|
Voiceless Lateral Fricative
The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K. The symbol is called "belted l" and is distinct from "l with tilde", , which transcribes a different sound, the velarized (or pharynɡealized) alveolar lateral approximant, often called "dark L". Some scholars also posit the voiceless alveolar lateral approximant distinct from the fricative. The approximant may be represented in the IPA as . Features Features of the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative: Occurrence The sound is fairly common among indigenous languages of the Americas, such as Nahuatl and Navajo, and in North Caucasian languages, such as Avar. It is also found in African languages, such as Zulu, and Asian languages, such as Chukchi, some Yue dialects like Tais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; , and , pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose ( nasals). Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, linguists have devised systems such as the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to assign a unique and unambiguous symbol to each attested consonant. The English alphabet has fewer consonant letters than the English language has consonant sounds, so digraphs like , , , and are used to extend the alphabet, though some letters and digraphs represent more than one consonant. For example, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
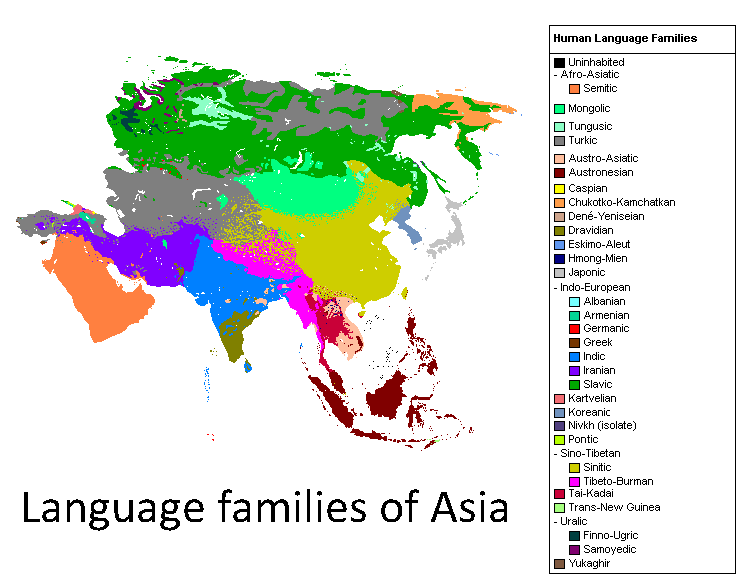
Asian Languages
A wide variety of languages are spoken throughout Asia, comprising different language families and some unrelated isolates. The major language families include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Caucasian, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan and Kra–Dai. Most, but not all, have a long history as a written language. Language groups The major families in terms of numbers are Indo-European and Indo-Aryan languages and Dravidian languages in South Asia and Sino-Tibetan in East Asia. Several other families are regionally dominant. Sino-Tibetan Sino-Tibetan includes Chinese, Tibetan, Burmese, Karen, Boro and numerous languages of the Tibetan Plateau, southern China, Burma, and North east India. Indo-European The Indo-European languages are primarily represented by the Indo-Iranian branch. The family includes both Indic languages (Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, Odia, Assamese, Punjabi, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Marathi, Gujarati, Sinhala and other languages spoken prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
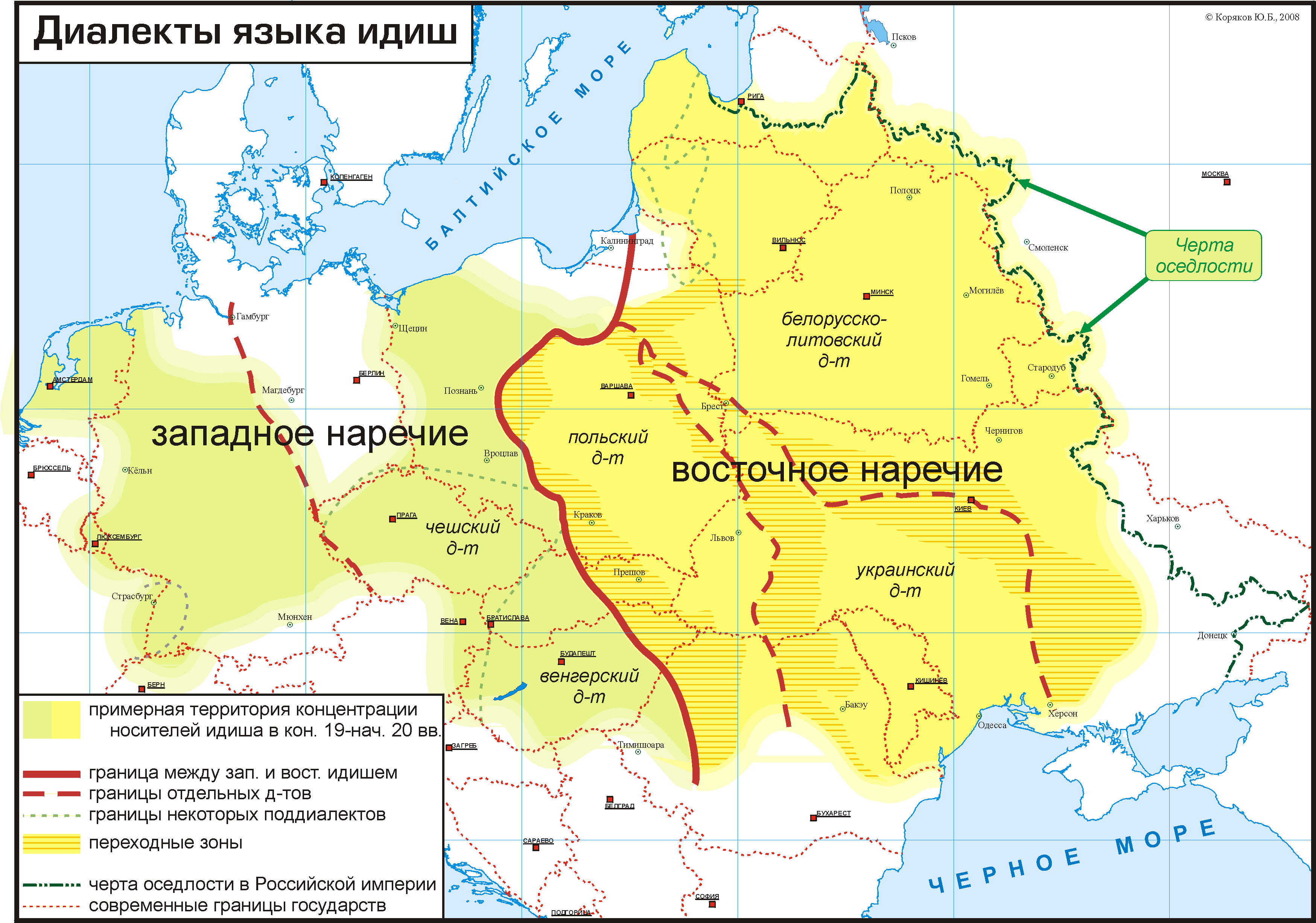
Northeastern Yiddish
Yiddish dialects are variants of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Shoah. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, since Yiddish is largely dying out everywhere due to language assimilation, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic communities, have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in Western-Central Europe, in the region which was called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabesdiker Losn
Der sabesdiker-losn (Yiddish: דער סאַבעסדיקער לשון (לאָסן)) is a dialectal feature characteristic of the Northeastern dialect of the Yiddish language ( NEY, ''Litvisher-vaysrusisher dialekt'', צפֿון ייִדיש ''Tsofn-yidish''), which is the replacement, or merger of the "hushing" (post-alveolar) consonants "ch", "sh" ( IPA: /tʃ/, /ʃ/), with the "hissing" (alveolar) ones, "ts", "s" (IPA: /ts/, /s/). The name of the term is a shibboleth: the phrase ''"דאָס שבתֿדיקע לשון" "dos shabesdike loshn"'' (in standard Yiddish) means " Sabbath speech", hinting at the perception that this feature is substandard. "History of the Yiddish Language", by Max Weinreichbr>p. 534/ref> In addition to the shibboleth, the use of the masculine article ''der'' indicates NEY's tendency to use either the masculine or the feminine gender for nouns where Standard Yiddish uses the neuter. It is similar to the dialectical feature of Polish language called ''mazurze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llywelyn (name)
Llywelyn is a Welsh personal name, which has also become a family name most commonly spelt Llewellyn (). The name has many variations and derivations, mainly as a result of the difficulty for non-Welsh speakers of representing the sound of the initial double ''ll'' (a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative). The name ''Lewis'' became closely associated with Llywelyn as early as the 13th century, when Anglo-Norman scribes often used the former as an anglicised version of the latter; many Welsh families came to do the same over the following centuries as the adoption of formal English-style surnames became more widespread. Etymology The name evolved from the Common Brittonic name ''Lugubelinos'', which was a compound of two names for Celtic deities. The first, ''Lugus'', is also the source of the first element in the names '' Llywarch'' and '' Lliwelydd'', and, as an independent name, evolved into Welsh ''Lleu''. The second element, '' Belenus'', evolved as an independent name into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloyd (name)
Lloyd is a Welsh surname originating with the Welsh adjective ''llwyd'', most often understood as meaning "grey" but with other meanings as well. The name can be used both as a given name and as a surname. The name has many variations and a few derivations, mainly as a result of the difficulty in representing the initial double-L for non-Welsh speakers and the translation of the Welsh diphthong ''wy''. Lloyd is the most common form of the name encountered in the modern era, with the Welsh spelling ''Llwyd'' increasingly common in recent times. The vast majority of Wales continued to use the patronymic system well into the early modern period, and the families that used family surnames passed on from one generation to the next remained exceptional. However, the name ''Lloyd/Llwyd'' and certain other Welsh adjectives such as ''goch'' ("red", evolving into the Welsh surname Gough) became "fixed epithet" passed on through the generations and functioned as family surnames as early a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic language family, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales, by some in England, and in Y Wladfa (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). Historically, it has also been known in English as "British", "Cambrian", "Cambric" and "Cymric". The Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011 gave the Welsh language official status in Wales. Both the Welsh and English languages are ''de jure'' official languages of the Welsh Parliament, the Senedd. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 17.8% (538,300 people) and nearly three quarters of the population in Wales said they had no Welsh language skills. Other estimates suggest that 29.7% (899,500) of people aged three or older in Wales could speak Welsh in June 2022. Almost half of all Welsh speakers consider themselves fluent Welsh speakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically been considered as a natural barrier between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Mount Elbrus in Russia, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands, part of which is in Turkey. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is occupied by several independent states, mostly by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Languages
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. Within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic, they have more than 200 million speakers each and together account for close to 90% of Europeans. Smaller phyla of Indo-European found in Europe include Hellenic (Greek, 13 million), Baltic ( 7 million), Albanian ( 5 million), Celtic ( 4 million), Armenian ( 4 million) and Indo-Aryan (Romani, 1.5 million). Of the approximately 45 million Europeans speaking non-Indo-European languages, most speak languages within either the Uralic or Turkic families. Still smaller groups — such as Basque (language isolate), Semitic languages ( Maltese, 0.5 million), and various languages of the Caucasus — account for less than 1% of the European population between them. Immigration has added sizeable communities of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formosan Languages
The Formosan languages are a geographic grouping comprising the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, all of which are Austronesian. They do not form a single subfamily of Austronesian but rather nine separate subfamilies. The Taiwanese indigenous peoples recognized by the government are about 2.3% of the island's population. However, only 35% speak their ancestral language, due to centuries of language shift. Of the approximately 26 languages of the Taiwanese indigenous peoples, at least ten are extinct, another four (perhaps five) are moribund, and all others are to some degree endangered. The aboriginal languages of Taiwan have great significance in historical linguistics since, in all likelihood, Taiwan is the place of origin of the entire Austronesian language family. According to American linguist Robert Blust, the Formosan languages form nine of the ten principal branches of the family, while the one remaining principal branch, Malayo-Polynesian, contains nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hlai Languages
The Hlai languages () are a primary branch of the Kra–Dai language family spoken in the mountains of central and south-central Hainan in China by the Hlai people, not to be confused with the colloquial name for the Leizhou branch of Min Chinese (). They include Cun, whose speakers are ethnically distinct. A quarter of Hlai speakers are monolingual. None of the Hlai languages had a writing system until the 1950s, when the Latin script was adopted for Ha. Classification Norquest (2007) classifies the Hlai languages as follows. Individual languages are highlighted in bold. There are some 750,000 Hlai speakers. *Proto-Hlai ** Bouhin (Heitu 黑土) – 73,000 **Greater Hlai ***Ha Em 哈炎 (Zhongsha 中沙) – 193,000 ***Central Hlai ****East Central Hlai – 344,000 ***** Lauhut (Baoding 保定) – 166,000, the basis of the literary language *****Qi 杞 also known as ''Gei'' – 178,000 ****** Tongzha (Tongshi 通什) – 125,000 ****** Zandui (Qiandui 堑对) – 29,000 ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |