4-2-4 (locomotive) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Under the
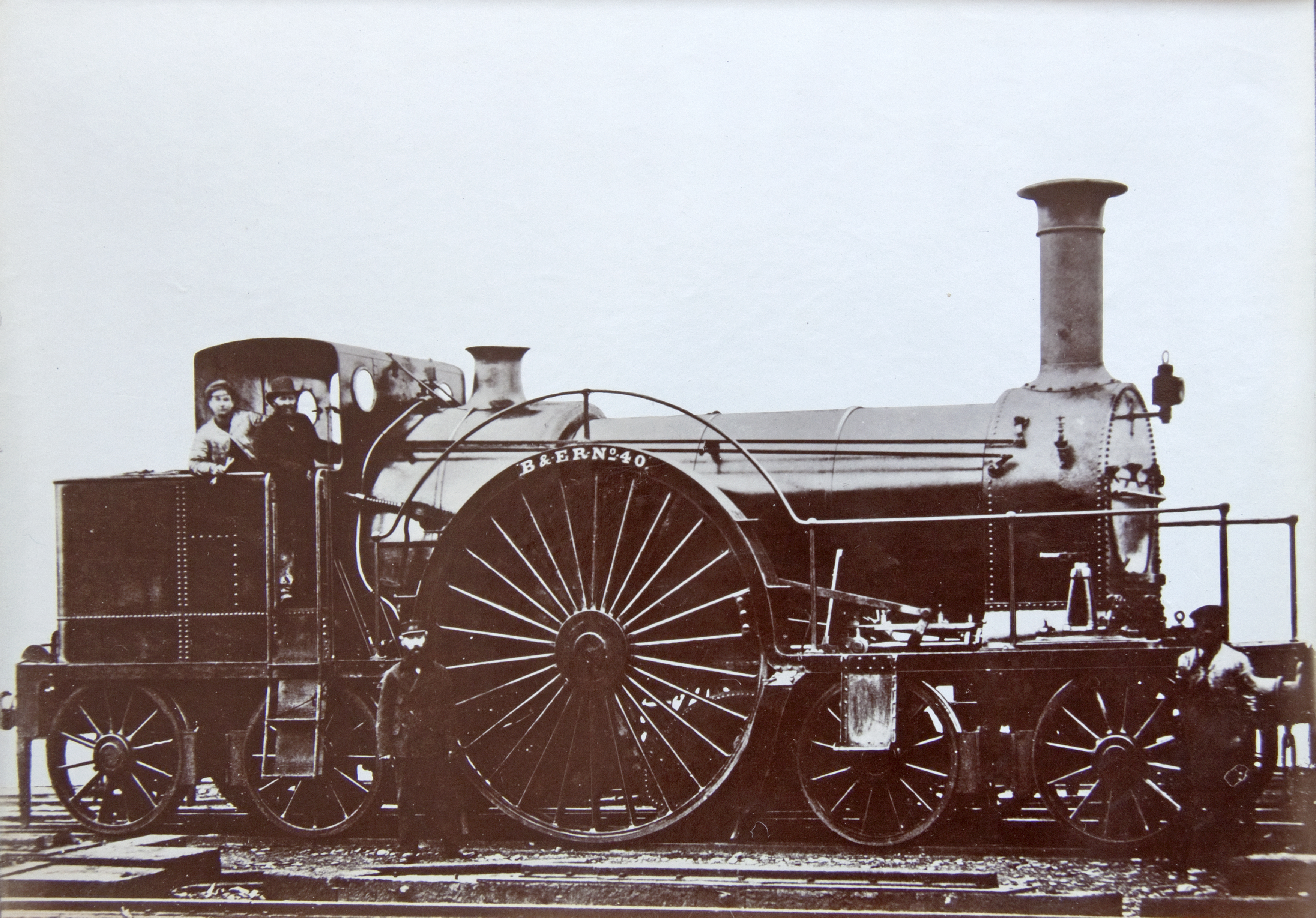 Between 1869 and 1873, new locomotives were built to replace four of the original diameter driving wheeled engines, re-using the engine numbers of the locomotives being replaced. These four replacement engines had slightly smaller diameter driving wheels.
In 1881, this wheel arrangement was also used by the
Between 1869 and 1873, new locomotives were built to replace four of the original diameter driving wheeled engines, re-using the engine numbers of the locomotives being replaced. These four replacement engines had slightly smaller diameter driving wheels.
In 1881, this wheel arrangement was also used by the
 The engine '' C. P. Huntington'' was one of three identical 4-2-4 tank locomotives. They were the first locomotives to be purchased by
The engine '' C. P. Huntington'' was one of three identical 4-2-4 tank locomotives. They were the first locomotives to be purchased by
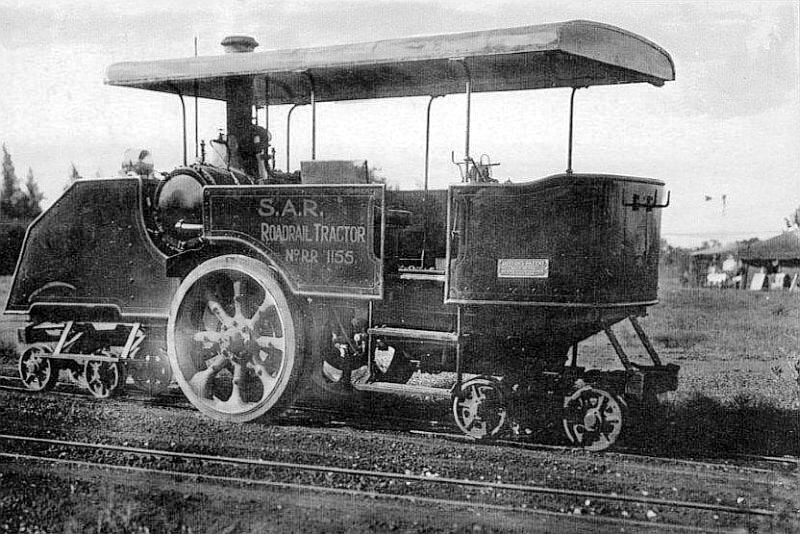 The designer, Major Frank Dutton, SAR Signal Engineer and the Motor Transport Superintendent, argued that a rubber tyre in contact with a hard road would be better at transferring tractive power than a steel wheel on steel rail. At least two Dutton Rail Tractors were built, both steam-powered and both rebuilt by the Britannia Engineering Works of Johannesburg from Yorkshire steam tractors.Stronach-Dutton Road-Rail - The Roadrail System of Traction
The designer, Major Frank Dutton, SAR Signal Engineer and the Motor Transport Superintendent, argued that a rubber tyre in contact with a hard road would be better at transferring tractive power than a steel wheel on steel rail. At least two Dutton Rail Tractors were built, both steam-powered and both rebuilt by the Britannia Engineering Works of Johannesburg from Yorkshire steam tractors.Stronach-Dutton Road-Rail - The Roadrail System of Traction
/ref> The second Dutton tractor, no. RR1155, was a rail-only vehicle. It had a bogie at either end with the single pair of driving wheels on a differential axle in the centre. It was arranged for forward and reverse movement at all speeds, but it could only be used on the rails. Since, on occasion, the vehicle had to be transported by road, its construction was such that it could be readily disassembled into more easily transportable units, to be moved on road wheels to a workshop or for transfer of any other kind. In service, the tractor was often equipped with a water tank tender loaded with additional bags of coal on its running boards.Patent: Dutton Light Railway System and Locomotive Therefor, US 1306051 A, Jun 10, 1919
/ref>Patent: Vehicle for Service on Roads and Rails, US 1561510 A, Nov 17, 1925
/ref>
Whyte notation
Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth ce ...
for the classification of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
s, represents the wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
of four leading wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used ...
s on two axles, two powered driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled ...
s on one axle, and four trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle ( wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing truck. On some large locomotives, ...
s on two axles. This type of locomotive is often called a Huntington type.
The configuration was most often used for tank engines, which is noted by adding letter suffixes to the configuration, such as for a conventional side-tank locomotive, for a saddle-tank locomotive, for a well-tank locomotive and for a rack-equipped tank locomotive.
Overview
This wheel arrangement was mainly used on varioustank locomotive
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locom ...
configurations. Eight 4-2-4 well- and back-tank locomotives which entered service on the Bristol and Exeter Railway
The Bristol & Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with ...
in 1853 appear to have been the first with this wheel arrangement. The engine was designed by James Pearson, the railway company's engineer, and featured single large flange
A flange is a protruded ridge, lip or rim (wheel), rim, either external or internal, that serves to increase shear strength, strength (as the flange of an iron beam (structure), beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam); for easy attachment/transfer of ...
less driving wheels between two supporting four-wheeled bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transp ...
s. The water was carried in both well- and back-tanks, leaving the boilers exposed in the same way as on most tender locomotives.
Usage
United Kingdom
The first eight known 4-2-4T locomotives entered service on thebroad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
Bristol and Exeter Railway
The Bristol & Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with ...
in 1853 and 1854, numbered in the range from 39 to 46. They had diameter flangeless driving wheels, supported by leading and trailing two-axle bogies. The water was carried in both well- and back-tanks. Two more engines were built in 1859 and 1862, but with much smaller diameter driving wheels.
 Between 1869 and 1873, new locomotives were built to replace four of the original diameter driving wheeled engines, re-using the engine numbers of the locomotives being replaced. These four replacement engines had slightly smaller diameter driving wheels.
In 1881, this wheel arrangement was also used by the
Between 1869 and 1873, new locomotives were built to replace four of the original diameter driving wheeled engines, re-using the engine numbers of the locomotives being replaced. These four replacement engines had slightly smaller diameter driving wheels.
In 1881, this wheel arrangement was also used by the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
on William Dean's experimental locomotive no. 9. Since it was so prone to derailing as to be unable to be moved from the workshops where it was built, it did no work and was rebuilt to a tender locomotive in 1884. Dugald Drummond
Dugald Drummond (1 January 1840 – 8 November 1912) was a Scottish steam locomotive engineer. He had a career with the North British Railway, LB&SCR, Caledonian Railway and London and South Western Railway. He was the older brother of the eng ...
of the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter ...
built a 4-2-4T F9 class combined locomotive and inspection saloon in 1899. It was little used after Drummond's death in 1912.D. L. Bradley, Locomotive of the London and South Western Railway, Part ii., Railway Correspondence and Travel Society, 1967. pp. 86-87.
United States
 The engine '' C. P. Huntington'' was one of three identical 4-2-4 tank locomotives. They were the first locomotives to be purchased by
The engine '' C. P. Huntington'' was one of three identical 4-2-4 tank locomotives. They were the first locomotives to be purchased by Southern Pacific Railroad
The Southern Pacific (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the ...
in 1863, for use on light commuter services in the Sacramento area. The locomotives had serious shortcomings. The single driving axle did not carry the full weight of the engine's rear end due to the trailing truck and, in addition to being too light, it therefore lacked adhesion to reliably pull trains, especially on gradients. The short water tank on the Forney-type frame prevented the locomotives from travelling any moderate distance without consuming all of their water. As a result, these locomotives were only used when absolutely necessary.
In 1863, a sister engine, the '' T. D. Judah'', was built by the Cooke Locomotive Works for a railroad which was unable to pay for it and was purchased by the Central Pacific Railroad
The Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR) was a rail company chartered by Pacific Railroad Acts, U.S. Congress in 1862 to build a railroad eastwards from Sacramento, California, to complete the western part of the "First transcontinental railroad" in N ...
. This locomotive was rebuilt to a 4-2-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle.
Other equivalent class ...
wheel arrangement in 1872.
South Africa
In 1923, the South African Railways (SAR) conducted trials with a prototype petrol-paraffin powered road-rail tractor and, in 1924, placed at least two Dutton steam rail tractors in service on the new narrow gauge line betweenNaboomspruit
Mookgophong, also known as Naboomspruit, is a town in the Limpopo province of South Africa. The town is located approximately 42 km north-east of Modimolle and 51 km south-west of Mokopane.
History
It was founded on the farm Vischgat in ...
and Singlewood in Transvaal. One of the latter had a wheel arrangement.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, October 1945. pp. 782-783.
 The designer, Major Frank Dutton, SAR Signal Engineer and the Motor Transport Superintendent, argued that a rubber tyre in contact with a hard road would be better at transferring tractive power than a steel wheel on steel rail. At least two Dutton Rail Tractors were built, both steam-powered and both rebuilt by the Britannia Engineering Works of Johannesburg from Yorkshire steam tractors.Stronach-Dutton Road-Rail - The Roadrail System of Traction
The designer, Major Frank Dutton, SAR Signal Engineer and the Motor Transport Superintendent, argued that a rubber tyre in contact with a hard road would be better at transferring tractive power than a steel wheel on steel rail. At least two Dutton Rail Tractors were built, both steam-powered and both rebuilt by the Britannia Engineering Works of Johannesburg from Yorkshire steam tractors.Stronach-Dutton Road-Rail - The Roadrail System of Traction/ref> The second Dutton tractor, no. RR1155, was a rail-only vehicle. It had a bogie at either end with the single pair of driving wheels on a differential axle in the centre. It was arranged for forward and reverse movement at all speeds, but it could only be used on the rails. Since, on occasion, the vehicle had to be transported by road, its construction was such that it could be readily disassembled into more easily transportable units, to be moved on road wheels to a workshop or for transfer of any other kind. In service, the tractor was often equipped with a water tank tender loaded with additional bags of coal on its running boards.Patent: Dutton Light Railway System and Locomotive Therefor, US 1306051 A, Jun 10, 1919
/ref>Patent: Vehicle for Service on Roads and Rails, US 1561510 A, Nov 17, 1925
/ref>
In fiction
The ''Little Blue Engine'' from the original 1906 book ''The Little Engine That Could
''The Little Engine That Could'' is an American folktale (existing in the form of several illustrated children's books and films) that became widely known in the United States after publication in 1930 by Platt & Munk. The story is used to teach ...
'' was a Forney locomotive
The Forney is a type of tank locomotive patented by Matthias N. Forney between 1861 and 1864 and used predominantly in the USA.
Forney design
Forney locomotives include the following characteristics:
* An wheel arrangement, that is four drivin ...
with this wheel arrangement.
References
{{whyte types 2, 4-2-4T Whyte notation