Eastern Crisis of 1875â78 began in the Ottoman Empire's territories on the Balkan peninsula in 1875, with the outbreak of several uprisings and wars that resulted in the intervention of international powers, and was ended with the T ...
in the empire's Balkan provinces. The crisis culminated in the Russo-Turkish War (1877â78) that devastated the already struggling Ottoman economy, and the establishment of the Ottoman Public Debt Administration in 1881, during the early years of Sultan AbdÞlhamid II's reign.
* The first Ottoman railroads were opened between Ä°zmirâAydÄąn
AydÄąn ( ''EYE-din''; ; formerly named ''GÞzelhisar'', Ancient and Modern Greek: ÎĪÏÎŽÎŧÎŧÎĩÎđÏ /''Tralleis''/) is a city in and the seat of AydÄąn Province in Turkey's Aegean Region. The city is located at the heart of the lower valley of B ...
and Alexandriaâ Cairo in 1856, during the reign of Sultan Abdulmejid I. The first large railway terminal within present-day Turkey, the Alsancak Terminal in Izmir, was opened in 1858. However, these were individual, unconnected railroads, without a railway network. Sultan Abdulaziz established the first Ottoman railway networks. On 17 April 1869, the concession for the Rumelia Railway (i.e. Balkan Railways, ''Rumeli'' (Rumelia) meaning the Balkan peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
in Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, ŲŲØģاŲŲ ØđŲØŦŲ
اŲŲ, LisÃĒn-Äą OsmÃĒnÃŪ, ; tr, OsmanlÄą TÞrkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extens ...
) which connected Istanbul to Vienna was awarded to Baron Maurice de Hirsch (Moritz Freiherr Hirsch auf Gereuth), a Bavaria-born banker from Belgium. The project foresaw a railway route from Istanbul via Edirne, Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, ÐÐŧÐūÐēÐīÐļÐē, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
and Sarajevo to the shore of the Sava River. In 1873, the first Sirkeci Terminal in Istanbul was opened. The temporary Sirkeci terminal building was later replaced with the current one which was built between 1888 and 1890 (during the reign of AbdÞlhamid II) and became the final destination terminus of the Orient Express. In 1871, Sultan Abdulaziz established the Anatolia Railway. Construction works of the on the Asian side of Istanbul, from HaydarpaÅa to Pendik
Pendik is a district of Istanbul, Turkey on the Asian side between Kartal and Tuzla, on the Marmara Sea. Home to Sabiha GÃķkçen International Airport. Population is 711,894. It also neighbours Sultanbeyli, Sancaktepe and ÃekmekÃķy from nort ...
, began in 1871. The line was opened on 22 September 1872.CFOA History- Trains and Railways of Turkey The railway was extended to Gebze, which opened on 1 January 1873. In August 1873 the railway reached Izmit. Another railway extension was built in 1871 to serve a populated area along
Bursa
( grc-gre, Î ÏÎŋáŋĶÏÎą, ProÃŧsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, ØĻŲØąØģŲ, Arabic:ØĻŲØąØĩØĐ) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
and the Sea of Marmara. The Anatolia Railway was then extended to Ankara and eventually to Mesopotamia, Syria
Syria ( ar, ØģŲŲØąŲŲŲا or ØģŲŲØąŲŲŲØĐ, translit=SÅŦriyÄ), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, اŲØŽŲ
ŲŲØąŲØĐ Ø§ŲØđØąØĻŲØĐ Ø§ŲØģŲØąŲØĐ, al-JumhÅŦrÄŦyah al-ĘŧArabÄŦyah as-SÅŦrÄŦyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Arabia during the reign of Sultan AbdÞlhamid II, with the completion of the Baghdad Railway and Hejaz Railway.
* Under his reign, Turkey's first postage stamps were issued in 1863, and the Ottoman Empire joined the Universal Postal Union in 1875 as a founding member.
* He also was responsible for the first civil code
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property, family, and obligations.
A jurisdiction that has a civil code generally also has a code of civil procedure. In some jurisdictions with a civil code, a number of the core ar ...
for the Ottoman Empire.
* He was the first Ottoman sultan who travelled to Western Europe. His voyage in visiting order (from 21 June 1867 to 7 August 1867): Istanbul â Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
â Naples â Toulon â Marseille â Paris â Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-MÃĐr; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
â Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
â London â Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
â Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
â Brussels â Koblenz
Koblenz (; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz''), spelled Coblenz before 1926, is a German city on the banks of the Rhine and the Moselle, a multi-nation tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman mili ...
â Vienna â Budapest â OrČova â Vidin â Ruse â Varna â Istanbul.
* Impressed by the museums in Paris (30 June â 10 July 1867), London (12â23 July 1867) and Vienna (28â30 July 1867) which he visited in the summer of 1867, he ordered the establishment of an Imperial Museum in Istanbul: the Istanbul Archaeology Museum.
Family
AbdÞlaziz's harem was known because, although slavery in the Ottoman Empire had already been abolished, her mother Pertevniyal Sultan continued to send it slave girls from the Caucasus.Consorts
AbdÞlaziz had six consorts: * DÞrrinev Kadin (15 March 1835 - 4 December 1895). BaÅKadin. Called also DÞrrunev KadÄąn. Georgian, born Princess Melek DziapÅ-lpa, before becoming a consort she was a lady-in-waiting to Servetseza Kadin, consort of AbdÞlmecid I. She had two sons and a daughter. * Edadil Kadin (1845 - 12 December 1875). Second KadÄąn. She was Abkhazian, born Princess Aredba. She became AbdÞlaziz's consort at the time of his accession to the throne. She had a son and a daughter. * Hayranidil Kadin (2 Novembre 1846 - 26 November 1895). Second KadÄąn after Edadil's death. She perhaps was of slave origin. She had a son and a daughter. * NeÅerek Kadin (1848 - 11 June 1876). Third Kadin. Called also Nesrin KadÄąn or Nesteren Kadin. Circassian, born in Sochi as Princess ZevÅ-Barakay. She had a son and a daughter. * Gevheri Kadin (8 July 1856 - 6 September 1884). Fourth KadÄąn. She was Abkhazian and her real name was Emine Hanim. She had a son and a daughter. * YÄąldÄąz Hanim. BaÅIkbal. Sister of Safinaz Nurefsun KadÄąn, consort of AbdÞlhamid II. She had two daughters. In addition to these, AbdÞlaziz planned to marry the Egyptian princess Tawhida Hanim, daughter of the Egyptian chedive Isma'il Pasha. His Grand Vizier, Mehmed FÞad PaÅah, was opposed to marriage and wrote a note for the sultan explaining that marriage would be politically counterproductive and would give Egypt an undue advantage. However, the Grand Chamberlain, instead of handing the note to the sultan, read it to him in public, humiliating him. Although the marriage project was abandoned, FÞad was fired for the accident.Sons
AbdÞlaziz had six sons: * Åehzade Yusuf Izzeddin (11 October 1857 - 1 February 1916) - with DÞrrinev KadÄąn. Favorite son of his father, he was born when AbdÞlaziz was still a prince and therefore was kept hidden until his accession to the throne. During his reign, AbdÞlaziz unsuccessfully attempted to change the law of succession to allow him to inherit the throne. He had six consorts, two sons and two daughters. * Åehzade Mahmud Celaleddin (14 November 1862 - 1 September 1888) - with Edadil Kadin. He was vice admiral, pianist and flutist. He was the favorite nephew of Adile Sultan, who dedicated several poetic components to him. He had a consort but no child. * Åehzade Mehmed Selim (28 October 1866 - 21 October 1867) - with DÞrrinev KadÄąn. Born and died in Dolmabahçe Palace, buried in Mahmud IImausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be consid ...
.
* AbdÞlmecid II (29 May 1868 - 23 August 1944) - with Hayranidil Kadin. He never became sultan due to the abolition of the Sultanate in 1922, and was the last caliph of the Ottoman Empire.
* Åehzade Mehmed Åevket (5 June 1872 - 22 October 1899) - with NeÅerek KadÄąn. Parentsless at the age of four, he was welcomed in YÄąldÄąz Palace
YÄąldÄąz Palace ( tr, YÄąldÄąz SarayÄą, ) is a vast complex of former imperial Ottoman pavilions and villas in Istanbul, Turkey, built in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It was used as a residence by the sultan and his court in the late 19th ...
by AbdÞlhamid II, who raised him with his children. He had a consort and a son.
* Åehzade Mehmed Seyfeddin (22 September 1874 - 19 October 1927) - with Gevheri Kadin. Fatherless at the Age of two, he was welcomed by Åehzade Yusuf Izzeddin. Vice admiral and musician. He had four consorts, three sons and a daughter.
Daughters
AbdÞlaziz had seven daughters: * Fatma Saliha Sultan (10 August 1862 - 1941) - with DÞrrinev KadÄąn. She married once and had a daughter. * Nazime Sultan (February 25, 1866 - 9 November 1947) - with Hayranidil Kadin. She married once but had no children. * Emine Sultan (30 November 1866 - 23 January 1867) - with Edadil Kadin. Born and died in Dolmabahçe Palace. Buried in the Mahmud IImausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be consid ...
.
* Esma Sultan (21 March 1873 - 7 May 1899) - with Gevheri Kadin. Fatherless at the age of three, she was welcomed with her mother by her half-brother Åehzade Yusuf Izzedin. She married once and had four sons and a daughter. She died in childbirth.
* Fatma Sultan (1874 - 1875) - with YÄąldÄąz Hanim. She was born and died in Dolmabahçe Palace, buried in Mahmud II mausoleum.
* Emine Sultan (24 August 1874 - 29 January 1920) - with NeÅerek KadÄąn. Parentsless at the age of two, she was welcomed with her mother by her half-brother Åehzade Yusuf Izzedin. She married once and had a daughter.
* MÞnire Sultan (1876/1877 - 1877) - with YÄąldÄąz Hanim. She born posthumously and died as a newborn.
Honours
* Mexican Empire: Grand Cross of the Mexican Eagle, with Collar, ''1865'' * : Stranger Knight of the Garter, ''14 August 1867'' * : Grand Cross of the Tower and Sword * : Knight of the Golden Fleece, ''24 June 1870'' * : Grand Cross of the Order of Duke Peter Friedrich Ludwig, with Golden Crown, ''14 December 1874''Annotations
References
Sources
* * *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Abdulaziz 1830 births 1876 deaths 1870s suicides Dethroned monarchs 19th-century Ottoman sultans Turks from the Ottoman Empire Composers of Ottoman classical music Composers of Turkish makam music Grand Crosses of the Order of Saint Stephen of Hungary Knights of the Golden Fleece of Spain Extra Knights Companion of the Garter