|
Ămar Ua DonnabĂĄin
Ămar ( non, Ăvarr ; died c. 873), who may be synonymous with Ivar the Boneless, was a Viking leader in Ireland and Scotland in the mid-late ninth century who founded the UĂ Ămair dynasty, and whose descendants would go on to dominate the Irish Sea region for several centuries. He was the son of the king of Lochlann, identified in the non-contemporary ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland'' as Gofraid of Lochlann, Gofraid. The ''Fragmentary Annals'' name Auisle and AmlaĂb Conung as his brothers. Another Viking leader, Halfdan Ragnarsson, is considered by some scholars to be another brother. The Irish Annals title AmlaĂb, Ămar and Auisle "kings of the foreigners". Modern scholars use the title "Kingdom of Dublin, Kings of Dublin" after the Viking settlement which formed the base of their power. Some scholars consider Ămar to be identical to Ivar the Boneless, a Viking commander of the Great Heathen Army named in contemporary English sources who also appears in the Icelandic sagas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Dublin
Vikings invaded the territory around Dublin in the 9th century, establishing the Norse Kingdom of Dublin, the earliest and longest-lasting Norse kingdom in Ireland. Its territory corresponded to most of present-day County Dublin. The Norse referred to the kingdom as ''Dyflin'', which is derived . The first reference to the Vikings comes from the '' Annals of Ulster'' and the first entry for 841 AD reads: "Pagans still on Lough Neagh". It is from this date onward that historians get references to ship fortresses or longphorts being established in Ireland. It may be safe to assume that the Vikings first over-wintered in 840â841 AD. The actual location of the longphort of Dublin is still a hotly debated issue. Norse rulers of Dublin were often co-kings, and occasionally also Kings of JĂłrvĂk in what is now Yorkshire. Under their rule, Dublin became the biggest slave port in Western Europe. Over time, the settlers in Dublin became increasingly Gaelicized. They began to exhibit a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halfdan Ragnarsson
Halfdan Ragnarsson ( non, HĂĄlfdan; oe, Halfdene or ''Healfdene''; sga, Albann; died 877) was a Viking leader and a commander of the Great Heathen Army which invaded the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England, starting in 865. One of six sons of Ragnar Lodbrok named in Norse sagas, Halfdan's brothers or half-brothers included Björn Ironside, Ivar the Boneless, Sigurd Snake-in-the-Eye, Ubba and Hvitserk. Because Halfdan is not mentioned in any source that mentions Hvitserk, some scholars have suggested that they are the same individual â a possibility reinforced by the fact that Halfdan was a relatively common name among Vikings and ''Hvitserk'' "white shirt" may have been an epithet or nickname that distinguished Halfdan from other men by the same name. Halfdan was the first Viking King of Northumbria and a pretender to the throne of Kingdom of Dublin. It is also possible he was for a time co-ruler of Denmark with his brother Sigurd Snake-in-the-eye, because Frankish sources ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumbarton Rock
Dumbarton (; also sco, Dumbairton; ) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 19,990. Dumbarton was the capital of the ancient Kingdom of Strathclyde, and later the county town of Dunbartonshire. Dumbarton Castle, on top of Dumbarton Rock, dominates the area. Dumbarton was a Royal burgh between 1222 and 1975. Dumbarton emerged from the 19th century as a centre for shipbuilding, glassmaking, and whisky production. However these industries have since declined, and Dumbarton today is increasingly a commuter town for Glasgow east-southeast of it. Dumbarton F.C. is the local football club. Dumbarton is home to BBC Scotland's drama studio. History Dumbarton history goes back at least as far as the Iron Age and probably much earlier. It has been suggested that in Ancient Rome, Roman times Dumbarton was the "place of importance" named as Alauna i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
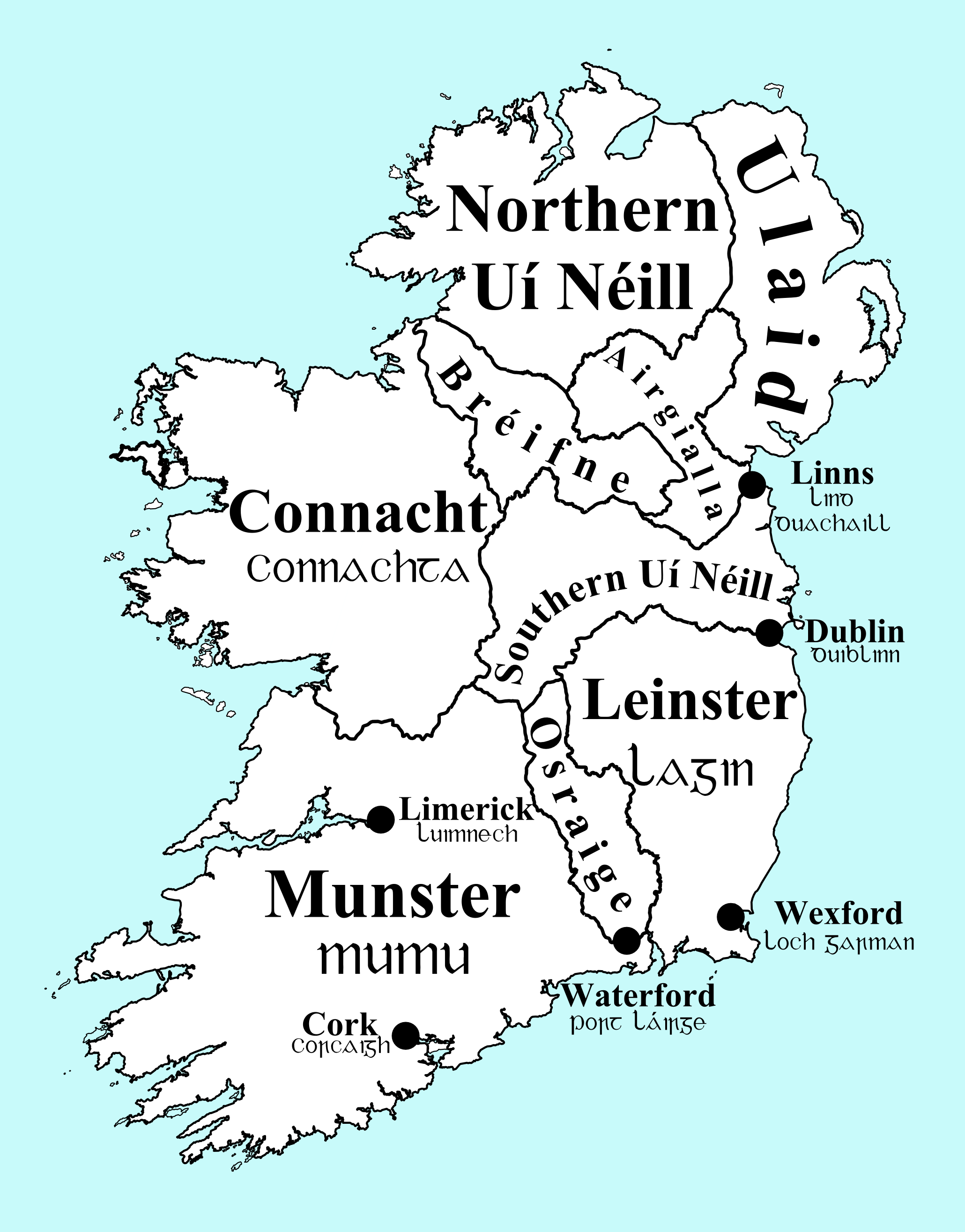
Northern UĂ NĂ©ill
The Northern UĂ NĂ©ill is any of several dynasties in north-western medieval Ireland that claimed descent from a common ancestor, Niall of the Nine Hostages. Other dynasties in central and eastern Ireland who also claimed descent from Niall were termed the Southern UĂ NĂ©ill (together they are known as the UĂ NĂ©ill dynasty). The dynasties of the Northern UĂ NĂ©ill were the CenĂ©l Conaill and CenĂ©l nEĂłgain, named after the two most powerful sons of Niall: Conall and EĂłgain. The Northern UĂ NĂ©ill's over-kingdom in its earliest days was known as In Fochla and In Tuaiscert, both meaning "the North", and was initially ruled by the CenĂ©l Conaill. After the CenĂ©l nEĂłgain's rise to dominance, it became known as Ailech. Mythical origins It is claimed in medieval Irish texts that around 425, three sons of Niall NoĂgiallach â Eoghan, Conal Gulban, and Enda â along with Erc, a son of Colla Uais, and his grandchildren, invaded north-western Ulster. The result was the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ăed Findliath
Ăed mac NĂ©ill (died 879), called Ăed Findliath ("fair-grey Ăed"; Modern Irish: ''Aodh Fionnadhliath'') to distinguish him from his paternal grandfather Ăed Oirdnide, was king of Ailech and High King of Ireland. He was also called Ăed Olach ("The anointing one") according to Baile in ScĂĄil, section 51. A member of the northern UĂ NĂ©ill kindred of the CenĂ©l nEĂłgain, Ăed was the son of Niall Caille. Background From the death of Ăed AllĂĄn in 743 until the overthrow of MĂĄel Sechnaill mac Domnaill by Brian Boru in 1002, the succession to the High Kingship of Ireland alternated between northern and southern branches of the UĂ NĂ©ill with the north represented by members of the CenĂ©l nĂogain, Ăed's paternal kindred, and the south by the Clann CholmĂĄin, his mother's kin. Francis John Byrne describes this as "a fragile convention, marked by watchful jealousy rather than friendly accord". During the reign of MĂĄel Sechnaill mac MĂĄele Ruanaid, who succeeded Ăed's fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Osraige
The kings of Osraige (alternately spelled ''Osraighe'' and Anglicised as ''Ossory'') reigned over the medieval Irish kingdom of Osraige from the first or second century AD until the late twelfth century. Osraige was a semi-provincial kingdom in south-east Ireland which disappeared following the Norman Invasion of Ireland. A number of important royal Ossorian genealogies are preserved, particularly MS Rawlinson B502, which traces the medieval Mac Giolla PhĂĄdraig dynasty back through Ăengus Osrithe, who supposedly flourished in the first or second century. and one in the ''Book of Leinster'' (also known as "''Lebor na NuachongbĂĄla''"). Recent analysis of ninth and tenth century regnal succession in Osraige has suggested that in peaceful times, kingship passed primarily from eldest to youngest brother, before crossing generations and passing to sons and nephews. Early kings of Osraige The following kings are listed in all major genealogies, but originate from an early period in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerball Mac DĂșnlainge
Cerball mac DĂșnlainge (patronymic sometimes spelled ''DĂșngaile'', ) (died 888) was king of Ossory in south-east Ireland. The kingdom of Ossory (''Osraige'') occupied roughly the area of modern County Kilkenny and western County Laois and lay between the larger provincial kingdoms of Munster and Leinster. Cerball came to prominence after the death of Fedelmid mac Crimthainn, King of Munster, in 847. Ossory had been subject for a period to the EĂłganachta kings of Munster, but Feidlimid was succeeded by a series of weak kings who had to contend with Viking incursions on the coasts of Munster. As a result, Cerball was in a strong position and is said to have been the second most powerful king in Ireland in his later years. Upon his death, he was succeeded by his brother Riagan mac DĂșnlainge. Kjarvalr Ărakonungr (Old Norse: ; Modern Icelandic: ), a figure in the Norse sagas who appears as an ancestor of many prominent Icelandic families, is identified with Cerball. Nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rĂ ruirech). Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the ancient kingdoms were shired into Counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has seen further sub-division of the historic counties. Munster has no official function for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government purposes. For the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization, ISO, the province is listed as one of the provincial sub-divisions of the State (ISO 3166-2:IE) and coded as "IE-M". Geographically, Munster covers a total area of and has a population of 1,364,098, with the most populated city being Cork (city), Cork. Other significant urban centres in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern UĂ NĂ©ill
The Southern UĂ NĂ©ill ( ga, UĂ NĂ©ill an Deiscirt, IPA: iËËnÊČeËlÌȘÊČËanË ËdÊČÉÊcÉÉŸË tÊČ were that branch of the UĂ NĂ©ill dynasty that invaded and settled in the Kingdom of Mide and its associated kingdoms. In the initial decades two sons of Niall Noigiallach, LĂłegaire and Coirpre and their immediate descendants led the dynasty. However, after the murder of TĂșathal MĂĄelgarb in about 549, it was left to another branch of the family descended from another of Niall's sons â Conall Cremthainne â to continue UĂ NĂ©ill expansion and consolidate their position. No descendants of either Lugaid mac LĂłegairi or TĂșathal MĂĄelgarb are recorded, and it is not unlikely that they were either erased from the genealogical record, or indeed literally erased from history. Just as their kinsmen the Northern UĂ NĂ©ill split into two main branches, so too did the Southern UĂ NĂ©ill, both being descended from sons of Diarmait mac Cerbaill, ColmĂĄn MĂĄr and Ăed SlĂĄine. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aslaug
Aslaug ( non, Ăslaug ), also called Aslög, KrĂĄka (O.N.: ) or Kraba, is a figure in Norse mythology who appears in Snorri's Edda, the Völsunga saga and in the saga of Ragnar Lodbrok as one of his wives. Aslaug in legend According to the 13th-century ''Tale of Ragnar Lodbrok'', Aslaug was the daughter of Sigurd and the shieldmaiden Brynhildr, but was raised by Brynhildr's foster father Heimer. At the deaths of Sigurd and Brynhildr, Heimer was concerned about Aslaug's security, so he made a harp large enough to hide the girl. He then traveled as a poor harp player carrying the harp containing the girl. They arrived at Spangereid at Lindesnes in Norway, where they stayed for the night in the house of the peasants Ăke and Grima. Ăke believed the harp contained valuable items and told his wife Grima. Grima then persuaded him to murder Heimer as he was sleeping. However, when they broke the harp open, they discovered a little girl, whom they raised as their own, calling her Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragnar Lodbrok
according to legends, was a Viking hero and a Danish and Swedish king.Gutenberg Project version published 13 December 2017. He is known from of the , Icelandic s, and near-contemporary chronicles. According to traditional literature, Ragnar distinguished himself by conducting many raids against the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |