|
Volar Carpal Ligament
The palmar carpal ligament (also volar carpal ligament or ''Guyon's Tunnel'') is the thickened portion of antebrachial fascia on the anterior of the wrist. It is officially unnamed.Moore, Keith L., Arthur F. Dalley II: ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 4th ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins,1999. The palmar carpal ligament is a different structure than the flexor retinaculum of the hand, but the two are frequently confused. The palmar carpal ligament lies superficial and proximal to the flexor retinaculum. The ulnar nerve and the ulnar artery run through the ulnar canal, which is deep to the palmar carpal ligament and superficial to the flexor retinaculum. The palmar carpal ligament is continuous with the extensor retinaculum of the hand, which is located on the posterior side of the wrist. References See also * Flexor retinaculum of the hand * Extensor retinaculum of the hand * Antebrachial fascia The antebrachial fascia (antibrachial fascia or deep fascia of forearm) conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antebrachial Fascia
The antebrachial fascia (antibrachial fascia or deep fascia of forearm) continuous above with the brachial fascia, is a dense, membranous investment, which forms a general sheath for the muscles in this region; it is attached, behind, to the olecranon and dorsal border of the ulna, and gives off from its deep surface numerous intermuscular septa, which enclose each muscle separately. Over the flexor muscles tendons as they approach the wrist it is especially thickened, and forms the volar carpal ligament. This is continuous with the transverse carpal ligament, and forms a sheath for the tendon of the palmaris longus which passes over the transverse carpal ligament to be inserted into the palmar aponeurosis. Behind, near the wrist-joint, it is thickened by the addition of many transverse fibers, and forms the dorsal carpal ligament. It is much thicker on the dorsal than on the volar surface, and at the lower than at the upper part of the forearm, and is strengthened above by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
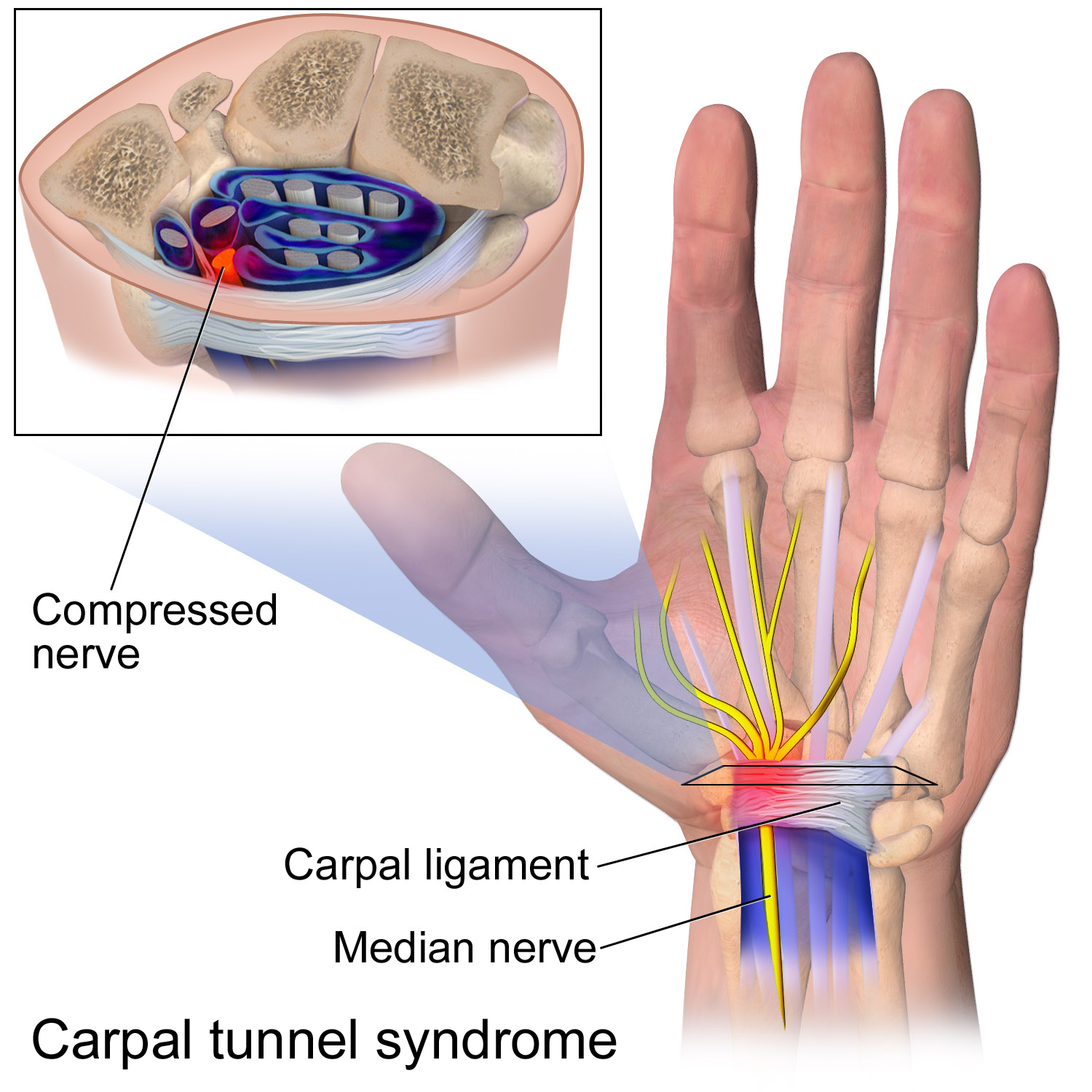
Flexor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament, or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel. Structure The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone. The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, and deeper with the palmar aponeurosis. The ulnar artery and ulnar nerve, and the cutaneous branches of the median and ulnar nerves, pass on top of the flexor retinaculum. On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds. This nerve can cause an electric shock-like sensation by striking the medial epicondyle of the humerus posteriorly, or inferiorly with the elbow flexed. The ulnar nerve is trapped between the bone and the overlying skin at this point. This is commonly referred to as bumping one's "funny bone". This name is thought to be a pun, based on the sound resemblance between the name of the bone of the upper arm, the humerus, and the word "humorous". Alternatively, according to the Oxford English Dictionary, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins. The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between the elbow and the wrist. It then runs along the ulnar border to the wrist, crosses the transverse carpal ligament on the radial side of the pisiform bone, and immediately beyond this bone divides into two branches, which enter into the formation of the superficial and deep volar arches. Branches Forearm: Anterior ulnar recurrent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Canal
The ulnar canal or ulnar tunnel (also known as Guyon's canal or tunnel) is a semi-rigid longitudinal canal in the wrist that allows passage of the ulnar artery and ulnar nerve into the hand. The roof of the canal is made up of the superficial palmar carpal ligament, while the deeper flexor retinaculum and hypothenar muscles comprise the floor. The space is medially bounded by the pisiform and pisohamate ligament more proximally, and laterally bounded by the hook of the hamate more distally. It is approximately 4 cm long, beginning proximally at the transverse carpal ligament and ending at the aponeurotic arch of the hypothenar muscles. Eponym The ulnar tunnel is eponymously named after the French surgeon Jean Casimir Félix Guyon, who originally described the canal in 1861. Clinical significance Entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the ulnar canal can result in symptoms of ulnar neuropathy, including numbness or weakness of certain parts of the hand. (''See full article on ulna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The extensor retinaculum (dorsal carpal ligament, or posterior annular ligament) is an anatomical term for the thickened part of the antebrachial fascia that holds the tendons of the extensor muscles in place. It is located on the back of the forearm, just proximal to the hand. It is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, which is located on the anterior side of the forearm. Structure The extensor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band, extending obliquely downward and medialward across the back of the wrist. It consists of part of the deep fascia of the back of the forearm, strengthened by the addition of some transverse fibers. The extensor retinaculum is attached laterally to the lateral margin of the radius. However, it is not attached to the ulna, as the distance between these two bones varies with supination and pronation of the forearm. Instead the medial attachment is to the pisiform bone and triquetral bone. Other authors may state the medial attachment of extensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament, or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel. Structure The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone. The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, and deeper with the palmar aponeurosis. The ulnar artery and ulnar nerve, and the cutaneous branches of the median and ulnar nerves, pass on top of the flexor retinaculum. On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The extensor retinaculum (dorsal carpal ligament, or posterior annular ligament) is an anatomical term for the thickened part of the antebrachial fascia that holds the tendons of the extensor muscles in place. It is located on the back of the forearm, just proximal to the hand. It is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, which is located on the anterior side of the forearm. Structure The extensor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band, extending obliquely downward and medialward across the back of the wrist. It consists of part of the deep fascia of the back of the forearm, strengthened by the addition of some transverse fibers. The extensor retinaculum is attached laterally to the lateral margin of the radius. However, it is not attached to the ulna, as the distance between these two bones varies with supination and pronation of the forearm. Instead the medial attachment is to the pisiform bone and triquetral bone. Other authors may state the medial attachment of extensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antebrachial Fascia
The antebrachial fascia (antibrachial fascia or deep fascia of forearm) continuous above with the brachial fascia, is a dense, membranous investment, which forms a general sheath for the muscles in this region; it is attached, behind, to the olecranon and dorsal border of the ulna, and gives off from its deep surface numerous intermuscular septa, which enclose each muscle separately. Over the flexor muscles tendons as they approach the wrist it is especially thickened, and forms the volar carpal ligament. This is continuous with the transverse carpal ligament, and forms a sheath for the tendon of the palmaris longus which passes over the transverse carpal ligament to be inserted into the palmar aponeurosis. Behind, near the wrist-joint, it is thickened by the addition of many transverse fibers, and forms the dorsal carpal ligament. It is much thicker on the dorsal than on the volar surface, and at the lower than at the upper part of the forearm, and is strengthened above by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligaments
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |