|
Luzon Volcanic Arc
The Luzon Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes in a north–south line across the Luzon Strait from Taiwan to Luzon. The name "Luzon Volcanic Arc" was first proposed by Carl Bowin et al. to describe a series of Miocene to recent volcanoes due to eastward subduction along the Manila Trench for approximately 1,200 km from the Coastal Range in Taiwan south to southern Mindoro in the Philippines. Islands that form part of the arc are the Eastern Coastal Range of Taiwan, Green Island, Taiwan, Orchid Island, Kaotai Rock, Mavudis or Y'ami Island, Mabudis, Siayan Island, Itbayat Island, Diogo Island, Batan Island, Unnamed volcano Ibuhos, Sabtang Island, Babuyan, Didicas, Camiguin Island. At the south end it terminates on Luzon. The geochemistry of a number of volcanoes along the arc have been measured. There are five distinct geochemical domains within the arc (Mindoro, Bataan, Northern Luzon, Babuyan, and Taiwan). The geochemistry of the segments verified that the volcanoes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith Volcano 1
Smith may refer to: People * Metalsmith, or simply smith, a craftsman fashioning tools or works of art out of various metals * Smith (given name) * Smith (surname), a family name originating in England, Scotland and Ireland ** List of people with surname Smith * Smith (artist) (born 1985), French visual artist Arts and entertainment * Smith (band), an American rock band 1969–1971 * ''Smith'' (EP), by Tokyo Police Club, 2007 * ''Smith'' (play), a 1909 play by W. Somerset Maugham * ''Smith'' (1917 film), a British silent film based on the play * ''Smith'' (1939 film), a short film * ''Smith!'', a 1969 Disney Western film * ''Smith'' (TV series), a 2006 American drama * ''Smith'', a 1932 novel by Warwick Deeping * ''Smith'', a 1967 novel by Leon Garfield and a 1970 TV adaptation Places North America * Smith, Indiana, U.S. * Smith, Kentucky, U.S. * Smith, Nevada, U.S. * Smith, South Carolina, U.S. * Smith Village, Oklahoma, U.S. * Smith Park (Middletown, Connecticut) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diogo Island
Diogo Island known as Di'nem Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the province of Batanes, the northernmost province in the Philippines. Also known as ''Di'nem'' Island in the native language, Diogo is a lone rock rising out of the sea, with steep cliffs on every side, and dangerous currents make landing there practically impossible. It is an extinct volcano which has suffered heavily from marine erosion.Ferguson, Henry G. (1908-02)"The Philippine Journal of Science, Vol.3 Part 1" p.12. Manila Bureau of Printing, 1908. Geography Diogo is a small, round island over high, about in diameter, lying southeastward of Itbayat Island. It is steep on the western side but has several small islets lying off the eastern side, the outermost being nearly distant. Geology In 1903, Diogo Island was observed to be volcanic, discharging vapor and dark material, but another observation in 1908 believe that those are small clouds which often hang around the mountain. It is listed as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaannum
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Miocene
The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is preceded by the Early Miocene The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma to 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). It was p .... The sub-epoch lasted from 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma to 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). During this period, a sharp drop in global temperatures took place. This event is known as the Middle Miocene Climate Transition. For the purpose of establishing European Land Mammal Ages this sub-epoch is equivalent to the Astaracian age. External links GeoWhen Database - Middle Miocene .02 02 * * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrigenous Sediment
In oceanography, terrigenous sediments are those derived from the erosion of rocks on land; that is, they are derived from ''terrestrial'' (as opposed to marine) environments. Consisting of sand, mud, and silt carried to sea by rivers, their composition is usually related to their source rocks; deposition of these sediments is largely limited to the continental shelf. Sources of terrigenous sediments include volcanoes, weathering of rocks, wind-blown dust, grinding by glaciers, and sediment carried by rivers or icebergs. Terrigenous sediments are responsible for a significant amount of the salt in today's oceans. Over time rivers continue to carry minerals to the ocean but when water evaporates, it leaves the minerals behind. Since chlorine and sodium are not consumed by biological processes, these two elements constitute the greatest portion of dissolved minerals. Quantity Some 1.35 billion tons, or 8% of global river-borne sediment (16.5-17 billion tons globally), is tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
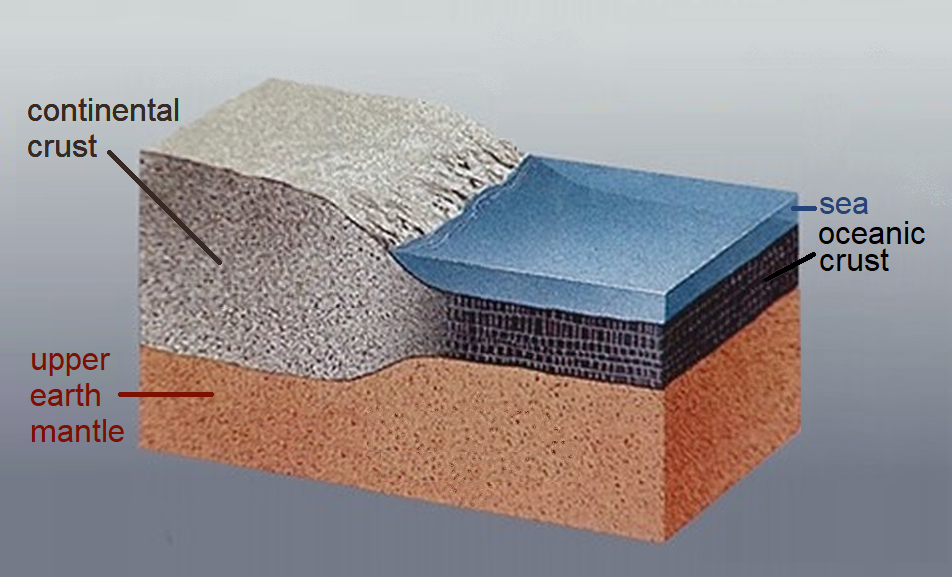
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma, which is high in magnesium and iron and produces basalt or gabbro, as it fractional crystallization (geology), fractionally crystallizes to become a felsic magma, which is low in magnesium and iron and produces rhyolite or granite. Calc-alkaline rock (geology), rocks are rich in alkaline earth metal#Etymology, alkaline earths (Magnesium oxide, magnesia and calcium oxide) and alkali metals and make up a major part of the Continental crust, crust of the continents. The diverse rock types in the calc-alkaline series include volcanic types such as basalt, andesite, dacite, rhyolite, and also their coarser-grained intrusive equivalents (gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and granite). They do not include normative mineralogy, silica-undersatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camiguin Island
Camiguin, officially the Province of Camiguin ( ceb, Probinsya sa Camiguin; tl, Lalawigan ng Camiguin; Kamigin: ''Probinsya ta Kamigin''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bohol Sea, about off the northern coast of Mindanao. It is geographically part of Region X, the Northern Mindanao Region of the country and formerly a part of Misamis Oriental province. Camiguin is the second-smallest province in the country in both population and land area after Batanes. The provincial capital is Mambajao, which is also the province's largest municipality in both area and population. The province is famous for its sweet lanzones, to which its annual Lanzones Festival is dedicated and celebrated every third weekend of October. It is home to lush interior forest reserves, collectively known as the Mount Hibok-Hibok Protected Landscape, which has been declared by all Southeast Asian nations as an ASEAN Heritage Park. The province also boasts three National Cultural Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didicas
Didicas Volcano is an active volcanic island in the province of Cagayan in northern Philippines. The island, which was a submarine volcano and re-emerged from the sea in 1952, is NE of Camiguin Island, one of the Babuyan Islands in Luzon Strait. Before 1952, the volcano first breached the ocean surface in 1857.Villamor, Ignacio. "Census of the Philippine Islands, 1918, Vol. I", p. 112. Manila Bureau of Printing, 1920. Physical features Didicas is topped with a lava dome with an elevation of and a base diameter of at sea level. It is at the southern end of the Luzon Volcanic Arc, and like all the volcanoes in the Philippines, is part of the Pacific ring of fire. Eruption history There have been six historical eruptions recorded from the volcano since the 18th century. *1773: The first recorded submarine eruption from the volcano, on what was known as Didicas reefs of the Farallones. *1856 September or October: The first activity started as a column of "smoke" in between the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babuyan
The Babuyan Islands ( ), also known as the Babuyan Group of Islands, is an archipelago in the Philippines, located in the Luzon Strait north of the main island of Luzon and south of Taiwan via Bashi Channel to Luzon Strait. The archipelago consists of five major islands and their surrounding smaller islands. These main islands are, counterclockwise starting from northeast, Babuyan, Calayan, Dalupiri, Fuga, and Camiguin. The Babuyan Islands are separated from Luzon by the Babuyan Channel, and from the province of Batanes to the north by the Balintang Channel. Geography The archipelago, comprising 24 volcanic-coralline islands, has a total area of about . The largest of these is Calayan with an area of , while the highest peak in the island group is Mount Pangasun () on Babuyan Claro. Islands The following are the islands of Babuyan and their adjoining islets and rocks, along with land areas and highest elevation: Geology The eastern islands of the archipelago are pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabtang Island
Sabtang, officially the Municipality of Sabtang ( ivv, Kavahayan nu Sabtang; tl, Bayan ng Sabtang), is a 6th class municipality in the province of Batanes, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 1,696 people. The southernmost island municipality of the Batanes island group, Sabtang comprises primarily ''Sabtang Island'', as well as two nearby smaller and uninhabited islands: Ivuhos and Dequey. The municipality is known for its lighthouse and the old stone houses of the Ivatan villages of Chavayan and Savidug. Like Batan Island to the north, Sabtang also has a few Mission-style churches and white sand beaches. History The Spanish missionary Fr. Artiquez first visited the Island of Sabtang in 1786González Alonzo, Fr. Julio, O.P. (1966). "The Batanes Islands", in Acta Manilana, Manila: University of Santo Tomas Research Center after receiving an affirmative response from the island to learn about the Christian faith. The success of the first visit le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |