|
Well-ordering Theorem
In mathematics, the well-ordering theorem, also known as Zermelo's theorem, states that every set can be well-ordered. A set ''X'' is ''well-ordered'' by a strict total order if every non-empty subset of ''X'' has a least element under the ordering. The well-ordering theorem together with Zorn's lemma are the most important mathematical statements that are equivalent to the axiom of choice (often called AC, see also ). Ernst Zermelo introduced the axiom of choice as an "unobjectionable logical principle" to prove the well-ordering theorem. One can conclude from the well-ordering theorem that every set is susceptible to transfinite induction, which is considered by mathematicians to be a powerful technique. One famous consequence of the theorem is the Banach–Tarski paradox. History Georg Cantor considered the well-ordering theorem to be a "fundamental principle of thought". However, it is considered difficult or even impossible to visualize a well-ordering of \mathbb; such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyula Kőnig
Gyula Kőnig (16 December 1849 – 8 April 1913) was a mathematician from Hungary. His mathematical publications in German appeared under the name Julius König. His son Dénes Kőnig was a graph theorist. Biography Gyula Kőnig was active literarily and mathematically. He studied medicine in Vienna and, from 1868 on, in Heidelberg. After having worked, instructed by Hermann von Helmholtz, on electrical stimulation of nerves, he switched to mathematics. He obtained his doctorate under the supervision of the mathematician Leo Königsberger. His thesis ''Zur Theorie der Modulargleichungen der elliptischen Functionen'' covers 24 pages. As a post-doc he completed his mathematical studies in Berlin attending lessons by Leopold Kronecker and Karl Weierstraß. He then returned to Budapest where he was appointed as a ''dozent'' at the University in 1871. He became a professor at the Teacher's College in Budapest in 1873 and, in the following year, was appointed professor at the Techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
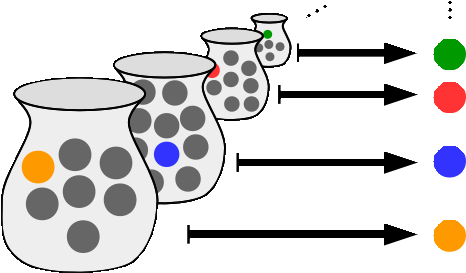
Axiom Of Choice
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, or AC, is an axiom of set theory equivalent to the statement that ''a Cartesian product of a collection of non-empty sets is non-empty''. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of sets, each containing at least one element, it is possible to construct a new set by arbitrarily choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family (S_i)_ of nonempty sets, there exists an indexed set (x_i)_ such that x_i \in S_i for every i \in I. The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem. In many cases, a set arising from choosing elements arbitrarily can be made without invoking the axiom of choice; this is, in particular, the case if the number of sets from which to choose the elements is finite, or if a canonical rule on how to choose the elements is available – some distinguishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizar System
The Mizar system consists of a formal language for writing mathematical definitions and proofs, a proof assistant, which is able to mechanically check proofs written in this language, and a library of formalized mathematics, which can be used in the proof of new theorems. The system is maintained and developed by the Mizar Project, formerly under the direction of its founder Andrzej Trybulec. In 2009 the Mizar Mathematical Library was the largest coherent body of strictly formalized mathematics in existence. History The Mizar Project was started around 1973 by Andrzej Trybulec as an attempt to reconstruct mathematical vernacular so it can be checked by a computer. Its current goal, apart from the continual development of the Mizar System, is the collaborative creation of a large library of formally verified proofs, covering most of the core of modern mathematics. This is in line with the influential QED manifesto. Currently the project is developed and maintained by researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Publishing
Springer Publishing Company is an American publishing company of academic journals and books, focusing on the fields of nursing, gerontology, psychology, social work, counseling, public health, and rehabilitation (neuropsychology). It was established in 1951 by Bernhard Springer, a great-grandson of Julius Springer, and is based in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. History Springer Publishing Company was founded in 1950 by Bernhard Springer, the Berlin-born great-grandson of Julius Springer, who founded Springer-Verlag (now Springer Science+Business Media). Springer Publishing's first landmark publications included ''Livestock Health Encyclopedia'' by R. Seiden and the 1952 ''Handbook of Cardiology for Nurses''. The company's books soon branched into other fields, including medicine and psychology. Nursing publications grew rapidly in number, as Modell's ''Drugs in Current Use'', a small annual paperback, sold over 150,000 copies over several editions. Solomon Garb's ''Labor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Order Logic
In logic and mathematics, second-order logic is an extension of first-order logic, which itself is an extension of Propositional calculus, propositional logic. Second-order logic is in turn extended by higher-order logic and type theory. First-order logic Quantifier (logic), quantifies only variables that range over individuals (elements of the domain of discourse); second-order logic, in addition, also quantifies over Finitary relation, relations. For example, the second-order Sentence (mathematical logic), sentence \forall P\,\forall x (Px \lor \neg Px) says that for every well-formed formula, formula ''P'', and every individual ''x'', either ''Px'' is true or not(''Px'') is true (this is the law of excluded middle). Second-order logic also includes quantification over set (mathematics), sets, function (mathematics), functions, and other variables (see section #Syntax and fragments, below). Both first-order and second-order logic use the idea of a domain of discourse (often called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Order Logic
First-order logic—also known as predicate logic, quantificational logic, and first-order predicate calculus—is a collection of formal systems used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. First-order logic uses quantified variables over non-logical objects, and allows the use of sentences that contain variables, so that rather than propositions such as "Socrates is a man", one can have expressions in the form "there exists x such that x is Socrates and x is a man", where "there exists''"'' is a quantifier, while ''x'' is a variable. This distinguishes it from propositional logic, which does not use quantifiers or relations; in this sense, propositional logic is the foundation of first-order logic. A theory about a topic is usually a first-order logic together with a specified domain of discourse (over which the quantified variables range), finitely many functions from that domain to itself, finitely many predicates defined on that domain, and a set of axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Hausdorff
Felix Hausdorff ( , ; November 8, 1868 – January 26, 1942) was a German mathematician who is considered to be one of the founders of modern topology and who contributed significantly to set theory, descriptive set theory, measure theory, and functional analysis. Life became difficult for Hausdorff and his family after Kristallnacht in 1938. The next year he initiated efforts to emigrate to the United States, but was unable to make arrangements to receive a research fellowship. On 26 January 1942, Felix Hausdorff, along with his wife and his sister-in-law, died by suicide by taking an overdose of veronal, rather than comply with German orders to move to the Endenich camp, and there suffer the likely implications, about which he held no illusions. Life Childhood and youth Hausdorff's father, the Jewish merchant Louis Hausdorff (1843–1896), moved with his young family to Leipzig in the autumn of 1870, and over time worked at various companies, including a linen-and cotton goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Cantor
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor ( , ; – January 6, 1918) was a German mathematician. He played a pivotal role in the creation of set theory, which has become a fundamental theory in mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence between the members of two sets, defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that the real numbers are more numerous than the natural numbers. In fact, Cantor's method of proof of this theorem implies the existence of an infinity of infinities. He defined the cardinal and ordinal numbers and their arithmetic. Cantor's work is of great philosophical interest, a fact he was well aware of. Originally, Cantor's theory of transfinite numbers was regarded as counter-intuitive – even shocking. This caused it to encounter resistance from mathematical contemporaries such as Leopold Kronecker and Henri Poincaré and later from Hermann Weyl and L. E. J. Brouwer, while Ludwig Wittgenstein raised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set (mathematics)
A set is the mathematical model for a collection of different things; a set contains '' elements'' or ''members'', which can be mathematical objects of any kind: numbers, symbols, points in space, lines, other geometrical shapes, variables, or even other sets. The set with no element is the empty set; a set with a single element is a singleton. A set may have a finite number of elements or be an infinite set. Two sets are equal if they have precisely the same elements. Sets are ubiquitous in modern mathematics. Indeed, set theory, more specifically Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, has been the standard way to provide rigorous foundations for all branches of mathematics since the first half of the 20th century. History The concept of a set emerged in mathematics at the end of the 19th century. The German word for set, ''Menge'', was coined by Bernard Bolzano in his work ''Paradoxes of the Infinite''. Georg Cantor, one of the founders of set theory, gave the following defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banach–Tarski Paradox
The Banach–Tarski paradox is a theorem in set-theoretic geometry, which states the following: Given a solid ball in three-dimensional space, there exists a decomposition of the ball into a finite number of disjoint subsets, which can then be put back together in a different way to yield two identical copies of the original ball. Indeed, the reassembly process involves only moving the pieces around and rotating them without changing their shape. However, the pieces themselves are not "solids" in the usual sense, but infinite scatterings of points. The reconstruction can work with as few as five pieces. An alternative form of the theorem states that given any two "reasonable" solid objects (such as a small ball and a huge ball), the cut pieces of either one can be reassembled into the other. This is often stated informally as "a pea can be chopped up and reassembled into the Sun" and called the "pea and the Sun paradox". The theorem is called a paradox because it contradicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |