|
Window Capping
In construction, capping or window capping (window cladding, window wrapping) refers to the application of aluminum or vinyl sheeting cut and formed with a brake to fit over the exterior, wood trim of a building. The aluminum is intended to make aging trim with peeling paint look better, reduce future paint maintenance, and provide a weather-proof layer to control the infiltration of water.Gibson, Greg. ''Remodel!: an architect's advice on home renovation''. New York: J. Wiley, 1996. 269. Print. Overview The capping application must direct water away from the original under-lying wood material and prevent infiltration of water into the structure. Cladding applied to exterior window and door casing (brick-moulding) and their associated parts is often referred to as ''window capping'' or ''window cladding''. This sort of capping is typically applied in order to eliminate the need to re-paint wood window trim. The aluminum capping helps to prevent wood rot by protecting the wood fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science of forming Physical object, objects, systems, or organizations."Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 It comes from the Latin word ''constructio'' (from ''com-'' "together" and ''struere'' "to pile up") and Old French ''construction''. To 'construct' is a verb: the act of building, and the noun is construction: how something is built or the nature of its structure. In its most widely used context, construction covers the processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the asset is built and ready for use. Construction also covers repairs and maintenance work, any works to expand, extend and improve the asset, and its eventual demolition, dismantling or wikt:de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brake (sheet Metal Bending)
A brake is a metalworking machine that allows the bending of sheet metal. A cornice brake only allows for simple bends and creases, while a box-and-pan brake also allows one to form box and pan shapes. It is also known as a bending machine or bending brake or in Britain as a sheet metal folder or just a folder. Description The brake consists of a flat surface onto which the material is placed, and a clamping bar which will come down and hold the material firmly during the bend. This clamping action may be manual, automatic or operated using a foot pedal. The front, gate-like, plate of the machine is hinged and may be lifted, forcing the material extended over a straight edge to bend to follow the plate. The bends can be to any angle up to a practical limit of about 120 degrees, somewhat more in the case of a bar folder. If the area to be bent is narrow enough, a sharper bend (e.g., for a hem) can be made by inserting the bend under the clamping bar and lowering it. Box-and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Proof
This is a list of television programs broadcast by the American television network The Weather Channel. There are four main types of programs on The Weather Channel: weather news programs, serial documentaries, Long-form shows, and specials such as the ''100 Biggest Weather Moments, Top 100 Weather Moments A spinning top, or simply a top, is a toy with a squat body and a sharp point at the bottom, designed to be rotation, spun on its vertical Axis of rotation, axis, balancing on the tip due to the gyroscopic effect. Once set in motion, a top will ...,'' and ''Coast Guard: HMS Bounty''. Programs Current programs News All current news programs broadcast in high definition. Long-form Note 1: Episodes premiering from 2009 on air in high definition. Episodes from earlier years are in standard definition Former programs '' {{The Weather Channel * Lists of television series by network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infiltration
Infiltration may refer to: Science, medicine, and engineering *Infiltration (hydrology), downward movement of water into soil *Infiltration (HVAC), a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning term for air leakage into buildings *Infiltration (medical), the diffusion or accumulation of substances or cells not normal to it or in amounts in excess of the normal *Infiltration/Inflow, leakage of groundwater into sanitary sewers Other uses *Entryism, the infiltration by a political organisation of another, usually larger, organisation *In espionage, using double agents to join an enemy organization *Infiltration tactics, tactics developed by the German army in early 1915 that broke the trench-warfare stalemate on the western front *Urban exploration, exploring parts of towns, etc. which are normally off-limits * ''Infiltration'' (zine), a popular urban exploration zine/website created by Jeff Chapman (Ninjalicious) *Seon-Woo Lee (born 1985), professional electronic sports players, spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Rot
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or it is defined more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree it performs a support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients between the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, or woodchips or fiber. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulking
Caulk or, less frequently, caulking is a material used to seal joints or seams against leakage in various structures and piping. The oldest form of caulk consisted of fibrous materials driven into the wedge-shaped seams between boards on wooden boats or ships. Cast iron sewerage pipe were formerly caulked in a similar way. Riveted seams in ships and boilers were formerly sealed by hammering the metal. Modern caulking compounds are flexible sealing compounds used to close up gaps in buildings and other structures against water, air, dust, insects, or as a component in firestopping. In the tunnelling industry, caulking is the sealing of joints in segmental precast concrete tunnels, commonly by using concrete. Historical uses Wooden shipbuilding Traditional caulking (also spelled calking) on wooden vessels uses fibers of cotton and oakum (hemp) soaked in pine tar. These fibers are driven into the wedge-shaped seam between planks, with a caulking mallet an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
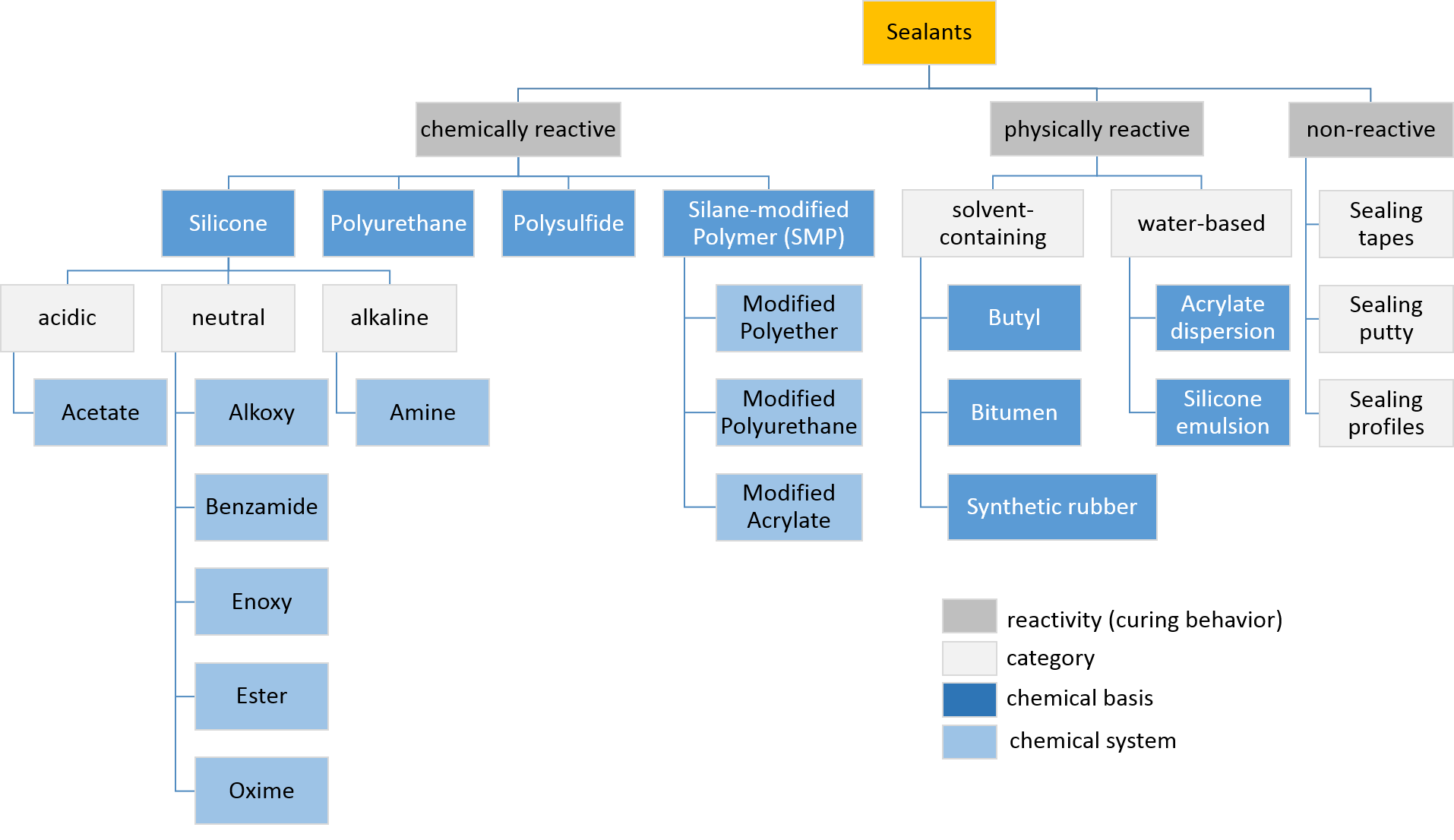
Sealant
Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of fluids through openings in materials, a type of mechanical seal. In building construction ''sealant'' is sometimes synonymous with ''caulking'' and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, sound and heat transmission. Sealants may be weak or strong, flexible or rigid, permanent or temporary. Sealants are not adhesives but some have adhesive qualities and are called ''adhesive-sealants'' or ''structural sealants''. History Sealants were first used in prehistory in the broadest sense as mud, grass and reeds to seal dwellings from the weather such as the daub in wattle and daub and thatching. Natural sealants and adhesive-sealants included plant resins such as pine pitch and birch pitch, bitumen, wax, tar, natural gum, clay (mud) mortar, lime mortar, lead, blood and egg. In the 17th century glazing putty was first used to seal window glass made with linseed oil and chalk, later other drying oils were also used to make oil-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window Sill
A windowsill (also written window sill or window-sill, and less frequently in British English, cill) is the horizontal structure or surface at the bottom of a window. Window sills serve to structurally support and hold the window in place. The exterior portion of a window sill provides a mechanism for shedding rainwater away from the wall at the window opening. Therefore, window sills are usually inclined slightly downward away from the window and wall, and often extend past the exterior face of the wall, so the water will drip off rather than run down the wall. Some windowsills are made of natural stone, cast stone, concrete, tile, or other non-porous materials to further increase their water resistance. Windows may not have a structural sill or the sill may not be sufficiently weather resistant. In these cases, a strip of waterproof and weather resistant material ( steel, vinyl, PVC) called a sill pan may be used to protect the wall and shed the water. Like the sill, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient Energy Use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses. There are many motivations to improve energy efficiency. Decreasing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy-efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)