|
Volvation
Volvation (from Latin ''volvere'' "roll", and the suffix ''-(a)tion''; sometimes called enrollment or conglobation), is a defensive behavior in certain animals, in which the animal rolls its own body into a ball, presenting only the hardest parts of its integument (the animal's "armor"), or its spines to predators. Among armadillos, only species in the genus Tolypeutes (South American three-banded armadillos) are able to roll into a defensive ball; the nine-banded armadillo and other species have too many plates.. Volvation is used by earthworms during periods of extreme heat or drought. Among pill millipedes, volvation is both a protection against external threats and against dehydration. Pillbugs curl themselves into "pills" not only for defense, but also to conserve moisture while resting or sleeping, because they must keep their pseudotrachaea ("gills") wet. Volvation is particularly well evolved in subterranean isopods, but only '' Caecosphaeroma burgundum'' is able to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecosphaeroma En Boule
''Caecosphaeroma'' is a troglodytic isopod genus in the family Sphaeromatidae found in caves of NE and SW France. The genus was split off from Monolistra by Adrien Dollfus in 1896; in both genera, the female carries about 10 fertilized eggs in its external marsupium (brood pouch); they are white in ''Monolistra'' but bluish-green in ''Caecosphaeroma''. ''C. burgundum'' is the most studied species. Description They measure from 2–20 mm long. As cave dwellers, they have lost their vision, but remain sensitive to light, which they shun. They are capable of volvation (rolling themselves into a ball) to protect themselves, rest, or sleep. During copulation the male and female embrace takes the form of two concentric spheres. Development Larva remain in the marsupium about 12 months, and the animals continue growing for several years, reaching a final length of 10–20 mm. Evolution The marine ancestors of ''Caecosphaeroma'' are believed to have migrated up the course ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecosphaeroma
''Caecosphaeroma'' is a troglodytic isopod genus in the family Sphaeromatidae found in caves of NE and SW France. The genus was split off from Monolistra by Adrien Dollfus in 1896; in both genera, the female carries about 10 fertilized eggs in its external marsupium (brood pouch); they are white in ''Monolistra'' but bluish-green in ''Caecosphaeroma''. ''C. burgundum'' is the most studied species. Description They measure from 2–20 mm long. As cave dwellers, they have lost their vision, but remain sensitive to light, which they shun. They are capable of volvation (rolling themselves into a ball) to protect themselves, rest, or sleep. During copulation the male and female embrace takes the form of two concentric spheres. Development Larva remain in the marsupium about 12 months, and the animals continue growing for several years, reaching a final length of 10–20 mm. Evolution The marine ancestors of ''Caecosphaeroma'' are believed to have migrated up the course ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period () and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last extant trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 252 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described. By the time trilobites first appeared in the fossil record, they were already highly diversified and geographically dispersed. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossilized exoskeleton, they left an extensive fossil record. The stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phacops Rana
''Eldredgeops rana'' (formerly ''Phacops rana'') is a species of trilobite from the middle Devonian period. Their fossils are found chiefly in the northeastern United States, and southwestern Ontario. Because of its abundance and popularity with collectors, ''Eldredgeops rana'' was designated the Pennsylvania state fossil by the state's General Assembly on December 5, 1988. Description ''Eldredgeops rana'' can be recognized by its large eyes (which remind some observers of a frog's eyes—the specific name ''rana'' is a reference to a common frog), its fairly large size (up to 6 inches long), and its habit of rolling up into a ball like a pill bug (" volvation"). In order to protect themselves from predators, ''Eldredgeops rana'' would roll into a ball with its hard exoskeleton on the outside as protection. Many other trilobites possessed the same ability, but ''Eldredgeops rana'' nearly perfected it. The slightest amount of sediment would trigger their senses, and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Three-banded Armadillo
The southern three-banded armadillo (''Tolypeutes matacus''), also known as La Plata three-banded armadillo or Azara's domed armadillo, is an armadillo species from South America. It is found in parts of southwestern Brazil, northern Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia, at elevations from sea level to . The southern three-banded armadillo and the other member of the genus ''Tolypeutes'', the Brazilian three-banded armadillo, are the only species of armadillos capable of rolling into a complete ball to defend themselves (volvation). The three characteristic bands that cover the back of the animal allow it enough flexibility to fit its tail and head together, allowing it to protect its underbelly, limbs, eyes, nose and ears from predators. The shell covering its body is armored and the outer layer is made out of keratin, the same protein that builds human fingernails. They are typically a yellow or brownish color. They are among the smaller armadillos, with a head-and-body length of ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomeris Marginata
''Glomeris marginata'' is a common European species of pill millipede. It is a short millipede, rounded in cross-section, which is capable of rolling itself up into a ball ("volvation") when disturbed. This behaviour is also found in the pill woodlouse ''Armadillidium'', with which ''G. marginata'' is often confused. Distribution ''Glomeris marginata'' is found throughout central and north-western Europe, from Poland and Scandinavia to Spain and Italy. In the British Isles, it is found in all areas south of the Central Belt of Scotland. Description ''Glomeris marginata'' grows up to long and wide, and is covered by twelve black dorsal plates with white rims. Each segment except those at the front and back bears two pairs of legs, with around 18 pairs in total. This distinguishes pill millipedes from pill woodlice, both of which are called "pillbugs" — woodlice have 7 pairs of walking legs, one per body segment, while millipedes have more pairs, and with two pairs to each ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments. Armadillos are characterized by a leathery armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Etymology The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Lions
The Asiatic lion is a population of ''Panthera leo leo'' that today survives in the wild only in India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat. Historically, it inhabited much of southwest Asia to northern India. The first scientific description of the Asiatic lion was published in 1826 by the Austrian zoologist Johann N. Meyer, who named it ''Felis leo persicus''. On the IUCN Red List, it is listed under its former scientific name ''Panthera leo persica'' as Endangered because of its small population size and area of occupancy. Until the 19th century, it occurred in Saudi Arabia, eastern Turkey, Iran, Mesopotamia, Pakistan, and from east of the Indus River to Bengal and the Narmada River in Central India. The population has steadily increased since 2010. In May 2015, the 14th Asiatic Lion Census was conducted over an area of about ; the lion population was estimated at 523 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millipede
Millipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from the Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery of ''Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eating decaying leaves and other dead plant matter. Some eat fungi or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachypodoiulus Niger
''Tachypodoiulus niger'', known variously as the white-legged snake millipede or the black millipede, is a European species of millipede. It is very similar to other species such as ''Cylindroiulus londinensis'', from which it can be reliably distinguished only by studying the shape of the telson. It occurs in Ireland, Great Britain, Britain, Spain, France, Benelux, Germany, Switzerland, Austria and the Czech Republic, and is especially common on chalky and limestone soils. ''T. niger'' has a roughly Cylinder (geometry), cylindrical shiny black body, with around 100 pairs of contrasting white arthropod leg, legs on its 41–56 body segments. It lives in leaf litter, under Bark (botany), bark or in moss, and feeds on encrusting algae, detritus and sometimes fruit such as raspberry, raspberries. Predators of ''T. niger'' include the centipedes ''Lithobius variegatus'' and ''Lithobius forficatus'' and West European Hedgehog, hedgehogs. ''T. niger'' is most active from one hour aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
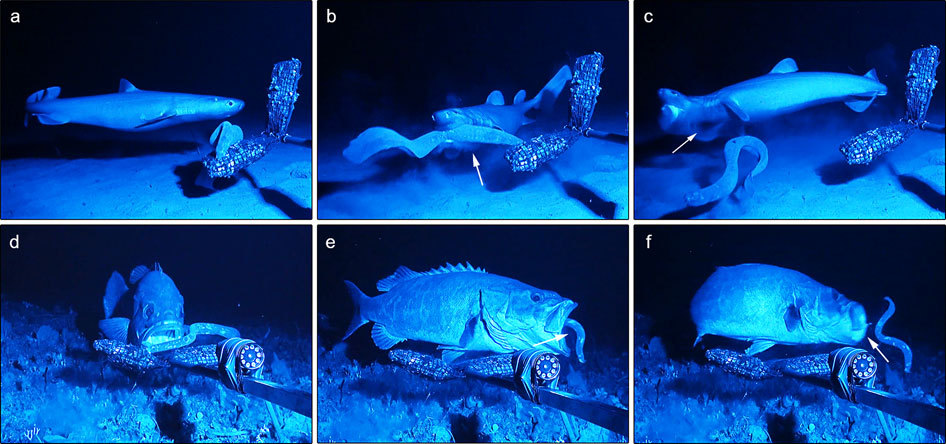
Anti-predator Adaptation
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by avoiding detection, warding off attack, fighting back, or escaping when caught. The first line of defence consists in avoiding detection, through mechanisms such as camouflage, masquerade, apostatic selection, living underground, or nocturnality. Alternatively, prey animals may ward off attack, whether by advertising the presence of strong defences in aposematism, by mimicking animals which do possess such defences, by startling the attacker, by signalling to the predator that pursuit is not worthwhile, by distraction, by using defensive structures such as spines, and by living in a group. Members of groups are at reduced risk of predation, despite the increased conspicuousness of a group, through improved vigilance, predator confusio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)