|
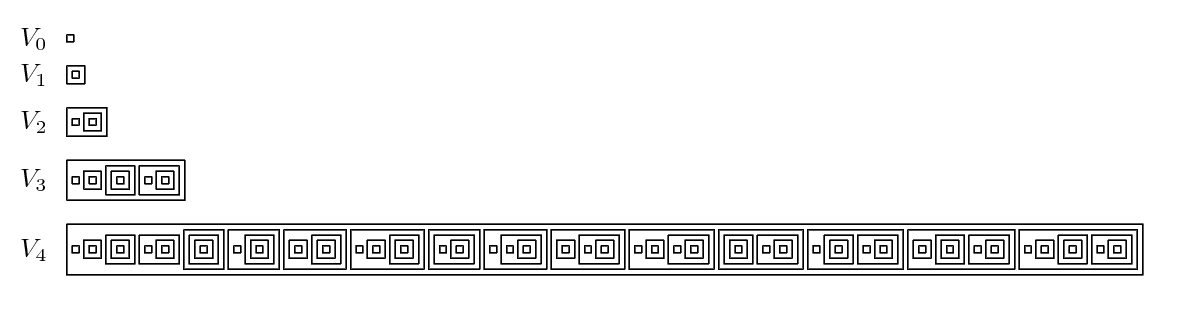
Von Neumann Universe
In set theory and related branches of mathematics, the von Neumann universe, or von Neumann hierarchy of sets, denoted by ''V'', is the class of hereditary well-founded sets. This collection, which is formalized by Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory (ZFC), is often used to provide an interpretation or motivation of the axioms of ZFC. The concept is named after John von Neumann, although it was first published by Ernst Zermelo in 1930. The rank of a well-founded set is defined inductively as the smallest ordinal number greater than the ranks of all members of the set. In particular, the rank of the empty set is zero, and every ordinal has a rank equal to itself. The sets in ''V'' are divided into the transfinite hierarchy ''Vα'', called the cumulative hierarchy, based on their rank. Definition The cumulative hierarchy is a collection of sets ''V''α indexed by the class of ordinal numbers; in particular, ''V''α is the set of all sets having ranks less than α. Thus there is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies Set (mathematics), sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory – as a branch of mathematics – is mostly concerned with those that are relevant to mathematics as a whole. The modern study of set theory was initiated by the German mathematicians Richard Dedekind and Georg Cantor in the 1870s. In particular, Georg Cantor is commonly considered the founder of set theory. The non-formalized systems investigated during this early stage go under the name of ''naive set theory''. After the discovery of Paradoxes of set theory, paradoxes within naive set theory (such as Russell's paradox, Cantor's paradox and the Burali-Forti paradox), various axiomatic systems were proposed in the early twentieth century, of which Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory (with or without the axiom of choice) is still the best-known and most studied. Set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrational
In mathematics, tetration (or hyper-4) is an operation (mathematics), operation based on iterated, or repeated, exponentiation. There is no standard mathematical notation, notation for tetration, though Knuth's up arrow notation \uparrow \uparrow and the left-exponent ^b are common. Under the definition as repeated exponentiation, means , where ' copies of ' are iterated via exponentiation, right-to-left, i.e. the application of exponentiation n-1 times. ' is called the "height" of the function, while ' is called the "base," analogous to exponentiation. It would be read as "the th tetration of ". For example, 2 tetrated to 4 (or the fourth tetration of 2) is =2^=2^=2^=65536. It is the next hyperoperation after exponentiation, but before pentation. The word was coined by Reuben Louis Goodstein from tetra- (four) and iterated function, iteration. Tetration is also defined recursively as : := \begin 1 &\textn=0, \\ a^ &\textn>0, \end allowing for the holomorphic function, hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Class
Proper may refer to: Mathematics * Proper map, in topology, a property of continuous function between topological spaces, if inverse images of compact subsets are compact * Proper morphism, in algebraic geometry, an analogue of a proper map for algebraic varieties * Proper transfer function, a transfer function in control theory in which the degree of the numerator does not exceed the degree of the denominator * Proper equilibrium, in game theory, a refinement of the Nash equilibrium * Proper subset * Proper space * Proper class * Proper complex random variable Other uses * Proper (liturgy), the part of a Christian liturgy that is specific to the date within the Liturgical Year * Proper frame, such system of reference in which object is stationary (non moving), sometimes also called a co-moving frame * Proper (heraldry), in heraldry, means depicted in natural colors * Proper Records, a UK record label * ''Proper'' (album), an album by Into It. Over It. released in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Of All Sets
In set theory, a universal set is a set which contains all objects, including itself. In set theory as usually formulated, it can be proven in multiple ways that a universal set does not exist. However, some non-standard variants of set theory include a universal set. Reasons for nonexistence Many set theories do not allow for the existence of a universal set. There are several different arguments for its non-existence, based on different choices of axioms for set theory. Russell's paradox Russell's paradox concerns the impossibility of a set of sets, whose members are all sets that do not contain themselves. If such a set could exist, it could neither contain itself (because its members all do not contain themselves) nor avoid containing itself (because if it did, it should be included as one of its members). This paradox prevents the existence of a universal set in set theories that include either Zermelo's axiom of restricted comprehension, or the axiom of regularity and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morse–Kelley Set Theory
In the foundations of mathematics, Morse–Kelley set theory (MK), Kelley–Morse set theory (KM), Morse–Tarski set theory (MT), Quine–Morse set theory (QM) or the system of Quine and Morse is a first-order axiomatic set theory that is closely related to von Neumann–Bernays–Gödel set theory (NBG). While von Neumann–Bernays–Gödel set theory restricts the bound variables in the schematic formula appearing in the axiom schema of Class Comprehension to range over sets alone, Morse–Kelley set theory allows these bound variables to range over proper classes as well as sets, as first suggested by Quine in 1940 for his system ML. Morse–Kelley set theory is named after mathematicians John L. Kelley and Anthony Morse and was first set out by and later in an appendix to Kelley's textbook ''General Topology'' (1955), a graduate level introduction to topology. Kelley said the system in his book was a variant of the systems due to Thoralf Skolem and Morse. Morse's own vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inaccessible Cardinal
In set theory, a cardinal number is a strongly inaccessible cardinal if it is uncountable, regular, and a strong limit cardinal. A cardinal is a weakly inaccessible cardinal if it is uncountable, regular, and a weak limit cardinal. Since about 1950, "inaccessible cardinal" has typically meant "strongly inaccessible cardinal" whereas before it has meant "weakly inaccessible cardinal". Weakly inaccessible cardinals were introduced by . Strongly inaccessible cardinals were introduced by and ; in the latter they were referred to along with \aleph_0 as ''Grenzzahlen'' ( English "limit numbers"). Every strongly inaccessible cardinal is a weakly inaccessible cardinal. The generalized continuum hypothesis implies that all weakly inaccessible cardinals are strongly inaccessible as well. The two notions of an inaccessible cardinal \kappa describe a cardinality \kappa which can not be obtained as the cardinality of a result of typical set-theoretic operations involving only sets of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom Of Replacement
In set theory, the axiom schema of replacement is a schema of axioms in Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory (ZF) that asserts that the image of any set under any definable mapping is also a set. It is necessary for the construction of certain infinite sets in ZF. The axiom schema is motivated by the idea that whether a class is a set depends only on the cardinality of the class, not on the rank of its elements. Thus, if one class is "small enough" to be a set, and there is a surjection from that class to a second class, the axiom states that the second class is also a set. However, because ZFC only speaks of sets, not proper classes, the schema is stated only for definable surjections, which are identified with their defining formulas. Statement Suppose P is a definable binary relation (which may be a proper class) such that for every set x there is a unique set y such that P(x,y) holds. There is a corresponding definable function F_P, where F_P(x)=y if and only if P(x,y). Consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zermelo Set Theory
Zermelo set theory (sometimes denoted by Z-), as set out in a seminal paper in 1908 by Ernst Zermelo, is the ancestor of modern Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory (ZF) and its extensions, such as von Neumann–Bernays–Gödel set theory (NBG). It bears certain differences from its descendants, which are not always understood, and are frequently misquoted. This article sets out the original axioms, with the original text (translated into English) and original numbering. The axioms of Zermelo set theory The axioms of Zermelo set theory are stated for objects, some of which (but not necessarily all) are sets, and the remaining objects are urelements and not sets. Zermelo's language implicitly includes a membership relation ∈, an equality relation = (if it is not included in the underlying logic), and a unary predicate saying whether an object is a set. Later versions of set theory often assume that all objects are sets so there are no urelements and there is no need for the unary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universe (set Theory)
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from sub-atomic particles to entire galactic filaments. Since the early 20th century, the field of cosmology establishes that space and time emerged together at the Big Bang ago and that the universe has been expanding since then. The portion of the universe that can be seen by humans is approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter at present, but the total size of the universe is not known. Some of the earliest cosmological models of the universe were developed by ancient Greek and Indian philosophers and were geocentric, placing Earth at the center. Over the centuries, more precise astronomical observations led Nicolaus Copernicus to develop the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. In developin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom Of Infinity
In axiomatic set theory and the branches of mathematics and philosophy that use it, the axiom of infinity is one of the axioms of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory. It guarantees the existence of at least one infinite set, namely a set containing the natural numbers. It was first published by Ernst Zermelo as part of his set theory in 1908. Formal statement Using first-order logic primitive symbols, the axiom can be expressed as follows: \exist \mathrm \ (\exist o \ (o \in \mathrm \ \land \lnot \exist n \ (n \in o)) \ \land \ \forall x \ (x \in \mathrm \Rightarrow \exist y \ (y \in \mathrm \ \land \ \forall a \ (a \in y \Leftrightarrow (a \in x \ \lor \ a = x))))). If the notations of both set-builder and empty set are allowed: \exists \mathrm \, ( \varnothing \in \mathrm \, \land \, \forall x \, (x \in \mathrm \Rightarrow \, ( x \cup \ ) \in \mathrm ) ). Some mathematicians may call a set built this way an inductive set. Hint: In English, it reads: " There exists a set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model (logic)
In universal algebra and in model theory, a structure consists of a set along with a collection of finitary operations and relations that are defined on it. Universal algebra studies structures that generalize the algebraic structures such as groups, rings, fields and vector spaces. The term universal algebra is used for structures of first-order theories with no relation symbols. Model theory has a different scope that encompasses more arbitrary first-order theories, including foundational structures such as models of set theory. From the model-theoretic point of view, structures are the objects used to define the semantics of first-order logic, cf. also Tarski's theory of truth or Tarskian semantics. For a given theory in model theory, a structure is called a model if it satisfies the defining axioms of that theory, although it is sometimes disambiguated as a '' semantic model'' when one discusses the notion in the more general setting of mathematical models. Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditarily Finite Set
In mathematics and set theory, hereditarily finite sets are defined as finite sets whose elements are all hereditarily finite sets. In other words, the set itself is finite, and all of its elements are finite sets, recursively all the way down to the empty set. Formal definition A recursive definition of well-founded hereditarily finite sets is as follows: : ''Base case'': The empty set is a hereditarily finite set. : ''Recursion rule'': If a_1,\dots a_k are hereditarily finite, then so is \. Only sets that can be built by a finite number of applications of these two rules are hereditarily finite. Representation This class of sets is naturally ranked by the number of bracket pairs necessary to represent the sets: * \ (i.e. \emptyset, the Neumann ordinal "0") * \ (i.e. \ or \, the Neumann ordinal "1") * \ * \ and then also \ (i.e. \, the Neumann ordinal "2"), * \, \ as well as \, * ... sets represented with 6 bracket pairs, e.g. \. There are six such sets * ... sets represented wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |