|
Иљara BГўrsei
Иљara BГўrsei, Burzenland () or BarcasГЎg is a Historical regions of Romania, historic and ethnographic area in southeastern Transylvania, Romania with a mixed population of Romanians, Germans of Romania, Germans, and Hungarians in Romania, Hungarians. Geography The Burzenland lies within the Southern Carpathians mountains ranges, bordered approximately by ApaИ›a in the north, Bran, BraИ™ov, Bran in the southwest and Prejmer in the east. Its most important city is BraИ™ov. Burzenland is named after the stream BГўrsa River (Olt), BГўrsa (''Barca'', ''Burzen'', 1231: ''Borza''), which flows into the Olt River, Olt river. The Romanian language, Romanian word ''bГўrsДѓ'' is supposedly of Dacian language, Dacian origin (''see List of Romanian words of possible Dacian origin''). History Middle Ages Based on archaeological evidence, it seems German colonization of the region started in the middle of the 12th century during the reign of King GГ©za II of Hungary. The German coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
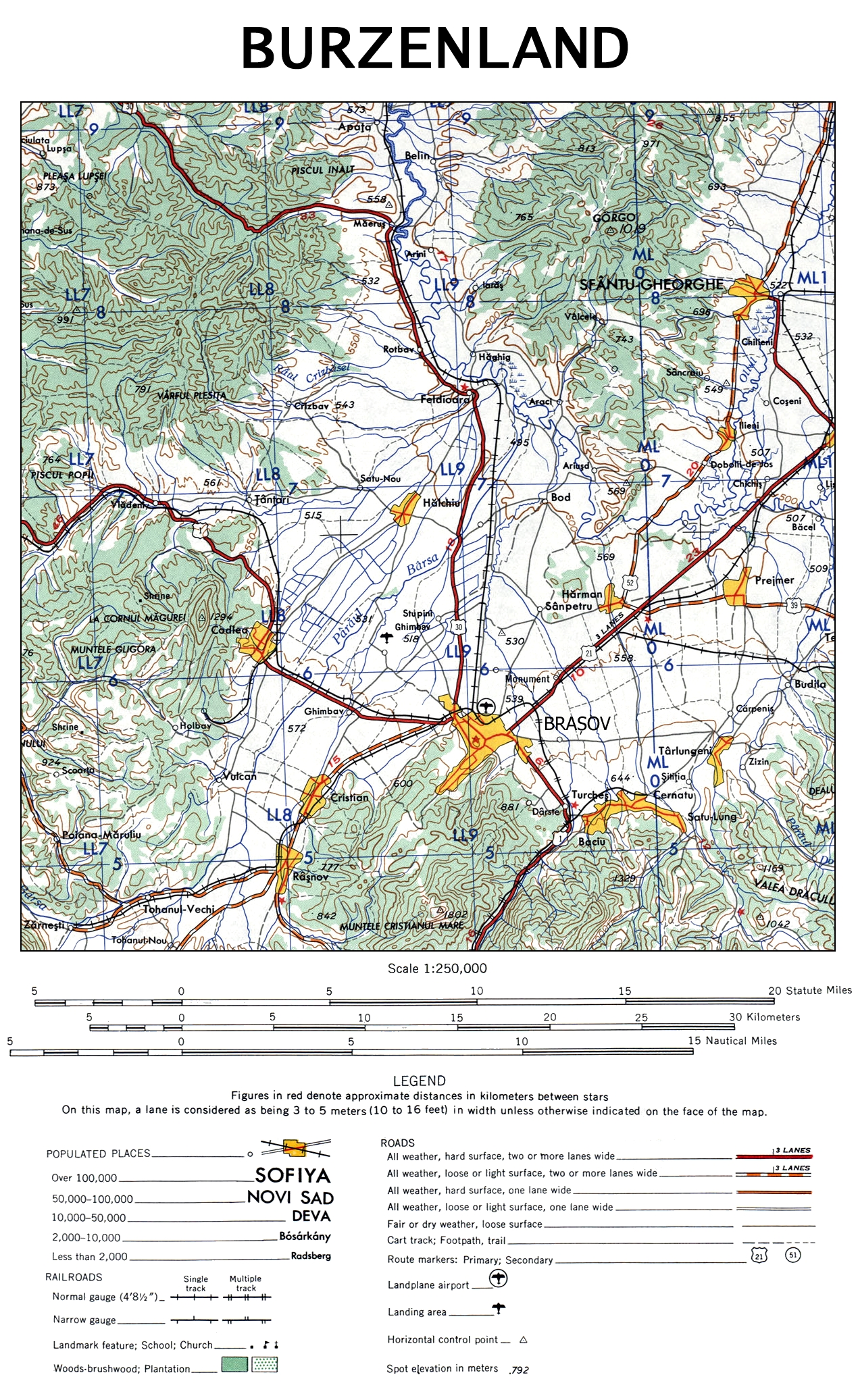
Map Of Burzenland, 1959
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacian Language
Dacian is an extinct language, generally believed to be Indo-European, that was spoken in the Carpathian region in antiquity. In the 1st century, it was probably the predominant language of the ancient regions of Dacia and Moesia and possibly of some surrounding regions. The language was extinct by the 4th century AD. While there is general agreement among scholars that Dacian was an Indo-European language, there are divergent opinions about its place within the IE family: * Dacian was a dialect of the extinct Thracian language, or vice versa, e. g . and . * Dacian was a language distinct from Thracian but closely related to it, belonging to the same branch of the Indo-European family (a "Thraco-Dacian", or "Daco-Thracian" branch has been theorised by some linguists). * Dacian, Thracian, the Baltic languages (Duridanov also adds Pelasgian) formed a distinct branch of Indo-European, e.g. Schall (1974), Duridanov (1976), Radulescu (1987) and Mayer (1996).Schall H., Sudbalt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd SchneidmГјller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian Dynasty, Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the List of Frankish kings, Frankish king Charlemagne as Carolingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |