|
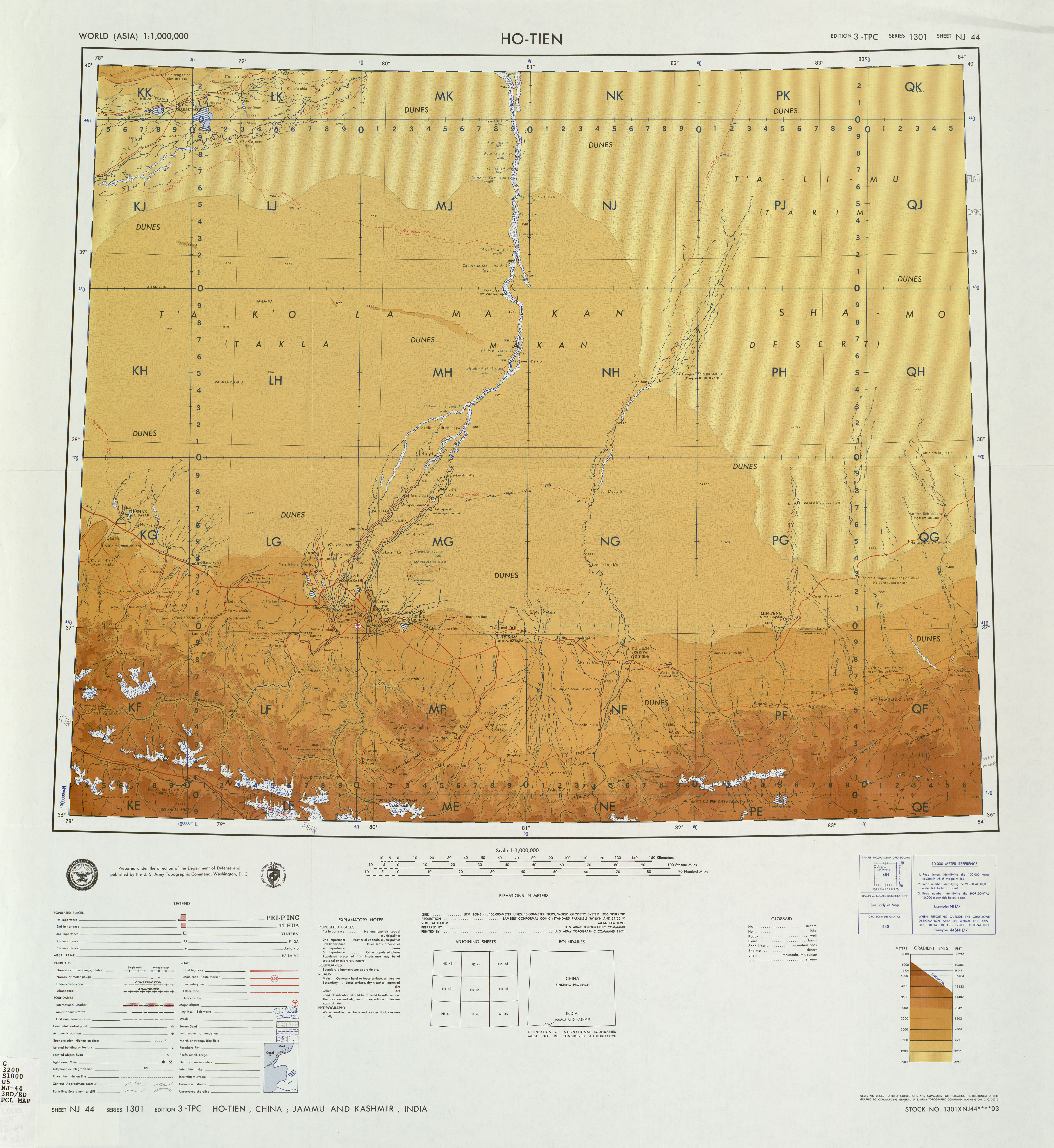
Śita River
The Tarim River ( zh, p=TŪÄlŪÉm├╣ H├®, c=ÕĪöķćīµ£©µ▓│; ug, ž¬ž¦ž▒┘ē┘ģ ž»█Ģž▒┘Ŗž¦ž│┘ē, Tarim deryasi), known in Sanskrit as the ┼Ü─½t─ü, is an endorheic river in Xinjiang, China. It is the principal river of the Tarim Basin, a desert region of Central Asia between the Tian Shan and Kunlun Mountains. The river historically terminated at Lop Nur, but today reaches no further than Taitema Lake before drying out. It is the longest inland river in China. The Tarim River originates from the Karakoram Mountains and flows into Lop Nur along the northern edge of the Taklimakan Desert. It has a total length of 2,327 kilometers and a drainage area of 1.02 million square kilometers. Its main tributaries include the Hotan River, the Aksu River, and the Kashgar River. The course of the Tarim River swings from north to south in history, and its migration is uncertain. The last major river change occurred in 1921, when the main stream was diverted to the east and flowed into Lop Nur th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkand River
The Yarkand River (or Yarkent River, Yeh-erh-ch'iang Ho) is a river in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of western China. It originates in the Siachen Muztagh in a part of the Karakoram range and flows into the Tarim River or Neinejoung River, with which it is sometimes identified. However, in modern times, the Yarkand river drains into the Midstream Reservoir and exhausts its supply without reaching the Tarim river. The Yarkand River is approximately in length, with an average discharge of . A part of the river valley is known to the Kyrgyz people as Raskam Valley, and the upper course of the river itself is called the Raskam River. Another name of the river is Zarafshan. The area was once claimed by the ruler of Hunza. Course The river originates from the Siachen Muztagh in the Karakoram range in IndiaŌĆōSinkiang border region, south of the Kashgar Prefecture. It flows roughly due north until reaching the foot of the Kunlun Mountains. Then it flows northwest where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, ╬ĀŽä╬┐╬╗╬Ą╬╝╬▒ß┐¢╬┐Žé, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Math─ōmatik─ō Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetr├Ībiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Licorice
Ural may refer to: *Ural (region), in Russia and Kazakhstan *Ural Mountains, in Russia and Kazakhstan *Ural (river), in Russia and Kazakhstan *Ual (tool), a mortar tool used by the Bodo people of India *Ural Federal District, in Russia *Ural economic region, in Russia *Ural Oblast (Russian Empire) (1868ŌĆō1920), an administrative division of the Russian Empire and the early Russian SFSR *Ural (computer) *Ural Airlines, a Russian airline based in Yekaterinburg *Ural Automotive Plant (brand name "Ural"): **Ural-375D, a military truck manufactured by Ural Automotive Plant **Ural-4320, a military truck manufactured by Ural Automotive Plant **Ural-5323, a military truck manufactured by Ural Automotive Plant *Ural 63055 and Ural-63059, variants of Ural Typhoon, a Russian armored vehicle *Ural bomber, aircraft design program to design a long-range bomber for Luftwaffe *IMZ-Ural, a Russian motorcycle manufacturer *Murat Ural (b. 1987), Swiss soccer player *Ural (rural locality), severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis Indica
''Cannabis indica'' is an annual plant species in the family Cannabaceae which produces large amounts of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and is cultivated for purposes including hashish in India. The high concentrations of THC provide euphoric effects making it popular for use both as a recreational drug, alternative medicine, and a clinical research drug. Taxonomy In 1785, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck published a description of a second species of ''Cannabis'', which he named ''Cannabis indica''. Lamarck based his description of the newly named species on plant specimens collected in India. Richard Evans Schultes described ''C. indica'' as relatively short, conical, and densely branched, whereas '' C. sativa'' was described as tall and laxly branched. Loran C. Anderson described ''C. indica'' plants as having short, broad leaflets whereas those of ''C. sativa'' were characterized as relatively long and narrow. ''C. indica'' plants conforming to Schultes's and Ander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Buckthorn
''Hippophae'' is the genus of sea buckthorns, deciduous shrubs in the family Elaeagnaceae. The name sea buckthorn may be hyphenated to avoid confusion with the unrelated true buckthorns (''Rhamnus'', family Rhamnaceae). It is also referred to as sandthorn, sallowthorn, or seaberry. It produces orange-yellow berries, which have been used over centuries as food, traditional medicine, and skin treatment in Mongolia, Ladakh, Russia, Ukraine, and northern Europe, which are its origin regions. It is an exceptionally hardy plant able to withstand winter temperatures as low as . Because ''Hippophae'' develops an aggressive and extensive root system, it is planted to inhibit soil erosion and is used in land reclamation for its nitrogen fixing properties, wildlife habitat, and soil enrichment. ''Hippophae'' berries and leaves are manufactured into various human and animal food and skincare products. Description The shrubs reach tall, rarely up to in central Asia. The leaf arrangement c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willows
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populus
''Populus'' is a genus of 25ŌĆō30 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar (), aspen, and cottonwood. The western balsam poplar ('' P. trichocarpa'') was the first tree to have its full DNA code determined by DNA sequencing, in 2006. Description The genus has a large genetic diversity, and can grow from tall, with trunks up to in diameter. The bark on young trees is smooth, white to greenish or dark gray, and often has conspicuous lenticels; on old trees, it remains smooth in some species, but becomes rough and deeply fissured in others. The shoots are stout, with (unlike in the related willows) the terminal bud present. The leaves are spirally arranged, and vary in shape from triangular to circular or (rarely) lobed, and with a long petiole; in species in the sections ''Populus'' and ''Aigeiros'', the petioles are laterally flattened, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tugay
Tugay is a form of riparian forest or woodland associated with fluvial and floodplain areas in arid climates. These wetlands are subject to periodic inundation, and largely dependent on floods and groundwater rather than directly from rainfall. Tugay habitats occur in semi-arid and desert climates in central Asia. Because Tugay habitat is usually linear, following the courses of rivers in arid landscapes, Tugay communities often function as wildlife corridors. They have disappeared or become fragmented over much of their former range. Distribution The centre of the range of Tugay vegetation is the Tarim Basin in north-western China, where the Tarim Huyanglin nature reserve in the middle reaches of the Tarim River holds the largest areas of intact Tugay forests, with a 1993 estimate of about 61% of the total. The Central Asian countries hold another 31%, with smaller areas remaining in the Middle East and Pakistan. Tugais also occur in the Caucasus. Vegetation Close to ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzat River
The Muzart River () or Muzat River (; ug, ┘ģ█ćž▓ž¦ž¬ ž»█Ģž▒┘Ŗž¦ž│┘ē, translit=Muzat Deryasi) is a river in Aksu Prefecture of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, People's Republic of China, a left tributary of the Tarim River. An early 20th-century source also gives an alternative name for this river, Sh─üh-Y─ür-Dary─ü."Tarim", in Sh─üh-Y─ür-Dary─ü (ž┤ž¦┘ćŌĆī█īž¦ž▒ž»ž▒█īž¦) is a Persian word meaning 'The King's aide River.' The Muzart River starts in the Muzart Glacier (µ£©µēÄÕ░öńē╣Õå░ÕĘØ) in the Tian Shan Mountains, not too far from the Khan Tengri Peak, and flows toward the southeast and east through Baicheng County, in the valley between the main range of the Tian Shan and the Queletage Mountains (ÕŹ┤ÕŗÆÕĪöµĀ╝Õ▒▒) to the south. Most of Baicheng County's population lives in the valley irrigated by this river. As the river flows east, toward Kucha, it crosses the Queletage Range in a steep valley. Cut into the northern walls of the valley are 230 caves and grottos, forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khotan River
The Hotan River (also known as the Khotan River or the Ho-t'ien River) is formed by the union of the White Jade (Yurungkash) and Karakash (Black Jade) Rivers, which flow north from the Kunlun Mountains into the Taklamakan Desert in northern China. The two rivers unite towards the middle of the desert, some north of the town of Hotan. The river then flows northwards across the desert and empties itself into the Tarim River."Khotan-Darya". 1911 Encyclop├”dia Britannica. Because the river is fed by melting snow from the mountains, it only carries water during the summer and is dry the rest of the year. Prior to construction of the Tarim Desert Highway in 1995, the Hotan river bed provided the only transportation system across the Tarim Basin The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aral, Xinjiang
AralThe official spelling according to , (Beijing, ''SinoMaps Press'' 1997); is a sub-prefecture-level city surrounded by Aksu Prefecture in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China. Aral means "island" in Uyghur. The city's name is also often written as Alar. History According to Radio Free Asia, a United States government-funded news service, Aral was created in the 1950s by the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps to facilitate Han Chinese immigration to the region. Aral became a city in 2002 and its population increased to 166,205 in 2010. On January 23, 2013, of territory was transferred from Awat County (Awati) to Aral city and of territory was transferred from Aksu city (Akesu) to Aral city. Geography The city has an administrative area of . It is bordered by mountainous regions to the north and northwest and the Taklamakan Desert to the east and south. Demographics As of 2015, 167,697 (93.6%) of the 179,214 residents of the county were Han Chinese, 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |