|
Video Messaging
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include multimedia content to and from a mobile phone over a cellular network. Users and providers may refer to such a message as a PXT, a picture message, or a multimedia message. The MMS standard extends the core SMS (Short Message Service) capability, allowing the exchange of text messages greater than 160 characters in length. Unlike text-only SMS, MMS can deliver a variety of media, including up to forty seconds of video, one image, a slideshow of multiple images, or audio. The most common use involves sending photographs from camera-equipped handsets. Media companies have utilized MMS on a commercial basis as a method of delivering news and entertainment content, and retailers have deployed it as a tool for delivering scannable coupon codes, product images, videos, and other information. The 3GPP and WAP groups fostered the development of the MMS standard, which is now continued by the Open Mobile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, or video into a single interactive presentation, in contrast to traditional mass media, such as printed material or audio recordings, which features little to no interaction between users. Popular examples of multimedia include video podcasts, audio slideshows and animated videos. Multimedia also contains the principles and application of effective interactive communication such as the building blocks of software, hardware, and other technologies. Multimedia can be recorded for playback on computers, laptops, smartphones, and other electronic devices, either on demand or in real time (streaming). In the early years of multimedia, the term "rich media" was synonymous with interactive multimedia. Over time, hypermedia extensions brought multimedia to the World Wide Web. Terminology The term ''multimedia'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content Adaptation
Content adaptation is the action of transforming Content (media and publishing), content to adapt to device capabilities. Content adaptation is usually related to mobile devices, which require special handling because of their limited computational power, small screen size, and constrained keyboard functionality. Content adaptation could roughly be divided to two fields: # Media content adaptation that adapts media files. # Browsing content adaptation that adapts a website to mobile devices. Browsing content adaptation Advances in the capabilities of small, mobile devices such as mobile phones (cell phones) and Personal Digital Assistants have led to an explosion in the number of types of device that can now access the World Wide Web, Web. Some commentators refer to the Web that can be accessed from mobile devices as the Mobile Web. The sheer number and variety of Web-enabled devices poses significant challenges for authors of websites who want to support access from mobile dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Marketing
Mobile marketing is a multi-channel online marketing technique focused at reaching a specific audience on their smartphones, feature phones, tablets, or any other related devices through websites, e-mail, SMS and MMS, social media, or mobile applications. Mobile marketing can provide customers with time and location sensitive, personalized information that promotes goods, services, appointment reminders and ideas. In a more theoretical manner, academic Andreas Kaplan defines mobile marketing as "any marketing activity conducted through a ubiquitous network to which consumers are constantly connected using a personal mobile device". SMS marketing Marketing through cellphones' SMS (Short Message Service) became increasingly popular in the early 2000s in Europe and some parts of Asia when businesses started to collect mobile phone numbers and send off wanted (or unwanted) content. On average, SMS messages have a 98% open rate and are read within 3 minutes, making them highly effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rich Communication Services
Rich Communication Services (RCS) is a communication protocol between mobile telephone carriers and between phone and carrier, aiming at replacing SMS messages with a text-message system that is richer, provides phonebook polling (for service discovery), and can transmit in-call multimedia. It is part of the broader IP Multimedia Subsystem. Google added support for end-to-end encryption for one-on-one conversations in their own extension. It is also marketed as Advanced Messaging, Chat, joyn, SMSoIP, Message+, and SMS+. In early 2020, it was estimated that RCS was available from 88 operators in 59 countries with approximately 390 million users per month. History The Rich Communication Suite industry initiative was formed by a group of industry promoters in 2007. In February 2008 the GSM Association officially became the project home of RCS and an RCS steering committee was established by the organisation. The steering committee specified the definition, testing, and integra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhanced Messaging Service
Enhanced Messaging Service (EMS) was a cross-industry collaboration between Samsung, Ericsson, Motorola, Siemens and Alcatel among others, which provided an application-level extension to Short Message Service (SMS) for cellular phones available on GSM, TDMA and CDMA networks. EMS was an intermediate technology, between SMS and MMS, providing some of the features of MMS. EMS was a technology designed to work with existing networks, but was ultimately made obsolete by MMS. An EMS-enabled mobile phone could send and receive messages that had special text formatting (such as bold or italic), animations, pictures, icons, sound effects and special ringtones. EMS messages sent to devices that did not support it would be displayed as SMS messages, though they may be unreadable due to the presence of additional data that cannot be rendered by the device. In some countries, EMS messages could not generally be sent between subscribers of different mobile phone carriers, as they will freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Charging System
Online charging system (OCS) is a system allowing a communications service provider to charge their customers, in real time, based on service usage. Architecture Event based charging An event-based charging function (EBCF) is used to charge events based on their occurrence rather than their duration or volume used in the event. Typical events are SMS, MMS, purchase of content (application, game, music, video on demand, etc.). Event-based charging function is used when the CC-Request-Type AVP = 4 i.e. for event request ex: diameter-sms or diameter-..... Let us consider one example of Event-based charging. 1. Cost of one apple is Rupees 25/- You pay the amount, take the apple and go. Similarly, if you send a text message it may cost you Rupee 1/- and that's it. You subscribe to Caller Ring Back Tone (CRBT) which costs you Rs.30/- a month irrespective of the number of calls you receive in a month. So we can term event-based charging as a one-time cost or one-time occurrence cost. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSM Core Network
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation ( 2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. GSM is also a trade mark owned by the GSM Association. GSM may also refer to the Full Rate voice codec. It was first implemented in Finland in December 1991. By the mid-2010s, it became a global standard for mobile communications achieving over 90% market share, and operating in over 193 countries and territories. 2G networks developed as a replacement for first generation ( 1G) analog cellular networks. The GSM standard originally described a digital, circuit-switched network optimized for full duplex voice telephony. This expanded over time to include data communications, first by circuit-switched transport, then by packet data transport via General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), and Enhanced Data Rates for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
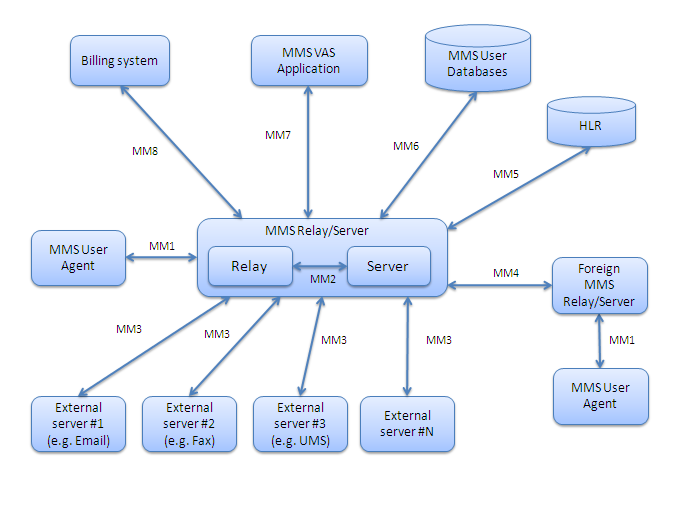
MMS Architecture
The MMS Architecture is the set of standards used by the Multimedia Messaging Service in mobile networks. The standards are prepared by 3GPP. Overview The standard consists of a number of interfaces between components found in the mobile network: * MM1: the interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server). Delivered as HTTP over a packet switched data session. * MM2: the interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server. * MM3: the interface between MMSC and other messaging systems. Using SMTP. * MM4: the interface between MMSC and foreign network providers. Using SMTP. * MM5: the interface between MMSC and HLR. * MM6: the interface between MMSC and user databases. * MM7: the interface between MMS Value-added service applications and MMSC. Typically Content Providers using HTTP / SOAP for delivery. * MM8: the interface between MMSC and the billing systems. * MM9: the interface between MMSC and an online charging system. * MM10: the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericsson
(lit. "Telephone Stock Company of LM Ericsson"), commonly known as Ericsson, is a Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in information and communications technology for telecommunications service providers and enterprises, including, among others, 3G, 4G, and 5G equipment, and Internet Protocol (IP) and optical transport systems. The company employs around 100,000 people and operates in more than 180 countries. Ericsson has over 57,000 granted patents. Ericsson has been a major contributor to the development of the telecommunications industry and is one of the leaders in 5G. The company was founded in 1876 by Lars Magnus Ericsson and is jointly controlled by the Wallenberg family through its holding company Investor AB, and the universal bank Handelsbanken through its investment company Industrivärden. The Wallenbergs and the Handelsbanken sphere acquired their v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAP Push
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a technical standard for accessing information over a mobile wireless network. A WAP browser is a web browser for mobile devices such as mobile phones that use the protocol. Introduced in 1999, WAP achieved some popularity in the early 2000s, but by the 2010s it had been largely superseded by more modern standards. Almost all modern handset internet browsers now fully support HTML, so they do not need to use WAP markup for web page compatibility, and therefore, most are no longer able to render and display pages written in WML, WAP's markup language. Before the introduction of WAP, mobile service providers had limited opportunities to offer interactive data services, but needed interactivity to support Internet and Web applications such as email, stock prices, news and sports headlines. The Japanese i-mode system offered another major competing wireless data protocol. Technical specifications WAP stack The WAP standard described a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over-the-air Programming
Over-the-air programming (OTA programming) refers to various methods of distributing new software, configuration settings, and even updating encryption keys to devices like mobile phones, set-top boxes, electric cars or secure voice communication equipment (encrypted two-way radios). One important feature of OTA is that one central location can send an update to all the users, who are unable to refuse, defeat, or alter that update, and that the update applies immediately to everyone on the channel. A user could 'refuse' OTA, but the 'channel manager' could also 'kick them off' the channel automatically. In the context of the mobile content world, these include firmware-over-the-air (FOTA), over-the-air service provisioning (OTASP), over-the-air provisioning (OTAP), or over-the-air parameter administration (OTAPA); or provisioning handsets with the necessary settings with which to access services such as wireless access point (WAP) or Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS). As mobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)