2867 Šteins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
2867 Šteins (provisional designation ) is an irregular, diamond-shaped background
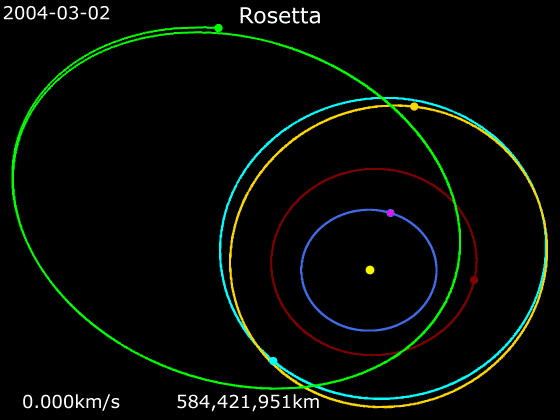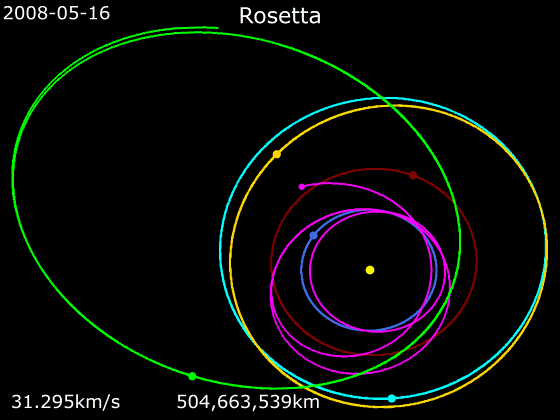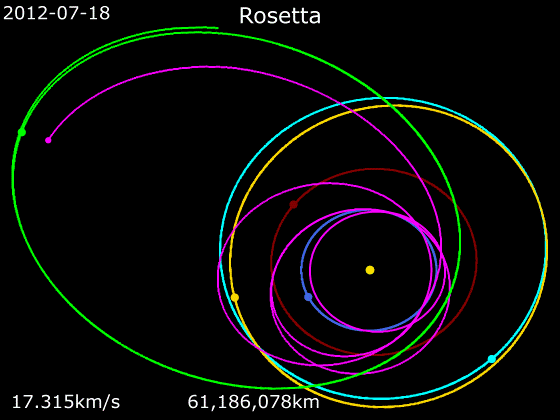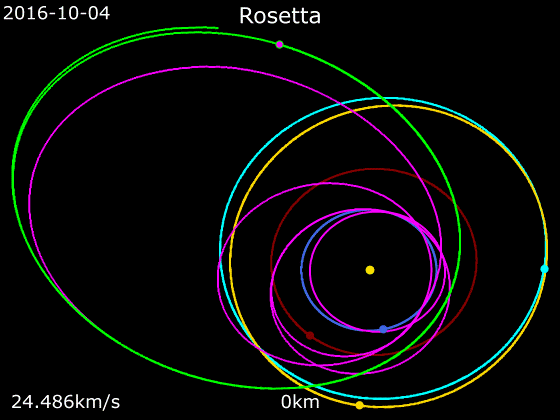 On 5 September 2008, the Rosetta space probe flew by ''Šteins'' at a distance of 800 km and a relatively slow speed of 8.6 km/s. Despite the short duration of this encounter (approximately 7 minutes in total), a great amount of data was obtained by the 15 scientific instruments operating on board the Rosetta spacecraft. This was the first of two planned asteroid flybys performed by the probe, the second being to the much larger
On 5 September 2008, the Rosetta space probe flew by ''Šteins'' at a distance of 800 km and a relatively slow speed of 8.6 km/s. Despite the short duration of this encounter (approximately 7 minutes in total), a great amount of data was obtained by the 15 scientific instruments operating on board the Rosetta spacecraft. This was the first of two planned asteroid flybys performed by the probe, the second being to the much larger
Steins: A diamond in the Sky
images, ESA
– Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
Rosetta's OSIRIS cameras reveal the nature of asteroid Steins
ESA, January 2010
Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB)
query form
)
Dictionary of Minor Planet Names
Google books
– Minor Planet Center * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Steins 002867 Discoveries by Nikolai Chernykh Named minor planets 2867 Steins 20080905 19691104
asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
from the inner regions of the asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called ...
, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 4 November 1969 by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Chernykh
Nikolai Stepanovich Chernykh (russian: Никола́й Степа́нович Черны́х) (6 October 1931 – 25 May 2004Казакова, Р.К. Памяти Николая Степановича Черных'. Труды Государст ...
at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory
The Crimean Astrophysical Observatory (CrAO, List of observatory codes, obs. code: IAU code#095, 095) is located at Nauchnij research campus, near the Central Crimean city of Bakhchysarai, on the Crimean peninsula. CrAO is often called ...
in Nauchnij on the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
n peninsula. In September 2008, ESA
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
's spacecraft ''Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Ro ...
'' flew by ''Šteins'', making it one of few minor planets ever visited by a spacecraft. The bright E-type asteroid
E-type asteroids are asteroids thought to have enstatite (MgSiO3) achondrite surfaces. They form a large proportion of asteroids inward of the asteroid belt known as Hungaria asteroids, but rapidly become very rare as the asteroid belt proper i ...
features 23 named craters and has a rotation period
The rotation period of a celestial object (e.g., star, gas giant, planet, moon, asteroid) may refer to its sidereal rotation period, i.e. the time that the object takes to complete a single revolution around its axis of rotation relative to the ...
of 6.05 hours. It was named for Soviet Latvian astronomer Kārlis Šteins
Kārlis Šteins (October 13, 1911 – April 4, 1983) was a Latvian and Soviet astronomer and populariser of this science.
Biography
Šteins was born on October 13, 1911 in Kazan, Russian Empire. In 1925 he finished the Riga 2nd Secondary school. ...
.
Orbit and classification
''Šteins'' is a non-family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
asteroid from the main belt's background population. It orbits the Sun in the inner
Interior may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Interior'' (Degas) (also known as ''The Rape''), painting by Edgar Degas
* ''Interior'' (play), 1895 play by Belgian playwright Maurice Maeterlinck
* ''The Interior'' (novel), by Lisa See
* Interior de ...
asteroid belt at a distance of 2.0–2.7 AU once every 3 years and 8 months (1,327 days; semi-major axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the long ...
of 2.36 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off-center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (graph theory) of a v ...
of 0.15 and an inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object ...
of 10 ° with respect to the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic again ...
. The body's observation arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly use ...
begins with a precovery
In astronomy, precovery (short for pre-discovery recovery) is the process of finding the image of an object in images or photographic plates predating its discovery, typically for the purpose of calculating a more accurate orbit. This happens mos ...
, taken at the Palomar Observatory
Palomar Observatory is an astronomical research observatory in San Diego County, California, United States, in the Palomar Mountain Range. It is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). Research time at the observat ...
in November 1951, or 18 years prior to its official discovery observation.
''Rosetta'' flyby
 On 5 September 2008, the Rosetta space probe flew by ''Šteins'' at a distance of 800 km and a relatively slow speed of 8.6 km/s. Despite the short duration of this encounter (approximately 7 minutes in total), a great amount of data was obtained by the 15 scientific instruments operating on board the Rosetta spacecraft. This was the first of two planned asteroid flybys performed by the probe, the second being to the much larger
On 5 September 2008, the Rosetta space probe flew by ''Šteins'' at a distance of 800 km and a relatively slow speed of 8.6 km/s. Despite the short duration of this encounter (approximately 7 minutes in total), a great amount of data was obtained by the 15 scientific instruments operating on board the Rosetta spacecraft. This was the first of two planned asteroid flybys performed by the probe, the second being to the much larger 21 Lutetia
)
, mp_category=Main belt
, mpc_name=(21) Lutetia
, orbit_ref =
, epoch=May 31, 2020 ( JD 2459000.5)
, semimajor=2.435 AU
, perihelion=2.037 AU
, aphelion=2.833 AU
, eccentricity=0.16339
, period=3.80 yr (1388.1 d)
, inclination=3.064� ...
in 2010. The timing of the fly-by meant that the asteroid was illuminated by the sun from the perspective of the spacecraft, making the transmitted images clear. The European Space Operations Centre
The European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) serves as the main mission control centre for the European Space Agency (ESA) and is located in Darmstadt, Germany. ESOC's primary function is the operation of unmanned spacecraft on behalf of ESA and ...
streamed a press conference on Šteins later that day.
Naming
Thisminor planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor ...
was named in memory of Kārlis Šteins
Kārlis Šteins (October 13, 1911 – April 4, 1983) was a Latvian and Soviet astronomer and populariser of this science.
Biography
Šteins was born on October 13, 1911 in Kazan, Russian Empire. In 1925 he finished the Riga 2nd Secondary school. ...
(1911–1983), a Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
n and Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
astronomer. He was a long-time observatory director at the University of Latvia
University of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Universitāte, shortened ''LU'') is a state-run university located in Riga, Latvia established in 1919.
The ''QS World University Rankings'' places the university between 801st and 1000th globally, seventh ...
in Riga and designed astronomical instruments. Šteins is known for his work on cometary cosmogony
Cosmogony is any model concerning the origin of the cosmos or the universe.
Overview
Scientific theories
In astronomy, cosmogony refers to the study of the origin of particular astrophysical objects or systems, and is most commonly used i ...
and the study of Earth's rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in retrograd ...
. The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
Function
...
on 18 September 1986 ().
Features on ''Šteins''
On 11 May 2012, IAU'sWorking Group for Planetary System Nomenclature
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach ...
announced a naming system for geographical features on ''Šteins''. Inspired by the asteroid's gem-like shape, its crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
*Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
*Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surfac ...
are given the English-language names of precious stones, with the largest being named Diamond crater ''(see below)''.
Except for the montes of Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
and the lunar maria
The lunar maria (; singular: mare ) are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient asteroid impacts on the far side on the Moon that triggered volcanic activity on the opposite (near) side. They were dubbed , Latin for 'seas' ...
(and proposed for 2 Pallas
Pallas (minor-planet designation: 2 Pallas) is the second asteroid to have been discovered, after Ceres. It is believed to have a mineral composition similar to carbonaceous chondrite meteorites, like Ceres, though significantly less hyd ...
and 7 Iris
Iris (minor planet designation: 7 Iris) is a large main-belt asteroid and perhaps remnant planetesimal orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. It is the fourth-brightest object in the asteroid belt. It is classified as an S-type asteroid, mea ...
), the craters of Šteins are the only features in the Solar System whose names are not derived from proper nouns. In addition, a distinct region on the asteroid has been named Chernykh Regio after the discoverer, Nikolai Chernykh
Nikolai Stepanovich Chernykh (russian: Никола́й Степа́нович Черны́х) (6 October 1931 – 25 May 2004Казакова, Р.К. Памяти Николая Степановича Черных'. Труды Государст ...
.
Physical characteristics
A study published in 2006 by astronomers at theEuropean Southern Observatory
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 mem ...
showed that ''Šteins'' is an E-type asteroid
E-type asteroids are asteroids thought to have enstatite (MgSiO3) achondrite surfaces. They form a large proportion of asteroids inward of the asteroid belt known as Hungaria asteroids, but rapidly become very rare as the asteroid belt proper i ...
with a diameter of approximately 4.6 kilometers. After the Rosetta flyby, the ESA described ''Šteins'' as a "diamond in the sky", as it has a wide body that tapers into a point. The wide section is dominated by the large Diamond crater with a diameter of 2.1 kilometers, which surprised scientists, who were at first amazed the asteroid survived such an impact, while later it turned out that the crater-to-body diameter ratio of 0.79 is in fact not abnormally large as it follows an already established trend. Besides its irregular in shape, it does not have any moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
s.
Diameter and albedo
According to the survey carried out by theNEOWISE
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 2011, ...
mission of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 2011, ...
and observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, f ...
, ''Šteins'' measures 5.16 and 4.92 kilometers in diameter and its surface has an albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of sunlight, solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body ...
of 0.30 and 0.34, respectively. Its overall Bond albedo is 0.24 ± 0.01. In 2012, the photographs of ''Šteins'' taken by ''Rosetta'' using stereophotoclinometry allowed scientists to determine that the asteroid's dimensions are kilometers, which equates to a mean diameter in volume of 5.26 km. (Asteroid was later named for the scientist using this 3D-method.) The ''Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link'' adopts an albedo of 0.34 and a diameter of 4.9 kilometers with an absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse Logarithmic scale, logarithmic Magnitude (astronomy), astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent mag ...
of 13.36.
Lightcurves and poles
Studying the asteroid withRosetta space probe
''Rosetta'' was a space probe built by the European Space Agency launched on 2 March 2004. Along with ''Philae'', its lander module, ''Rosetta'' performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the c ...
onboard OSIRIS cameras shortly before its flyby showed via a lightcurve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequ ...
analysis that Šteins has a rotation period
The rotation period of a celestial object (e.g., star, gas giant, planet, moon, asteroid) may refer to its sidereal rotation period, i.e. the time that the object takes to complete a single revolution around its axis of rotation relative to the ...
of hours. The results of the rotational lightcurve agree with ground-based photometric observations of ''Šteins'' with a period of 6.049 hours and a brightness amplitude between 0.18 and 0.31 magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
().
A lightcurve inversion
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequ ...
also modeled a concurring sidereal period of 6.04681 hours and determined a spin axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rot ...
at (250.0°, −89.0°) in ecliptic coordinates
The ecliptic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system commonly used for representing the apparent positions, orbits, and pole orientations of Solar System objects. Because most planets (except Mercury) and many small Solar System bodi ...
(λ, β). The modeling was done by compiling a set of 26 previously obtained visible lightcurves.
See also
* List of craters on minor planets *List of minor planets and comets visited by spacecraft
The following tables list all minor planets and comets that have been visited by robotic spacecraft.
List of minor planets visited by spacecraft
A total of 17 minor planets (asteroids, dwarf planets, and Kuiper belt objects) have been visit ...
Notes
References
External links
Steins: A diamond in the Sky
images, ESA
– Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
Rosetta's OSIRIS cameras reveal the nature of asteroid Steins
ESA, January 2010
Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB)
query form
)
Dictionary of Minor Planet Names
Google books
– Minor Planet Center * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Steins 002867 Discoveries by Nikolai Chernykh Named minor planets 2867 Steins 20080905 19691104