|
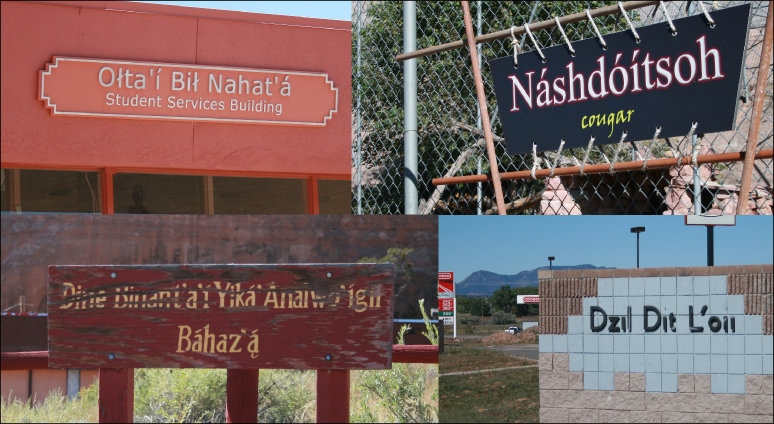
Navajo Language
Navajo or Navaho (; Navajo: or ) is a Southern Athabaskan language of the Na-Dené family, through which it is related to languages spoken across the western areas of North America. Navajo is spoken primarily in the Southwestern United States, especially on the Navajo Nation. It is one of the most widely spoken Native American languages and is the most widely spoken north of the Mexico–United States border, with almost 170,000 Americans speaking Navajo at home as of 2011. The language has struggled to keep a healthy speaker base, although this problem has been alleviated to some extent by extensive education programs in the Navajo Nation, including the creation of versions of the films Finding Nemo and Star Wars dubbed into Navajo. The United States in World War II used the Navajo language to develop a system of code talkers to relay messages that could not be cracked. Navajo has a fairly large phoneme inventory, including several uncommon consonants that are not found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
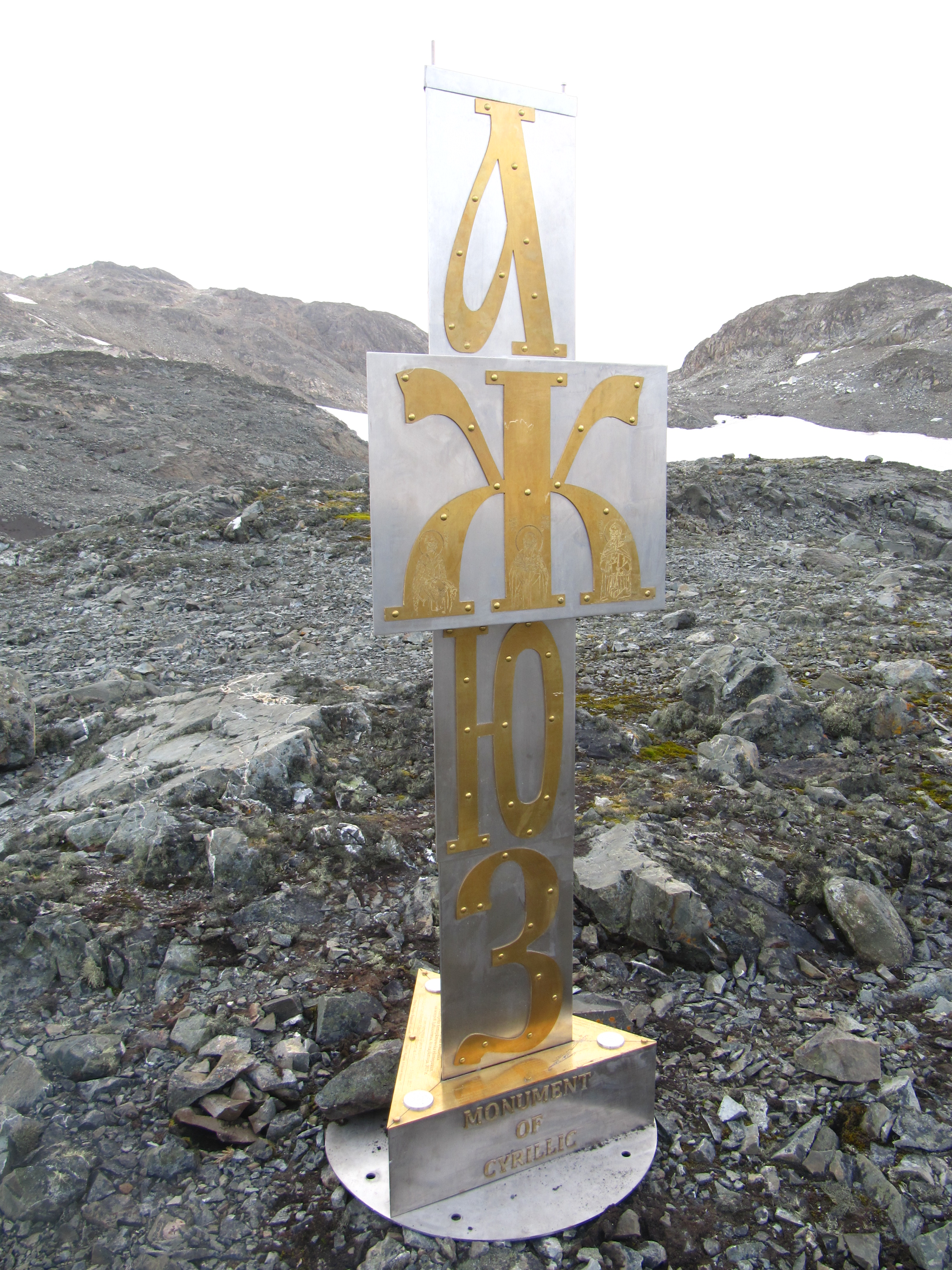
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (linguistics)
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in tone. The terms ''stress'' and ''accent'' are often used synonymously in that context but are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called ''pitch accent'', and when produced through length alone, it is called ''quantitative accent''. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called ''stress accent'' or ''dynamic accent''; English uses what is called ''variable stress accent''. Since stress can be realised through a wide range of phonetic properties, such as loudness, vowel length, and pitch (which are also used for other linguistic functions), it is difficult to define stress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (linguistics)
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in tone. The terms ''stress'' and ''accent'' are often used synonymously in that context but are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called ''pitch accent'', and when produced through length alone, it is called ''quantitative accent''. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called ''stress accent'' or ''dynamic accent''; English uses what is called ''variable stress accent''. Since stress can be realised through a wide range of phonetic properties, such as loudness, vowel length, and pitch (which are also used for other linguistic functions), it is difficult to define stress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacritic'' is a noun, though it is sometimes used in an attributive sense, whereas ''diacritical'' is only an adjective. Some diacritics, such as the acute ( ◌́ ) and grave ( ◌̀ ), are often called ''accents''. Diacritics may appear above or below a letter or in some other position such as within the letter or between two letters. The main use of diacritics in Latin script is to change the sound-values of the letters to which they are added. Historically, English has used the diaeresis diacritic to indicate the correct pronunciation of ambiguous words, such as "coöperate", without which the letter sequence could be misinterpreted to be pronounced . Other examples are the acute and grave accents, which can indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Accent
A pitch-accent language, when spoken, has word accents in which one syllable in a word or morpheme is more prominent than the others, but the accentuated syllable is indicated by a contrasting pitch ( linguistic tone) rather than by loudness (or length), as in many languages, like English. Pitch-accent also contrasts with fully tonal languages like Vietnamese and Standard Chinese, in which each syllable can have an independent tone. Some have claimed that the term "pitch accent" is not coherently defined and that pitch-accent languages are just a sub-category of tonal languages in general. Languages that have been described as pitch-accent languages include: most dialects of Serbo-Croatian, Slovene, Baltic languages, Ancient Greek, Vedic Sanskrit, Tlingit, Turkish, Japanese, Norwegian, Swedish (but not in Finland), Western Basque,Hualde, J.I. (1986)"Tone and Stress in Basque: A Preliminary Survey"(PDF). ''Anuario del Seminario Julio de Urquijo'' XX-3, 1986, pp. 867-896. Yaq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italy (geographical region), Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a fusional language, highly inflected language, with three distinct grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the other modern European languages. With modifications, it is also used for other alphabets, such as the Vietnamese alphabet. Its modern repertoire is standardised as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new letters, like the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. Letter shapes have evolved over the centuries, including the development in Medieval Latin of lower-case, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BCE, the Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard and it is this version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , /ς, , , , , , . The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of the Latin script, Latin and Cyrillic scripts. Like Latin and Cyrillic, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter; it developed the letter case distinction between uppercase and lowercase in parallel with Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apex (diacritic)
In written Latin, the apex (plural "apices") is a mark with roughly the shape of an acute accent which was sometimes placed over vowels to indicate that they are long. The shape and length of the apex can vary, sometimes within a single inscription. While virtually all apices consist of a line sloping up to the right, the line can be more or less curved, and varies in length from less than half the height of a letter to more than the height of a letter. Sometimes, it is adorned at the top with a distinct hook, protruding to the left. Rather than being centered over the vowel it modifies, the apex is often considerably displaced to the right. Essentially the same diacritic, conventionally called in English the acute accent, is used today for the same purpose of denoting long vowels in a number of languages with Latin orthography, such as Irish (called in it the or simply "long"), Hungarian ( , from the words for "long" and "wedge"), Czech (called in it , "small line") and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Diacritics
Greek orthography has used a variety of diacritics starting in the Hellenistic period. The more complex polytonic orthography ( el, πολυτονικό σύστημα γραφής, translit=polytonikó sýstīma grafī́s), which includes five diacritics, notates Ancient Greek phonology. The simpler monotonic orthography ( el, μονοτονικό σύστημα γραφής, translit=monotonikó sýstīma grafīs), introduced in 1982, corresponds to Modern Greek phonology, and requires only two diacritics. Polytonic orthography () is the standard system for Ancient Greek and Medieval Greek. The acute accent (), the circumflex (), and the grave accent () indicate different kinds of pitch accent. The rough breathing () indicates the presence of the sound before a letter, while the smooth breathing () indicates the absence of . Since in Modern Greek the pitch accent has been replaced by a dynamic accent (stress), and was lost, most polytonic diacritics have no phonetic si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |