|
β-sandwich
Beta-sandwich, β-sandwich domains consisting of 80 to 350 amino acids occur commonly in proteins. They are characterized by two opposing antiparallel beta sheets (β-sheets). The number of strands found in such domains may differ from one protein to another. β-sandwich domains are subdivided in a variety of different folds. The immunoglobulin-type fold found in antibodies (Ig-fold) consists of a sandwich arrangement of 7 and 9 antiparallel β-strands arranged in two β-sheets with a Greek-key topology. The Greek-key topology is also found in Human Transthyretin. The jelly-roll topology is found in carbohydrate binding proteins such as concanavalin A and various lectins, in the collagen binding domain of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' Adhesin and in modules that bind fibronectin as found in Tenascin (Third Fibronectin Type III Repeat). The L-type lectin domain is a variation of the jelly roll fold. The C2 domain in its typical version (PKC-C2) is a β-sandwich composed of 8 beta-str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-strand
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common structural motif, motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone chain, backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of peptide, polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformational isomerism, conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the Amyloid fibril, fibrils and Amyloid plaques, protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-strand
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C2 Domain
A C2 domain is a protein structural domain involved in targeting proteins to cell membranes. The typical version (PKC-C2) has a beta-sandwich composed of 8 beta sheet, β-strands that co-ordinates two or three calcium ions, which bind in a cavity formed by the first and final loops of the domain, on the membrane binding face. Many other C2 domain families don't have calcium binding activity. Coupling with other domains C2 domains are frequently found coupled to enzyme, enzymatic domains; for example, the C2 domain in PTEN (gene), PTEN, brings the phosphatase domain into contact with the plasma membrane, where it can dephosphorylate its substrate, Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3), without removing it from the membrane - which would be energetically very costly. PTEN consists of two domains, a protein tyrosine phosphatase domain and a C2 domain. This domain pair constitutes a superdomain, a heritable unit that is found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-type Lectin Domain
In molecular biology the L-like lectin domain is a protein domain found in lectins which are similar to the leguminous plant lectins. Lectins are structurally diverse proteins that bind to specific carbohydrates. This family includes the VIP36 and ERGIC-53 lectins. Although proteins containing this domain were originally identified as a family of animal lectins, there are also yeast representatives. ERGIC-53 is a 53kDa protein, localised to the intermediate region between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus (ER-Golgi-Intermediate Compartment, ERGIC). It was identified as a calcium-dependent, mannose-specific lectin. Its dysfunction has been associated with combined factors V and VIII deficiency, suggesting an important and substrate-specific role for ERGIC-53 in the glycoprotein-secreting pathway. The L-like lectin domain has an overall globular shape composed of a beta-sandwich of two major twisted antiparallel beta-sheets. The beta-sandwich comprises a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenascin
Tenascins are extracellular matrix glycoproteins. They are abundant in the extracellular matrix of developing vertebrate embryos and they reappear around healing wounds and in the stroma of some tumors. Types There are four members of the tenascin gene family: tenascin-C, tenascin-R, tenascin-X and tenascin-W. * Tenascin-C is the founding member of the gene family. In the embryo it is made by migrating cells like the neural crest; it is also abundant in developing tendons, bone and cartilage. * Tenascin-R is found in the developing and adult nervous system. * Tenascin-X is found primarily in loose connective tissue; mutations in the human tenascin-X gene can lead to a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. * Tenascin-W is found in the kidney and in developing bone. The basic structure is 14 EGF-like repeats towards the N-terminal end, and 8 or more fibronectin-III domains which vary upon species and variant. Tenascin-C is the most intensely studied member of the family. It has an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
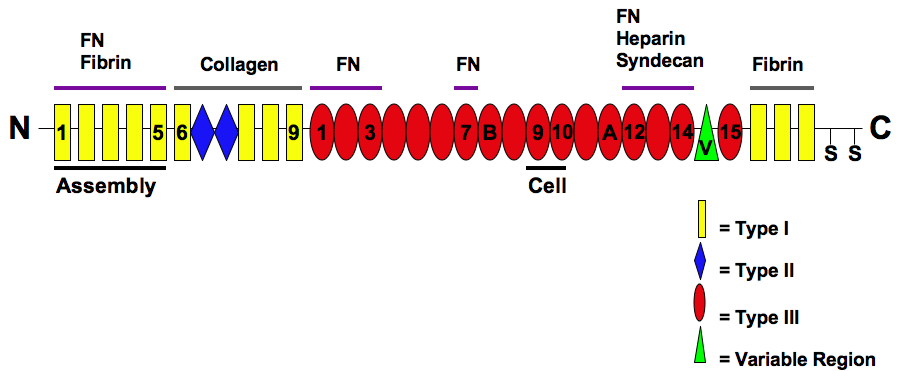
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 ÎĽg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is then ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Adhesin
Adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate adhesion or adherence to other cells or to surfaces, usually in the host they are infecting or living in. Adhesins are a type of virulence factor. Adherence is an essential step in bacterial pathogenesis or infection, required for colonizing a new host. Adhesion and bacterial adhesins are also a potential target for prophylaxis or treatment of bacterial infections. Background Bacteria are typically found attached to and living in close association with surfaces. During the bacterial lifespan, a bacterium is subjected to frequent shear-forces. In the crudest sense, bacterial adhesins serve as anchors allowing bacteria to overcome these environmental shear forces, thus remaining in their desired environment. However, bacterial adhesins do not serve as a sort of universal bacterial Velcro. Rather, they act as specific surface recognition molecules, allowing the targeting of a particular bacterium to a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein TNC PDB 1ten
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectins
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in recognition at the cellular and molecular level and play numerous roles in biological recognition phenomena involving cells, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lectins also mediate attachment and binding of bacteria, viruses, and fungi to their intended targets. Lectins are ubiquitous in nature and are found in many foods. Some foods, such as beans and grains, need to be cooked, fermented or sprouted to reduce lectin content. Some lectins are beneficial, such as CLEC11A, which promotes bone growth, while others may be powerful toxins such as ricin. Lectins may be disabled by specific mono- and oligosaccharides, which bind to ingested lectins from grains, legumes, nightshade plants, and dairy; binding can prevent their attachment to the carbohydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |