|
öre
Öre () is the centesimal subdivision of the Swedish krona. In the Swedish language, the plural of ''öre'' is either ''öre'' or ''ören''. The name ''öre'' derives from the Latin word ''aereus/aurum'', meaning gold. The corresponding subdivisions of the Norwegian and Danish krones are called øre. History During the Middle Ages, the öre was a unit of Swedish currency equal to 1/8 of a ''mark'', 3 ''örtugar'' or either 24, 36 or 48 '' penningar'' (depending on the geographical area in which it was used). It was already a unit of account in the 11th century, but was not minted as a coin until 1522. This öre was withdrawn in 1776, but returned in 1855 as 1/100 of the riksdaler. The riksdaler was replaced by the ''krona'' in 1873 (one riksdaler equalling one krona), but ''öre'' remained the name of the minor unit. The last öre coin was withdrawn in 2010, but the centesimal subdivision is still used in non-cash contexts such as bank balances and cashless transactions, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Krona
The krona (; plural: ''kronor''; sign: kr; code: SEK) is the official currency of the Kingdom of Sweden. Both the ISO code "SEK" and currency sign "kr" are in common use; the former precedes or follows the value, the latter usually follows it but, especially in the past, it sometimes preceded the value. In English, the currency is sometimes referred to as the Swedish crown, as means "crown" in Swedish. The Swedish krona was the ninth-most traded currency in the world by value in April 2016. One krona is subdivided into 100 ''öre'' (singular; plural ''öre'' or ''ören'', where the former is always used after a cardinal number, hence "50 öre", but otherwise the latter is often preferred in contemporary speech). However, all öre coins were discontinued from 30 September 2010. Goods can still be priced in ''öre'', but all sums are rounded to the nearest krona when paying with cash. The word ''öre'' is ultimately derived from the Latin word for gold (''aurum''). History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cash Rounding
Cash rounding or Swedish rounding (New Zealand English) occurs when the minimum unit of account is smaller than the lowest physical denomination of currency. The amount payable for a cash transaction is rounded to the nearest multiple of the minimum currency unit available, whereas transactions paid in other ways are not rounded (for example electronic funds transfer like credit cards, or negotiable instruments like cheques). Cash rounding typically occurs when low-denomination coins are removed from circulation owing to inflation. Cash rounding may be a compulsory legal requirement if such coins are no longer legal tender, or a voluntary practice where they remain in circulation but are scarce or impractical. Cash rounding ("öre rounding", ) was introduced in Sweden in 1972 when 1 and 2 öre coins were withdrawn from circulation, and has continued to be applied at incremental levels as smaller denomination coins have been withdrawn. The current level of cash rounding in Sweden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Riksdaler
The svenska riksdaler () was the name of a Swedish coin first minted in 1604. Between 1777 and 1873, it was the currency of Sweden. The daler, like the dollar,''National Geographic''. June 2002. p. 1. ''Ask Us''. was named after the German Thaler. The similarly named Reichsthaler, rijksdaalder, and rigsdaler were used in Germany and Austria-Hungary, the Netherlands, and Denmark-Norway, respectively. ''Riksdaler'' is still used as a colloquial term for Sweden's modern-day currency. History Penning accounting system The ''daler'' was introduced in 1534. It was initially intended for international use and was divided into 4 marks and then a mark is further subdivided into 8 öre and then an öre is further subdivided into 24 pennings. In 1604, the name was changed to ''riksdaler'' ("daler of the realm", c.f. Reichsthaler). In 1609, the riksdaler rose to a value of 6 mark when the other Swedish coins were debased but the riksdaler remained constant. From 1624, daler were issued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Penning
The penning or penny was the Swedish variant of the Norwegian penning that was minted from about 1150 until 1548, and which remained as a unit of account in Sweden until 1777. Originally penning was first minted in Norway by the Norwegian king Olaf Tryggvason from the year 995, and was later adapted in both Sweden and Denmark as a coin system. The penning was minted in imitation of the pennies, pfennig and deniers issued elsewhere in Europe. However, although based on these coins, the accounting system was distinct, with different systems operating in different regions. All used the ''öre'' (derived from the Latin ''aureus'') which was worth 1/8 of a mark or 3 örtugar. However in Svealand, one öre was worth 24 penningar, but in Götaland it was worth 48 penningar and 36 in roughly the Diocese of Linköping and on Gotland. Around 1300, by royal command, the Svealand standard became the national standard, except on Gotland. The örtug was first minted around 1370 and the öre was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Withdrawal Of Low-denomination Coins
The withdrawal of a country's lowest-denomination coins from circulation (usually a one- cent coin or equivalent) may either be through a decision to remove the coins from circulation, or simply through ceasing minting. Reasons This withdrawal may be due to the high cost of production, since the coin may be worth less than its cost of production. For example, when Canada phased out its penny in 2012, its production cost was 1.6 cents per penny. Other reasons include low purchasing power and low utility. Often coins are withdrawn after their purchasing power has been eroded after decades of inflation. In Switzerland, the 1 Rappen coin had fallen into disuse by the early 1980s, but was still produced until 2006, albeit in ever decreasing quantities. Conversely, the British Treasury department initially argued for the retention of the ''decimal'' halfpenny, on the grounds that its withdrawal would drive up inflation. In some countries, such as New Zealand, withdrawn coins are decla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
√∏re
Øre (plural ''øre'', ) is the centesimal subdivision of the Danish and Norwegian krones. The Faroese division is called the ''oyra'', but is equal in value to the Danish coin. Before their discontinuation, the corresponding divisions of the Swedish krona and the Icelandic króna were the öre and the eyrir, respectively. The name ''øre/öre'' derives from the Latin word ''aereus/aurum'', meaning gold. The Norwegian 10-øre coin was deprecated on 23 February 1992 and ceased to be legal tender in 1993. From then on, the only Norwegian coin in use with a value below NOK 1 was the 50-øre coin, which was also deprecated on 1 May 2012. The original value were the 1-, 2-, 5-, 10-, 25- and 50-øre coins. The Danish 25 øre coin ceased to be legal tender on 1 October 2008. The only Danish coin currently in use with a value below DKK 1 is the 50 øre. See also * Heller (money) (subdivision of Czech and Slovak crowns) * Fillér (subdivision of Hungarian Forint) * Other coin names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
√òre
Øre (plural ''øre'', , ) is the centesimal subdivision of the Danish and Norwegian krone. The Faroese division is called the ''oyra'', but is equal in value to the Danish coin. Before their discontinuation, the corresponding divisions of the Swedish krona and the Icelandic króna were the öre and the eyrir, respectively. The name ''øre/öre'' derives from the Latin word ''aereus/aurum'', meaning gold. The Norwegian 10-øre coin was deprecated on 23 February 1992 and ceased to be legal tender in 1993. From then on, the only Norwegian coin in use with a value below NOK 1 was the 50-øre coin, which was also deprecated on 1 May 2012. The original value were the 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, and 50-øre coins. The Danish 25 øre coin ceased to be legal tender on 1 October 2008. The only Danish coin currently in use with a value below DKr 1 is the 50 øre. See also * Heller (money) (subdivision of Czech and Slovak crowns) * Fillér (subdivision of Hungarian forint) * Other coin n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
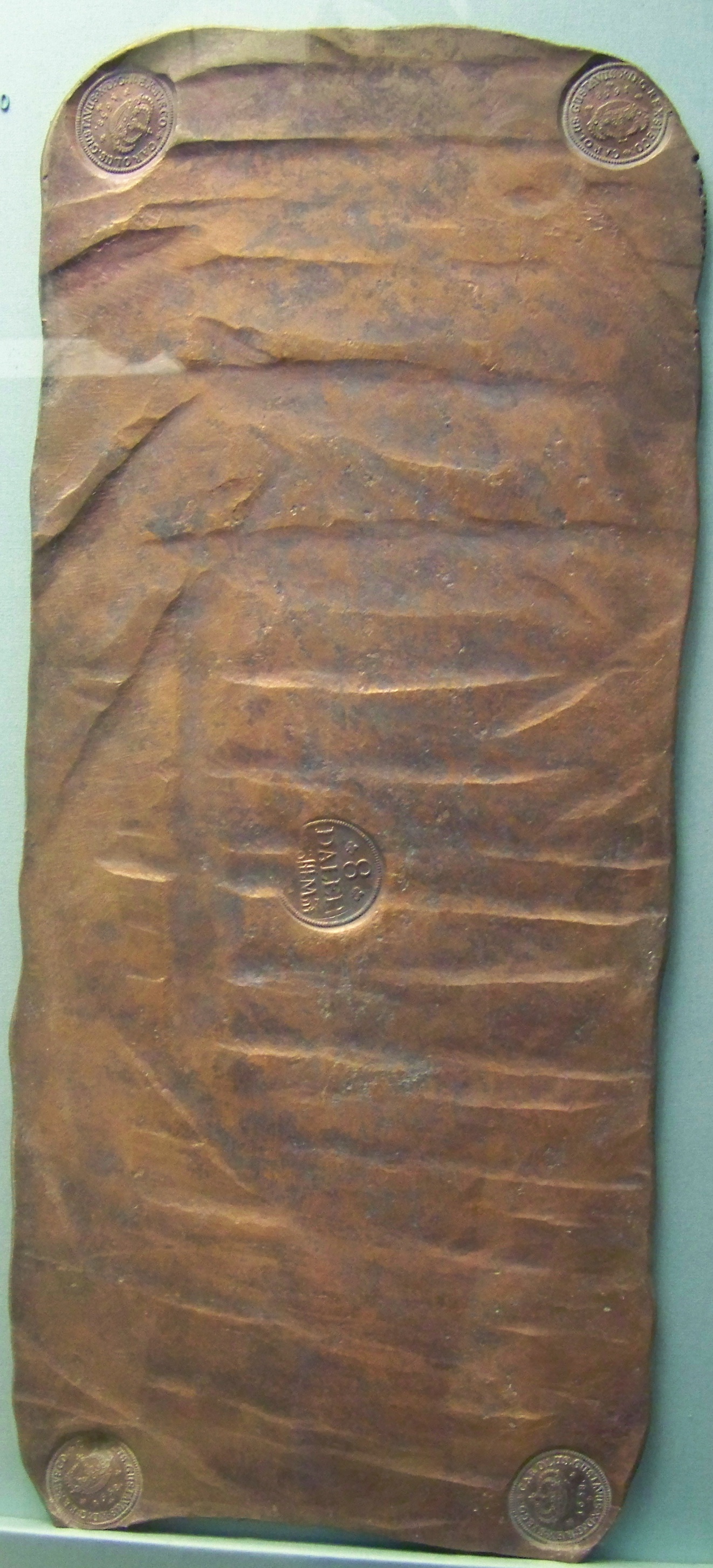
örtug
Örtug or ortig (Finnish: ''äyrityinen'', ''aurto'' or ''aurtua'') was a medieval currency unit in Sweden. It was originally minted as a silver coin in 1370 during the reign of king Albert of Sweden. The coin weighed about 1.3 grams and consisted of 81% silver. As time passed, the örtug was debased: during the reign of Eric of Pomerania, the örtug contained 0.88 grams of silver; under Christian I, 0.7 grams; and in 1534 only 0.54 grams of silver. During the reign of Gustav Vasa (1523–1560), the monetary system of Sweden was reformed: an örtug was now subdivided into 12 pennings, not 8 as before, while still valued as one third of an öre. Örtug coins were struck during the years 1523–1534; 1535–1540 in Stockholm; 1528–1531 in Västerås and 1589–1589 in Stockholm and Uppsala. Production ceased after another monetary reform in 1776. The örtug is also used as the official name of the currency in the artist Lars Vilks' micronation of Ladonia. See also *Swedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles XV Of Sweden
Charles XV also Carl (''Carl Ludvig Eugen''); Swedish: ''Karl XV'' and Norwegian: ''Karl IV'' (3 May 1826 – 18 September 1872) was King of Sweden (''Charles XV'') and Norway, there often referred to accurately as Charles IV, from 1859 until his death in 1872. Though known as King Charles XV in Sweden (and also on contemporary Norwegian coins), he was actually the ninth Swedish king by that name, as his predecessor Charles IX (reigned 1604–1611) had adopted a numeral according to a fictitious history of Sweden. Charles XV was the third Swedish monarch from the House of Bernadotte and the first one to be born in Sweden. Biography Early life He was born in Stockholm Palace, Stockholm, in 1826 and dubbed Duke of Scania at birth. Born the eldest son of Crown Prince Oscar of Sweden and his wife Crown Princess Josephine, he would be second in line to the throne of his grandfather, the ruling King Charles XIV John of Sweden. During his childhood he was placed in the care o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagens Nyheter
''Dagens Nyheter'' (, ), abbreviated ''DN'', is a daily newspaper in Sweden. It is published in Stockholm and aspires to full national and international coverage, and is widely considered Sweden's newspaper of record. History and profile ''Dagens Nyheter'' was founded by Rudolf Wall in December 1864. The first issue was published on 23 December 1864. During its initial period the paper was published in the morning. In 1874 the paper became a joint stock company. Its circulation in 1880 was 15,000 copies. In the 1890s, Wall left ''Dagens Nyheter'' and soon after, the paper became the organ of the Liberal Party. From 1946 to 1959, Herbert Tingsten was the executive editor. The newspaper is owned by the Bonnier Group since 1909, when Karl Otto Bonnier acquired the remaining shares that his family had not owned (his father Albert had already acquired some shares since 1888). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_örtug_från_medeltiden.png)
