1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines' Luzon Volcanic Arc was the second-largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century, behind only the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in
 On July 16, 1990, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck northern Central Luzon and the Cordilleras. This was the largest earthquake recorded in 1990, comparable in size to the
On July 16, 1990, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck northern Central Luzon and the Cordilleras. This was the largest earthquake recorded in 1990, comparable in size to the  In early June, tiltmeter measurements had shown that the volcano was gradually inflating, evidently due to fast-growing amounts of magma filling the
In early June, tiltmeter measurements had shown that the volcano was gradually inflating, evidently due to fast-growing amounts of magma filling the
 A small blast at 03:41 PST on June 12 marked the beginning of a new, more violent phase of the eruption. A few hours later the same day, massive blasts lasting about half an hour generated big eruption columns, which quickly reached heights of over and which generated large
A small blast at 03:41 PST on June 12 marked the beginning of a new, more violent phase of the eruption. A few hours later the same day, massive blasts lasting about half an hour generated big eruption columns, which quickly reached heights of over and which generated large  The final, climactic eruption of Mount Pinatubo began at 13:42 PST on June 15. It caused numerous major
The final, climactic eruption of Mount Pinatubo began at 13:42 PST on June 15. It caused numerous major  The volcanic column from the crater covered an area of some , bringing total darkness to much of Central Luzon for 36 hours. Almost all of the island received some wet ash fall, which formed a heavy, rain-saturated snow-like blanket. Tephra fell over most of the
The volcanic column from the crater covered an area of some , bringing total darkness to much of Central Luzon for 36 hours. Almost all of the island received some wet ash fall, which formed a heavy, rain-saturated snow-like blanket. Tephra fell over most of the
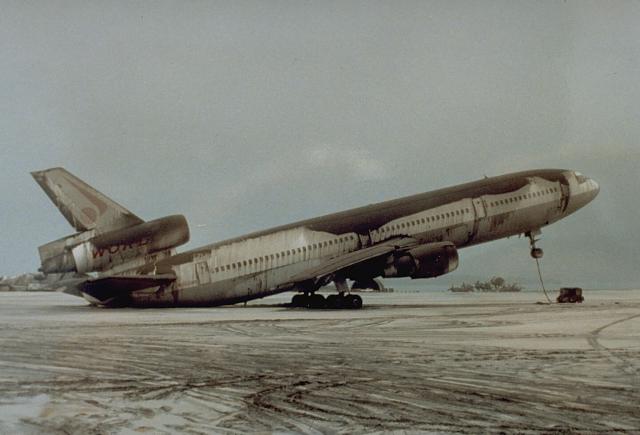 At least 16 commercial aircraft had damaging in-flight encounters with the ash cloud ejected by the June 15 eruption, and many grounded aircraft were also significantly damaged. In-flight encounters caused loss of power to one engine on each of the two aircraft. Ten engines were damaged and replaced, including all three engines of one
At least 16 commercial aircraft had damaging in-flight encounters with the ash cloud ejected by the June 15 eruption, and many grounded aircraft were also significantly damaged. In-flight encounters caused loss of power to one engine on each of the two aircraft. Ten engines were damaged and replaced, including all three engines of one


 Many
Many
 The eruption of Pinatubo severely hampered the
The eruption of Pinatubo severely hampered the
 The
The
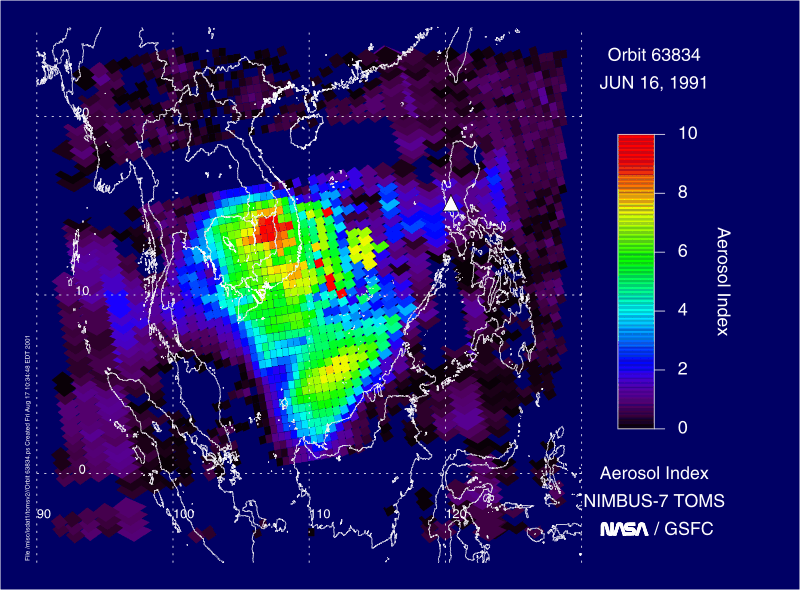 This very large stratospheric injection resulted in a
This very large stratospheric injection resulted in a
/ref> 1. Resettlement 2. Livelihood programs focused on agriculture and industry (quick-generating income opportunities to affected families) 3. Basic social services 4. Infrastructure rehabilitation and reconstruction
File:4259jfDapdap Halls Mabalacat Pampangafvf 20.JPG, Madapdap Resettlement Center in
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
. Eruptive activity began on April 2 as a series of phreatic explosions from a fissure that opened on the north side of Mount Pinatubo. Seismograph
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output ...
s were set up and began monitoring the volcano for earthquakes. In late May, the number of seismic events under the volcano fluctuated from day-to-day. Beginning June 6, a swarm of progressively shallower earthquakes accompanied by inflationary tilt on the upper east flank of the mountain, culminated in the extrusion of a small lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on ...
.
On June 12, the volcano’s first spectacular eruption sent an ash column into the atmosphere. Additional explosions occurred overnight and the morning of June 13. Seismic activity during this period became intense. When even more highly gas-charged magma reached Pinatubo's surface on June 15, the volcano exploded, sending an ash cloud into the atmosphere. Volcanic ash and pumice blanketed the countryside. Huge pyroclastic flows roared down the flanks of Pinatubo, filling once-deep valleys with fresh volcanic deposits as much as thick. The eruption removed so much magma and rock from beneath the volcano that the summit collapsed to form a small caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
across.
Fine ash from the eruption fell as far away as the Indian Ocean and satellites tracked the ash cloud as it traveled several times around the globe. At least 16 commercial jets inadvertently flew through the drifting ash cloud, sustaining about $100 million in damage. With the ashfall came darkness and the sounds of lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extreme ...
s rumbling down nearby river valleys. Several smaller lahars washed through the Clark Air Base
Clark Air Base is a Philippine Air Force base on Luzon Island in the Philippines, located west of Angeles City, about northwest of Metro Manila. Clark Air Base was previously a United States military facility, operated by the U.S. Air Forc ...
, flowing across the base in enormously powerful sheets, slamming into buildings and scattering cars. Nearly every bridge within of Mount Pinatubo was destroyed. Several lowland towns were flooded or partially buried in mud. More than 840 people were killed from the collapse of roofs under wet heavy ash and several more were injured.
Rain continued to create hazards over the next several years, as the volcanic deposits were remobilized into secondary mudflows. Damage to bridges, irrigation-canal systems, roads, cropland, and urban areas occurred in the wake of each significant rainfall. Many more people were affected for much longer by rain-induced lahars than by the eruption itself.
Build-up and evacuations
 On July 16, 1990, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck northern Central Luzon and the Cordilleras. This was the largest earthquake recorded in 1990, comparable in size to the
On July 16, 1990, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck northern Central Luzon and the Cordilleras. This was the largest earthquake recorded in 1990, comparable in size to the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
and the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. Its epicenter was in the municipality of Rizal, Nueva Ecija, about northeast of Pinatubo, and faulted northwest-southeast through three provinces. It also followed the Philippine Fault System west as far as Baguio, which was devastated, and is located about north-northeast of Pinatubo, leading volcanologist
A volcanologist, or volcano scientist, is a geologist who focuses on understanding the formation and eruptive activity of volcanoes. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, sometimes active ones, to observe and monitor volcanic eruptions, col ...
s to speculate that it might ultimately have triggered the 1991 eruption, although this is impossible to prove conclusively.
Two weeks after the earthquake, local residents reported steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporizat ...
coming from the volcano, but scientists who visited there in response found only small rockslide
A rockslide is a type of landslide caused by rock failure in which part of the bedding plane of failure passes through compacted rock and material collapses ''en masse'' and not in individual blocks. Note that a rockslide is similar to an avalanc ...
s rather than any pre-eruptive activity. On March 15, 1991, a succession of earthquakes were felt by villagers on the northwestern side of the volcano. Further earthquakes of increasing intensity were felt over the next two weeks, and it became clear some kind of volcanic activity was likely.
On April 2, the volcano woke up, with phreatic eruptions occurring near the summit along a long fissure
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes.
Ground fissure
A ...
. Over the next few weeks, small eruptions continued, dusting the surrounding areas with volcanic ash. Seismographs recorded hundreds of small earthquakes every day. Scientists immediately installed monitoring equipment and analyzed the volcano for clues as to its previous eruptive history. Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
of charcoal found in old volcanic deposits revealed the last three major explosive eruption periods in recent millennia
A millennium (plural millennia or millenniums) is a period of one thousand years, sometimes called a kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting point (ini ...
, about 5500, 3500 and 500 years ago. Geological mapping showed that much of the surrounding plains were formed by lahar flood deposits from previous eruptions.
Volcanic activity increased throughout May. Measurements of sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide ( IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic ...
emissions showed a rapid increase from per day by May 13 to per day by May 28. This implied that there was a rising column of fresh magma beneath the volcano. After May 28, the amount of being emitted decreased substantially, raising fears that the degassing of the magma had been blocked somehow, leading to a pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
build-up in the magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it up ...
and a high likelihood of violent explosive eruptions.
 In early June, tiltmeter measurements had shown that the volcano was gradually inflating, evidently due to fast-growing amounts of magma filling the
In early June, tiltmeter measurements had shown that the volcano was gradually inflating, evidently due to fast-growing amounts of magma filling the reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
beneath the summit. At the same time, seismic activity, previously concentrated at a depth of a few kilometers below a point about northwest of the summit, shifted to shallow depths just below the summit. Such an event is a precursor of volcano tectonic earthquakes.
Given all the signs that a very large eruption was imminent, the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology
The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS, ; tl, Surian ng Pilipinas sa Bulkanolohiya at Sismolohiya) is a Philippine national institution dedicated to provide information on the activities of volcanoes, earthquakes, and ...
– assisted by the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
– worked to convince local inhabitants of the high severity of the threat. A false warning might have led to cynicism about any later warnings, but delaying a warning until an eruption began might lead to thousands of deaths, so the volcanologists were under some pressure to deliver a timely and accurate assessment of the volcanic risk.
Three successive evacuation zones were defined, the innermost containing everything within of the volcano's summit, the second extending from the summit, and the third extending from from the summit (Clark Air Base and Angeles City
, anthem = Himno ning Angeles (Angeles Hymn)
, subdivision_type3 = District
, subdivision_name3 =
, established_title = Settled
, established_date = 1796
, established_title1 = Charter ...
were in this zone). The and zones had a total population of about 40,000 inhabitants, while some more 331,000 inhabitants lived in the zone.
Five stages of volcanic alert were defined, from level 1 (low level seismic disturbances) up to level 5 (major eruption in progress). Daily alerts were issued stating the alert level and associated danger area, and the information was announced in major regional and national newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sport ...
s, on radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transm ...
and television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication Media (communication), medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of Transmission (telecommunications), television tra ...
stations, by nongovernmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
s (NGOs) and directly to the endangered inhabitants.
Many of the Aeta
The Aeta (Ayta ), Agta, or Dumagat, are collective terms for several Filipino indigenous peoples who live in various parts of the island of Luzon in the Philippines. They are considered to be part of the Negrito ethnic groups and share commo ...
s who lived on the slopes of the volcano left their villages of their own volition when the first blasts began in April, gathering in a village about from the summit. They moved to increasingly distant settlements as the eruptions escalated, some Aetas moving up to nine times in the two months before the colossal eruption.
The first formal evacuations were ordered for the zone on April 7. Evacuation of the zone was ordered when a level 4 alert was issued on June 7. A level 5 alert triggered evacuation of the zone on June 13, and in all some 60,000 people had left the area within of the volcano before June 15. Most people temporarily relocated to Metro Manila
Metropolitan Manila (often shortened as Metro Manila; fil, Kalakhang Maynila), officially the National Capital Region (NCR; fil, link=no, Pambansang Punong Rehiyon), is the capital region, seat of government and one of three List of metrop ...
, with some 30,000 using the Amoranto Velodrome in Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 2,960,048 people. It was foun ...
as an evacuee camp.
On June 7, the first magmatic eruptions took place with the formation of a lava dome at the summit of the volcano. The dome grew substantially over the next five days, reaching a maximum diameter of about and a height of .
Escalation of eruption
 A small blast at 03:41 PST on June 12 marked the beginning of a new, more violent phase of the eruption. A few hours later the same day, massive blasts lasting about half an hour generated big eruption columns, which quickly reached heights of over and which generated large
A small blast at 03:41 PST on June 12 marked the beginning of a new, more violent phase of the eruption. A few hours later the same day, massive blasts lasting about half an hour generated big eruption columns, which quickly reached heights of over and which generated large pyroclastic surge
A pyroclastic surge is a fluidised mass of turbulent gas and rock fragments that is ejected during some volcanic eruptions. It is similar to a pyroclastic flow but it has a lower density or contains a much higher ratio of gas to rock, which makes ...
s extending up to from the summit in some river valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
s. Fourteen hours later, a 15-minute blast hurled volcanic matter to heights of . Friction in the up-rushing ash column generated abundant volcanic lightning.
A third large eruption began at 08:41 on June 13, after an intense swarm of small earthquakes over the previous two hours. It lasted about five minutes, and the eruption column once again reached . After three hours of quiet, seismic activity began, growing more and more intense over the next twenty-four hours, until a three-minute eruptive blast generated a high eruption column at 13:09 on June 14.
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they re ...
fall from these four large eruptions was extensive to the southwest of the volcano. Two hours after the last of these four explosions, a series of eruptions began which lasted for the next twenty-four hours, and which saw the production of much larger pyroclastic flows and surges which travelled several kilometres down river valleys on the flanks of the volcano.
Dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained ( aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhy ...
was the dominant igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or l ...
making up the tephra in these eruptions and in the following climactic event. The most abundant phenocryst
300px, Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter 2.3 cm) for scale.
A phenocryst is an early forming, relati ...
minerals were hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic ro ...
and plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more pro ...
, but an unusual phenocryst mineral was also present – the calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris, ...
called anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with t ...
. The dacite magma was more oxidized than most magmas, and the sulfur-rich nature of the eruption was probably causally related to the redox state.
 The final, climactic eruption of Mount Pinatubo began at 13:42 PST on June 15. It caused numerous major
The final, climactic eruption of Mount Pinatubo began at 13:42 PST on June 15. It caused numerous major earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s due to the collapse of the summit and the creation of a caldera in diameter, reducing the peak from to .
All the seismographs close to Clark Air Base
Clark Air Base is a Philippine Air Force base on Luzon Island in the Philippines, located west of Angeles City, about northwest of Metro Manila. Clark Air Base was previously a United States military facility, operated by the U.S. Air Forc ...
had been rendered completely inoperative by 14:30, mostly by super-massive pyroclastic surges. Intense atmospheric
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
pressure variation was also recorded.
On the same day, Typhoon Yunya, locally named Diding, struck the island, with its center passing about north of the volcano. The typhoon rains mostly obscured the eruption, but measurements showed that ash was ejected to a height of by the most violent phase of the eruption, which lasted about three hours. Pyroclastic surges poured from the summit, reaching as far as away from their origin point. Typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
rains and flooding, mixed with the ash deposits, caused a messy rain of mud and massive lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extreme ...
s.
 The volcanic column from the crater covered an area of some , bringing total darkness to much of Central Luzon for 36 hours. Almost all of the island received some wet ash fall, which formed a heavy, rain-saturated snow-like blanket. Tephra fell over most of the
The volcanic column from the crater covered an area of some , bringing total darkness to much of Central Luzon for 36 hours. Almost all of the island received some wet ash fall, which formed a heavy, rain-saturated snow-like blanket. Tephra fell over most of the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
and ash falls were recorded as far away as Vietnam, Cambodia, Singapore, Malaysia and Indonesia.
Twelve days after the first magmatic eruptions of June 3, on June 15, 1991, by about 22:30, and about nine hours after the onset of the most recent climactic phase, atmospheric pressure wave
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
s had decreased to the pre-eruption levels. No seismic records were available at this time, but volcanologists believe 22:30 PST marked the end of the climactic eruption.
Vast quantities of light and heavy metal minerals were brought to the surface. Overall an estimated of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
-, of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
-, of chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and h ...
-, of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
-, and massive amounts of potentially toxic heavy metal mineral such as of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
-, of arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, bu ...
-, of cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
-, and of mercury-minerals comingled with the other magmatic rock, came forth.
Effects on aircraft
 At least 16 commercial aircraft had damaging in-flight encounters with the ash cloud ejected by the June 15 eruption, and many grounded aircraft were also significantly damaged. In-flight encounters caused loss of power to one engine on each of the two aircraft. Ten engines were damaged and replaced, including all three engines of one
At least 16 commercial aircraft had damaging in-flight encounters with the ash cloud ejected by the June 15 eruption, and many grounded aircraft were also significantly damaged. In-flight encounters caused loss of power to one engine on each of the two aircraft. Ten engines were damaged and replaced, including all three engines of one DC-10
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas.
The DC-10 was intended to succeed the Douglas DC-8, DC-8 for long-Range (aeronautics), range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; i ...
. Longer-term damage to aircraft and engines was reported, including accumulation of sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salt (chemistry), ...
deposits on engines. The eruption also irreparably damaged the Philippine Air Force
The Philippine Air Force (PAF) ( tgl, Hukbong Himpapawid ng Pilipinas, , Army of the Air of the Philippines) ( es, Ejército Aérea del Filipinas, , Ejército de la Aérea de la Filipinas) is the aerial warfare service branch of the Armed Forc ...
's recently retired fleet of Vought F-8s, as these were in open storage at Basa Air Base at the time.
Aftermath


Explosivity of the eruption
The 1991 eruption rated 6 on the Volcanic Explosivity Index and came some 450–500 years after the volcano's last known eruptive activity. The eruption ejected about of material, making it the largest eruption of the 20th century since that of Novarupta in 1912 and some ten times larger than the1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
On March 27, 1980, a series of volcanic explosions and pyroclastic flows began at Mount St. Helens in Skamania County, Washington, United States. A series of phreatic blasts occurred from the summit and escalated until a major explosive eru ...
. Ejected material such as tephra fallout and pyroclastic flow deposits are much less dense than magma, and the volume of ejected material was equivalent to about of unerupted material.
The former summit of the volcano was obliterated and replaced by a caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
wide. The highest point on the caldera rim now stood above sea level, some lower than the pre-eruption summit.
Death toll
A reported 847 people were killed by the eruption, mostly by roofs collapsing under a load of accumulated volcanic matter, a hazard amplified by the simultaneous arrival of Typhoon Yunya. The evacuation in the days before the eruption certainly saved tens of thousands of lives, and has been hailed as a great success forvolcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word '' vulcan''. Vulcan was the a ...
and eruption prediction.
After the eruption, about 500,000 people continue to live within of the volcano, with population centers including the 150,000 in Angeles City
, anthem = Himno ning Angeles (Angeles Hymn)
, subdivision_type3 = District
, subdivision_name3 =
, established_title = Settled
, established_date = 1796
, established_title1 = Charter ...
and 30,000 at Clark Freeport Zone
The Clark Freeport and Special Economic Zone (CFEZ), often shortened to Clark, refers to an area in Central Luzon, Philippines.
The CFEZ in Pampanga covers portions of the cities of Angeles and Mabalacat and portions of the town of Porac whil ...
.
Effects on agriculture
 Many
Many reforestation
Reforestation (occasionally, reafforestation) is the natural or intentional restocking of existing forests and woodlands ( forestation) that have been depleted, usually through deforestation, but also after clearcutting.
Management
A debat ...
projects were destroyed in the eruption, with a total area of valued at 125 million pesos destroyed. Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
was heavily disrupted, with of rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domestica ...
-growing farmland destroyed, and almost 800,000 head of livestock and poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quail ...
killed, destroying the livelihoods of thousands of farmers. The cost to agriculture of eruption effects was estimated to be 1.5 billion pesos.
Many farmers near Pinatubo began growing quick-ripening crops such as peanuts, cassava, and sweet potatoes, which could be harvested before the threat of lahar floods during the late summer rainy season.
Local economic and social effects
In total, 364 communities and 2.1 million people were affected by the eruption, with livelihoods and houses being damaged and destroyed. More than 8,000 houses were destroyed, and a further 73,000 were damaged. In addition to the severe damage sustained by these communities, roads and communications were damaged or destroyed by pyroclastic surges and lahar floods throughout the areas surrounding the volcano. Total losses in 1991 and 1992 alone were estimated at 10.6 and 1.2 billion pesos respectively, including damage to public infrastructure estimated at 3.8 billion pesos (c. US$92 million, or $175 million today, adjusted for inflation).School
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compu ...
classes for thousands of children was temporarily suspended by the destruction of schools in the eruption.
 The eruption of Pinatubo severely hampered the
The eruption of Pinatubo severely hampered the economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals a ...
of the surrounding areas. The gross regional domestic product of the Pinatubo area accounted for about 10% of the total Philippine gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
. The GRDP had been growing at 5% annually before the eruption but fell by more than 3% from 1990 to 1991. In 1991, damage to crops and property was estimated at $374 million (or $711 million today), to which continuing lahar floods added a further $69 million (or $127 million today) in 1992. In total, 42 percent of the cropland around the volcano was affected by more lahar floods, dealing a severe blow to the agricultural economy in the region.
Lahars
Since the eruption, each heavy rain has brought massive lahars from the volcano, displacing thousands of people and inflicting extensive damage to buildings and infrastructure costing billions to repair. Funds were spent constructing dikes and dams to control post-eruption lahar flows. Several important river systems stem from Mount Pinatubo, the major rivers being theTarlac
Tarlac, officially the Province of Tarlac ( pam, Lalawigan ning Tarlac; pag, Luyag/Probinsia na Tarlac; ilo, Probinsia ti Tarlac; tgl, Lalawigan ng Tarlac; ), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. I ...
, Abacan, Pasig-Potrero, Sta. Lucia, Bucao, Santo Tomas, Maloma, Tanguay, Ashley and Kileng rivers. Before the eruption, these river systems were important ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s, but the eruption filled many valleys with deep pyroclastic
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroc ...
deposits. Since 1991, the rivers have been clogged with sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
, and the valleys have seen frequent lahars which continued for years after the eruption. Studies show that the river systems will take decades to recover from the June 1991 eruption.
On September 3, 1995, a lahar buried San Guillermo Parish Church in Bacolor, Pampanga to half its height.
Military impact
 The
The United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army S ...
initiated a massive airlift
An airlift is the organized delivery of supplies or personnel primarily via military transport aircraft.
Airlifting consists of two distinct types: strategic and tactical. Typically, strategic airlifting involves moving material long distan ...
effort to evacuate American service members and their families from the two affected bases during and immediately following the eruption, named Operation Fiery Vigil
Operation Fiery Vigil was the Noncombatant Evacuation Operation (NEO) emergency evacuation of all non-essential military and U.S. Department of Defense civilian personnel and their dependents from Clark Air Base and U.S. Naval Base Subic Bay d ...
. The first sea-based evacuations departed June 16 from Alava Wharf, Naval Base Subic Bay aboard USS Rodney M. Davis, USS Curts, and USS Arkansas
USS ''Arkansas'' may refer to one of these ships of the United States Navy named in honor of the 25th state.
* , a screw steamer originally named the ''Tonawanda'' that served in the American Civil War. After that war, she was renamed ''Tonowand ...
, all of whom were in port or who had made port immediately after the initial plume of June 12. Each made two passages from Subic Bay transporting evacuees to Cebu City, Mindanao for subsequent transport by USAF units to Andersen AFB, Guam. Additional maritime evacuations commenced several days later with the arrival of the USS Abraham Lincoln battle group, USS Midway, and USS Peleliu
USS ''Peleliu'' (LHA-5) is a of the United States Navy, named for the Battle of Peleliu of World War II. Entering service in 1980, she has been deployed to the Persian Gulf on several occasions, performed an evacuation of U.S. Naval Base Subic ...
. Most personnel were initially relocated to Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic ce ...
, Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
and the U.S. state of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
, although some returned to the continental United States. Clark Air Base was ultimately abandoned by the United States military because of the eruption, and Subic Bay reverted to Philippine control in November 1992 following the breakdown of lease negotiations and the expiration of the Military Bases Agreement of 1947.
Global environmental effects
The powerful eruption of such an enormous volume of lava and ash injected significant quantities ofaerosols
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog o ...
and dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ...
into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air ...
. Sulfur dioxide oxidized in the atmosphere to produce a haze of sulfuric acid droplets, which gradually spread throughout the stratosphere over the year following the eruption. The injection of aerosols into the stratosphere is thought to have been the largest since the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa
The 1883 eruption of Krakatoa ( id, Letusan Krakatau 1883) in the Sunda Strait occurred from 20 May until 21 October 1883, peaking in the late morning hours of 27 August when over 70% of the island of Krakatoa and its surrounding archipelago w ...
, with a total mass of of about being injected – the largest volume ever recorded by modern instruments (see chart and figure).
 This very large stratospheric injection resulted in a
This very large stratospheric injection resulted in a volcanic winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by volcanic ash and droplets of sulfuric acid and water obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, particularly explosi ...
, a reduction in the normal amount of sunlight reaching the Earth's surface by roughly 10% (see figure). This led to a decrease in Northern Hemisphere average temperatures of and a global decrease of about . At the same time, the temperature in the stratosphere rose to several degrees higher than normal, due to the absorption of radiation by the aerosol. The stratospheric cloud from the eruption persisted in the atmosphere for three years. The eruption, while not directly responsible, may have played a part in the formation of the 1993 Storm of the Century
The 1993 Storm of the Century (also known as the 93 Superstorm, The No Name Storm, or the Great Blizzard of '93/1993) was a cyclonic storm that formed over the Gulf of Mexico on March 12, 1993. The cold weather, heavy snowfall, high winds and s ...
.
The eruption had a significant effect on ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
levels in the atmosphere, causing a large increase in the destruction rate of ozone. Ozone levels at middle latitudes reached their lowest recorded levels, while in the Southern Hemisphere winter of 1992, the ozone hole
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone lay ...
over Antarctica reached its largest ever size until then, with the fastest recorded ozone depletion rates. The eruption of Mount Hudson in Chile in August 1991 also contributed to southern hemisphere ozone destruction, with measurements showing a sharp decrease in ozone levels at the tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere; which are two of the five layers of the atmosphere of Earth. The tropopause is a thermodynamic gradient-stratification layer, that marks the end of ...
when the aerosol clouds from Pinatubo and Hudson arrived.
Another noticeable effect of the dust in the atmosphere was the appearance of lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Eart ...
s. Normally even at mid-eclipse, the moon is still visible although much dimmed, whereas in the year following the Pinatubo eruption, the moon was hardly visible at all during eclipses, due to much greater absorption of sunlight by dust in the atmosphere. It has also been suggested that excess cloud condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), also known as cloud seeds, are small particles typically 0.2 µm, or one hundredth the size of a cloud droplet. CCNs are a unique subset of aerosols in the atmosphere on which water vapour condenses. This c ...
from the eruption were responsible for the "Great Flood of 1993
The Great Flood of 1993 (or Great Mississippi and Missouri Rivers Flood of 1993) was a flood that occurred in the Midwestern United States, along the Mississippi and Missouri rivers and their tributaries, from April to October 1993. The flood wa ...
" in the Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
.
Aeta people
TheAeta people
The Aeta (Ayta ), Agta, or Dumagat, are collective terms for several Filipino indigenous peoples who live in various parts of the island of Luzon in the Philippines. They are considered to be part of the Negrito ethnic groups and share common ...
were the hardest hit by the eruption. After the areas surrounding the volcano were declared safe, many Aetas returned to their old villages only to find them destroyed by pyroclastic and lahar deposits. Some were able to return to their former way of life, but most moved instead to government-organized resettlement areas. Conditions on these were poor, with each family receiving only small plots of land not ideal for growing crops. Many Aeta found casual labor working for lowland farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer mig ...
s, and overall Aeta society became much more fragmented, and reliant on and integrated with lowland culture.
Humanitarian aid
Humanitarian aid received due to the eruption is as follows:Local
Government
The government implemented several rehabilitative and reconstructive programs. Projects that will help deal with the aftermath brought about by lahar were also implemented. Among these is the construction of mega dikes. Moreover, to hasten the implementation of the basic services for the afflicted, private sectors, including the NGOs, took part in offering relief. They provided support and coordinated on the services that were deemed lacking from the side of the government.''Eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in June 1991''/ref> 1. Resettlement 2. Livelihood programs focused on agriculture and industry (quick-generating income opportunities to affected families) 3. Basic social services 4. Infrastructure rehabilitation and reconstruction
Asian Disaster Reduction Center
The Asian Disaster Reduction Center was founded in Kobe, Hyogo prefecture, in 1998, with a mission to improvedisaster
A disaster is a serious problem occurring over a short or long period of time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources ...
resilience of its fifty member countries, to build safe communities, and to create a society where there is an achievable sustainable development. The Center works to build and establish networks among countries through many programs such as personnel exchanges in this field. The Center addresses this issue from a global perspective in cooperation with various UN agencies and international organizations including the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (ISDR), the Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
(UNESCO), the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to increase economic ...
(ESCAP), the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Intern ...
(WMO), and the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
Regional Office for the Western Pacific (WHO/WPRO). The Asian Disaster Reduction Center focuses mainly on the following forms of aid:
= Resettlement
= After the eruption, many of the homes were destroyed and many of the areas affected by lahar were deemed uninhabitable. There was need to resettle the people particularly the Aetas and lowlanders. Resettlement for these two needs to take into consideration the factors of their socio-cultural and socioeconomic differences.Mabalacat, Pampanga
Mabalacat, officially the City of Mabalacat ( pam, Lakanbalen ning Mabalacat; fil, Lungsod ng Mabalacat), is a 3rd class component city in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 293,244 pe ...
File:9828Bulaon Resettlement San Fernando, Pampanga 30.jpg, Bulaon Resettlement Center in San Fernando, Pampanga
San Fernando, officially the City of San Fernando ( pam, Lakanbalen ning Sampernandu; fil, Lungsod ng San Fernando), is a 1st class component city and capital of the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a pop ...
File:8054jfResettlement Pandacaqui Mexico Pampangafvf 35.JPG, Pandacaqui Resettlement Center in Mexico, Pampanga
File:Jf3029Pio Model Porac Pampangafvf 14.JPG, Pio Model Community in Porac, Pampanga
File:09417jfDapdap Resettlement Area Bamban Tarlacfvf 29.JPG, Dapdap Resettlement Center in Bamban, Tarlac
= Livelihood
= Faced with the destruction of many of the farmlands and the displacement of farmers and other workers the government had to search for a long-term solution to address the issue. Agricultural-based industries were also greatly affected. The closure of Clark Air base also raised an issue of finding short-term livelihoods and the need to use the base lands to cushion the repercussions of the worker's displacement.= Social services
= The destruction brought about by the incident pressured social service sectors to continue their efforts in assisting in terms of health, social welfare, and education. The services offered are not limited to the victims within the evacuation centers but also offered to the others affected. While the event happened during the opening of a school year, classes were needed to be pushed back as school facilities were destroyed. Providing resettlement for the evacuees was also a major concern. Social services were also provided in the prospective resettlement areas to prepare the victims when settling down.= Infrastructure
= Destruction of many infrastructures was mostly due to the wet ash after the explosion. The region's roads, bridges, public buildings, facilities, communication, and structures for river and flood control were some of the great concerns of the government. A need to establish measures for the flash floods and the threat caused by lahar also became an imperative demand to the government.= Land use and environmental management
= The aftereffects of the eruption damaged not only man-made structures but also farmlands, forestlands, and watersheds. River systems and the overall environment of the affected region are also heavily damaged by the heavy lahar flow. To address this careful replanning of the land area region is necessary.= Science and technology
= This event showed the need to engage in scientific studies to reassess the current policies and knowledge on areas with risk of eruption. Studies should also be allocated on a possible application for the ash fall for industrial and commercial purposes. The significance of this concern affects both the government and private sectors.International
Even before the Philippine government officially appealed for international assistance, the Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance (USAID/OFDA) shipped shelter material for victims of the floods and lahars in late July 1992. In the following month, they provided $375 000 to be used for relief and rehabilitation projects. TheDepartment of Social Welfare and Development
The Philippines' Department of Social Welfare and Development ( fil, Kagawaran ng Kagalingan at Pagpapaunlad Panlipunan, Kagawaran ng Kagalingang Panlipunan at Pagpapaunlad, abbreviated as DSWD) is the executive department of the Philippine Go ...
had claimed during an informal donors’ meeting with representatives from mostly international agencies who compose the donor community that the national government was still well-equipped and had sufficient resources to aid the victims. The UN-Disaster Management Team (DMT) and the United Nations’ Department of Humanitarian Affairs/United Nations Disaster Relief Organization (DHA/UNDRO) continued cooperating with the national government to monitor the situation and formulate ideas for further assistance.
It was not until then-President Fidel V. Ramos had declared the affected provinces and areas to be in a state of emergency that the national government officially requested for international assistance and for aid in projects for rehabilitation and relief provisions in the aforementioned areas. In response to this, the DHA/UNDRO reached out to the international community to respond to the appeal, and continued their operations, coordinating with the government.
Among the countries that extended humanitarian relief assistance were Australia, Belgium, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Malta, Myanmar, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. International organizations including the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human de ...
), the Office of the United Nations Disaster Relief Coordinator (UNDRO
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) is a United Nations (UN) body established in December 1991 by the General Assembly to strengthen the international response to complex emergencies and natural disaster ...
, predecessor to the current United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs or OCHA), the United Nations Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid t ...
), the World Food Programme (WFP
The World Food Programme; it, Programma alimentare mondiale; es, Programa Mundial de Alimentos; ar, برنامج الأغذية العالمي, translit=barnamaj al'aghdhiat alealami; russian: Всемирная продовольствен� ...
), and the World Health Organization ( WHO) also offered assistance. Relief assistance from these organizations and countries were in the form of either cash donation or relief items such as food packs, medicines, and shelter materials.
United Nations
Contributions made by the different systems of the United Nations (UN) are as follows: Contributions made by participating countries in the UN are as follows:Others
Some specific projects under the auspices of the DPWH, which were made possible by foreign assistance, included: * ADB-funded Mt. Pinatubo Damage Rehabilitation Project * German Bank for Reconstruction-funded Mt. Pinatubo Emergency Aide Project * Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)-funded Mt. Pinatubo Relief and Rehab Project * USAID-funded United States Army Corps of Engineers' Mt. Pinatubo recovery action * Dutch-funded dredging of the Pasac- Guagua-San Fernando Waterway * Overseas Economic Cooperation Fund (OECF)-funded Pinatubo Hazard Urgent Mitigation Project * German Centrum for International Migration (CIM)-funded technical assistance for Mount Pinatubo Emergency-PMO * JICA-funded grant aid for water supply in Mt. Pinatubo resettlement areas and study on flood and mudflow control for Sacobia Bamban/Abacan Rivers * IBRD-funded technical assistance for Mt. Pinatubo and Rehabilitation Works * Swiss Disaster Relief-funded technical assistance for Mt. Pinatubo Rehabilitation * JBIC Yen Loan Package-funded Pinatubo hazard Urgent Mitigation ProjectIn popular culture
The eruption is featured in volcano and disaster documentaries: * The eruption has been a subject of the 1993PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of ed ...
''Nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
'' episode " In the Path of a Killer Volcano".
* On the 1997 National Geographic documentary ''Volcano: Nature's Inferno''.
* On Philippine TV network ABS-CBN
ABS-CBN (an initialism of its two predecessors' names, Alto Broadcasting System and Chronicle Broadcasting Network) is a Philippine commercial broadcast network that serves as the flagship property of ABS-CBN Corporation, a company under L ...
's program ''Red Alert'' part of the '' Pinoy True Stories''.
* On GRB Entertainment program '' Earth's Fury'' episode "Volcano" aired in 1997, aired on television networks around the world such as The Learning Channel in the United States as ''Anatomy of Disaster''.
* On the 2006 documentary on hypothetical disaster scenarios, ''Mega Disaster'' produced by NHNZ
NHNZ, formerly Natural History New Zealand, is a New Zealand-based television production house.
It works and co-produces with multiple major global broadcasters: Discovery Channel, Animal Planet, Science Channel, Discovery Science, A&E Televisio ...
.
* On PBS- ITV program in 1998, ''Savage Earth'' in an episode called "Out of the Inferno".
* On the 1996 direct-to-video documentary ''The Amazing Video Collection: Natural Disasters''.
* On the 2010 television special
A television special (often TV special, or rarely television spectacular) is a standalone television show which may also temporarily interrupt episodic programming normally scheduled for a given time slot. Some specials provide a full range of e ...
produced by the GMA News and Public Affairs
GMA Integrated News and Public Affairs (formerly known as ''RBS News Department'', ''GMA Radio-Television News'' and ''GMA Rainbow Satellite News''; and commonly GMA (Integrated) News) is the news division of the GMA Network Inc.
The division ...
during its 50th anniversary titled ''Limang Dekada: The GMA News 50th Anniversary Special''.
* On the 2003 television special produced by the ABS-CBN News and Current Affairs
ABS-CBN Integrated News and Current Affairs, known on-air as ABS-CBN News (formerly known as ''ABS-CBN News and Public Affairs'' and later ''ABS-CBN News and Current Affairs''), is the news and current affairs production and distribution divis ...
during its 50th anniversary titled ''Sa Mata ng Balita''.
* The eruption has been an subject of the 2006 television documentary aired on the National Geographic Channel
National Geographic (formerly National Geographic Channel; abbreviated and trademarked as Nat Geo or Nat Geo TV) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by the National Geographic Global Networks unit of Disney General ...
titled ''Surviving the Eruption at Pinatubo''.
The eruption is also mentioned in the disaster film ''Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ...
'' (1997).
The story of the eruption as shown in the episode of the ABS-CBN
ABS-CBN (an initialism of its two predecessors' names, Alto Broadcasting System and Chronicle Broadcasting Network) is a Philippine commercial broadcast network that serves as the flagship property of ABS-CBN Corporation, a company under L ...
educational program '' Bayani''.
See also
* List of volcanoes in the Philippines * List of large volcanic eruptions of the 20th century * List of volcanic eruptions by death toll *Volcanic winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by volcanic ash and droplets of sulfuric acid and water obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, particularly explosi ...
(a recent one having been caused by this eruption)
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Pinatubo, Mount 20th-century volcanic events VEI-6 eruptions 1991 natural disasters 1991 disasters in the Philippines Volcanic eruptions in the Philippines Events that forced the climate Phreatic eruptions Plinian eruptions Explosive eruptions Phreatomagmatic eruptions Volcanic winters