3D XPoint on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
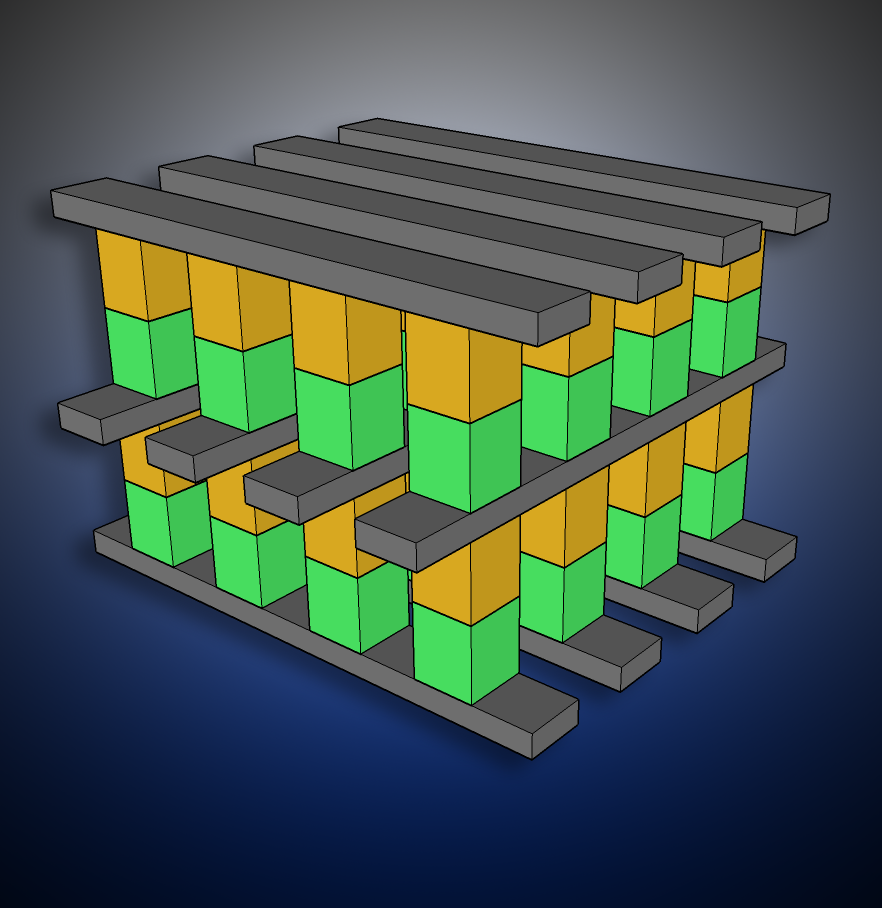 3D XPoint (pronounced ''three-D cross point'') is a discontinued
3D XPoint (pronounced ''three-D cross point'') is a discontinued
 3D XPoint (pronounced ''three-D cross point'') is a discontinued
3D XPoint (pronounced ''three-D cross point'') is a discontinued non-volatile memory
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data.
Non-volatile memory typ ...
(NVM) technology developed jointly by Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
and Micron Technology
Micron Technology, Inc. is an American producer of computer memory and computer data storage including dynamic random-access memory, flash memory, and USB flash drives. It is headquartered in Boise, Idaho. Its consumer products, including ...
. It was announced in July 2015 and is available on the open market under the brand name Optane (Intel) from April 2017 until July 2022. Bit storage is based on a change of bulk resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
, in conjunction with a stackable cross-grid data access array. Initial prices are less than dynamic random-access memory
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-oxi ...
(DRAM) but more than flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
.
As a non-volatile memory, 3D XPoint has a number of features that distinguish it from other currently available RAM and NVRAM
Non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) is random-access memory that retains data without applied power. This is in contrast to dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) and static random-access memory (SRAM), which both maintain data only for as lon ...
. Although the first generations of 3D XPoint were not especially large or fast, as of 2019 3D XPoint is used to create some of the fastest SSD
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is ...
s available, with small-write latency. As the memory is inherently fast, and byte-addressable, techniques such as read-modify-write and caching
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewher ...
used to enhance traditional SSDs are not needed to obtain high performance. In addition, chipsets such as Cascade Lake are designed with inbuilt support for 3D XPoint, that allow it to be used as a caching or acceleration disk, and it is also fast enough to be used as non-volatile RAM (NVRAM) in a DIMM
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal compute ...
package.
History
Development
Development of 3D XPoint began around 2012. Intel and Micron had developed other non-volatile phase-change memory (PCM) technologies previously; Mark Durcan of Micron said 3D XPoint architecture differs from previous offerings of PCM, and uses chalcogenide materials for both selector and storage parts of the memory cell that are faster and more stable than traditional PCM materials likeGST GST may refer to:
Taxes
* General sales tax
* Goods and Services Tax, the name for the value-added tax in several jurisdictions:
** Goods and services tax (Australia)
** Goods and Services Tax (Canada)
** Goods and Services Tax (Hong Kong)
** ...
. But today, it is thought of as a subset of ReRAM
Resistive random-access memory (ReRAM or RRAM) is a type of non-volatile (NV) random-access (RAM) computer memory that works by changing the resistance across a dielectric solid-state material, often referred to as a memristor.
ReRAM bears som ...
.
3D XPoint has been stated to use electrical resistance and to be bit addressable. Similarities to the resistive random-access memory
Resistive random-access memory (ReRAM or RRAM) is a type of non-volatile (NV) random-access (RAM) computer memory that works by changing the resistance across a dielectric solid-state material, often referred to as a memristor.
ReRAM bears som ...
under development by Crossbar Inc. have been noted, but 3D XPoint uses different storage physics. Specifically, transistors are replaced by threshold switches as selectors in the memory cells. 3D XPoint developers indicate that it is based on changes in resistance of the bulk material. Intel CEO Brian Krzanich
Brian Matthew Krzanich (born May 9, 1960) is an American engineer and Krzanich joined Intel as an engineer in 1982 and served as chief operating officer (COO) before being promoted to CEO in May 2013. As CEO, Krzanich was credited for diversifyin ...
responded to ongoing questions on the XPoint material that the switching was based on "bulk material properties". Intel has stated that 3D XPoint does not use a phase-change or memristor
A memristor (; a portmanteau of ''memory resistor'') is a non-linear two-terminal electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. It was described and named in 1971 by Leon Chua, completing a theoretical quartet of ...
technology, although this is disputed by independent reviewers.
3D XPoint has been the most widely produced standalone memory based on other than charge storage, whereas other alternative memories, like ReRAM or MRAM, have so far only been widely developed on embedded platforms.
Initial production
In mid-2015, Intel announced the Optane brand for storage products based on 3D XPoint technology. Micron (using the QuantX brand) estimated the memory to be sold for about half the price of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), but four to five times the price offlash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
. Initially, a wafer fabrication facility in Lehi, Utah
Lehi ( ) is a city in Utah County, Utah, United States. It is named after Lehi, a prophet in the Book of Mormon. The population was 75,907 at the 2020 census, up from 47,407 in 2010. The rapid growth in Lehi is due, in part, to the rapid develo ...
, operated by IM Flash Technologies LLC (an Intel-Micron joint venture) made small quantities of 128 Gbit chips in 2015. They stack two 64 Gbit planes. In early 2016 mass production of the chips was expected in 12 to 18 months.
In early 2016, IM Flash announced that the first generation of solid-state drives would achieve 95000 IOPS
Input/output operations per second (IOPS, pronounced ''eye-ops'') is an input/output performance measurement used to characterize computer storage devices like hard disk drives (HDD), solid state drives (SSD), and storage area networks (SAN). ...
throughput with 9 microsecond latency. This low latency significantly increases IOPS at low queue depths for random operations. At Intel Developer Forum
The Intel Developer Forum (IDF) was a biannual gathering of technologists to discuss Intel products and products based on Intel products. The first IDF was held in 1997.
To emphasize the importance of China, the Spring 2007 IDF was held in Beij ...
2016, Intel demonstrated PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common m ...
(PCIe) 140 GB development boards showing 2.4–3× improvement in benchmarks compared to PCIe NAND flash solid-state drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It i ...
s (SSDs). On March 19, 2017, Intel announced their first product: a PCIe card available in the second half of 2017.
Reception
Despite the initial lukewarm reception when first released, 3D XPoint – particularly in the form of Intel's Optane range – has been highly acclaimed and widely recommended for tasks where its specific features are of value, with reviewers such as ''Storage Review'' concluding in August 2018 that for low-latency workloads, 3D XPoint was producing 500,000 4K sustainedIOPS
Input/output operations per second (IOPS, pronounced ''eye-ops'') is an input/output performance measurement used to characterize computer storage devices like hard disk drives (HDD), solid state drives (SSD), and storage area networks (SAN). ...
for both reads and writes, with 3–15 microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is equal to 100 ...
latencies, and that at present "there is currently nothing lsethat comes close", while Tom's Hardware
''Tom's Hardware'' is an online publication owned by Future plc and focused on technology. It was founded in 1996 by Thomas Pabst. It provides articles, news, price comparisons, videos and reviews on computer hardware and high technology. The si ...
described the Optane 900p in December 2017 as being like a "mythical creature" that must be seen to be believed, and which doubled the speed of the best previous consumer devices. ServeTheHome concluded in 2017 that in read, write and mixed tests, Optane SSDs were consistently around 2.5× as fast as the best Intel datacentre SSDs which had preceded them, the P3700 NVMe. AnandTech
''AnandTech'' is an online computer hardware magazine owned by Future plc. It was founded in 1997 by then-14-year-old Anand Lal Shimpi, who served as CEO and editor-in-chief until August 30, 2014, with Ryan Smith replacing him as editor-in-chie ...
noted that consumer Optane-based SSDs were similar in performance to the best non-3D-XPoint SSDs for large transfers, with both being "blown away" by the large transfer performance of enterprise Optane SSDs.
Sale of Lehi fab
On March 16, 2021, Micron announced that it would cease development of 3D XPoint in order to develop products based on Compute Express Link (CXL). The Lehi fab is being put up for sale. Intel responded that its ability to supply Intel Optane products would not be affected.Discontinuation
In July 2022, Intel announced the winding down of the Optane division, effectively discontinuing the development of 3D XPoint.Compatibility
Intel
Intel distinguishes between "Intel Optane Memory" and "Intel Optane SSDs". As a memory component, Optane requires specific chipset and CPU support. As an ordinary SSD, Optane is broadly compatible with a very wide range of systems, and its main requirements are much like any other SSD – ability to be plugged into the hardware, operating system, BIOS/UEFI and driver support for NVMe, and adequate cooling. * As a standards-based NVMe-PCIe SSD: Optane devices can be used as the storage element of an ordinarysolid-state drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It i ...
(SSD), typically in M.2 card format, NVMe
NVM Express (NVMe) or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMHCIS) is an open, logical-device interface specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media usually attached via PCI Express (PCIe) bus. The ...
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common m ...
format, or U.2 standalone format. When Optane is used as an ordinary SSD (in any of these formats), its compatibility requirements are the same as for any traditional SSD. Therefore, compatibility depends only upon whether the hardware, operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
and drivers can support NVMe and similar SSDs. Optane SSDs are therefore compatible with a wide range of older and newer chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in one or more integrated circuits known as a "Data Flow Management System" that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on t ...
s and CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
s (including non-Intel chipsets and CPUs).
* As a memory or on-board acceleration device: Optane devices can also be used as NVDIMM
A NVDIMM (pronounced "en-vee-dimm") or non-volatile DIMM is a type of persistent random-access memory for computers using widely used DIMM form-factors. Non-volatile memory is memory that retains its contents even when electrical power is removed, ...
(non volatile main memory) or for certain kinds of caching or accelerating roles, but unlike general SSD roles, this requires newer hardware, since the chipset and motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
must be designed to work specifically with Optane in those roles.
Micron
Micron offers NVMe AIC SSD drives (QuantX X100) which maintain compatibility with NVMe capable systems. Native support as an acceleration device is not supported (although tiered storage can be used).See also
*Intel Turbo Memory Intel Turbo Memory is a technology introduced by Intel Corporation that uses NAND flash memory modules to reduce the time it takes for a computer to power up, access programs, and write data to the hard drive. During development, the technology was ...
* NAND flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both use ...
* NOR flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
Notes
References
External links
* , 44 minutes {{Primary storage technologies Computer memory Intel products Non-volatile random-access memory