|
Weloganite
Weloganite is a rare carbonate mineral with formula: It was discovered by Canadian government mineralogist Ann P. Sabina in 1967 and named for Canadian geologist Sir William Edmond Logan (1798–1875). It was first discovered in Francon Quarry, Montreal, Quebec, Canada and has only been reported from a few localities worldwide. Properties It is usually white, lemon yellow, or amber in color, and can be translucent. It crystallizes in the triclinic system and shows pseudo-hexagonal crystal forms due to twinning. The width of the crystals typically undulates down the length, forming crystals that widen in the middle or flare out at the end. Crystals are affected by light and can develop a white alteration coating over time. Weloganite is triboluminescent, producing blue light. Occurrence It occurs in an igneous carbonatite sill in Montreal, Quebec, Canada in the Francon Quarry where it was first discovered. It also occurs in the Mont Saint-Hilaire district. Associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Mineral
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal **Calcite CaCO3 **Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 **Otavite CdCO3 **Rhodochrosite MnCO3 **Siderite FeCO3 **Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic **Aragonite CaCO3 **Cerussite PbCO3 **Strontianite SrCO3 **Witherite BaCO3 **Rutherfordine UO2CO3 **Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal **Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 **Dolomite (mineral), Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 **Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 **Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 **Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 **Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 **Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 **Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 **Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates *Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O *Ikaite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Mineral
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal **Calcite CaCO3 **Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 **Otavite CdCO3 **Rhodochrosite MnCO3 **Siderite FeCO3 **Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic **Aragonite CaCO3 **Cerussite PbCO3 **Strontianite SrCO3 **Witherite BaCO3 **Rutherfordine UO2CO3 **Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal **Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 **Dolomite (mineral), Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 **Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 **Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 **Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 **Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 **Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 **Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 **Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates *Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O *Ikaite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minerals
This is a list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia. Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a mineral species there may be variation in physical properties or minor amounts of impurities that are recognized by mineralogists or wider society as a mineral ''variety''. Mineral variety names are listed after the valid minerals for each letter. For a more complete listing of all mineral names, see List of minerals recognized by the International Mineralogical Association. A :Varieties that are not valid species: *Adamantine spar (variety of corundum) *Agate (variety of chalcedony and quartz) *Alabaster (variety of gypsum) *Alexandrite (variety of chrysoberyl) *Allingite (synonym of amber) *Alum *Amazonite (variety of microcline) *Amethyst (purple variety of quartz) *Ametrine (variety of quartz) *Ammolite (organic; also a gems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francon Quarry
Francon () is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France. It is situated about 55 km southwest of Toulouse Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Pa .... Population See also * Communes of the Haute-Garonne department References Communes of Haute-Garonne {{HauteGaronne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
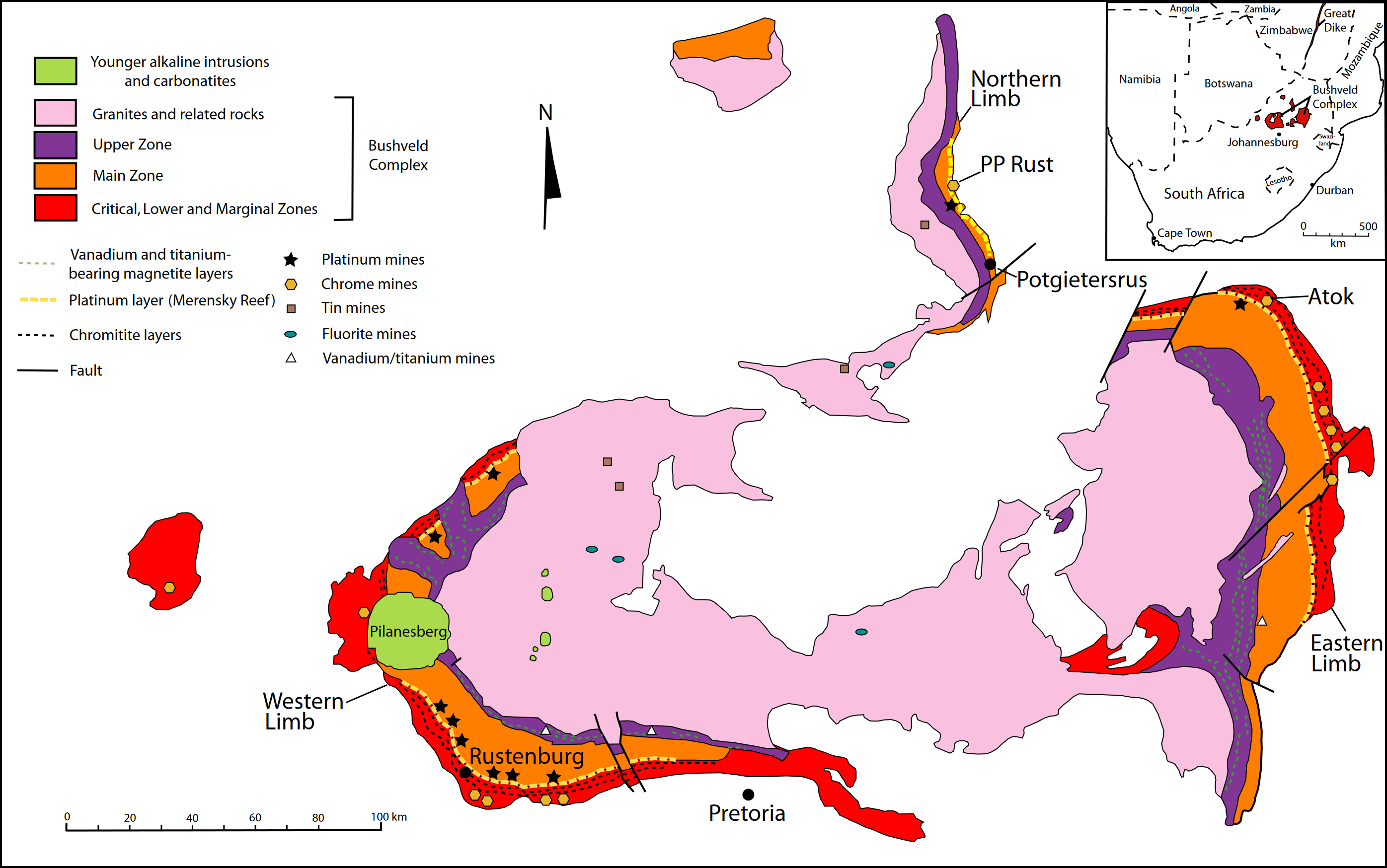
Bushveld Igneous Complex
The Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) is the largest layered igneous intrusion within the Earth's crust. It has been tilted and eroded forming the outcrops around what appears to be the edge of a great geological basin: the Transvaal Basin. It is approximately 2 billion years old and is divided into four different limbs: the northern, southern, eastern, and western limbs. The Bushveld Complex comprises the Rustenburg Layered suite, the Lebowa Granites and the Rooiberg Felsics, that are overlain by the Karoo sediments. The site was first discovered around 1897 by Gustaaf Molengraaff. Located in South Africa, the BIC contains some of the richest ore deposits on Earth. The complex contains the world's largest reserves of platinum-group metals (PGMs) or platinum group elements (PGEs)—platinum, palladium, osmium, iridium, rhodium, and ruthenium along with vast quantities of iron, tin, chromium, titanium and vanadium. These are used in, but not limited to, jewellery, automobiles and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on Scratch hardness, scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for Lime (material), lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeology, archaeologists and stone trade pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawsonite
Dawsonite is a mineral composed of sodium aluminium carbonate hydroxide, chemical formula NaAlCO3(OH)2. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system. It is not mined for ore. It was discovered in 1874 during the construction of the Redpath Museum in a feldspathic dike on the campus of McGill University on the Island of Montreal, Canada. It is named after geologist Sir John William Dawson (1820–1899). The type material is preserved in the collection of the Redpath Museum. See also *List of minerals *List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition follows name. A * Abelsonite: C31H32N4Ni – American physicist Philip Hauge Abelson (1913–2004)alfred *Abswurmbachite: Cu2+Mn3+6O8SiO4 – German mineralogist I ... * Dihydroxialumini sodium carbonate, the commercial (artificial) form, used as an antacid References Sodium minerals Aluminium minerals Carbonate minerals Orthorhombic minerals Miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strontianite
Strontianite ( Sr C O3) is an important raw material for the extraction of strontium. It is a rare carbonate mineral and one of only a few strontium minerals. It is a member of the aragonite group. Aragonite group members: aragonite (CaCO3), witherite (BaCO3), strontianite (SrCO3), cerussite (PbCO3) The ideal formula of strontianite is SrCO3, with molar mass 147.63 g, but calcium (Ca) can substitute for up to 27% of the strontium (Sr) cations, and barium (Ba) up to 3.3%. The mineral was named in 1791 for the locality, Strontian, Argyllshire, Scotland, where the element strontium had been discovered the previous year. Although good mineral specimens of strontianite are rare, strontium is a fairly common element, with abundance in the Earth's crust of 370 parts per million by weight, 87 parts per million by moles, much more common than copper with only 60 parts per million by weight, 19 by moles. Strontium is never found free in nature. The principal strontium ores are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mont Saint-Hilaire
Mont Saint-Hilaire (English: Mount Saint-Hilaire; abe, Wigwômadenizibo; see for other names) is an isolated hill, high, in the Montérégie region of southern Quebec. It is about thirty kilometres east of Montreal, and immediately east of the Richelieu River. It is one of the Monteregian Hills. Around the mountains are the towns of Mont-Saint-Hilaire and Saint-Jean-Baptiste. Other nearby towns include Otterburn Park, Beloeil and McMasterville. The area surrounding the mountain is a biosphere reserve, as one of the last remnants of the primeval forests of the Saint-Lawrence valley. Most of the mountain is currently the property of McGill University, as the ''Gault Nature Reserve'', which is considered the third McGill campus. The University has opened the western half of the mountain to visitors (at a fee) for hiking and cross-country skiing, as the ''Milieu Naturel'' (natural area). The eastern half, or ''Milieu de Conservation'' (preservation area) is not accessible to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
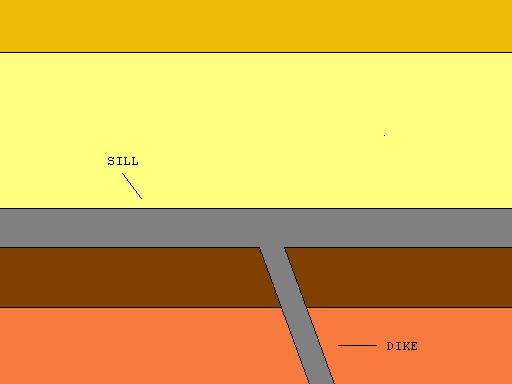
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A ''sill'' is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that a sill does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex . and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existing bedding pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive rock, intrusive or extrusive rock, extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geochemical verification. Carbonatites usually occur as small volcanic plug, plugs within zoned alkalic intrusive complexes, or as dike (geology), dikes, sill (geology), sills, breccias, and vein (geology), veins. They are almost exclusively associated with continental rift-related tectonic settings. It seems that there has been a steady increase in the carbonatitic igneous activity through the Earth's history, from the Archean Eon (geology), eon to the present. Nearly all carbonatite occurrences are intrusives or subvolcanic rock, subvolcanic intrusives. This is because carbonatite lava flows, being composed largely of soluble carbonates, are easily weathered and are therefore unlikely to be preserved in the geologic record. Carbonatite erupti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |