|
Shanghaiese
The Shanghainese language, also known as the Shanghai dialect, or Hu language, is a variety of Wu Chinese spoken in the Districts of Shanghai, central districts of the Shanghai, City of Shanghai and its surrounding areas. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Shanghainese, like the rest of the Wu language group, is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, such as Mandarin. Shanghainese belongs a separate group of the Taihu Wu subgroup. With nearly 14 million speakers, Shanghainese is also the largest single form of Wu Chinese. Since the late 19th century it has served as the lingua franca of the entire Yangtze River Delta region, but in recent decades its status has declined relative to Mandarin, which most Shanghainese speakers can also speak. Like other Wu varieties, Shanghainese is rich in vowels and consonants, with around twenty unique vowel qualities, twelve of which are phonemic. Similarly, Shanghainese also has voiced obstruent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu (shaman)
''Wu'' () is a Chinese term translating to "shaman" or "sorcerer", originally the practitioners of Chinese shamanism or "Wuism" (巫教 ''wū jiào''). Terminology The glyph ancestral to modern is first recorded in bronze script, where it could refer to shamans or sorcerers of either sex. Modern Mandarin ''wu'' (Cantonese ''mouh'') continues a Middle Chinese ''mju'' or ''mjo''. The Old Chinese reconstruction is uncertain, given as *''mywo'' or as *''myag'', the presence of a final velar ''-g'' or ''-ɣ'' in Old Chinese being uncertain. By the late Zhou Dynasty (4th to 3rd centuries BCE), ''wu'' referred mostly to female shamans or "sorceresses", while male sorcerers were named ''xi'' "male shaman; sorcerer", first attested in the ''Guoyu'' or '' Discourses of the States'' (4th century BCE). Other sex-differentiated shaman names include ''nanwu'' for "male shaman; sorcerer; wizard"; and ''nüwu'' , ''wunü'' , ''wupo'' , and ''wuyu'' for "female shaman; sorceress; witch". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
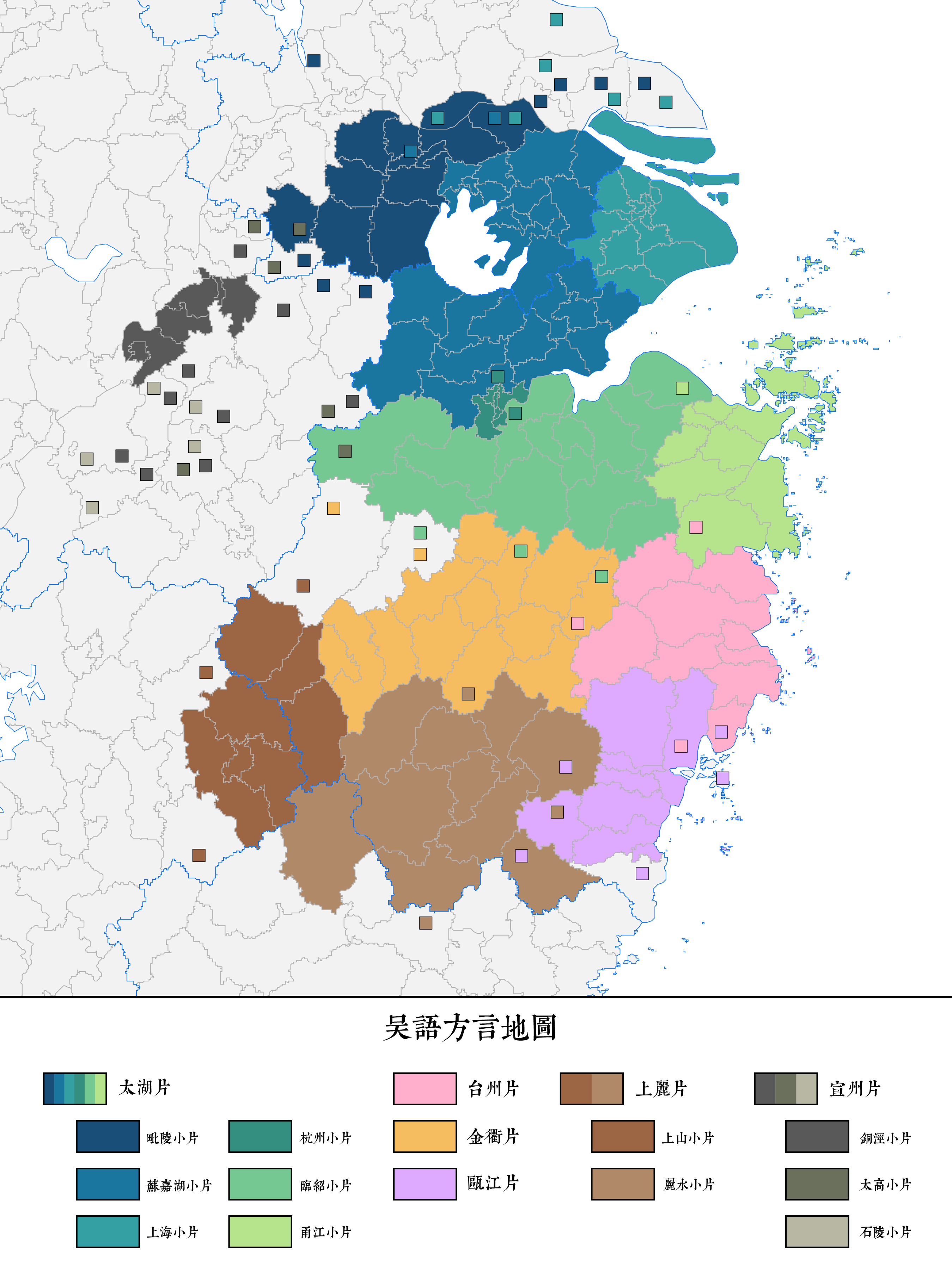
Wu Chinese
The Wu languages (; Wu romanization and IPA: ''wu6 gniu6'' [] ( Shanghainese), ''ng2 gniu6'' [] (Suzhounese), Mandarin pinyin and IPA: ''Wúyǔ'' []) is a major group of Sinitic languages spoken primarily in Shanghai, Zhejiang, Zhejiang Province, and the part of Jiangsu, Jiangsu Province south of the Yangtze River, which makes up the cultural region of Wu. The Suzhou dialect was the prestige dialect of Wu as of the 19th century, and formed the basis of Wu's koiné dialect, Shanghainese, at the turn of the 20th century. Speakers of various Wu languages sometimes inaccurately labelled their mother tongue as "Shanghainese" when introduced to foreigners. The languages of Northern Wu are mutually intelligible with each other, while those of Southern Wu are not. Historical linguists view Wu of great significance because it distinguished itself from other varieties of Chinese by preserving the voiced initials of the ancient Middle Chinese and by preserving the checked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Wu
Wu ( Chinese: 吳; pinyin: ''Wú''; Middle Chinese *''ŋuo'' < Eastern Han Chinese: ''*ŋuɑ''), known in historiography as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over in the Three Kingdoms period (220–280). It previously existed from 220–222 as a vassal kingdom nominally under Cao Wei, its rival state, but declared independence from Wei and became a sovereign state in 222. It became an empire in 229 after its founding ruler, |
Wú (negative)
The Japanese and Korean term ' () or Chinese (), meaning "not have; without", is a key word in Buddhism, especially Zen traditions. Etymology The Old Chinese * () is cognate with the Proto-Tibeto-Burman *''ma'', meaning "not". This reconstructed root is widely represented in Tibeto-Burman languages; for instance, means "not" in both Written Tibetan and Written Burmese. Pronunciations The Standard Chinese pronunciation of (, "not; nothing") historically derives from the Middle Chinese , the Late Han Chinese ''muɑ'', and the reconstructed Old Chinese *., p. 518. Other varieties of Chinese have differing pronunciations of . Compare Cantonese ; and Southern Min (Quanzhou) and (Zhangzhou). The common Chinese word () was adopted in the Sino-Japanese, Sino-Korean, and Sino-Vietnamese vocabularies. The Japanese kanji has readings of or , and a (Japanese reading) of . The Korean is read (in Revised, McCune–Reischauer, and Yale romanization systems). The Vietna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trade and commerce. Administratively, Suzhou is a prefecture-level city with a population of 6,715,559 in the city proper, and a total resident population of 12,748,262 as of the 2020 census in its administrative area. The city jurisdiction area's north waterfront is on a lower reach of the Yangtze whereas it has its more focal south-western waterfront on Lake Tai – crossed by several waterways, its district belongs to the Yangtze River Delta region. Suzhou is now part of the Greater Shanghai metro area, incorporating most of Changzhou, Wuxi and Suzhou urban districts plus Kunshan and Taicang, with a population of more than 38,000,000 residents as of 2020. Its urban population grew at an unprecedented rate of 6.5% between 2000 and 2014, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Zetian
Wu Zetian (17 February 624 – 16 December 705), personal name Wu Zhao, was the ''de facto'' ruler of the Tang dynasty from 665 to 705, ruling first through others and then (from 690) in her own right. From 665 to 690, she was first List of Chinese consorts, empress consort of the Tang dynasty (as wife of the Emperor Gaozong of Tang, Emperor Gaozong) and then, after his death, List of Chinese consorts, empress dowager (ruling through her sons Emperors Emperor Zhongzong of Tang, Zhongzong and Emperor Ruizong of Tang, Ruizong). Unprecedented in Chinese history, she subsequently founded and ruled as empress regnant of the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty of China from 690 to 705. She was the only female Chinese sovereign, sovereign in the history of China widely regarded as legitimate. Under her 40-year reign, China grew larger, becoming one of the great powers of the world, its culture and economy were revitalized, and corruption in the court was reduced. She was remov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu (state)
Wu (; Old Chinese: ''*'') was one of the states during the Western Zhou dynasty and the Spring and Autumn period. It was also known as Gouwu ( /''*''/) or Gongwu ( /''*''/) from the pronunciation of the local language. Wu was located at the mouth of the Yangtze River east of the State of Chu. Its first capital was at Meili (probably in modern Wuxi) and was later moved to Gusu (姑蘇, modern Suzhou) and then Helu City (the old town of present-day Suzhou). History A founding myth of Wu, first recorded by Sima Qian in the Han dynasty, traced its royal lineage to Taibo, a relative of King Wen of Zhou. According to the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', Taibo was the oldest son of Gugong Danfu and the elder uncle of King Wen who started the Zhou Dynasty. Gugong Danfu had three sons named Taibo, Zhongyong, and Jili. Taibo was the oldest of three brothers, Jili being the youngest. Realizing that his youngest brother, Jili, was favored by his father to inherit the throne o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Surname
Chinese surnames are used by Han Chinese and Sinicized ethnic groups in China, Taiwan, Korea, Vietnam, and among overseas Chinese communities around the world such as Singapore and Malaysia. Written Chinese names begin with surnames, unlike the Western tradition in which surnames are written last. Around 2,000 Han Chinese surnames are currently in use, but the great proportion of Han Chinese people use only a relatively small number of these surnames; 19 surnames are used by around half of the Han Chinese people, while 100 surnames are used by around 87% of the population. A report in 2019 gives the most common Chinese surnames as Wang and Li, each shared by over 100 million people in China. The remaining top ten most common Chinese surnames are Zhang, Liu, Chen, Yang, Huang, Zhao, Wu and Zhou. Two distinct types of Chinese surnames existed in ancient China, namely ''xing'' () ancestral clan names and ''shi'' () branch lineage names. Later, the two terms began to be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu (Ten Kingdoms)
Wu (), also referred to as Huainan (), Hongnong (), Southern Wu (), or Yang Wu (楊吳), was one of the Ten Kingdoms in eastern China which was in existence from 907 to 937. Its capital was Jiangdu Municipality () (modern Yangzhou in Jiangsu Province). Some historians consider Wu to have begun in 902, when Yang Xingmi was named Prince of Wu by the Tang dynasty. All three rulers of Wu after 907 (when the Tang dynasty collapsed and Zhu Wen established Later Liang) were Yang Xingmi's sons. The first ruler Yang Wo was murdered by his ministers Xu Wen and Zhang Hao, and his two brothers after him were effectively puppets dominated by Xu Wen at first, and later Xu Wen's adopted son Xu Zhigao (Li Bian) who in 937 usurped power to establish Southern Tang. Yang Pu, the last ruler, was the only one to claim the title of Emperor; the other rulers were kings or princes. Founding The founder of Wu, Yang Xingmi, started his career as a volunteer soldier before seizing power in his home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuyue
Wuyue (; ), 907–978, was an independent coastal kingdom founded during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960) of Chinese history. It was ruled by the Haiyan Qian clan (海盐钱氏), whose family name remains widespread in the kingdom's former territory. Founding Beginning in 887, the Qian family provided military leaders (or ''jiedushi'') to the Tang dynasty. Qian Liu was named Prince of Yue in 902, with the title of Prince of Wu added two years later. In 907, when the Tang dynasty fell and was replaced in the north by the Later Liang, military leaders in the south formed their own kingdoms. Qian Liu used his position to proclaim himself the King of Wuyue. This signaled the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period which would last until the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. Origin of name The name Wuyue comes from the combination of Wu Kingdom and Yue Kingdom, two ancient kingdoms during the Spring and Autumn period from 770 to 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu (awareness)
''Wu'' () is a concept of awareness, consciousness, or spiritual enlightenment in the Chinese folk religion. According to scholarly studies, many practitioners who have recently "reverted" to the Chinese traditional religion speak of an "opening of awareness" (' ) or "awakening of awareness" (' ) of the interconnectedness of reality in terms of the cosmic-moral harmony ('' bào yìng'') as it relates to '' mìng yùn'' and '' yuán fèn''. This spiritual awareness, ''wu'', works as an engine that moves these themes from being mere ideas to be motivating forces in one's life: * awareness of ''mìng yùn'' ignites responsibility towards life; * awareness of ''yuan fen'' stirs one to respond to events rather than resigning. Awareness is a dynamic factor and appears in two guises: first, as a realisation that arrives as a gift, often unbidden, then as a practice that the person intentionally follows. See also * Chinese folk religion Chinese folk religion, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





%2C_King_of_Wuyue.jpg)