5th Century BCE on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 5th century BC started the first day of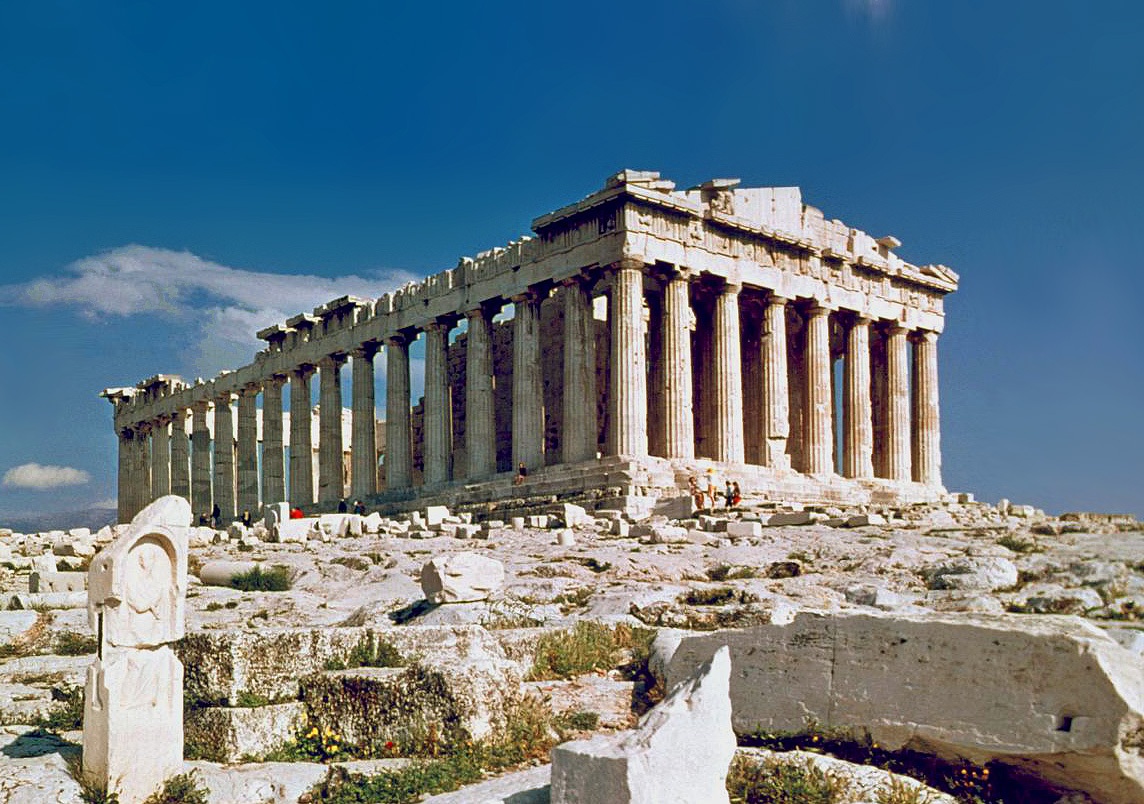  This century saw the establishment of Pataliputra as a capital of the Magadha Empire. This city would later become the ruling capital of different Indian kingdoms for about a thousand years. This period saw the rise of two great philosophical schools of the east, Jainism and Buddhism.
This period saw
This century saw the establishment of Pataliputra as a capital of the Magadha Empire. This city would later become the ruling capital of different Indian kingdoms for about a thousand years. This period saw the rise of two great philosophical schools of the east, Jainism and Buddhism.
This period saw

500 BC
__NOTOC__
The year 500 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Camerinus and Longus (or, less frequently, year 254 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 500 BC for thi ...
and ended the last day of 401 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 401 BC was a year of the Roman calendar, pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Potitus, Cossus, Camillus, Ambustus, Mamercinus and Iullus (or, less frequently, year 353 ''Ab urbe cond ...
.
 This century saw the establishment of Pataliputra as a capital of the Magadha Empire. This city would later become the ruling capital of different Indian kingdoms for about a thousand years. This period saw the rise of two great philosophical schools of the east, Jainism and Buddhism.
This period saw
This century saw the establishment of Pataliputra as a capital of the Magadha Empire. This city would later become the ruling capital of different Indian kingdoms for about a thousand years. This period saw the rise of two great philosophical schools of the east, Jainism and Buddhism.
This period saw Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6t ...
and Buddha spreading their respective teachings in the northern plains of India. This essentially changed the socio-cultural and political dynamics of the region of South Asia. Buddhism would later go on to become one of the major world religions.
This period also saw the work of Yaska, who created Nirukta, that would lay the foundation stone for Sanskrit grammar and is one of the oldest works on grammar known to mankind.
This century is also traditionally recognized as the classical period of the Greeks, which would continue all the way through the 4th century
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 (Roman numerals, CCCI) through 400 (Roman numerals, CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Grea ...
until the time of Alexander the Great. The life of Socrates represented a major milestone in Greek philosophy though his teachings only survive through the work of his students, most notably Plato and Xenophon. The tragedians Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides, as well as the comedian Aristophanes all date from this era and many of their works are still considered classics of the western theatrical canon.
The Persian Wars, fought between a coalition of Greek cities and the vast Achaemenid Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
was a pivotal moment in Greek politics. After having successfully prevented the annexation of Greece by the Persians, Sparta, the dominant power in the coalition, had no intention of further offensive action and considered the war over. Meanwhile, Athens counter-attacked, liberating Greek subjects of the Persian Empire up and down the Ionian coast and mobilizing a new coalition, the Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pl ...
. Tensions between Athens, and its growing imperialistic ambitions as leader of the Delian League, and the traditionally dominant Sparta led to a protracted stalemate in the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
.
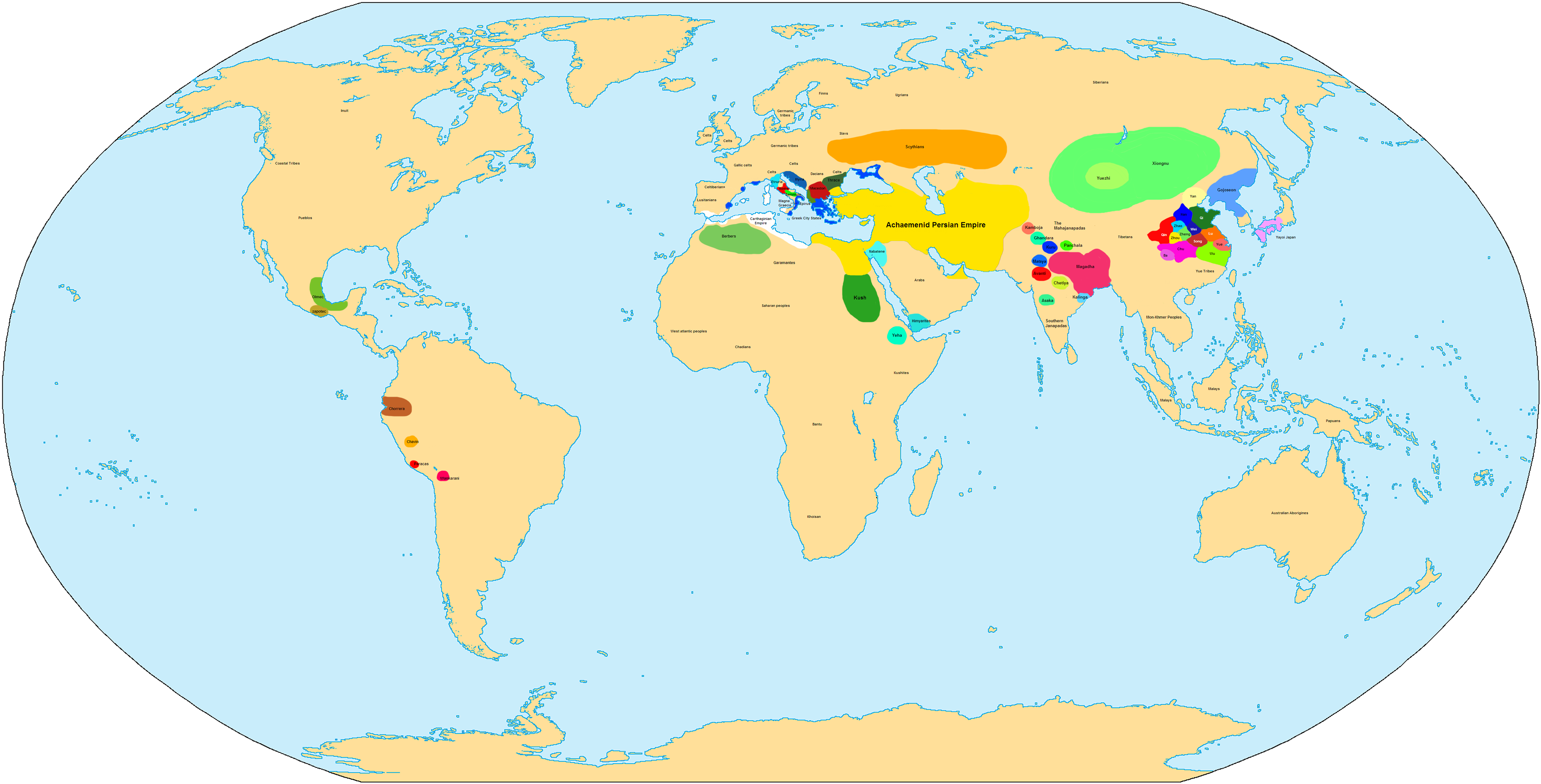
The world in the 5th century BC


Events
* Demotic becomes the dominant script of ancient Egypt.
490s BC
This article concerns the period 499 BC – 490 BC.
References
External links
*
{{Short pages monitor