|
┼╣im
, , , or (┌ü) is a Pashto letter representing the sibilant affricative (IPA: ) sound. In size and shape, it is a ßĖź─ü╩Š with a hamza Hamza ( ar, ┘ć┘ģž▓ž® ') () is a letter in the Arabic alphabet, representing the glottal stop . Hamza is not one of the 28 "full" letters and owes its existence to historical inconsistencies in the standard writing system. It is derived from ... above. It is written in several ways depending on its position in the word: Pashto {{ie-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
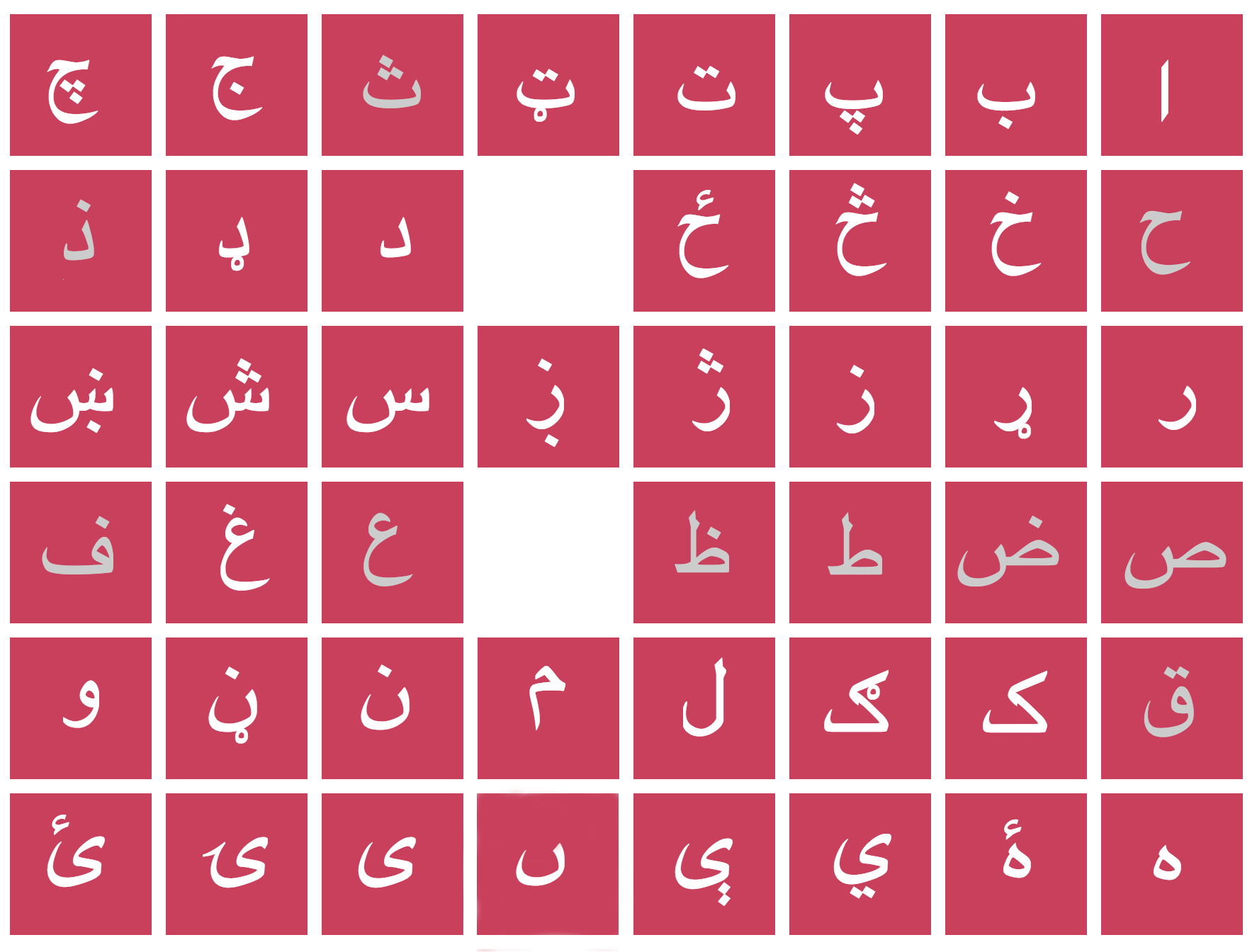
Pashto Alphabet
The Pashto alphabet () is a version of Perso-Arabic script used to write the Pashto language. Form Pashto is written in the Arabic Naskh. Pashto uses all 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet, and shares 3 letters (, , and ) with Persian in the additional letters. Differences from Persian alphabet Pashto has several letters which do not appear in any other Perso-Arabic scripts, which are shown in the table below: All the additional characters are derived from existing Arabic letters by adding diacritics; for example, the consonants ''x╠ī─½n/ß╣Ż╠ī─½n'' and ''ŪĄe/ß║ō╠īe'' look like Arabic's ''s─½n'' and ''re'' respectively with a dot above and beneath. Similarly, note that the letters representing retroflex consonants are written with a small circle (known as a "panßĖŹak", "─¤aß╣øwanday" or "sk╔Öß╣ćay") attached underneath the corresponding dental consonants. The consonant is written as either or . In addition to Persian vowels, Pashto has , , , and for additional vowels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affricate
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pair. English has two affricate phonemes, and , often spelled ''ch'' and ''j'', respectively. Examples The English sounds spelled "ch" and "j" ( broadly transcribed as and in the IPA), German and Italian ''z'' and Italian ''z'' are typical affricates, and sounds like these are fairly common in the world's languages, as are other affricates with similar sounds, such as those in Polish and Chinese. However, voiced affricates other than are relatively uncommon. For several places of articulation they are not attested at all. Much less common are labiodental affricates, such as in German and Izi, or velar affricates, such as in Tswana (written ''kg'') or in High Alemannic Swiss German dialects. Worldwide, relatively few languages have af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ßĖź─ü╩Š
Heth, sometimes written Chet, but more accurately ßĖżet, is the eighth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ßĖż─ōt Éżć , Hebrew ßĖż─ōth , Aramaic ßĖż─ōth , Syriac ßĖż─ōß╣» ▄Ü, Arabic ßĖż─ü' , and Maltese ─”, ─¦. Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either pharyngeal , or velar . In Arabic, two corresponding letters were created for both phonemic sounds: unmodified ' represents , while ' represents . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek eta , Etruscan , Latin H, and Cyrillic ąś. While H is a consonant in the Latin alphabet, the Greek and Cyrillic equivalents represent vowel sounds, though the letter was originally a consonant in Greek and this usage later evolved into the rough breathing character. Origins The shape of the letter ßĖżet ultimately goes back either to the Egyptian hieroglyph for 'courtyard': O6 (compare Hebrew ūŚųĖū”ųĄū© ßĖźatser of identical meaning, which begins with ßĖżet) or to the one for 'thread, wick' represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamza
Hamza ( ar, ┘ć┘ģž▓ž® ') () is a letter in the Arabic alphabet, representing the glottal stop . Hamza is not one of the 28 "full" letters and owes its existence to historical inconsistencies in the standard writing system. It is derived from the Arabic letter ''╩┐Ayn'' (). In the Phoenician and Aramaic alphabets, from which the Arabic alphabet is descended, the glottal stop was expressed by '' alif'' (), continued by ''Alif'' ( ) in the Arabic alphabet. However, Alif was used to express both a glottal stop and also a long vowel . In order to indicate that a glottal stop is used, and not a mere vowel, it was added to Alif diacritically. In modern orthography, hamza may also appear on the line, under certain circumstances as though it were a full letter, independent of an Alif. Etymology ''Hamza'' is derived from the verb ' () meaning 'to prick, goad, drive' or 'to provide (a letter or word) with hamzah'. Hamzat al-waß╣Żl ( ┘▒ ) The letter hamza () on its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |