|
Precovery
In astronomy, precovery (short for pre-discovery recovery) is the process of finding the image of an object in images or photographic plates predating its discovery, typically for the purpose of calculating a more accurate orbit. This happens most often with minor planets, but sometimes a comet, a dwarf planet, a natural satellite, or a star is found in old archived images; even exoplanet precovery observations have been obtained. "Precovery" refers to a pre-discovery image; "recovery" refers to imaging of a body which was lost to our view (as behind the Sun), but is now visible again ''(also see lost minor planet and lost comet)''. Orbit determination requires measuring an object's position on multiple occasions. The longer the interval between observations, the more accurately the orbit can be calculated; however, for a newly discovered object, only a few days' or weeks' worth of measured positions may be available, sufficient only for a preliminary (imprecise) orbit calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2060 Chiron
2060 Chiron is a small Solar System body in the outer Solar System, orbiting the Sun between Saturn and Uranus. Discovered in 1977 by Charles Kowal, it was the first-identified member of a new class of objects now known as centaurs—bodies orbiting between the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt.944 Hidalgo, discovered in 1920, also fits this definition, but was not identified as belonging to a distinct population. Although it was initially called an asteroid and classified only as a minor planet with the designation "2060 Chiron", in 1989 it was found to exhibit behavior typical of a comet. Today it is classified as both a minor planet and a comet, and is accordingly also known by the cometary designation 95P/Chiron. Chiron is named after the centaur Chiron in Greek mythology. History Discovery Chiron was discovered on 1 November 1977 by Charles Kowal from images taken on 18 October at Palomar Observatory. It was given the temporary designation of . It was found near ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
69230 Hermes
69230 Hermes is a sub-kilometer sized asteroid and binary system on an eccentric orbit, classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, that passed Earth at approximately twice the distance of the Moon on 30 October 1937. The asteroid was named after Hermes from Greek mythology. It is noted for having been the last remaining named lost asteroid, rediscovered in 2003. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 13.9 hours. Its synchronous companion was discovered in 2003. The primary and secondary are similar in size; they measure approximately and in diameter, respectively. Discovery ''Hermes'' was discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth in images taken at Heidelberg Observatory on 28 October 1937. Only four days of observations could be made before it became too faint to be seen in the telescopes of the day. This was not enough to calculate an orbit, and ''Hermes'' became a lost asteroid. It thus did not receive a number, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly used in the discovery and tracking of asteroids and comets. Arc length has the greatest influence on the accuracy of an orbit. The number and spacing of intermediate observations has a lesser effect. Short arcs A very short arc leaves a high uncertainty parameter. The object might be in one of many different orbits, at many distances from Earth. In some cases, the initial arc was too short to determine if the object was in orbit around the Earth, or orbiting out in the asteroid belt. With a 1-day observation arc, was thought to be a trans-Neptunian dwarf planet, but is now known to be a 1 km main-belt asteroid. With an observation arc of 3 days, was thought to be a Mars-crossing asteroid that could be a threat to Earth, but was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped Earth's history, and have been implicated in the formation of the Earth–Moon system. Impact events also appear to have played a significant role in the evolutionary h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Comet
A lost comet is one which was not detected during its most recent perihelion passage. This generally happens when data is insufficient to reliably calculate the comet's location or if the solar elongation is unfavorable near perihelion passage. The ''D/'' designation is used for a periodic comet that no longer exists or is deemed to have disappeared. Lost comets can be compared to lost asteroids ( lost minor planets), although calculation of comet orbits differs because of nongravitational forces, such as emission of jets of gas from the nucleus. Some astronomers have specialized in this area, such as Brian G. Marsden, who successfully predicted the 1992 return of the once-lost periodic comet Swift–Tuttle. Overview Loss There are a number of reasons why a comet might be missed by astronomers during subsequent apparitions. Firstly, cometary orbits may be perturbed by interaction with the giant planets, such as Jupiter. This, along with nongravitational forces, can result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Minor Planet
A minor planet is "lost" when today's observers cannot find it, because its location is too uncertain to target observations. This happens if the orbital elements of a minor planet are not known accurately enough, typically because the observation arc for the object is too short, or too few observations were made before the object became unobservable (e.g. too faint due to increasing distance, or too close to the Sun to view at night). By some definitions thousands, if not tens of thousands, of mostly small observed minor planets are lost. Some lost minor planets discovered in decades past cannot be found because the available observational data is insufficient for reliable orbit determination. With limited information astronomers cannot know where to look for the object at future dates. Lost objects are sometimes recovered when serendipitously re-observed by a later astronomical survey. If the orbital elements of the newly found object are sufficiently close to those of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
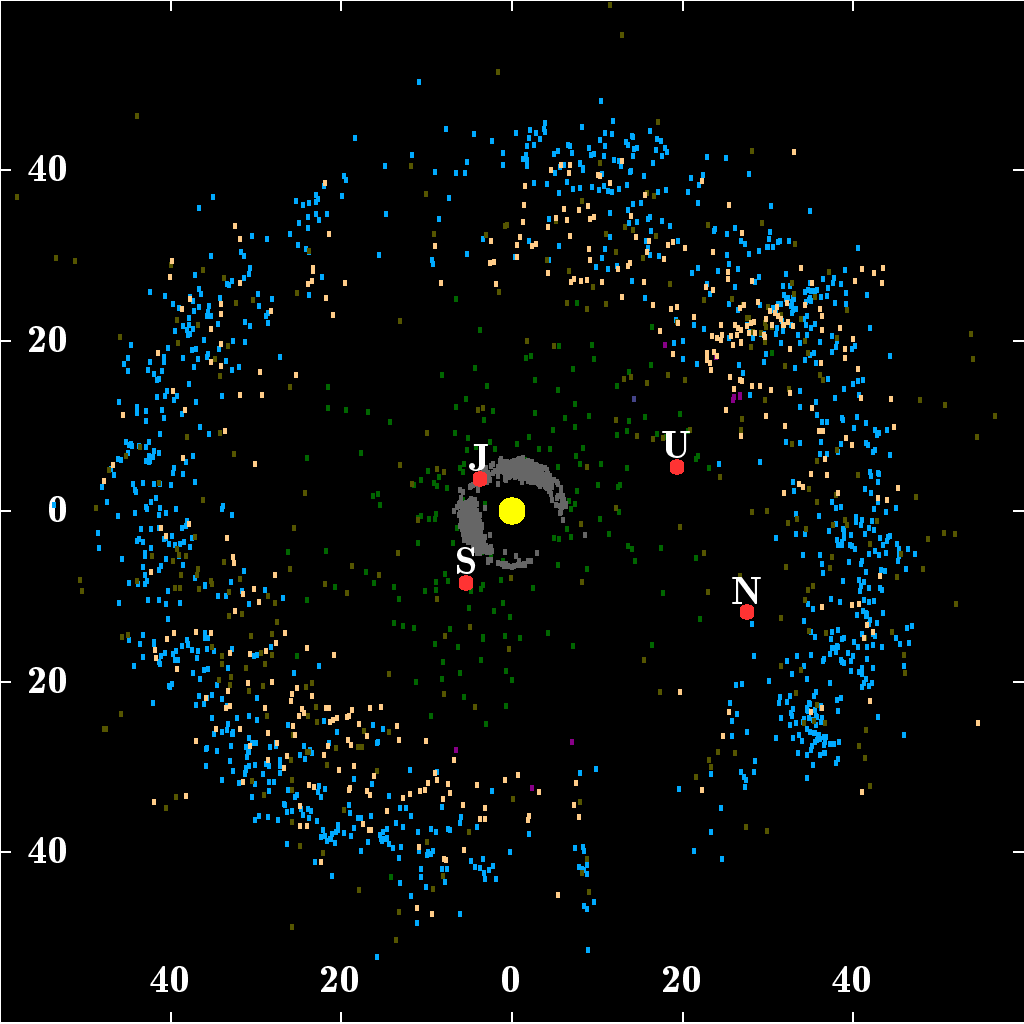
Valetudo CFHT Precovery 2003-02-28 Annotated
Valetudo may refer to: * The Roman name for the Greek goddess Hygieia * Valetudo (moon), a moon of the planet Jupiter, also known as Jupiter LXII See also * Vale tudo Vale Tudo (; en, Everything Goes/Everything Allowed), also known No Holds Barred (NHB) in the United States, is an unarmed, full-contact combat sport with relatively few rules. It became popular in Brazil during the 20th century and would even ..., a Brazilian full-contact combat event * ''Vale Tudo'' (TV series), a 1988 Brazilian telenovela {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur (minor Planet)
In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body with either a perihelion or a semi-major axis between those of the outer planets (between Jupiter and Neptune). Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable (though retrograde) orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000. The first centaur to be discovered, under the definition of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus). Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined "solid surface". The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 years at an average distance of . It is named after the Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction rather than by empirical observation. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Designation
Provisional designation in astronomy is the naming convention applied to astronomical objects immediately following their discovery. The provisional designation is usually superseded by a permanent designation once a reliable orbit has been calculated. Approximately 47% of the more than 1,100,000 known minor planets remain provisionally designated, as hundreds of thousands have been discovered in the last two decades. __TOC__ Minor planets The current system of provisional designation of minor planets (asteroids, centaurs and trans-Neptunian objects) has been in place since 1925. It superseded several previous conventions, each of which was in turn rendered obsolete by the increasing numbers of minor planet discoveries. A modern or new-style provisional designation consists of the year of discovery, followed by two letters and, possibly, a suffixed number. New-style provisional designation For example, the provisional designation stands for the 3910th body identified du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and " hydrostatic balances". He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, observation of Satur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Star
In astronomy, fixed stars ( la, stellae fixae) is a term to name the full set of glowing points, astronomical objects actually and mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background, unlike the few lights visible at naked eye, including comets, which appear to move slowly between those "fixed" stars along days, weeks or months on the foreground. Generally speaking, the fixed stars comprise all visible stars other than the Sun, plus the faint strip of the Milky Way. Due to their star-like appareance when sighted at naked eye, individual nebulae and other deep-sky objects also are counted among the fixed stars, despite the fact they are not true stars. The term is actually a misnomer due to the fact that those celestial objects are not really fixed with respect to one another; this is only a perceptual illusion, as stars and other extrasolar astronomical objects are so far away from Earth that human visio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |