|
Xerocomorubin
Xerocomorubin is a pigment from the fungus order Boletales. It is the oxidized form of isoxerocomic acid. Air oxidation is responsible its formation, and it oxidizes faster to a similar pulvinic acid type pigment oxidized variant, variegatorubin. The long wavelength has an absorption at 497 nm, 106 nm higher than its precursor isoxerocomic acid. Synthesis experiments have shown tetra-acetylation by acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid. Although xerocomorubin and variegatorubin give off the same deep red color and could simultaneously occur in a mushroom, extracts from the deep red colored mushroom '' Boletus rubellus'' Krombh. identified only variegatorubin by thin layer chromatography Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a t ... (TLC), leading to the question the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoxerocomic Acid
Isoxerocomic acid is a red-orange pigment found in ''Boletales''. It is the precursor to variegatic acid, and is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from ''Serpula lacrymans''. It is soluble in methanol. It is the isomer of xerocomic acid Xerocomic acid is a red-orange pigment found in fungi of the order ''Boletales'' (and is named after the genus '' Xerocomus''). It is the precursor to variegatic acid, and is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin. As an example, it is isolate ... and precursor to xerocomorubin. References {{Reflist, refs= Gill, M., and Steglich, W. (1987) Pigments of fungi (Macromycetes). Prog Chem Org Nat Prod 51: 1–317. Catechols Furanones 3-Hydroxypropenals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boletales
The Boletales are an order of Agaricomycetes containing over 1300 species with a diverse array of fruiting body types. The boletes are the best known members of this group, and until recently, the Boletales were thought to only contain boletes. The Boletales are now known to contain distinct groups of agarics, puffballs, and other fruiting-body types. Taxonomy The order Boletales originally was created to describe boletes, but based on micromorphological and molecular phylogenetic characteristics, a large number of nonbolete species have recently been reclassified to belong to this group, as well. The order also includes some gilled mushrooms, in the families Gomphidiaceae, Serpulaceae, Tapinellaceae, Hygrophoropsidaceae, and Paxillaceae, which often have the same flesh texture as the boletes, spore-bearing tissue which is also easily separable from the cap, and similar microscopic characteristics of spores and cystidia. Taxonomic studies using secondary metabolites and la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variegatorubin
Variegatorubin is a pulvinic acid derivative. It is a red pigment that is present in many members of the Boletales, an order of the division Basidiomycota. It is generated from the oxidation of variegatic acid. Bolete species that contain variegatorubin include '' Neoboletus luridiformis'', ''Chalciporus piperatus'', '' Rhizopogon roseolus'', '' Exsudoporus frostii'', '' Suillellus luridus'', ''Rubroboletus rhodoxanthus'', and '' R. satanas''. Variegatorubin was discovered by Wolfgang Steglich Wolfgang Steglich (born 12 August 1933) is a German chemist . Life Wolfgang Steglich was born in Kamenz and studied chemistry at the Technical University of Berlin and later at the Technical University of Munich where he received his PhD in 19 ... and colleagues, and described as a new compound in 1970. References {{Reflist, refs= {{cite book , author1=Gill, M. , author2=Steglich, W. , title=Pigments of Fungi (Macromycetes) , series=Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air. Structure and properties Acetic anhydride, like most acid anhydrides, is a flexible molecule with a nonplanar structure. The pi system linkage through the central oxygen offers very weak resonance stabilization compared to the dipole-dipole repulsion between the two carbonyl oxygens. The energy barriers to bond rotation between each of the optimal aplanar conformations are quite low. Like most acid anhydrides, the carbonyl carbon atom of acetic anhydride has electrophilic character, as the leaving group is carboxylate. The internal asymmetry may contribute to acetic anhydride's potent electrophilicity as the asymmetric geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not exist naturally on Earth due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid, but to the contrary dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boletus Rubellus
''Hortiboletus rubellus'', commonly known as the ruby bolete, is a small, dainty, brightly coloured member of the family Boletaceae, with a reddish cap and stipe, and yellow pores. Like many boletes, it stains blue when cut or bruised. It is found in deciduous woodland in autumn. There is some question over its edibility, and it is reportedly of poor quality with a taste of soap. Until 2015, the species was known as ''Boletus rubellus''. Taxonomy ''Boletus rubellus'' was one of the pored basidiomycetes to be placed in the genus ''Xerocomus'' in the past, and is still regarded as such in some texts. The previously commonly used binomial name ''Boletus versicolor'' (Rostk.), published in 1844, is now reduced to synonymy as it postdates the current name by German mycologist Julius Vincenz von Krombholz which dates from 1836. Its present specific epithet ' is Latin for "somewhat red". The fungus was transferred to the new genus '' Hortiboletus'' in 2015, following molecular eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Layer Chromatography
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose. This layer of adsorbent is known as the stationary phase. After the sample has been applied on the plate, a solvent or solvent mixture (known as the mobile phase) is drawn up the plate via capillary action. Because different analytes ascend the TLC plate at different rates, separation is achieved. It may be performed on the analytical scale as a means of monitoring the progress of a reaction, or on the preparative scale to purify small amounts of a compound. TLC is an analytical tool widely used because of its simplicity, relative low cost, high sensitivity, and speed of separation. TLC functions on the same principle as all chromatography: a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
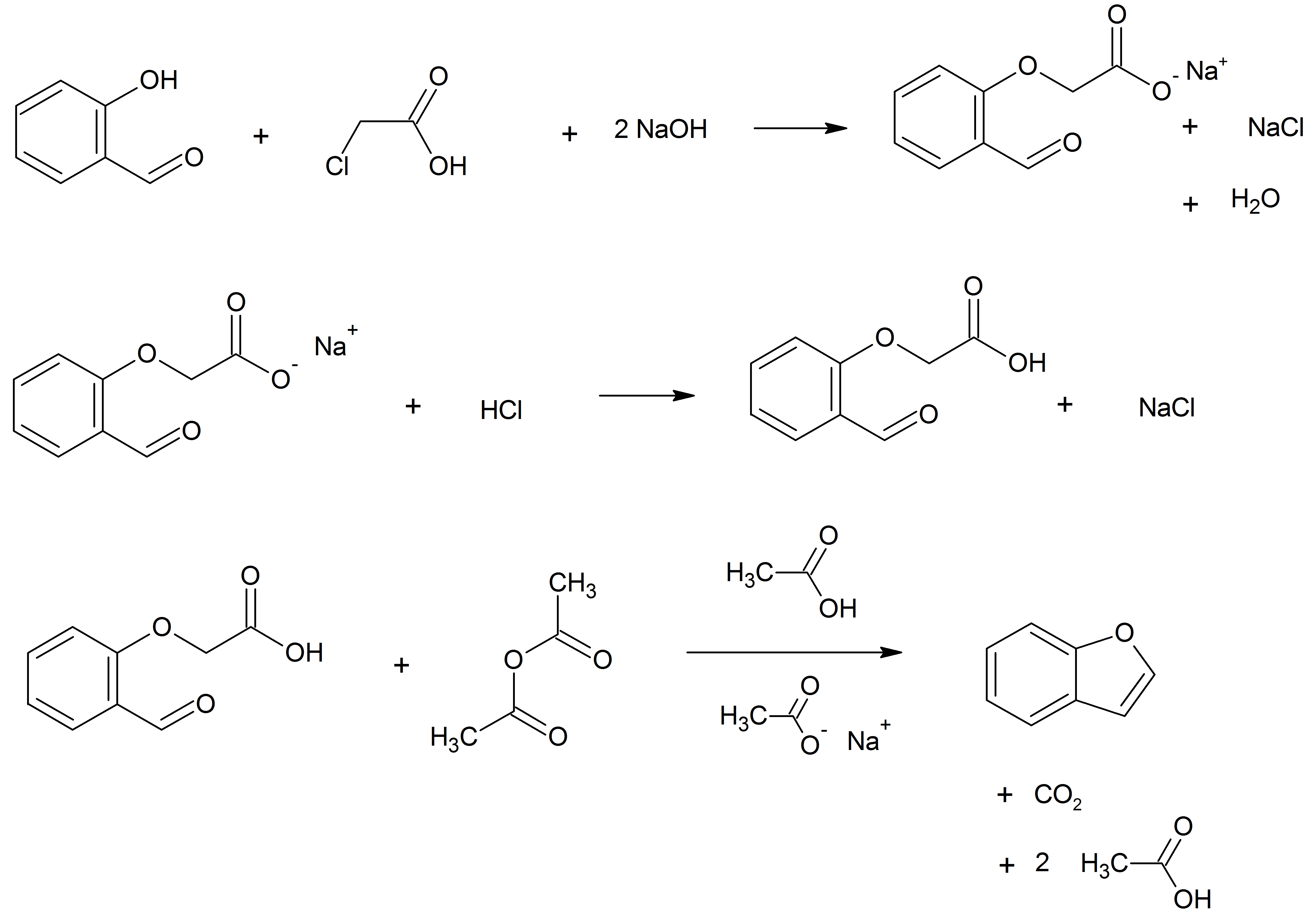
Benzofurans
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the "parent" of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants. Production Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol. Laboratory methods Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. * Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide: : * Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles: : Diels–Alder reaction yielding a substituted benzofuran, 450px * Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols: : Benzofurans via Cycloisomerization, 400px Related c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphenols
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments. Etymology The name derives from the Ancient Greek word (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and the word phenol which refers to a chemical structure formed by attaching to an aromatic benzenoid ( phenyl) ring to a hydroxyl (-OH) group as is found in alcohols (hence the ''-ol'' suffix). The term polyphenol has been in use at least since 1894. Definition The term polyphenol is not well-defined, but is generally agreed that they are natural products "having a polyphenol structure (i.e., several hydroxyl groups on aromatic rings)" including four principal classes: "phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans". *Flavonoids include flavones, flavonols, flavanols, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |