|
Ventricular Dyssynchrony
In cardiology, ventricular dyssynchrony is a difference in the timing, or lack of synchrony, of contractions in different ventricles in the heart. Large differences in timing of contractions can reduce cardiac efficiency and is correlated with heart failure. Types of dyssynchrony Three chief presentations of dyssynchrony can occur: Atrioventricular (AV) dyssynchrony occurs when there is an unfavorable difference in timing between atrial and ventricular contractions. Interventricular dyssynchrony occurs when there is a difference in timing between right ventricular (RV) and left ventricular (LV) Systole. Intraventricular dyssynchrony occurs when the timing in a sequence of activations and contractions of segments of the LV wall becomes abnormal. In all three types, changes in timing lead to changes in the dynamic behavior of the myocardial tissues, leading to ''mechanical dyssynchrony''. All three presentations allow distinct and easily reproducible electrical signatures as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
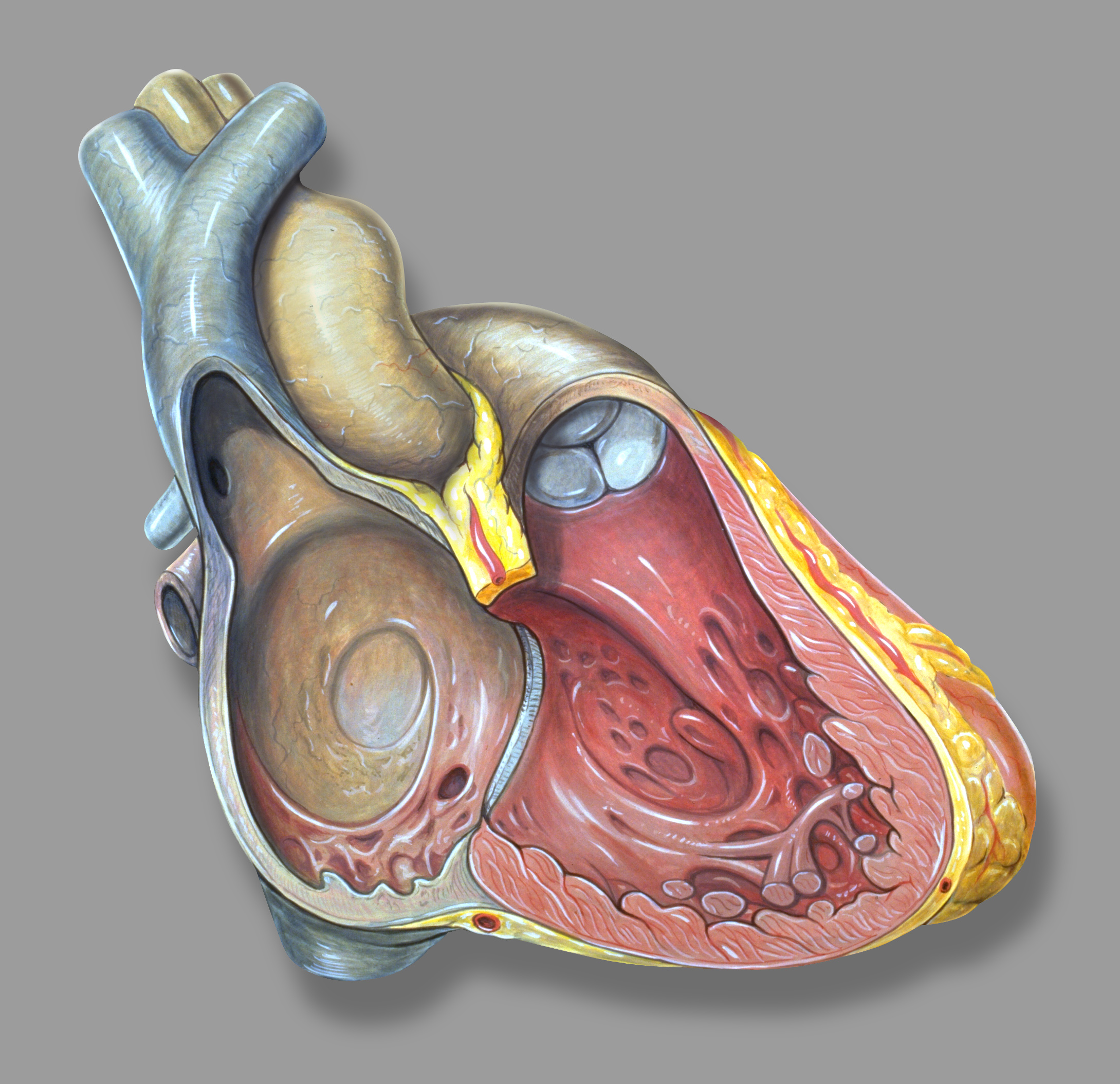
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricular
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricular
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Doppler Echocardiography
Tissue Doppler echocardiography (TDE) is a medical ultrasound technology, specifically a form of echocardiography that measures the velocity of the heart muscle (myocardium) through the phases of one or more heartbeats by the Doppler effect (frequency shift) of the reflected ultrasound. The technique is the same as for flow Doppler echocardiography measuring flow velocities. Tissue signals, however, have higher amplitude and lower velocities, and the signals are extracted by using different filter and gain settings. The terms tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) and tissue velocity imaging (TVI) are usually synonymous with TDE because echocardiography is the main use of tissue Doppler. Like Doppler flow, tissue Doppler can be acquired both by spectral analysis (spectral density estimation) as pulsed Doppler and by the autocorrelation technique as colour tissue Doppler (duplex ultrasonography). While pulsed Doppler only acquires the velocity at one point at a time, colour Doppler can acquire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT or CRT-P) is the insertion of electrodes in the left and right ventricles of the heart, as well as on occasion the right atrium, to treat heart failure by coordinating the function of the left and right ventricles via a pacemaker, a small device inserted into the anterior chest wall. CRT is indicated in patients with a low ejection fraction (typically 120 ms. The insertion of electrodes into the ventricles is done under local anesthetic, with access to the ventricles most commonly via the subclavian vein, although access may be conferred from the axillary or cephalic veins. Right ventricular access is direct, while left ventricular access is conferred via the coronary sinus (CS). CRT defibrillators (CRT-D) also incorporate the additional function of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), to quickly terminate an abnormally fast, life-threatening heart rhythm. CRT and CRT-D have become increasingly important therapeutic options ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundle Branch Block
A bundle branch block is a defect in one the bundle branches in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Anatomy and physiology The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatrial node (the heart's natural pacemaker), which is situated on the upper right atrium. The impulse travels next through the left and right atria and summates at the atrioventricular node. From the AV node the electrical impulse travels down the bundle of His and divides into the right and left bundle branches. The right bundle branch contains one fascicle. The left bundle branch subdivides into two fascicles: the left anterior fascicle, and the left posterior fascicle. Other sources divide the left bundle branch into three fascicles: the left anterior, the left posterior, and the left septal fascicle. The thicker left posterior fascicle bifurcates, with one fascicle being in the septal aspect. Ultimately, the fascicles divide into millions of Purkinje fibres, which in turn interdigitate with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejection Fraction
An ejection fraction (EF) is the volumetric fraction (or portion of the total) of fluid (usually blood) ejected from a chamber (usually the heart) with each contraction (or heartbeat). It can refer to the cardiac atrium, ventricle, gall bladder, or leg veins, although if unspecified it usually refers to the left ventricle of the heart. EF is widely used as a measure of the pumping efficiency of the heart and is used to classify heart failure types. It is also used as an indicator of the severity of heart failure, although it has recognized limitations. The EF of the left heart, known as the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), is calculated by dividing the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat (stroke volume) by the volume of blood collected in the left ventricle at the end of diastolic filling (end-diastolic volume). LVEF is an indicator of the effectiveness of pumping into the systemic circulation. The EF of the right heart, or right ventricular ejection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |