|
Malta - Zurrieq - Triq Sant' Andrija 01 Ies
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies south of Sicily (Italy), east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The official languages are Maltese and English, and 66% of the current Maltese population is at least conversational in the Italian language. Malta has been inhabited since approximately 5900 BC. Its location in the centre of the Mediterranean has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, with a succession of powers having contested and ruled the islands, including the Phoenicians and Carthaginians, Romans, Greeks, Arabs, Normans, Aragonese, Knights of St. John, French, and British, amongst others. With a population of about 516,000 over an area of , Malta is the world's tenth-smallest country in area and fourth most densely populated sovereign co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Alphabet
The Polish alphabet (Polish: ''alfabet polski'', ''abecadło'') is the script of the Polish language, the basis for the Polish system of orthography. It is based on the Latin alphabet but includes certain letters with diacritics: the ''kreska'', or acute accent (''ć'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź''); the overdot, or ''kropka'' (''ż''); the tail, or ''ogonek'' (''ą'', ''ę''); and the stroke (''ł''). The letters ''q'', ''v'', and ''x'', which are used only in foreign words, are usually absent from the Polish alphabet. However, prior to the standardization of the Polish language, the letter "x" was sometimes used in place of "ks". Modified variations of the Polish alphabet are used for writing Silesian and Kashubian, whereas the Sorbian languages use a mixture of the Polish and Czech orthographies. Letters There are 32 letters in the Polish alphabet: 9 vowels and 23 consonants. The letters ''q'', ''v'', and ''x'' are not used in any native Polish words and are mostly fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashubian Alphabet
The Kashubian or Cassubian alphabet (''kaszëbsczi alfabét'', ''kaszëbsczé abecadło'') is the script of the Kashubian language, based on the Latin alphabet. The Kashubian alphabet consists of 34 letters: A, Ą, Ã, B, C, D, E, É, Ë, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, Ł, M, N, Ń, O, Ò, Ó, Ô, P, R, S, T, U, Ù, W, Y, Z, Ż The Kashubian language also uses some digraphs: ch, cz, dz, dż, rz and sz. The digraphs ''cz'', ''dż'', ''sz'', ''ż'' are pronounced in a different manner from their Polish counterparts – they are palato-alveolar, not retroflex – but ''rz'' is pronounced the same as in Polish. Pronunciation Consonants combination Literature * Eugeniusz Gòłąbk: Wkôzë kaszëbsczégò pisënkù. Oficyna Czec, Gduńsk 1997, p. 25 . See also * Ł-l merger * Polish language References {{Reflist External links OmniglotKaszëbskô Mowa: Freeing the Kashubian Language Alphabet An alphabet is a standardized set o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
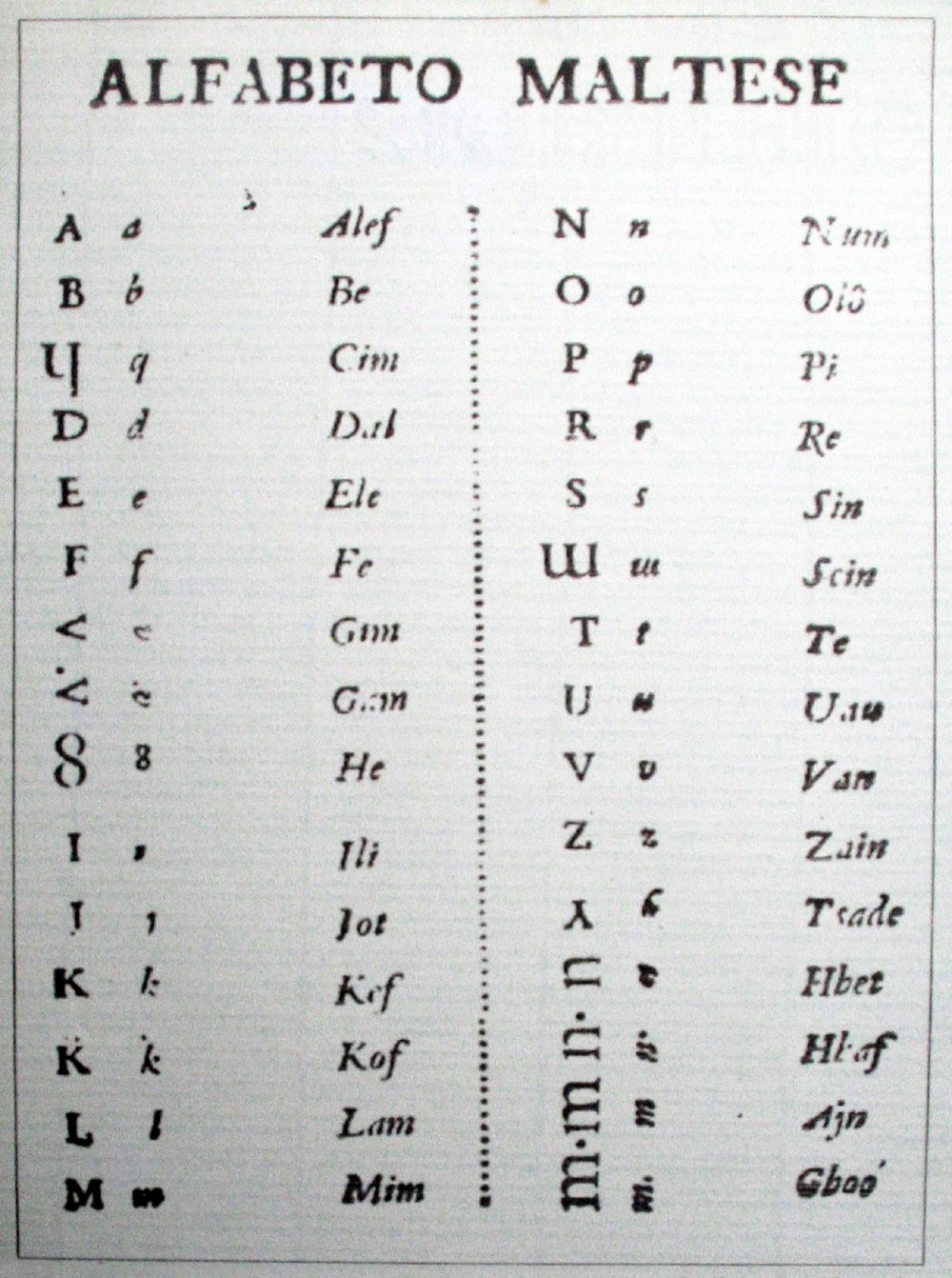
Maltese Alphabet
The Maltese alphabet is based on the Latin alphabet with the addition of some letters with diacritic marks and digraphs. It is used to write the Maltese language, which evolved from the otherwise extinct Siculo-Arabic dialect, as a result of 800 years independent development. It contains 30 letters: 24 consonants and 6 vowels (a, e, i, o, u, ie). There are two types of Maltese consonants: * Konsonanti xemxin ( sun consonants): ċ d n r s t x ż z * Konsonanti qamrin ( moon consonants): b f ġ g għ h ħ j k l m p q v w Samples In the alphabetic sequence ''c'' is identical either to ''k'' (in front of ''a'', ''o'', ''u'' or consonant or as the last letter of the word) or to ''z'' (in front of ''e'' or ''i''). The letter ''y'' is identical to 'i'. Older versions of the alphabet Before the standardisation of the Maltese alphabet, there were several ways of writing the sounds peculiar to Maltese, namely , , , , , , and . was formerly written as (in front of and , in Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows-1257
Windows-1257 (Windows Baltic) is an 8-bit, single-byte extended ASCII code page used to support the Estonian, Latvian and Lithuanian languages under Microsoft Windows. In Lithuania, it is standardised as LST 1590-3, alongside a modified variant named LST 1590-4. The label Windows-1257 was registered with the IANA in 1996, citing a publication of the specification in 1995 and inclusion with pan-European versions of Windows 95. The later ISO 8859-13 encoding (first published in 1998) is similar, but differs in reserving the range 0x80–9F for control characters, and accordingly locating certain quotation marks at codepoints 0xA1, 0xA5, 0xB4 and 0xFF instead (the latter two are used for spacing diacritics in Windows-1257). Windows-1257 is not compatible with the older ISO 8859-4 and ISO 8859-10 encodings. For the letters of the Estonian alphabet, Windows-1257 is compatible with IBM-922. IBM uses code page 1257 (CCSID 1257, euro sign extended CCSID 5353, and the further e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO-8859-2
ISO/IEC 8859-2:1999, ''Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 2: Latin alphabet No. 2'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. It is informally referred to as "Latin-2". It is generally intended for Central or "Eastern European" languages that are written in the Latin script. Note that ISO/IEC 8859-2 is very different from code page 852 (MS-DOS Latin 2, PC Latin 2) which is also referred to as "Latin-2" in Czech and Slovak regions. Code page 912 is an extension. Almost half the use of the encoding is for Polish, and it's the main legacy encoding for Polish, while virtually all use of it has been replaced by UTF-8 (on the web). ISO-8859-2 is the IANA preferred charset name for this standard when supplemented with the C0 and C1 control codes from ISO/IEC 6429. Less than 0.04% of all web pages use ISO-8859-2 as of October 2022. Microsoft has assigned code page 28592 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows-1250
Windows-1250 is a code page used under Microsoft Windows to represent texts in Central European and Eastern European languages that use Latin script, such as Czech (which is its main user with half its use, though Czech has 96.6% use of UTF-8, and mostly abandoned (this) legacy encoding), Polish, Slovak, Hungarian, Slovene, Serbo-Croatian (Latin script), Romanian (before 1993 spelling reform), Rotokas and Albanian. It may also be used with the German language (though it's missing uppercase ẞ); German-language texts encoded with Windows-1250 and Windows-1252 are identical. This has been replaced by Unicode (such as UTF-8) far more than Windows-1252. As of October 2022, less than 0.04% of all web pages use Windows-1250. Windows-1250 is similar to ISO-8859-2 and has all the printable characters it has and more. However a few of them are rearranged (unlike Windows-1252, which keeps all printable characters from ISO-8859-1 in the same place). Most of the rearrangements seem to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazovia Encoding
Mazovia encoding is used under DOS to represent Polish texts. Basically it is code page 437 with some positions filled with Polish letters. An important feature was that the block graphic characters of code page 437 remained unchanged. In contrast, IBM's later official Central European code page 852 did not preserve all block graphics, causing incorrect display in programs such as Norton Commander. The Mazovia encoding was designed in 1984 by Jan Klimowicz of . It was designed as part of a project to develop and produce a Polish IBM PC clone codenamed "". The code page was therefore optimized for that computer's typical peripheral devices, a graphics card with dual switchable graphics, a keyboard using US English and Russian layouts and printers with Polish fonts. In 1986, the Polish National Bank (NBP) adopted the Mazovia encoding as a standard, thereby causing its widespread acceptance and distribution in Poland. They also were instrumental in Ipaco producing compatible comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP 775
Code page 775 (CCSID 775) (also known as CP 775, IBM 00775, and OEM 775, MS-DOS Baltic Rim) is a code page used under DOS to write the Estonian, Lithuanian and Latvian languages. In Lithuania, this code page is standardised as LST 1590-1, alongside the related Code page 778 (LST 1590-2). It is possible, but unusual, to write Polish, Swedish, Finnish, Norwegian, Danish and German using this code page. The other code page used for Baltic languages is Windows-1257. Character set The following table shows code page 775. Each character is shown with its equivalent Unicode code point. Only the second half of the table (code points 128–255) is shown, the first half (code points 0–127) being the same as code page 437. References {{character encoding 775 __NOTOC__ Year 775 (Roman numerals, DCCLXXV) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 775 for this year has been used since the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP 852
Code page 852 (CCSID 852) (also known as CP 852, IBM 00852, OEM 852 (Latin II), MS-DOS Latin 2) is a code page used under DOS to write Central European languages that use Latin script (such as Bosnian, Croatian, Czech, Hungarian, Polish, Romanian, Serbian, Slovak or Slovene). CCSID 9044 is the euro currency update of code page/CCSID 852. Byte AA replaces ¬ with € in that update. Note that code page 852 (DOS Latin 2) is very different from ISO/IEC 8859-2 (ISO Latin-2), although both are informally referred to as "Latin-2" in different language regions. However, all printable characters from ISO 8859-2 are included, in a different arrangement which preserves a subset of the box-drawing characters of the original DOS code page 437, while sacrificing others (those combining both single and double lining) in order to include more letters with diacritics. This is the same approach taken by code page 850, the equivalent for ISO 8859-1. This reduced box-drawing support cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO-8859-13
ISO/IEC 8859-13:1998, ''Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 13: Latin alphabet No. 7'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1998. It is informally referred to as Latin-7 or ''Baltic Rim''. It was designed to cover the Baltic languages, and added characters used in Polish missing from the earlier encodings ISO 8859-4 and ISO 8859-10. Unlike these two, it does not cover the Nordic languages. It is similar to the earlier-published Windows-1257; its encoding of the Estonian alphabet also matches IBM-922. ISO-8859-13 is the IANA preferred charset name for this standard when supplemented with the C0 and C1 control codes from ISO/IEC 6429. Microsoft has assigned code page 28603 a.k.a. Windows-28603 to ISO-8859-13. IBM has assigned Code page 921 to ISO-8859-13. ISO-IR 206 replaces the currency sign at position A4 with the euro sign (€). Codepage layout Differences from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |