3-center-2-electron Bond on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A three-center two-electron (3c–2e) bond is an
 The monomer BH3 is unstable since the boron atom has an empty p-orbital. A B−H−B 3-center-2-electron bond is formed when a boron atom shares electrons with a B−H bond on another boron atom. The two electrons (corresponding to one bond) in a B−H−B bonding molecular orbital are spread out across three internuclear spaces.
In diborane (B2H6), there are two such 3c-2e bonds: two H atoms bridge the two B atoms, leaving two additional H atoms in ordinary B−H bonds on each B. As a result, the molecule achieves stability since each B participates in a total of four bonds and all bonding molecular orbitals are filled, although two of the four bonds are 3-center B−H−B bonds. The reported
The monomer BH3 is unstable since the boron atom has an empty p-orbital. A B−H−B 3-center-2-electron bond is formed when a boron atom shares electrons with a B−H bond on another boron atom. The two electrons (corresponding to one bond) in a B−H−B bonding molecular orbital are spread out across three internuclear spaces.
In diborane (B2H6), there are two such 3c-2e bonds: two H atoms bridge the two B atoms, leaving two additional H atoms in ordinary B−H bonds on each B. As a result, the molecule achieves stability since each B participates in a total of four bonds and all bonding molecular orbitals are filled, although two of the four bonds are 3-center B−H−B bonds. The reported 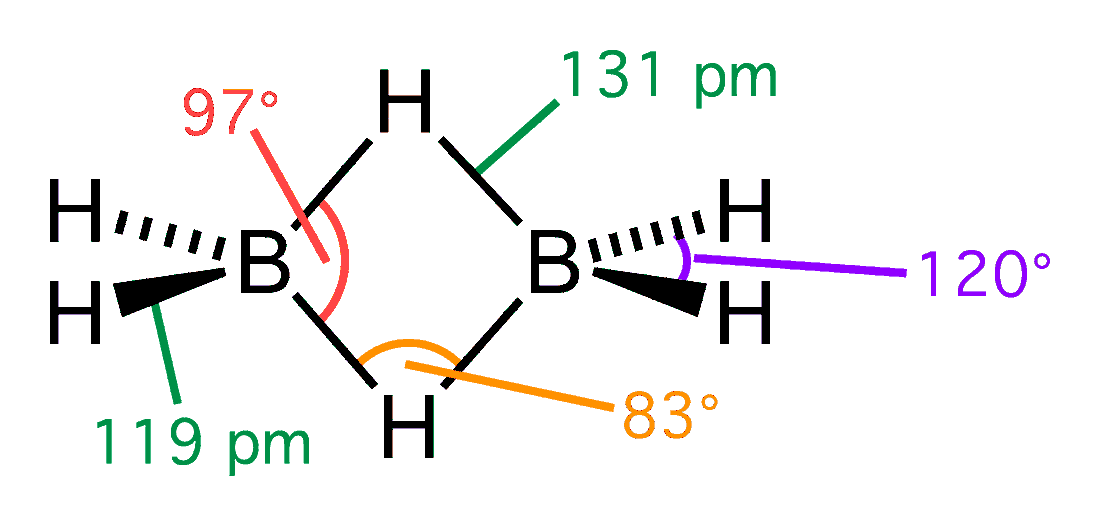
 Three-center, two-electron bonding is pervasive in organotransition metal chemistry. A celebrated family of compounds featuring such interactions as called agostic complexes.
Three-center, two-electron bonding is pervasive in organotransition metal chemistry. A celebrated family of compounds featuring such interactions as called agostic complexes.
electron-deficient Electron deficiency (and electron-deficient) is jargon that is used in two contexts: species that violate the octet rule because they have too few valence electrons and species that happen to follow the octet rule but have electron-acceptor properti ...
chemical bond where three atoms share two electrons. The combination of three atomic orbitals form three molecular orbitals: one bonding, one ''non''-bonding, and one ''anti''-bonding. The two electrons go into the bonding orbital, resulting in a net bonding effect and constituting a chemical bond among all three atoms. In many common bonds of this type, the bonding orbital is shifted towards two of the three atoms instead of being spread equally among all three. Example molecules with 3c–2e bonds are the trihydrogen cation () and diborane (). In these two structures, the three atoms in each 3c-2e bond form an angular geometry, leading to a bent bond
In organic chemistry, a bent bond, also known as a banana bond, is a type of covalent chemical bond with a geometry somewhat reminiscent of a banana. The term itself is a general representation of electron density or configuration resembling a ...
.
Boranes and carboranes
An extended version of the 3c–2e bond model features heavily in cluster compounds described by the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory, such as boranes andcarborane
Carboranes are electron-delocalized (non-classically bonded) clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms.Grimes, R. N., ''Carboranes 3rd Ed.'', Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York (2016), . Like many of the related boron hydrides, these cl ...
s. These molecules derive their stability from having a completely filled set of bonding molecular orbitals as outlined by Wade's rules
In chemistry the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory (PSEPT) provides electron counting rules useful for predicting the structures of cluster compound, clusters such as borane and carborane clusters. The electron counting rules were originall ...
.
bond order
In chemistry, bond order, as introduced by Linus Pauling, is defined as the difference between the number of bonds and anti-bonds.
The bond order itself is the number of electron pairs (covalent bonds) between two atoms. For example, in diat ...
for each B−H interaction in a bridge is 0.5, F. Albert Cotton, Geoffrey Wilkinson and Paul L. Gaus, ''Basic Inorganic Chemistry'', 2nd ed. (Wiley 1987), p.113 so that the bridging B−H−B bonds are weaker and longer than the terminal B−H bonds, as shown by the bond lengths in the structural diagram.
:
Transition metal complexes
 Three-center, two-electron bonding is pervasive in organotransition metal chemistry. A celebrated family of compounds featuring such interactions as called agostic complexes.
Three-center, two-electron bonding is pervasive in organotransition metal chemistry. A celebrated family of compounds featuring such interactions as called agostic complexes.
Other compounds
This bonding pattern is also seen intrimethylaluminium
Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2( CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industriall ...
, which forms a dimer Al2(CH3)6 with the carbon atoms of two of the methyl groups in bridging positions. This type of bond also occurs in carbon compounds, where it is sometimes referred to as hyperconjugation; another name for asymmetrical three-center two-electron bonds.
Beryllium
The first stable subvalent Be complex ever observed contains a three-center two-electron π-bond that consists of donor-acceptor interactions over the C-Be-C core of a Be(0)-carbene adduct.Carbocations
Carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountere ...
rearrangement reaction
In organic chemistry, a rearrangement reaction is a broad class of organic reactions where the carbon skeleton of a molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of the original molecule. Often a substituent moves from one atom to another ...
s occur through three-center bond transition states. Because the three center bond structures have about the same energy as carbocations, there is generally virtually no activation energy for these rearrangements so they occur with extraordinarily high rates.
Carbonium ion
In chemistry, a carbonium ion is any cation that has a pentavalent carbon atom. The name carbonium may also be used for the simplest member of the class, properly called methanium (), where the five valences are filled with hydrogen atoms.
The nex ...
s such as ethanium have three-center two-electron bonds. Perhaps the best known and studied structure of this sort is the 2-Norbornyl cation
In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (or 2-bicyclo .2.1eptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studie ...
.
See also
* Three-center four-electron bond *2-Norbornyl cation
In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (or 2-bicyclo .2.1eptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studie ...
* Dihydrogen complex
References
{{Chemical bonds Chemical bonding