1st Century BCE on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century
The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century
 *
*
 *
*

 *
*
 The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century
The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero
A year zero does not exist in the Anno Domini (AD) calendar year system commonly used to number years in the Gregorian calendar (nor in its predecessor, the Julian calendar); in this system, the year is followed directly by year . However, the ...
; however, astronomical year numbering
Astronomical year numbering is based on AD/ CE year numbering, but follows normal decimal integer numbering more strictly. Thus, it has a year 0; the years before that are designated with negative numbers and the years after that are designated ...
does use a zero, as well as a minus sign, so "''2 BC''" is equal to "''year –1''". 1st century AD
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of t ...
(Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
) follows.
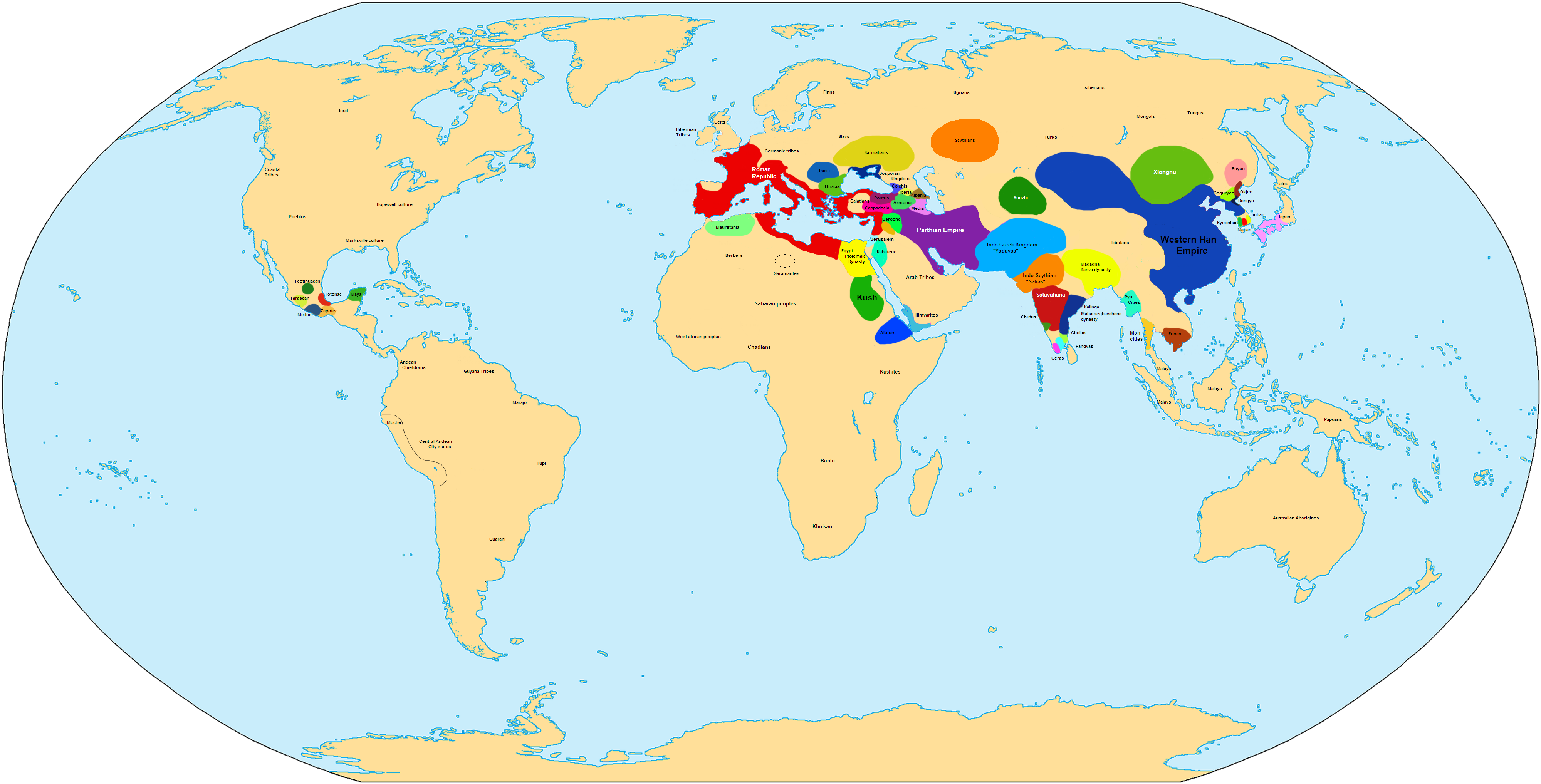
In the course of the century, all the remaining independent lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
were steadily brought under Roman control, being ruled either directly under governors or through puppet kings appointed by Rome. The Roman state itself was plunged into civil war several times, finally resulting in the marginalization of its 500-year-old Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
, and the embodiment of total state power in a single man—the Roman emperor.
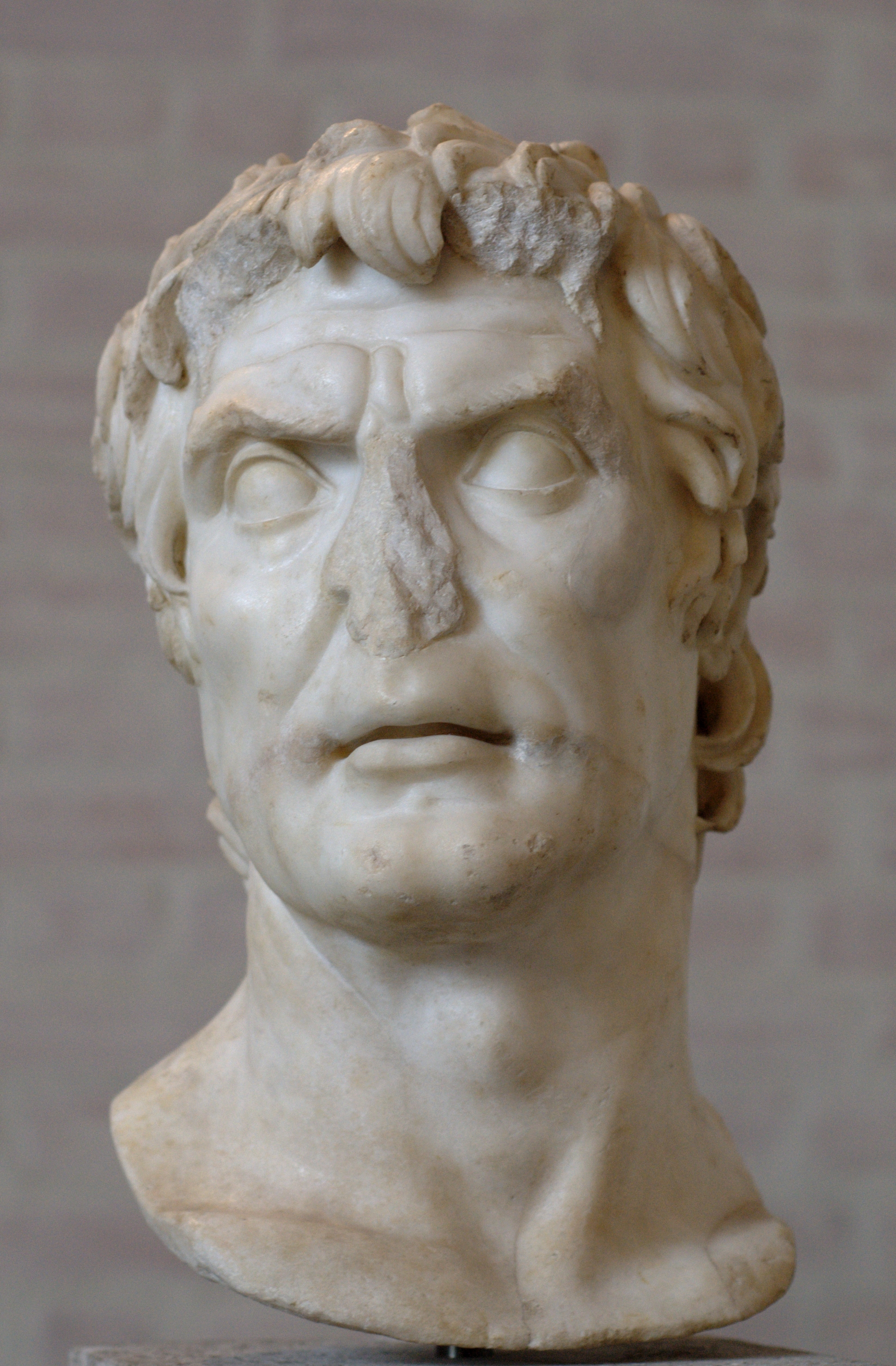
The internal turbulence that plagued Rome at this time can be seen as the death throes of the Roman Republic, as it finally gave way to the autocratic ambitions of powerful men like Sulla, Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
, Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
and Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
. Octavian's ascension to total power as the emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
is considered to mark the point in history where the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
ends and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
begins. Some scholars refer to this event as the Roman Revolution
''The Roman Revolution'' (1939) is a scholarly study of the final years of the ancient Roman Republic and the creation of the Roman Empire by Caesar Augustus. The book was the work of Sir Ronald Syme (1903–1989), a noted Tacitean scholar, and ...
. The birth of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
, the central figure of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, took place around the close of this century.
In the eastern mainland, the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
began to decline and the court of China was in chaos in the latter half of this century. Trapped in a difficult situation, the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
had to begin emigration to the west or attach themselves to the Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
.
Events
 *
* 97 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 97 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Crassus (or, less frequently, year 657 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the Fourth Year of Tianhan. The denominatio ...
: Ariarathes VIII is forced out of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
by Mithridates VI of Pontus, and dies soon afterwards.
* 96 BC: Cyrene is left to the people of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
by its ruler Ptolemy Apion
Ptolemy Apion or simply known as Apion ( grc, Πτολεμαῖος Ἀπίων; between 150 BC and 145 BC – 96 BC) was the last Greek King of Cyrenaica who separated it from the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, and in his last will bequeathed his ...
.
* 96 BC: King Alexander Jannaeus
Alexander Jannaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξανδρος Ἰανναῖος ; he, ''Yannaʾy''; born Jonathan ) was the second king of the Hasmonean dynasty, who ruled over an expanding kingdom of Judea from 103 to 76 BCE. A son of John Hyrcanus, ...
of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
wins the Siege of Gaza.
* 95 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 95 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crassus and Scaevola (or, less frequently, year 659 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the Second Year of Taishi. The denomination ...
: Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
becomes king of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
* 93 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 93 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flaccus and Herennius (or, less frequently, year 661 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 93 BC for this year has been ...
: Ariobarzanes I Philoromaios becomes king of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
with Roman backing.
* 91 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 91 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Philippus and Caesar (or, less frequently, year 663 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the Second Year of Zhenghe. The denominatio ...
: The assassination of Marcus Livius Drusus leads to the Social War (91–87 BC)
The Social War (from Latin , properly 'war of the allies'), also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought from 91 to 87 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies () in Italy. The Italian allies wanted Rom ...
in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
* 91 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 91 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Philippus and Caesar (or, less frequently, year 663 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the Second Year of Zhenghe. The denominatio ...
: Crown Prince Ju Revolt in China.

89 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 89 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Strabo and Cato (or, less frequently, year 665 '' Ab urbe condita'') and the Fourth Year of Zhenghe. The denomination 8 ...
: Mithridates VI of Pontus's invasion of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
leads to the First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridates ...
with the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
.
* 89 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 89 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Strabo and Cato (or, less frequently, year 665 '' Ab urbe condita'') and the Fourth Year of Zhenghe. The denomination 8 ...
: Valagamba
Valagamba (Sinhala: වළගම්බා), also known as Wattagamani Abhaya and Valagambahu, was a king of the Anuradhapura Kingdom of Sri Lanka. Five months after becoming king, he was overthrown by a rebellion and an invasion from South India, ...
of Anuradhapura
Anuradhapura ( si, අනුරාධපුරය, translit=Anurādhapuraya; ta, அனுராதபுரம், translit=Aṉurātapuram) is a major city located in north central plain of Sri Lanka. It is the capital city of North Central ...
gains control of all of Sri Lanka
* 88 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 88 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 666 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the First Year of Houyuan. The denomination 88 BC ...
: 80,000 Roman civilians killed in the Asiatic Vespers
The Asiatic Vespers (also known as the Asian Vespers, Ephesian Vespers, or the Vespers of 88 BC) refers to the massacres of Roman and other Latin-speaking peoples living in parts of western Anatolia in 88 BC by forces loyal to Mithridates VI Eupat ...
in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
* 87 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 87 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavius and Cinna/Merula (or, less frequently, year 667 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the Second Year of Houyuan. The denomi ...
: Emperor Wu of Han dies and is succeeded by his eight-year-old son Zhao, with Jin Midi
Jin Midi (134–86 BC) (, courtesy name Wengshu (翁叔), formally Marquess Jing of Du (秺敬侯), was a foreign prince and a warrior of the Western Han Dynasty. He was a Five Barbarians, Hu (胡) "barbarian" from a kingdom in central Ga ...
, Shangguang Jie and Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
as regents.
* 88 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 88 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 666 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the First Year of Houyuan. The denomination 88 BC ...
: Sulla becomes the first Roman general in history to march on Rome
* 87 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 87 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavius and Cinna/Merula (or, less frequently, year 667 ''Ab urbe condita'') and the Second Year of Houyuan. The denomi ...
: Civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
between the Roman consuls Cornelius Cinna and Octavius
* 86 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 86 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cinna and Marius/Flaccus (or, less frequently, year 668 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 86 BC for this year has be ...
: Siege of Athens ends with Roman conquest of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
.
* 86 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 86 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cinna and Marius/Flaccus (or, less frequently, year 668 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 86 BC for this year has be ...
: The death of the regent of China Jin Midi
Jin Midi (134–86 BC) (, courtesy name Wengshu (翁叔), formally Marquess Jing of Du (秺敬侯), was a foreign prince and a warrior of the Western Han Dynasty. He was a Five Barbarians, Hu (胡) "barbarian" from a kingdom in central Ga ...
unleashes the rivalry of his co-regents Shangguang Jie and Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
.
* 85 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 85 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cinna and Carbo (or, less frequently, year 669 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 85 BC for this year has been used s ...
: Sulla defeats the forces of Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
in Greece at the Battle of Orchomenus
The Battle of Orchomenus was fought in 85 BC between Rome and the forces of Mithridates VI of Pontus. The Roman army was led by Lucius Cornelius Sulla, while Mithridates' army was led by Archelaus. The Roman force was victorious, and Archel ...
* 85 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 85 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cinna and Carbo (or, less frequently, year 669 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 85 BC for this year has been used s ...
: Aretas III
Aretas III (; Nabataean Aramaic:
''Ḥārīṯat''; Ancient Greek: ) was king of the Nabataean kingdom from 87 to 62 BCE. Aretas ascended to the throne upon the death of his brother, Obodas I, in 87 BCE. During his reign, he extended his ki ...
of the Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
conquers Damascus.
* 83 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 83 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asiaticus and Norbanus (or, less frequently, year 671 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 83 BC for this year has bee ...
: Sulla makes peace with Mithridates VI and marches on Rome.
* 83-81 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 81 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Decula and Dolabella (or, less frequently, year 673 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 81 BC for this year has been u ...
: Lucius Licinius Murena wages the Second Mithridatic War.
* 82 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 82 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Carbo (or, less frequently, year 672 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 82 BC for this year has been used ...
: Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius (c. 126 – 73 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian peninsula. He had been a prominent member of the populist faction of Cinna and Marius. During the l ...
flees from Sulla to North Africa via Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
* c.83 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 83 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asiaticus and Norbanus (or, less frequently, year 671 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 83 BC for this year has bee ...
: Tigranes
Tigranes (, grc, Τιγράνης) is the Greek transliteration of the Old Iranian name ''*Tigrāna''. This was the name of a number of historical figures, primarily kings of Armenia.
The name of Tigranes, which was theophoric in nature, was u ...
of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
takes control of Syria after the implosion of the Seleucid dynasty.
* 81 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 81 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Decula and Dolabella (or, less frequently, year 673 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 81 BC for this year has been u ...
: Sulla is appointed dictator
A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power. A dictatorship is a state ruled by one dictator or by a small clique. The word originated as the title of a Roman dictator elected by the Roman Senate to rule the republic in tim ...
of the Roman state, and brings about major reforms.
* 80 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 80 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Metellus Pius (or, less frequently, year 674 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 80 BC for this year has bee ...
: Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius (c. 126 – 73 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian peninsula. He had been a prominent member of the populist faction of Cinna and Marius. During the l ...
invades Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
and sets up his own regime, beginning the Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war fought from 80 to 72 BC between a faction of Roman rebels ( Sertorians) and the government in Rome (Sullans). The war was fought on the Iberian Peninsula (called ''Hispania'' by the Romans) and was one of the ...
(80-72).
* 80 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 80 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Metellus Pius (or, less frequently, year 674 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 80 BC for this year has bee ...
: Conflict between the regents Shangguang Jie and Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
results in the destruction of the Shangguang clan and Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
becoming the ''de facto'' ruler of China.
* c.80 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 80 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Metellus Pius (or, less frequently, year 674 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 80 BC for this year has bee ...
: Maues
Maues (Greek: ; (epigraphic); Kharosthi: , , called , on the Taxila copper plate; also called , in the Mathura lion capital inscription,) was the first Indo-Scythian king, ruling from 98/85 to 60/57 BCE. He invaded India and establi ...
, King of the Sakas
The Saka (Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who histor ...
, conquers Gandhara and Taxila.

 *
* 77 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 77 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Brutus and Lepidus (or less frequently, year 677 AUC). The denomination 77 BC for this year has been used since the ear ...
: Fu Jiezi assassinated the king of Loulan
Loulan, also called Krorän or Kroraina ( zh, s=, t=, p=Lóulán < ''lo-lɑn'' < on behalf of the
*
 *
*

 *
*
 *
*
 *
*






Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
.
* c.75 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 75 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Octavius and Cotta (or, less frequently, year 679 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 75 BC for this year has been use ...
: Kanva dynasty
The Kanva dynasty or Kanvayana that overthrew the Shunga dynasty in parts of eastern and central India, and ruled from 73 BCE to 28 BCE.
Although the Puranic literature indicates that the Kanva Dynasty ruled from the former capital of the Sh ...
replaces the Shunga dynasty in Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
.
* 74 BC: Mithridates VI of Pontus disputes Nicomedes IV of Bithynia
Nicomedes IV Philopator ( grc-gre, Νικομήδης Φιλοπάτωρ) was the king of Bithynia from c. 94 BC to 74 BC. (''numbered as III. not IV.'') He was the first son and successor of Nicomedes III of Bithynia.
Life
Memnon of Heraclea wro ...
's bequest of his kingdom to the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
, beginning the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
.
* 74 BC: Emperor Zhao of Han
Emperor Zhao of Han (Liu Fuling 劉弗陵; 94 BC – 5 June 74 BC) was the emperor of the Western Han dynasty from 87 to 74 BC.
Emperor Zhao was the youngest son of Emperor Wu of Han. By the time he was born, Emperor Wu was already 62. Prince Fu ...
dies and is succeeded by the unsuitable Prince He of Changyi and then by Xuan. Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
continues to be ''de facto'' ruler of China.
* 73 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 73 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lucullus and Longinus (or, less frequently, year 681 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 73 BC for this year has bee ...
: A slave rebellion led by the escaped gladiator Spartacus
Spartacus ( el, Σπάρτακος '; la, Spartacus; c. 103–71 BC) was a Thracian gladiator who, along with Crixus, Gannicus, Castus, and Oenomaus, was one of the escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major slave uprisin ...
leads to the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directly ...
.
* 73-72 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 72 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Publicola and Lentulus (or, less frequently, year 682 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 72 BC for this year has be ...
: Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
defeats Mithridates at Tenedos
Tenedos (, ''Tenedhos'', ), or Bozcaada in Turkish, is an island of Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively, the island constitutes the Bozcaada district of Çanakkale Province. With an area of it is the third l ...
, Cyzicus
Cyzicus (; grc, Κύζικος ''Kúzikos''; ota, آیدینجق, ''Aydıncıḳ'') was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peni ...
, and the Rhyndacus and he flees east to Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
* 71 BC: Pompey the Great
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
ends the Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war fought from 80 to 72 BC between a faction of Roman rebels ( Sertorians) and the government in Rome (Sullans). The war was fought on the Iberian Peninsula (called ''Hispania'' by the Romans) and was one of the ...
(restoring Roman control of Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
) and the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directly ...
(restoring Roman control of southern Italy).
* 71 BC: Wusun
The Wusun (; Eastern Han Chinese *''ʔɑ-suən'' < (140 BCE < 436 BCE): *''Ɂâ-sûn'') were an ancient semi-
and China attack the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
.
69 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 69 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Hortensius and Metellus (or, less frequently, year 685 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 69 BC for this year has bee ...
: Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
invades Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
( Battle of Tigranocerta) and reestablishes the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
in Syria.
* 68 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 68 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Metellus/Vatia and Rex (or, less frequently, year 686 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 68 BC for this year has been ...
: Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
replaces Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
as leader of the Roman forces in the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
.
* 68 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 68 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Metellus/Vatia and Rex (or, less frequently, year 686 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 68 BC for this year has been ...
: Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
dies and Emperor Xuan of Han
Emperor Xuan of Han (Liu Xun 劉詢, né Liu Bingyi 劉病已; born 91 BC – 10 January 48 BC) was the tenth emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty, reigning from 74 to 48 BC, and was one of the only four Western Han emperors to receive a temple na ...
assumes full power. The Huo clan is eliminated over the following two years.
* 67 BC 67 may refer to:
* 67 (number)
* one of the years 67 BC, AD 67, 1967, 2067
* ''67'', a 1992 song by Love Battery from the album ''Between the Eyes''
* 67 (rap group), a drill music group from London
See also
* 67th Regiment (disambiguation)
* 67th ...
: Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
is given a three-year extraordinary command against the pirates plaguing the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
and defeats them in forty days.
* 66 BC: Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
drives Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
out of Asia Minor ( Battle of the Lycus).
* 66 BC: Aristobulus II
Aristobulus II (, grc, Ἀριστόβουλος ''Aristóboulos'') was the Jewish High Priest and King of Judea, 66 BCE to 63 BCE, from the Hasmonean dynasty.
Family
Aristobulus was the younger son of Alexander Jannaeus, King and High Pries ...
seizes power from John Hyrcanus II in Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
.
* 63 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 63 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cicero and Hybrida (or, less frequently, year 691 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 63 BC for this year has been use ...
: Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
commits suicide, ending the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
.
* 63 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 63 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cicero and Hybrida (or, less frequently, year 691 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 63 BC for this year has been use ...
: Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
denounces and defeats the Catilinarian conspiracy
The Catilinarian conspiracy (sometimes Second Catilinarian conspiracy) was an attempted coup d'état by Lucius Sergius Catilina (Catiline) to overthrow the Roman consuls of 63 BC – Marcus Tullius Cicero and Gaius Antonius Hybrida – a ...
.
* 63 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 63 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cicero and Hybrida (or, less frequently, year 691 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 63 BC for this year has been use ...
: Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
captures Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, and establishes Roman annexation of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
as a client kingdom. He also permanently abolishes Seleucid Syria
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
. Aristobulus II
Aristobulus II (, grc, Ἀριστόβουλος ''Aristóboulos'') was the Jewish High Priest and King of Judea, 66 BCE to 63 BCE, from the Hasmonean dynasty.
Family
Aristobulus was the younger son of Alexander Jannaeus, King and High Pries ...
of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
removed from power & John Hyrcanus II restored as Roman vassal.
* 62 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 62 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Silanus and Murena (or, less frequently, year 692 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 62 BC for this year has been use ...
: Nabataean kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom ( Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity.
The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, ...
becomes a Roman vassal.
* 61 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 61 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Calpurnianus and Messalla (or, less frequently, year 693 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 61 BC for this year has ...
: Orgetorix
Orgetorix was a wealthy aristocrat among the Helvetii, a Celtic-speaking people residing in what is now Switzerland during the consulship of Julius Caesar of the Roman Republic.
Planned migration
In 61 BC, he convinced the Helvetians to attempt ...
and the Helvetii's attempt to migrate into southwestern France leads Julius Caesar to take military action, beginning the Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
* 60 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 60 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Metellus Celer and Afranius (or, less frequently, year 694 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 60 BC for this year h ...
: Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
, Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, and Crassus form the First Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gaius Julius Caesar, Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus and Marcus Licinius Crassus. The constitution of the Roman republic had many ve ...
* c. 60 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 60 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Metellus Celer and Afranius (or, less frequently, year 694 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 60 BC for this year h ...
: The Sakas
The Saka (Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who histor ...
conquer Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
.
50s BC
This article concerns the period 59 BC – 50 BC.
Significant people
* Julius Caesar, Roman politician and general (lived 100– 44 BC)
* Pharaoh Cleopatra VII of Egypt (lived 70/ 69–30 BC, reigned 51–30 BC)—meets Julius Caesar and late ...
58 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 58 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Gabinius (or, less frequently, year 696 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 58 BC for this year has been us ...
: Battle of Bibracte
The Battle of Bibracte was fought between the Helvetii and six Roman legions, under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. It was the second major battle of the Gallic Wars.
Prelude
The Helvetii, a confederation of Gallic tribes, had begun a total ...
- Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
conquers the Helvetii
* 58 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 58 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Gabinius (or, less frequently, year 696 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 58 BC for this year has been us ...
: Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
invade Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and are defeated by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
at Battle of Vosges (58 BC)
The Battle of Vosges, also referred to as the Battle of Vesontio, was fought on September 14,Alex Schweizer, Allgemeine schweizerische Militärzeitung, 1903, 31. Januar 202/ref> 58 BC between the Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe of the Suebi, un ...
.
* 58 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 58 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Gabinius (or, less frequently, year 696 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 58 BC for this year has been us ...
: Clodius
Clodius is an alternate form of the Roman '' nomen'' Claudius, a patrician ''gens'' that was traditionally regarded as Sabine in origin. The alternation of ''o'' and ''au'' is characteristic of the Sabine dialect. The feminine form is Clodia.
R ...
becomes the leading figure in Roman urban politics. Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
goes into exile.
* 58 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 58 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Gabinius (or, less frequently, year 696 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 58 BC for this year has been us ...
: Huhanye
Huhanye (), born Jihoushan (), was a Chanyu of the Xiongnu Empire, the son of Xulüquanqu Chanyu. He rebelled in 59 BC with the aid of Wushanmu and Woyanqudi Chanyu soon committed suicide, leaving the Xiongnu torn apart by factional strife. By 55 ...
rebels against his distant cousin Woyanqudi Chanyu of the Xiongyu, beginning the Xiongnu civil war.
* 57 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 57 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. Contemporaneously, in the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Metellus (or, less frequently, year 697 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination ...
: Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
invades and defeats the Belgae at the Battle of the Sabis
The Battle of the Sabis, also (arguably erroneously) known as the Battle of the Sambre or the Battle against the Nervians (or Nervii), was fought in 57 BC near modern Saulzoir in Northern France, between Caesar's legions and an association of B ...
.
* 57 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 57 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. Contemporaneously, in the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Metellus (or, less frequently, year 697 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination ...
: Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
recalled from exile through the machinations of Milo
Milo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Milo'' (magazine), a strength sports magazine
*'' Milo: Sticky Notes and Brain Freeze'', a 2011 children's novel by Alan Silberberg
* ''Milo'' (video game), a first-person adventure-puzzle computer ga ...
and his mob.
* 57 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 57 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. Contemporaneously, in the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Metellus (or, less frequently, year 697 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination ...
: Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms ...
is founded in southeastern Korea (traditional date according to ''Samguk Sagi
''Samguk Sagi'' (, ''History of the Three Kingdoms'') is a historical record of the Three Kingdoms of Korea: Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla. The ''Samguk Sagi'' is written in Classical Chinese, the written language of the literati of ancient Korea, ...
'', a 12th-century historical document).
* 56 BC: Vikramaditya
Vikramaditya (IAST: ') was a legendary king who has been featured in hundreds of traditional stories including those in ''Baital Pachisi'' and '' Singhasan Battisi''. Many describe him as ruler with his capital at Ujjain (Pataliputra or Prati ...
defeats the Sakas
The Saka (Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who histor ...
at Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani pronunciation: �d͡ːʒɛːn is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain ...
and founds the Vikram Samvat
Vikram Samvat (IAST: ''Vikrama Samvat''; abbreviated VS) or Bikram Sambat B.S. and also known as the Vikrami calendar, is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent. Vikram Samvat is generally 57 years ahead of Gregorian Calend ...
calendar era.
* 55- 54 BC: Caesar's invasions of Britain.
* 54-53 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 53 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Calvinus (or, less frequently, year 701 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 53 BC for this year has been ...
: Ambiorix's revolt against Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
* 53 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 53 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Calvinus (or, less frequently, year 701 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 53 BC for this year has been ...
: The Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
ns defeat the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
under Crassus in the Battle of Carrhae
The Battle of Carrhae () was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae (present-day Harran, Turkey). An invading force of seven legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Liciniu ...
, ending the First Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gaius Julius Caesar, Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus and Marcus Licinius Crassus. The constitution of the Roman republic had many ve ...
.
* 53 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 53 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Calvinus (or, less frequently, year 701 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 53 BC for this year has been ...
: Clodius
Clodius is an alternate form of the Roman '' nomen'' Claudius, a patrician ''gens'' that was traditionally regarded as Sabine in origin. The alternation of ''o'' and ''au'' is characteristic of the Sabine dialect. The feminine form is Clodia.
R ...
dies during mob violence in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. His followers burn down the Senate house.
* 53 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 53 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Calvinus (or, less frequently, year 701 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 53 BC for this year has been ...
: Huhanye
Huhanye (), born Jihoushan (), was a Chanyu of the Xiongnu Empire, the son of Xulüquanqu Chanyu. He rebelled in 59 BC with the aid of Wushanmu and Woyanqudi Chanyu soon committed suicide, leaving the Xiongnu torn apart by factional strife. By 55 ...
Chanyu of the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
become a Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
vassal.
* 52 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 52 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pompeius and Scipio (or, less frequently, year 702 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 52 BC for this year has b ...
: Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
joins the Optimates
Optimates (; Latin for "best ones", ) and populares (; Latin for "supporters of the people", ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated academic dis ...
and becomes sole Consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
in Rome.
* 52 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 52 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pompeius and Scipio (or, less frequently, year 702 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 52 BC for this year has b ...
: Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; Greek: Οὐερκιγγετόριξ; – 46 BC) was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Despite ha ...
's revolt in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
(Battle of Gergovia
The Battle of Gergovia took place in 52 BC in Gaul at Gergovia, the chief oppidum (fortified town) of the Arverni. The battle was fought between a Roman Republican army, led by proconsul Julius Caesar, and Gallic forces led by Vercingetorix, wh ...
, Battle of Alesia).
*51 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 51 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcellus and Sulpicius (or, less frequently, year 703 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 51 BC for this year has be ...
: Siege of Uxellodunum
The siege of Uxellodunum was one of the last battles of the Gallic Wars. It took place in 51 BC at Uxellodunum. It was the last major military confrontation of the Gallic Wars and marked the pacification of Gaul under Roman rule. The battle re ...
marks the end of the Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
and the final Roman conquest of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
* Mid 1st century BC – East torana
''Torana'' ( sa, तोरण; '' awr-uh-nuh') is a free-standing ornamental or arched gateway for ceremonial purposes in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain architecture of the Indian subcontinent. Toranas can also be widely seen in Southeast Asia and ...
of the Great Stupa at Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen town, district headquarter and north-east of Bh ...
, is made. Early Andhra period. According to an inscription, it is sculpted by ivory carvers from the nearby town of Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from th ...
.

 *
* 49 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 49 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Marcellus (or, less frequently, year 705 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 49 BC for this year has be ...
: Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
crosses the Rubicon
The Rubicon ( la, Rubico; it, Rubicone ; rgn, Rubicôn ) is a shallow river in northeastern Italy, just north of Rimini.
It was known as Fiumicino until 1933, when it was identified with the ancient river Rubicon, famously crossed by Julius Ca ...
river and takes the city of Rome, beginning Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and ...
.
* 48 BC: Ptolemy XIII
Ptolemy XIII Theos Philopator ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Θεός Φιλοπάτωρ, ''Ptolemaĩos''; c. 62 BC – 13 January 47 BC) was Pharaoh of Egypt from 51 to 47 BC, and one of the last members of the Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC) ...
deposes his co-regent Cleopatra, beginning the Ptolemaic civil war in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
* 48 BC: Emperor Xuan of Han
Emperor Xuan of Han (Liu Xun 劉詢, né Liu Bingyi 劉病已; born 91 BC – 10 January 48 BC) was the tenth emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty, reigning from 74 to 48 BC, and was one of the only four Western Han emperors to receive a temple na ...
dies and is succeeded by his son Yuan. Wang Zhengjun
Wang Zhengjun (; 71 BC – 13 AD), officially Empress Xiaoyuan (孝元皇后), later and more commonly known as Grand Empress Dowager Wang, born in Yuancheng (modern Handan, Hebei), was an empress during the Western Han dynasty of China, who p ...
is made Empress, as a result of which her clan would eventually topple the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
.
* 48 BC: Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
decisively defeats Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
at the Battle of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. P ...
.
* 47 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 47 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Calenius and Vatinius (or, less frequently, year 707 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 47 BC for this year has been ...
: Cleopatra restored to the Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
throne after the Battle of the Nile (47 BC)
The Battle of the Nile in 47 BC saw the combined Roman– Egyptian armies of Julius Caesar and Cleopatra VII defeat those of the rival Queen Arsinoe IV and King Ptolemy XIII and secure the throne of Egypt.
Prelude
After pursuing his ...
* 47 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 47 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Calenius and Vatinius (or, less frequently, year 707 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 47 BC for this year has been ...
: Year of six kings in Anuradhapura
Anuradhapura ( si, අනුරාධපුරය, translit=Anurādhapuraya; ta, அனுராதபுரம், translit=Aṉurātapuram) is a major city located in north central plain of Sri Lanka. It is the capital city of North Central ...
in Sri Lanka
* 46 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 46 BC was the last year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Lepidus (or, less frequently, year 708 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 46 BC for this year has ...
: Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
takes control of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
at the Battle of Thapsus
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
.
* 46 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 46 BC was the last year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Lepidus (or, less frequently, year 708 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 46 BC for this year has ...
: China abandons control of Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
as a cost-cutting measure.
* 45 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 45 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Friday or Saturday (link will display the full calendar) (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) an ...
: Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
wins the Battle of Munda
The Battle of Munda (17 March 45 BC), in southern Hispania Ulterior, was the final battle of Caesar's civil war against the leaders of the Optimates. With the military victory at Munda and the deaths of Titus Labienus and Gnaeus Pompeius (elde ...
, regaining control of Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
and ending the Roman Civil War
This is a list of civil wars and organized civil disorder, revolts and rebellions in ancient Rome (Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic, and Roman Empire) until the fall of the Western Roman Empire (753 BCE – 476 CE). For the Eastern Roman Empire or B ...
.
* 44 BC: Julius Caesar named ''Dictator perpetuo
''Dictator perpetuo'' (English: "dictator in perpetuity"), also called ''dictator in perpetuum'', was the office held by Julius Caesar from between 26 January and 15 February during the year 44 BCE until his death on 15 March. By abandoning the t ...
''
* 44 BC: Julius Caesar re-founds Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
and Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government refor ...
as Roman colonies.
* 44 BC: Assassination of Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator, was assassinated by a group of senators on the Ides of March (15 March) of 44 BC during a meeting of the Senate at the Curia of Pompey of the Theatre of Pompey in Rome where the senators stabbed Caesar 23 t ...
on the Ides of March
The Ides of March (; la, Idus Martiae, Late Latin: ) is the 74th day in the Roman calendar, corresponding to 15 March. It was marked by several religious observances and was notable in Rome as a deadline for settling debts. In 44 BC, it became ...
.
* 43 BC: Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
, and Lepidus form the Second Triumvirate and take control of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
.
* 42 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 42 BC was either a common year starting on Monday, Tuesday or Wednesday or a leap year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further inform ...
: Second Triumvirate defeats Julius Caesar's assassins at the Battle of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Wars of the Second Triumvirate between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, at ...
* 41-40 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 40 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday or Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furthe ...
: Lucius Antonius and Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
fight the Perusine War
The Perusine War (also Perusian or Perusinian War, or the War of Perusia) was a civil war of the Roman Republic, which lasted from 41 to 40 BC. It was fought by Lucius Antonius and Fulvia to support Mark Antony against his political enemy Octav ...
* 40 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 40 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday or Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furthe ...
: Pacorus I
Pacorus I (also spelled Pakoros I; xpr, 𐭐𐭊𐭅𐭓; died 38 BC) was a Parthian prince, who was the son and heir of Orodes II (). The numismatist David Sellwood deduced that Pacorus ruled in . It is uncertain whether Pacorus ruled alongsid ...
conquers Roman Syria.
30s BC
This article concerns the period 39 BC – 30 BC.
Significant people
* Mark Antony, Roman politician and general ( 83–30 BC)
* Pharaoh Cleopatra VII of Egypt (lived 70/ 69–30 BC, reigned 51–30 BC)
* Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus, known ...
 *
* 38 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 38 BC was either a common year starting on Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Saturday, Sunday or Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further i ...
: Ventidius
Publius Ventidius ( 89–38 BC) was a Roman general and one of Julius Caesar's protégés. He won key victories against the Parthians which resulted in the deaths of key leaders – victories which redeemed the losses of Crassus and paved the w ...
defeats the Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
at the Battle of Mount Gindarus, reclaiming Roman Syria.
* 37 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 37 BC was either a common year starting on Monday, Tuesday or Wednesday or a leap year starting on Monday or Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furthe ...
: Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
becomes king of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
.
* 37 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 37 BC was either a common year starting on Monday, Tuesday or Wednesday or a leap year starting on Monday or Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furthe ...
: Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
invades Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
.
* 37 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 37 BC was either a common year starting on Monday, Tuesday or Wednesday or a leap year starting on Monday or Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furthe ...
: Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
is founded in southern Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
(traditional date according to ''Samguk Sagi'').
* 36 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 36 BC was either a common year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further inf ...
: Battle of Naulochus
The naval Battle of Naulochus ( it, Battaglia di Nauloco) was fought on 3 September 36 BC between the fleets of Sextus Pompeius and Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, off Naulochus, Sicily. The victory of Agrippa, admiral of Octavian, marked the end ...
: Second Triumvirate gains control of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
from the rebel Sextus Pompey
Sextus Pompeius Magnus Pius ( 67 – 35 BC), also known in English as Sextus Pompey, was a Roman military leader who, throughout his life, upheld the cause of his father, Pompey the Great, against Julius Caesar and his supporters during the las ...
.
* 36 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 36 BC was either a common year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further inf ...
: Battle of Zhizhi
The Battle of Zhizhi (郅支之戰) was fought in 36 BC between the Han Dynasty and the Xiongnu chieftain Zhizhi Chanyu. Zhizhi was defeated and killed. The battle was probably fought near Taraz on the Talas River in eastern Kazakhstan, whi ...
: Gan Yanshou and Chen Tang
Chen Tang (), born in Jining, Shandong, was a Han dynasty Chinese general famous for his battle against Zhizhi in 36 BC during the Han–Xiongnu War.
Battle of Zhizhi
At approximately 36 BC, the governor of the Western Regions was Gan Y ...
launch an unauthorised expedition which prevents the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
from extending their power into Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
.
* 34 BC
34 may refer to:
* 34 (number), the natural number following 33 and preceding 35
* one of the years 34 BC, AD 34, 1934, 2034
* ''34'' (album), a 2015 album by Dre Murray
* "#34" (song), a 1994 song by Dave Matthews Band
* "34", a 2006 song by ...
: Cleopatra and Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
perform the Donations of Alexandria
The Donations of Alexandria (Autumn 34 BC) were a political act by Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony in which they distributed lands held by Rome and Parthia amongst Cleopatra's children and granted them many titles, especially for Caesarion, son of ...
.
* 33 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 33 BC was either a common year starting on Saturday, Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) ...
: Emperor Yuan of Han
Emperor Yuan of Han (Liu Shi 劉奭; 75 BC – 8 July 33 BC) was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty. He reigned from 48 BC to 33 BC. Emperor Yuan promoted Confucianism as the official creed of the Chinese government. He appointed Confucius ...
dies and is succeeded by his son Cheng. Empress Wang Zhengjun
Wang Zhengjun (; 71 BC – 13 AD), officially Empress Xiaoyuan (孝元皇后), later and more commonly known as Grand Empress Dowager Wang, born in Yuancheng (modern Handan, Hebei), was an empress during the Western Han dynasty of China, who pla ...
becomes Empress Dowager and her brother is placed in command of the armed forces and administration.
* 32 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 32 BC was either a common year starting on Monday or Tuesday or a leap year starting on Sunday, Monday or Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further in ...
: Disagreements between Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
and Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
cause the outbreak of the Final War of the Roman Republic
The War of Actium (32–30 BC) was the last civil war of the Roman Republic, fought between Mark Antony (assisted by Cleopatra and by extension Ptolemaic Egypt) and Octavian. In 32 BC, Octavian convinced the Roman Senate to declare war on the E ...
.
* 31 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 31 BC was either a common year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Tuesday or Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for ...
: Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, ...
: Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
defeats troops under Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
and Cleopatra, becoming ''de facto'' ruler of the Roman empire.
* 30 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 30 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further inform ...
: Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
annexes Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
.
* c.30 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 30 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further inform ...
: Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the la ...
replaces the Kanva dynasty
The Kanva dynasty or Kanvayana that overthrew the Shunga dynasty in parts of eastern and central India, and ruled from 73 BCE to 28 BCE.
Although the Puranic literature indicates that the Kanva Dynasty ruled from the former capital of the Sh ...
in Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
.
20s BC
This article concerns the period 29 BC – 20 BC.
Significant people
* Caesar Augustus, Roman Emperor (27 BC–AD 14
__NOTOC__
AD 14 ( XIV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. A ...
 *
* 27 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 27 BC was either a common year starting on Sunday, Monday or Tuesday or a leap year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) ...
: The Roman Senate votes Octavian the title of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
. Augustus eventually assumes all authority formerly held by the Roman senate becoming the first emperor. This is traditionally taken as the end of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
and the beginning of the Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate.
...
(27 BC-AD 235).
* 25 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 25 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Wednesday or Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for fu ...
: Galatia annexed by Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
after the death of Amyntas of Galatia
Amyntas ( grc, Ἀμύντας), Tetrarch of the Trocmi was a King of Galatia and of several adjacent countries between 36 and 25 BC, mentioned by StraboStrabo, ''Geographia'', xii as contemporary with himself. He was the son of Brogitarus, kin ...
.
* Second half of 1st century BC – Chaitya
A chaitya, chaitya hall, chaitya-griha, (Sanskrit:''Caitya''; Pāli: ''Cetiya'') refers to a shrine, sanctuary, temple or prayer hall in Indian religions. The term is most common in Buddhism, where it refers to a space with a stupa and a rounded ...
hall at Karli, India
Karli (also Karla) is a town on the highway between Pune and Mumbai in the Mawal taluka of the Pune district in the southern Maharashtra of India. It is on a major trade route that runs from the Arabian Sea eastward, into the Deccan. Karli's l ...
, Maharashtra, is made. Early Andhra period.
10s BC
This article concerns the period 19 BC – 10 BC.
Significant people
* Caesar Augustus, Roman Emperor (27 BC–AD 14
__NOTOC__
AD 14 ( XIV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. ...
* 19 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 19 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday or Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furt ...
: Conclusion of major fighting in the Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what tod ...
marks the end of the Roman conquest of Hispania
* 18 BC: Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder Jum ...
is founded in mid-western Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
(traditional date according to ''Samguk Sagi'').
* 16-13 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 13 BC was either a common year starting on Friday, Common year starting on Saturday, Saturday or Common year starting on Sunday, Sunday or a leap year starting on Friday or Leap year starting on Saturday, Saturday (link will displ ...
: Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
establishes the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
''limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a ...
''.
* Maison Carrée
Maison (French for "house") may refer to:
People
* Edna Maison (1892–1946), American silent-film actress
* Jérémy Maison (born 1993), French cyclist
* Leonard Maison, New York state senator 1834–1837
* Nicolas Joseph Maison (1771–1840), Ma ...
and Pont du Gard
The Pont du Gard is an ancient Roman aqueduct bridge built in the first century AD to carry water over to the Roman colony of ''Nemausus'' ( Nîmes). It crosses the river Gardon near the town of Vers-Pont-du-Gard in southern France. The Po ...
built.
0s BC
The 0s BC were the period between 9 BC and 1 BC, the last nine years of the before Christ era. It is one of two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans that contain nine years, along with the 0s.
This is a list of events occurring in the 0s BC ordered ...
* 9 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 9 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further informat ...
: Pannonia annexed to the Roman empire by the future emperor Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
* 8 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 8 BC was either a common year starting on Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a ...
: Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the thron ...
becomes head of the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
armed forces and administration.
* 7 BC: Emperor Cheng of Han
Emperor Cheng of Han (51 BC – 17 April 7 BC) was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty ruling from 33 until 7 BC. He succeeded his father Emperor Yuan of Han. Under Emperor Cheng, the Han dynasty continued its growing disintegration as the em ...
dies and is succeeded by his nephew Ai. Empress Dowager Wang Zhengjun becomes Grand Empress Dowager
Grand empress dowager (also grand dowager empress or grand empress mother) ( (太皇太后)) was a title given to the grandmother, or a woman from the same generation, of a Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Vietnamese emperor in the Chinese cultural ...
and the Emperor's grandmother Consort Fu becomes Empress Dowager. Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the thron ...
resigns as head of the armed forces and administration. The reign is dominated by the destabilising intrigues of the Wang and Fu clans.
* c. 6 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 6 BC was a common year starting on Sunday or Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a common year starting on Friday of the Prolept ...
– 4 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 4 BC was a common year starting on Tuesday or Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a common year starting on Monday of the Pr ...
: Birth of Jesus of Nazareth (see Chronology of Jesus' birth and death, Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
, and Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the o ...
for further details).
* 4 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 4 BC was a common year starting on Tuesday or Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a common year starting on Monday of the Pr ...
: Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
annexed to the Roman province of Syria after the death of King Herod.
* 2 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 2 BC was a common year starting on Thursday or Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Pr ...
: Emperor Ai of Han
Emperor Ai of Han (27 BCE – 15 August 1 BCE) was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty. He ascended the throne when he was 20, having been made heir by his childless uncle Emperor Cheng, and he reigned from 7 to 1 BCE.
The people and the o ...
appoints his unpopular homosexual lover Dong Xian
Dong Xian ( 董 賢) (23 BCE(?) – 1 BCE) was a Han Dynasty politician who quickly rose from obscurity as a minor official to being the most powerful official in the imperial administration of Emperor Ai within a span of a few years, and he ...
as head of armed forces and administration.
* 1 BC: Emperor Ai of Han
Emperor Ai of Han (27 BCE – 15 August 1 BCE) was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty. He ascended the throne when he was 20, having been made heir by his childless uncle Emperor Cheng, and he reigned from 7 to 1 BCE.
The people and the o ...
dies and is succeeded by his eight year old cousin Ping
Ping may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Ping, a domesticated Chinese duck in the illustrated book '' The Story about Ping'', first published in 1933
* Ping, a minor character in ''Seinfeld'', an NBC sitcom
* Ping, a c ...
. Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the thron ...
is appointed regent and begins wide-ranging reforms.
Significant people




Politics (and relatives of political figures)
* Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, Roman politician *Agrippa Agrippa may refer to:
People Antiquity
* Agrippa (mythology), semi-mythological king of Alba Longa
* Agrippa (astronomer), Greek astronomer from the late 1st century
* Agrippa the Skeptic, Skeptic philosopher at the end of the 1st century
* Agri ...
, Roman statesman and general
* Ambiorix
Ambiorix (Gaulish "king of the surroundings", or "king-protector") ( 54–53 BC) was, together with Cativolcus, prince of the Eburones, leader of a Belgic tribe of north-eastern Gaul (Gallia Belgica), where modern Belgium is located. In the n ...
, prince of the Eburones
The Eburones (Greek: ) were a Gallic- Germanic tribe dwelling in the northeast of Gaul, in what is now the southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium and the German Rhineland, in the period immediately preceding the Roman conquest of the region. Thou ...
, Gallic tribal chief
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
Tribe
The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia.
Tribal societies are sometimes categorized a ...
* Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
, Roman general and politician
* Ariovistus, leader of the Suebi, Germanic tribal chief
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
Tribe
The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia.
Tribal societies are sometimes categorized a ...
* Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, Roman Emperor
* Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Serv ...
, Roman politician
* Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
, king of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
* Cassivellaunus
Cassivellaunus was a historical Celtic Britons, British military leader who led the defence against Caesar's invasions of Britain, Julius Caesar's second expedition to Britain in 54 BC. He led an alliance of tribes against Ancient Rome, Roman for ...
, Celtic Briton tribal chief
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
Tribe
The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia.
Tribal societies are sometimes categorized a ...
* Catiline
Lucius Sergius Catilina ( 108 BC – January 62 BC), known in English as Catiline (), was a Roman politician and soldier. He is best known for instigating the Catilinarian conspiracy, a failed attempt to violently seize control of the ...
, attempted to overthrow Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
* Cato the Younger
Marcus Porcius Cato "Uticensis" ("of Utica"; ; 95 BC – April 46 BC), also known as Cato the Younger ( la, Cato Minor), was an influential conservative Roman senator during the late Republic. His conservative principles were focused on the ...
, Roman politician
* Cleopatra VII of Egypt
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler. ...
, Ruler of Egypt
* Publius Clodius Pulcher
Publius Clodius Pulcher (93–52 BC) was a populist Roman politician and street agitator during the time of the First Triumvirate. One of the most colourful personalities of his era, Clodius was descended from the aristocratic Claudia gens, one ...
, Roman politician, demagogue
A demagogue (from Greek , a popular leader, a leader of a mob, from , people, populace, the commons + leading, leader) or rabble-rouser is a political leader in a democracy who gains popularity by arousing the common people against elites, ...
* Crassus, Roman general and politician
* Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
, king of Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
* Huo Guang
Huo Guang (; died 68 BC), courtesy name Zimeng (子孟), was a Chinese military general and politician who served as the dominant state official of the Western Han dynasty from 87 BCE until his death in 68 BCE. The younger half-brother of the re ...
, Chinese politician
* Juba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
, last king of Numidia
* Julia the Elder
Julia the Elder (30 October 39 BC – AD 14), known to her contemporaries as Julia Caesaris filia or Julia Augusti filia (Classical Latin: IVLIA•CAESARIS•FILIA or IVLIA•AVGVSTI•FILIA), was the daughter and only biological child of August ...
, Roman noblewoman, wife of Agrippa and Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
* Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
, Roman general and statesman
* Livia, Empress of Rome
This is a list of Roman and Byzantine empresses. A Roman empress was a woman who was the wife of a Roman emperor, the ruler of the Roman Empire.
The Romans had no single term for the position: Latin and Greek titles such as '' augusta'' (Gree ...
, mother of Tiberius
* Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
, Roman general and politician
* Maecenas
Gaius Cilnius Maecenas ( – 8 BC) was a friend and political advisor to Octavian (who later reigned as emperor Augustus). He was also an important patron for the new generation of Augustan poets, including both Horace and Virgil. During the re ...
, Roman politician and famous philanthropist
* Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
, Roman general and statesman
* Nalankilli
Nalankilli was one of the Tamil kings of Early Cholas of the Chola Dynasty mentioned in Sangam Literature. He is the son of Karikala Chola. Nalankilli is mentioned in context with a civil war between him and another Chola king Nedunkilli. The ...
, king of the early Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE ...
in South India
* Octavia the Younger
Octavia the Younger ( la, Octavia Minor; c. 66 BC – 11 BC) was the elder sister of the first Roman Emperor, Augustus (known also as Octavian), the half-sister of Octavia the Elder, and the fourth wife of Mark Antony. She was also the great-gra ...
, Roman noblewoman, sister of Augustus and wife of Mark Antony.
* Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, Roman general and politician
* Sextus Pompey
Sextus Pompeius Magnus Pius ( 67 – 35 BC), also known in English as Sextus Pompey, was a Roman military leader who, throughout his life, upheld the cause of his father, Pompey the Great, against Julius Caesar and his supporters during the las ...
, Roman general and son of Pompey
* Ptolemy XIII of Egypt
Ptolemy XIII Theos Philopator ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Θεός Φιλοπάτωρ, ''Ptolemaĩos''; c. 62 BC – 13 January 47 BC) was Pharaoh of Egypt from 51 to 47 BC, and one of the last members of the Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC ...
, pharaoh of Egypt
* Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius (c. 126 – 73 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian peninsula. He had been a prominent member of the populist faction of Cinna and Marius. During the l ...
, Roman statesman and general
* Sulla, Roman general and statesman
* Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
, king of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
* Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; Greek: Οὐερκιγγετόριξ; – 46 BC) was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Despite ha ...
, Gallic king and chieftain
* Xuan of Han, Chinese emperor
Religion
* Hillel the Elder, Jewishrabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
* Jesus of Nazareth, The Son of God in various beliefs
* John the Baptist
John the Baptist or , , or , ;Wetterau, Bruce. ''World history''. New York: Henry Holt and Company. 1994. syc, ܝܘܿܚܲܢܵܢ ܡܲܥܡܕ݂ܵܢܵܐ, Yoḥanān Maʿmḏānā; he, יוחנן המטביל, Yohanān HaMatbil; la, Ioannes Bapti ...
, Jewish prophet in Christianity and Islam
* Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
, according to the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
the foster father of Jesus.
* Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religious contexts
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also calle ...
, according to the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
and the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
the mother of Jesus.
* Zarmanochegas
Zarmanochegas ( el, Ζαρμανοχηγάς; according to Strabo) or Zarmarus (according to Dio Cassius) was a gymnosophist (naked philosopher), a monk of the Sramana tradition (possibly, but not necessarily a Buddhist) who, according to ancient ...
, Indian gymnosophist
Gymnosophists ( grc, γυμνοσοφισταί, ''gymnosophistaí'', i.e. "naked philosophers" or "naked wise men" (from Greek γυμνός ''gymnós'' "naked" and σοφία ''sophía'' "wisdom")) is the name given by the Greeks to certain anc ...
Literature, science, and philosophy
*Aemilius Macer
Aemilius Macer of Verona was a Roman didactic poet. He authored two poems, one on birds (''Ornithogonia''), a translation of a work by Boios, and the other on the antidotes against the poison of serpents (''Theriaca''), which he imitated from ...
, Roman didactic poet
* Alfenus Varus, Roman jurist
* Afranius, Roman dramatist
* Antiochus of Ascalon
Antiochus of Ascalon (; grc-gre, Άντίοχος ὁ Ἀσκαλώνιος; c. 125 – c. 68 BC) was an Academic philosopher. He was a pupil of Philo of Larissa at the Academy, but he diverged from the Academic skepticism of Philo and his p ...
, Syrian Greek philosopher
* Antipater of Thessalonica
Antipater of Thessalonica ( grc-gre, Ἀντίπατρος ὁ Θεσσαλονικεύς; c. 10 BC - c. AD 38) was a Greek epigrammatist of the Roman period.
Biography
Antipater lived during the latter part of the reign of Augustus, and perha ...
, Greek poet
* Apollonius of Citium, Cypriot Greek doctor
* Asinius Pollio, Roman poet and historian
* Asclepiodotus, Greek philosopher and writer on tactics
* Athenaeus Mechanicus
Athenaeus Mechanicus is the author of a book on siegecraft, ''On Machines'' ( grc, Περὶ μηχανημάτων '). He is identified by modern scholars with Athenaeus of Seleucia, a member of the Peripatetic school active in the mid-to-late 1 ...
, Greek writer on siege weapons
* Consort Ban
Consort Ban (c. 48 BCE – c. 2 BCE), or Ban Jieyu (), also known as Lady Ban (Pan), was a Chinese scholar and poet during the Western Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 23 CE). ''Jieyu'' (婕妤) was a title for a third-rank palace lady, one rank below th ...
, Chinese poet
* Calvus, Roman poet and orator
* Catullus
Gaius Valerius Catullus (; 84 - 54 BCE), often referred to simply as Catullus (, ), was a Latin poet of the late Roman Republic who wrote chiefly in the neoteric style of poetry, focusing on personal life rather than classical heroes. His ...
, Roman poet
* Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
, Roman writer, philosopher and politician
* Cornelius Gallus
Gaius Cornelius Gallus (c. 70 – 26 BC) was a Roman poet, orator and politician.
Birthplace
The identity of Gallus' purported birthplace, '' Forum Iulii'', is still uncertain, and it is based on the epithet "Foroiuliensis" that Jerome gave to h ...
, Roman poet and politician
* Cornelius Nepos
Cornelius Nepos (; c. 110 BC – c. 25 BC) was a Roman biographer. He was born at Hostilia, a village in Cisalpine Gaul not far from Verona.
Biography
Nepos's Cisalpine birth is attested by Ausonius, and Pliny the Elder calls him ''Pad ...
, Roman biographer
* Crinagoras of Mytilene
Crinagoras of Mytilene, also known as Crinogoras, sometimes spelt as Krinagorasis or Krinagoras (name in Greek: Κριναγόρας ὁ Μυτιληναῖος, 70 BC-18) was a Greek epigrammatist and ambassador, who lived in Rome as a court poet. ...
, Greek poet
* Didymus Chalcenterus
Didymus Chalcenterus (Latin; Greek: , ''Dídymos Chalkéderos'', "Didymus Bronze-Guts"; c. 63 BC – c. AD 10), was an Ancient Greek scholar and grammarian who flourished in the time of Cicero and Augustus.
Life
The epithet "Bronze-Guts" came f ...
, Alexandrian Greek grammarian
* Diodorus Siculus, Sicilian Greek historian
* Dionysius of Halicarnassus, Greek historian and grammarian
* Elephantis
Elephantis ( grc, Ἐλεφαντίς) (fl. late 1st century BC) was a Greek poet and physician apparently renowned in the classical world as the author of a notorious sex manual. Due to the popularity of courtesans taking animal names in classi ...
, Greek poet and medical writer
* Geminus
Geminus of Rhodes ( el, Γεμῖνος ὁ Ῥόδιος), was a Greek astronomer and mathematician, who flourished in the 1st century BC. An astronomy work of his, the ''Introduction to the Phenomena'', still survives; it was intended as an int ...
, Rhodian Greek astronomer and mathematician
* Helvius Cinna Gaius Helvius Cinna (died 20 March 44 BC) was an influential neoteric poet of the late Roman Republic, a little older than the generation of Catullus and Calvus. He was lynched at the funeral of Julius Caesar after being mistaken for an unrelated ...
, Roman poet
* Horace, Roman poet
* Huan Tan
Huan Tan (BC– AD28) was a Chinese philosopher, poet, and politician of the Western Han and its short-lived interregnum between AD9 and 23, known as the Xin Dynasty.
Life
Huan worked as an official under the administrations of Emperor Ai of ...
, Chinese poet, philosopher and politician
* Jing Fang
Jing Fang (, 78–37 BC), born Li Fang (), courtesy name Junming (), was born in present-day 東郡頓丘 (Puyang, Puyang, Henan) during the Han Dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD). He was a Chinese people, Chinese music theory, music theorist, ma ...
, Chinese mathematician and music theorist
* Marcus Antistius Labeo
Marcus Antistius Labeo (d. 10 or 11 AD) was a Roman jurist.
Marcus Antistius Labeo was the son of Pacuvius Labeo, a jurist who caused himself to be slain after the defeat of his party at Philippi. Since his name was different from his father's, ...
, Roman jurist
* Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
, Roman historian
* Liu Xiang, Chinese poet and librarian
* Liu Xin, Chinese astronomer, mathematician, and librarian
* Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus ( , ; – ) was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is the philosophical poem ''De rerum natura'', a didactic work about the tenets and philosophy of Epicureanism, and which usually is translated into En ...
, Roman poet and philosopher
* Meleager of Gadara
Meleager of Gadara ( grc-gre, Μελέαγρος ; fl. 1st century BC) was a poet and collector of epigrams. He wrote some satirical prose, now lost, and some sensual poetry, of which 134 epigrams survive.
Life
Meleager was the son of Eucrates, ...
, Syrian Greek poet and anthologist
* Nigidius Figulus
Publius Nigidius Figulus (c. 98 – 45 BC) was a scholar of the Late Roman Republic and one of the praetors for 58 BC. He was a friend of Cicero, to whom he gave his support at the time of the Catilinarian conspiracy. Nigidius sided with the Optim ...
, Roman philosopher and polymath
* Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
, Roman poet
* Parmenion
Parmenion (also Parmenio; grc-gre, Παρμενίων; c. 400 – 330 BC), son of Philotas, was a Macedonian general in the service of Philip II of Macedon and Alexander the Great. A nobleman, Parmenion rose to become Philip's chief milita ...
, Greek poet
* Parthenius of Nicaea Parthenius of Nicaea ( el, Παρθένιος ὁ Νικαεύς) or Myrlea ( el, ὁ Μυρλεανός) in Bithynia was a Greek grammarian and poet. According to the '' Suda'', he was the son of Heraclides and Eudora, or according to Hermippus ...
, Bithynian Greek poet and grammarian
* Philodemus, Syrian Greek poet and philosopher
* Lucius Pomponius, Roman dramatist
* Pompeius Trogus
Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus also anglicized as was a Gallo-Roman historian from the Celtic Vocontii tribe in Narbonese Gaul who lived during the reign of the emperor Augustus. He was nearly contemporary with Livy.
Life
Pompeius Trogus's grandfat ...
, Roman historian
* Marcus Porcius Latro
Marcus Porcius Latro (died 4 BC) was a celebrated Roman rhetorician who is considered one of the founders of scholastic rhetoric.
He was born in Roman Spain, and is mentioned often in the works of his friend and contemporary Seneca the Elder, with ...
, Roman orator
* Posidonius
Posidonius (; grc-gre, Ποσειδώνιος , "of Poseidon") "of Apameia" (ὁ Ἀπαμεύς) or "of Rhodes" (ὁ Ῥόδιος) (), was a Greek politician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, historian, mathematician, and teacher nativ ...
, Syrian Greek philosopher, geographer, and polymath
* Propertius, Roman poet
* Rutilius Lupus
The gens Rutilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens appear in history beginning in the second century BC. The first to obtain the consulship was Publius Rutilius Rufus in 105 BC.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biograph ...
, Roman rhetorician
* Publilius Syrus
__NOTOC__
Publilius Syrus (fl. 85–43 BC), was a Latin writer, best known for his sententiae. He was a Syrian from Antioch who was brought as a slave to Roman Italy. Syrus was brought to Rome on the same ship that brought a certain Manilius, a ...
, Syrian/Roman poet and dramatist
* Sallust
Gaius Sallustius Crispus, usually anglicised as Sallust (; 86 – ), was a Roman historian and politician from an Italian plebeian family. Probably born at Amiternum in the country of the Sabines, Sallust became during the 50s BC a partisan ...
, Roman historian, politician
* Sima Qian, Chinese historian, father of Chinese historiography
* Sisenna Lucius Cornelius Sisenna (c. 120 – 67 BC) was a Roman soldier, historian, and annalist.
Life
Little is known of Sisenna's life or family. The first Cornelius Sisenna (perhaps Lucius' grandfather or great-grandfather) appears as urban prae ...
, Roman historian
* Strabo, Pontian Greek geographer and historian
* Themison of Laodicea Themison of Laodicea ( el, Θεμίσων, ''gen.'' Θεμίσωνος; 123 BC - 43 BC) was the founder of the Methodic school of medicine, and one of the most eminent physicians of his time.
Biography
Themison was a native of Laodicea in Syria, an ...
, Syrian Greek doctor, founder of Methodic school
The Methodic school of medicine (''Methodics'', ''Methodists'', or ''Methodici'', el, Μεθοδικοί) was a school of medicine in ancient Greece and Rome. The Methodic school arose in reaction to both the Empiric school and the Dogmatic sch ...
of medicine
* Tibullus
Albius Tibullus ( BC19 BC) was a Latin poet and writer of elegies. His first and second books of poetry are extant; many other texts attributed to him are of questionable origins.
Little is known about the life of Tibullus. There are only a f ...
, Roman poet
* Tryphon
Tryphon or Trypho ( el, Τρύφων, ''gen''.: Τρύφωνος; c. 60 BC – 10 BC) was a Greek grammarian who lived and worked in Alexandria. He was a contemporary of Didymus Chalcenterus.
He wrote several specialized works on aspects of lan ...
, Alexandrian Greek grammarian
* Valerius Antias
Valerius Antias ( century BC) was an ancient Roman annalist whom Livy mentions as a source. No complete works of his survive but from the sixty-five fragments said to be his in the works of other authors it has been deduced that he wrote a chroni ...
, Roman historian
* Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
, Roman polymath
* Verrius Flaccus
Marcus Verrius Flaccus (c. 55 BCAD 20) was a Roman grammarian and teacher who flourished under Augustus and Tiberius.
Life
He was a freedman, and his manumitter has been identified with Verrius Flaccus, an authority on pontifical law; but for c ...
, Roman grammarian
* Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
, Roman poet
* Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
, Roman writer, architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
and engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limit ...
* Wang Bao, Chinese poet
* Yang Xiong, Chinese poet and philosopher
* Sangam literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes ...
, ancient Tamil literary works.
Others
* Crixus, Gallic gladiator and rebel leader *Jin Midi
Jin Midi (134–86 BC) (, courtesy name Wengshu (翁叔), formally Marquess Jing of Du (秺敬侯), was a foreign prince and a warrior of the Western Han Dynasty. He was a Five Barbarians, Hu (胡) "barbarian" from a kingdom in central Ga ...
, Chinese official
* Spartacus
Spartacus ( el, Σπάρτακος '; la, Spartacus; c. 103–71 BC) was a Thracian gladiator who, along with Crixus, Gannicus, Castus, and Oenomaus, was one of the escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major slave uprisin ...
, gladiator and insurgent leader of the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directly ...
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
* TheAntikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-yea ...
is made.
*The Chinese ''Ji Jiu Pian'' dictionary published in 40 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 40 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday or Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for furthe ...
during the Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
is the earliest known reference to the hydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
-powered trip hammer
A trip hammer, also known as a tilt hammer or helve hammer, is a massive powered hammer. Traditional uses of trip hammers include pounding, wikt:decorticate, decorticating and polishing of grain in agriculture. In mining, trip hammers were used f ...
device.
* 36 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 36 BC was either a common year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further inf ...
: Maya numeral for Zero was written in Chiapa, it is the oldest zero in The Americas.
Sovereign states
See: List of sovereign states in the 1st century BC.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:1st Century Bc -9 -99