|
69230 Hermes
69230 Hermes is a sub-kilometer sized asteroid and binary system on an eccentric orbit, classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, that passed Earth at approximately twice the distance of the Moon on 30 October 1937. The asteroid was named after Hermes from Greek mythology. It is noted for having been the last remaining named lost asteroid, rediscovered in 2003. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 13.9 hours. Its synchronous companion was discovered in 2003. The primary and secondary are similar in size; they measure approximately and in diameter, respectively. Discovery ''Hermes'' was discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth in images taken at Heidelberg Observatory on 28 October 1937. Only four days of observations could be made before it became too faint to be seen in the telescopes of the day. This was not enough to calculate an orbit, and ''Hermes'' became a lost asteroid. It thus did not receive a number, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Reinmuth
Karl Wilhelm Reinmuth (4 April 1892 in Heidelberg – 6 May 1979 in Heidelberg) was a German astronomer and a prolific discoverer of 395 minor planets. Scientific career From 1912 to 1957, Reinmuth was working as an astronomer at the Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl, Heidelberg Observatory (german: Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl) an astronomical observatory on the Königstuhl (Odenwald), Königstuhl hill above Heidelberg in southern Germany. He was a member at the minor planet studies group at Astronomisches Rechen-Institut between 1947 and 1950, and later became "Oberobservator" or chief-observer at Heidelberg Observatory until his retirement in 1957. Reinmuth obtained more than 12,500 precise astrometric measurements of minor planets' positions on photographic plates, an enormous accomplishment before computer-based assistance existed. Honours The outer main-belt asteroid 1111 Reinmuthia, discovered by himself at Heidelberg in 1912, was named in his hono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
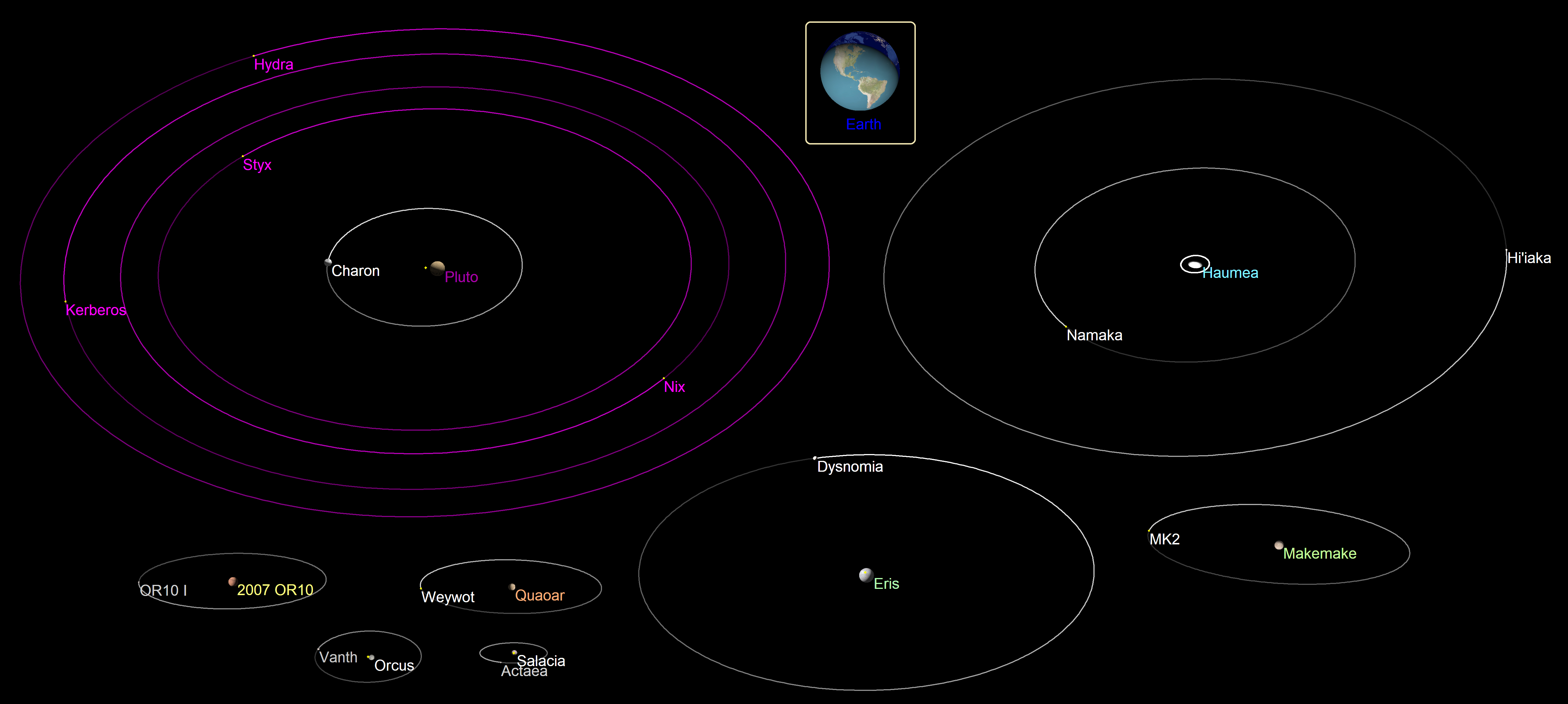
Binary Asteroid
A binary asteroid is a system of two asteroids orbiting their common barycenter. The binary nature of 243 Ida was discovered when the Galileo spacecraft flew by the asteroid in 1993. Since then numerous binary asteroids and several triple asteroids have been detected. The mass ratio of the two components – called the "primary" and "secondary" of a binary system – is an important characteristic. Most binary asteroids have a large mass ratio, i.e. a relatively small satellite in orbit around the main component. Systems with a small minor-planet moon – also called "companion" or simply "satellite" – include 87 Sylvia, 107 Camilla, 45 Eugenia, 121 Hermione, 130 Elektra, 22 Kalliope, 283 Emma, 379 Huenna, 243 Ida and 4337 Arecibo (in order of decreasing primary size). Some binary systems have a mass ratio near unity, i.e., two components of similar mass. They include 90 Antiope, , and 69230 Hermes, with average compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPG/ESO Telescope
The MPG/ESO telescope is a 2.2-metre f/8.0 (17.6-metre) ground-based telescope at the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in La Silla, Chile. It was built by Zeiss and has been operating since 1984. It was on indefinite loan to the European Southern Observatory from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA). In October 2013 it was returned to the MPIA. Telescope time is shared between MPIA and MPE observing programmes, while the operation and maintenance of the telescope are ESO's responsibility. The telescope hosts three instruments: the 67-million-pixel Wide Field Imager with a field of view as large as the full Moon, which has taken many amazing images of celestial objects; GROND, the Gamma-Ray Burst Optical/Near-Infrared Detector, which chases the afterglows of the most powerful explosions in the universe, known as gamma-ray bursts; and the high-resolution spectrograph, FEROS, used to make detailed studies of stars. In November 2010 it was used to observe HIP 13044, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Function The Minor Planet Center is the official worldwide organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets (such as asteroids), calculating their orbits and publishing this information via the '' Minor Planet Circulars''. Under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory. The MPC runs a number of free online services for observers to assist them in observing minor planets and comets. The complete catalogue of minor planet orbits (sometimes referred to as the "Minor Planet Catalogue") may also be freely downloaded. In addition to astrometric data, the MPC collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy B
''Timothy B'' is the second studio solo album by Timothy B. Schmit, the bass guitarist and co-lead vocalist for the Eagles. The album was released in 1987 on MCA in the United States and Europe, three years after Schmit's debut solo album, '' Playin' It Cool'' and seven years after the demise of the Eagles. The album peaked at #106 on the ''Billboard'' 200 chart, and the single, " Boys Night Out", hit #25 on the ''Billboard'' Hot 100 chart, Schmit's best selling single. The album was produced by Richard Rudolph, and it was co-produced by Bruce Gaitsch. Background When Schmit was asked about why there were less notable musicians compared to his last album, he said "I decided to stay out of the real glamour studios and to keep the clientele down too. I did it on purpose mainly for less distractions. I mean I really knew what I wanted to do on this album and I decided purposely not to use my famous and semi-famous friends just to have it be more of what I can do on my own. And that' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LONEOS
Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search (LONEOS) was a project designed to discover asteroids and comets that orbit near the Earth. The project, funded by NASA, was directed by astronomer Ted Bowell of Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona. The LONEOS project began in 1993 and ran until the end of February 2008. Hardware LONEOS, in its final configuration, used a 0.6-meter f/1.8 Schmidt telescope, acquired from Ohio Wesleyan University in 1990, and a Lowell-built 16 megapixel CCD detector. This combination of instruments provided a field of view of 2.88 by 2.88 degrees (8.3 square degrees). It had a maximum nightly scan area of about 1,000 square degrees (covered four times). The instrument could cover the entire accessible dark sky in about a month. The CCD has detected asteroids as faint as visual magnitude 19.8 but its typical limiting visual magnitude was 19.3. The instrument is located at Lowell Observatory's dark sky site, Anderson Mesa Station, near Flagstaff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian A
Brian (sometimes spelled Bryan in English) is a male given name of Irish and Breton origin, as well as a surname of Occitan origin. It is common in the English-speaking world. It is possible that the name is derived from an Old Celtic word meaning "high" or "noble". For example, the element ''bre'' means "hill"; which could be transferred to mean "eminence" or "exalted one". The name is quite popular in Ireland, on account of Brian Boru, a 10th-century High King of Ireland. The name was also quite popular in East Anglia during the Middle Ages. This is because the name was introduced to England by Bretons following the Norman Conquest. Bretons also settled in Ireland along with the Normans in the 12th century, and 'their' name was mingled with the 'Irish' version. Also, in the north-west of England, the 'Irish' name was introduced by Scandinavian settlers from Ireland. Within the Gaelic speaking areas of Scotland, the name was at first only used by professional families of Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2101 Adonis
2101 Adonis, ''provisional designation'': , is an asteroid on an extremely eccentric orbit, classified as potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group. ''Adonis'' measures approximately in diameter. Discovered by Eugène Delporte at Uccle in 1936, it became a lost asteroid until 1977. It may also be an extinct comet and a source of meteor showers. It was named after Adonis from Greek mythology. Discovery ''Adonis'' was discovered on 12 February 1936, by Belgian astronomer Eugène Delporte at the Royal Observatory of Belgium in Uccle. After its initial discovery, which happened during a close approach with Earth, the asteroid was observed for two months, before it became a lost asteroid, as not enough observations could be made to calculate a sufficiently accurate orbit. It took 41 years until it was finally rediscovered by the American astronomer Charles Kowal in 1977, based on mathematical predictions made by Dr. Brian Marsden. Orbit and classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1862 Apollo
1862 Apollo is a stony asteroid, approximately 1.5 kilometers in diameter, classified as a near-Earth object (NEO). It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory on 24 April 1932, but lost and not recovered until 1973. It is the namesake and the first recognized member of the Apollo asteroids, a subgroup of NEOs which are Earth-crossers, that is, they cross the orbit of the Earth when viewed perpendicularly to the ecliptic plane (crossing an orbit is a more general term than actually intersecting it). In addition, since Apollo's orbit is highly eccentric, it crosses the orbits of Venus and Mars and is therefore called a Venus-crosser and Mars-crosser as well. Although Apollo was the first Apollo asteroid to be discovered, its official IAU-number (1862) is higher than that of some other Apollo asteroids such as 1566 Icarus, due to the fact that it was a lost asteroid for more than 40 years and other bodies were numbered in the meantime. The anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidelberg Observatory
Heidelberg (; Palatine German: '''') is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of students. Located about south of Frankfurt, Heidelberg is the fifth-largest city in Baden-Württemberg. Heidelberg is part of the densely populated Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region. Heidelberg University, founded in 1386, is Germany's oldest and one of Europe's most reputable universities. Heidelberg is a scientific hub in Germany and home to several internationally renowned research facilities adjacent to its university, including the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and four Max Planck Institutes. The city has also been a hub for the arts, especially literature, throughout the centuries, and it was designated a "City of Literature" by the UNESCO Creative Cities Network. Heidelberg was a seat of government of the former Electorate of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Moon
A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important because the determination of their orbits provides estimates on the mass and density of the primary, allowing insights into their physical properties that are generally not otherwise accessible. Several of the moons are quite large compared to their primaries: 90 Antiope, Mors–Somnus and Sila–Nunam (95%), Patroclus–Menoetius, Altjira and Lempo–Hiisi (90%, with Lempo–Paha at 50%). The largest known minor-planet moon in ''absolute'' size is Pluto's largest moon Charon, which itself has about half the diameter of Pluto. The first modern era mention of the possibility of an asteroid satellite was in connection with an occultation of the bright star Gamma Ceti by the asteroid 6 Hebe in 1977. The observer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation Period
The rotation period of a celestial object (e.g., star, gas giant, planet, moon, asteroid) may refer to its sidereal rotation period, i.e. the time that the object takes to complete a single revolution around its axis of rotation relative to the background stars, measured in sidereal time. The other type of commonly used rotation period is the object's synodic rotation period (or ''solar day''), measured in solar time, which may differ by a fraction of a rotation or more than one rotation to accommodate the portion of the object's orbital period during one day. Measuring rotation For solid objects, such as rocky planets and asteroids, the rotation period is a single value. For gaseous or fluid bodies, such as stars and gas giants, the period of rotation varies from the object's equator to its pole due to a phenomenon called differential rotation. Typically, the stated rotation period for a gas giant (such as Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) is its internal rotation period, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |